Polyphenols anthocyanins
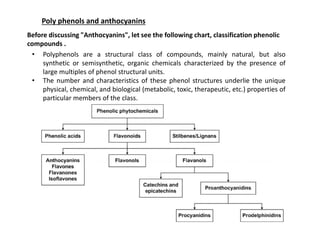
- 1. Poly phenols and anthocyanins Before discussing "Anthocyanins", let see the following chart, classification phenolic compounds . • Polyphenols are a structural class of compounds, mainly natural, but also synthetic or semisynthetic, organic chemicals characterized by the presence of large multiples of phenol structural units. • The number and characteristics of these phenol structures underlie the unique physical, chemical, and biological (metabolic, toxic, therapeutic, etc.) properties of particular members of the class.
- 2. Flavonoids • More than 4000 naturally occurring flavonoids have been described; many are common in higher plants. • These compounds frequently serve as pigments in plants and are involved in many biological interactions . • The color of a pigment is determined by the particular wavelengths of visible light that are absorbed by the molecule and those that are reflected or scattered.that are absorbed by the molecule and those that are reflected or scattered. • Key structural features of a flavonoid pigment are the degrees of double bond conjugation and oxygenation (in the form of hydroxylation).
- 3. Primary structures • Flavonoids have a 15-carbon (C15) base structure comprised of • Two phenyl rings(called the AA-- andand BB--ringsrings) • Connected by a three-carbon bridge that usually forms a third ring (called the CC--ringring) (Fig.). chalcone aurone Fig. Base structures of a chalcone (top left), an aurone (top right) and the main anthocyanidins (bottom). chalcone aurone anthocyanidins
- 5. Anthocyanins Anthocyanins are naturally occuring pigments belonging to the group of flavonoids, a subclass of the polyphenol family. Anthocyanins (also anthocyans has been derived from Greek: ἄνθος (anthos) "flower" and κυάνεος/κυανοῦς kyaneos/kyanous "dark blue") are water-soluble vacuolar pigments that, depending on their pH, may appear red, purple, blue or black. They are common components of the human diet, as they are present in many foods,They are common components of the human diet, as they are present in many foods, fruits and vegetables, especially in berries and red wine. Food plants rich in anthocyanins include the blueberry, raspberry, black rice, and black soybean, among many others that are red, blue, purple, or black. Some of the colors of autumn leaves are derived from anthocyanins. They occur in all tissues of higher plants, including leaves, stems, roots, flowers, and fruits. Anthocyanins are derived from anthocyanidins by adding sugars They are odorless and moderately astringent.
- 6. Purple cauliflower contains anthocyanins Anthocyanins and carotenoids contribute distinctive pigmentationdistinctive pigmentation to blood oranges • Willstätter and Everest identified the first anthocyanin in 1913, from the blue cornflower Centaurea cyanus (cited in Bohm, 1998). Since then approximately 630 different anthocyanins have been structurally defined.
- 7. Chemical Structure The skeleton of the structure contains two benzyl rings (A and B) and the heterocyclic ring (benzopyranring), known as ring C. • Fig. R1, R2 and R3 substitutions determine the various common anthocyanidins. Anthocyanidin Name R1 R2 R3 1 Apigeninidin H H H 2 luteolinidin OH H H2 luteolinidin OH H H 3 Tricetinidin OH OH H 4 Cyanidin OH H OH 5 Delphinidin OH OH OH 6 Peonidin OCH3 H OH 7 Petunidin OCH3 OH OH 8 Malvidin OCH3 OCH3 OH • A hydroxyl group or rather the lack thereof at the C-3 position(at R3) in the C-ring also dramatically influences the color of the pigment. • The common anthocyanidins have 3- hydroxylation (S/No. 4 to 8). 3- Deoxyanthocyanidins lack this hydroxyl group (S/No.1 to 3).
- 8. • 3-Deoxyanthocyanidins lack this hydroxyl group (Fig above), and show a marked difference in wavelength absorbance, with the derived pigments giving yellow, orange and bright red flower colours. • 3-Deoxyanthocyanins are relatively rare. • Anthocyanin modification typically involves O-glycosylation, O-acylation and O- methylation.methylation. • Substitutions are targeted to one or more of the hydroxyl groups of the chromophore or to substituents attached to these groups. • The hydroxylation pattern for most anthocyanins includes the C-3 position of the C- ring, the C-5 and C-7 positions of the A-ring and the C-4’ position of the B-ring
- 9. • Most anthocyanins are 3-glycosides (sugar molecule attached at position 3) or 3,5- diglycosides, and in some ornamentals (e.g. Pelargonium, Punica and Matthiola) • 3,5-diglycosides produce a more intense colour than the corresponding 3-glycosides (Harborne, 1976; Forkmann, 1991). • O-methylation is a commonly encountered modification and it most frequently • occurs on the B-ring hydroxyl groups.• occurs on the B-ring hydroxyl groups. • Methylation has a small reddening effect on • the colour of the molecule, but this may be masked by the influence of other • factors contributing to flower colour.
- 10. • However, O-methylation alone can alter flower colours in some cases. For example, in Primula sinensis mutants lacking co-pigments, lines containing only delphinidin anthocyanins had blue flowers while those with mainly methylated derivatives of delphinidin were pink or maroon (Harborne & Sherratt, 1961). • Based on the variations in hydroxylation and O-methylation described above, at least 18 naturally occurring anthocyanidins have been identified (listed in Bohm, 1998). • The historical and chemical definition is that anthocyanidin refers to the aglycone• The historical and chemical definition is that anthocyanidin refers to the aglycone of the anthocyanin, i.e. the base structure of the anthocyanin without the glycosyl groups. • The yellow flavonoid pigments are the chalcones, aurones and some flavonols. Carotenoids play the predominant role in yellow floral pigmentation; however, in some instances, flavonoids are responsible for the colour. More frequently, the yellow flavonoids co-occur with carotenoids. In these cases, the primary role of the yellow flavonoids is as UV-absorbing nectar or honey guides for pollinators.
- 11. • Chemically, anthocyanins are glycosylated polyhydroxy or polymethoxy derivatives of 2-phenylbenzopyrilium. • usually with molecular weights ranging from 400 to 1200 (medium-size biomolecules) • usually contain a single glucoside unit, but many anthocyanins contain two, three, or more sugars attached at multiple positions, or occurring as oligosaccharide side chains.chains. • They absorb light at the longest wavelengths, and are the basis for most orange, pink, red, magenta, purple, blue and blue-black floral colours. • Intensity and type of the color of anthocyanins is affected by the number of hydroxyl and methoxyl groups: • if more hydroxyl groups are present then the color goes toward a more bluish shade; and redness is increased if more methoxyl groups are present.
- 12. • In general, there is a strong correlation between the flower colour and the predominant type of anthocyaninanthocyanin that accumulates. • Orange and pink colours tend to be based on pelargonidin derivatives, • Magenta colours on cyanidincyanidin derivatives • Purple and blue colours on delphinidindelphinidin derivatives (Harborne, 1976). • Most anthocyanins are derived from just three basic anthocyanidin types: pelargonidin, cyanidin and delphinidin. The difference between them is in the number of hydroxyl groups on the B-ring (Fig) Table: Major anthocyanins-3-O-glucoside present in fruits • Purple and blue colours on delphinidindelphinidin derivatives (Harborne, 1976).
- 13. Source Plant Plants rich in anthocyanins are Vaccinium species, such as blueberry, cranberry, and bilberry; Rubus berries, including black raspberry, red raspberry, and blackberry; blackcurrant, cherry, eggplant (aubergine) peel, black rice, ube, Okinawan sweet potato, Concord grape, muscadine grape, red cabbage, and violet petals. • Red-fleshed peaches and apples contain anthocyanins. Anthocyanins are less abundant in banana, asparagus, pea, fennel, pear, and potato, and may be totally absent in certain cultivars of green gooseberries.cultivars of green gooseberries. • The reds, purples, and their blended combinations responsible for autumn foliage are derived from anthocyanins. Unlike carotenoids, anthocyanins are not present in the leaf throughout the growing season, but are produced actively, toward the end of summer. • They develop in late summer in the sap of leaf cells, resulting from complex interactions of factors inside and outside the plant. Their formation depends on the breakdown of sugars in the presence of light as the level of phosphate in the leaf is reduced.Orange leaves in autumn result from a combination of anthocyanins and carotenoids.
- 14. Importance for Plants: • Anthocyanins may have a protective role in plants against extreme temperatures. Tomato plants protect against cold stress with anthocyanins countering reactive oxygen species, leading to a lower rate of cell death in leaves • The absorbance pattern responsible for the red color of anthocyanins may be complementary to that of green chlorophyll in photosynthetically-active tissues such as young Quercus coccifera leaves. It may protect the leaves from attacks bysuch as young Quercus coccifera leaves. It may protect the leaves from attacks by herbivores that may be attracted by green color.
