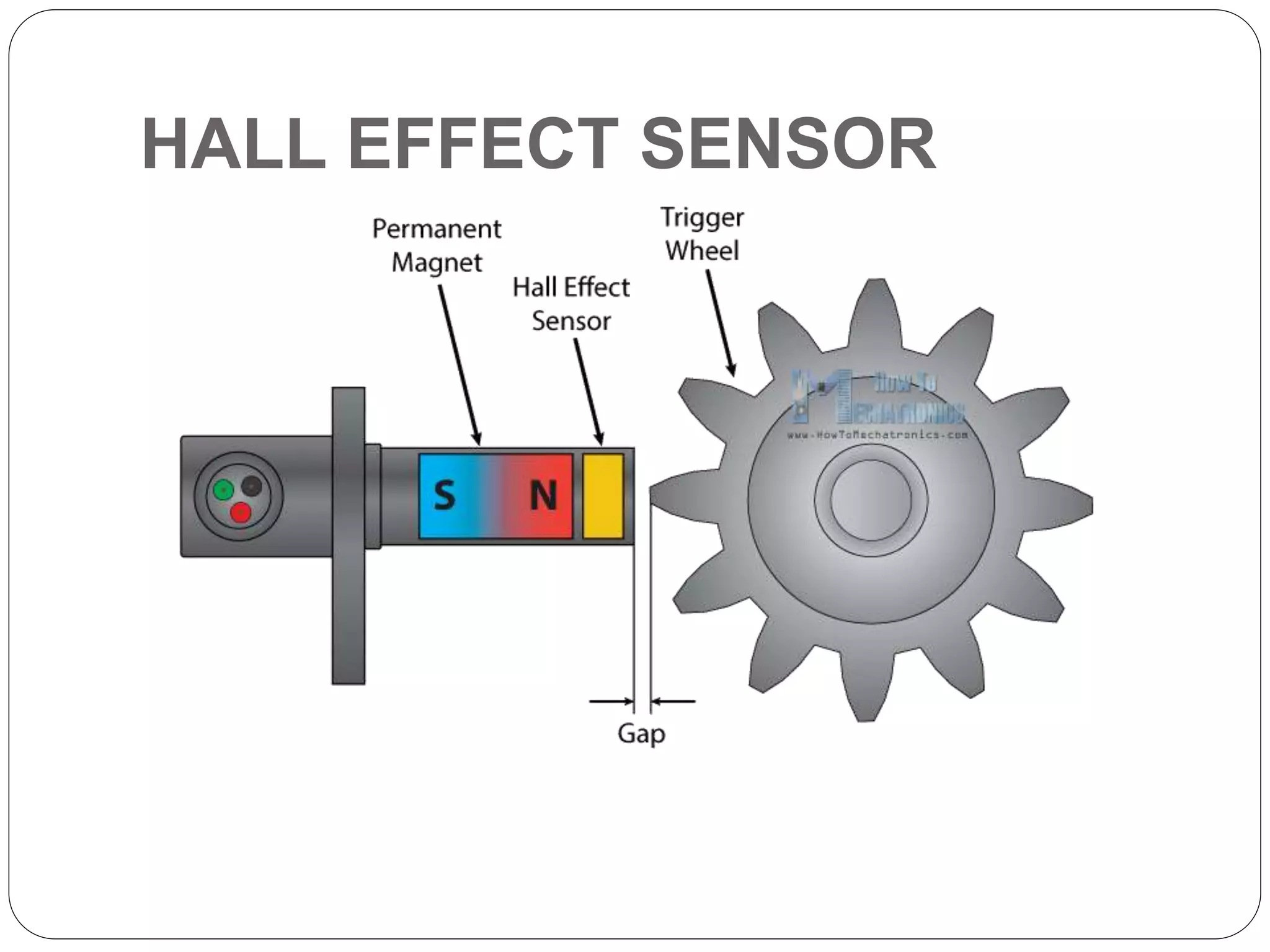
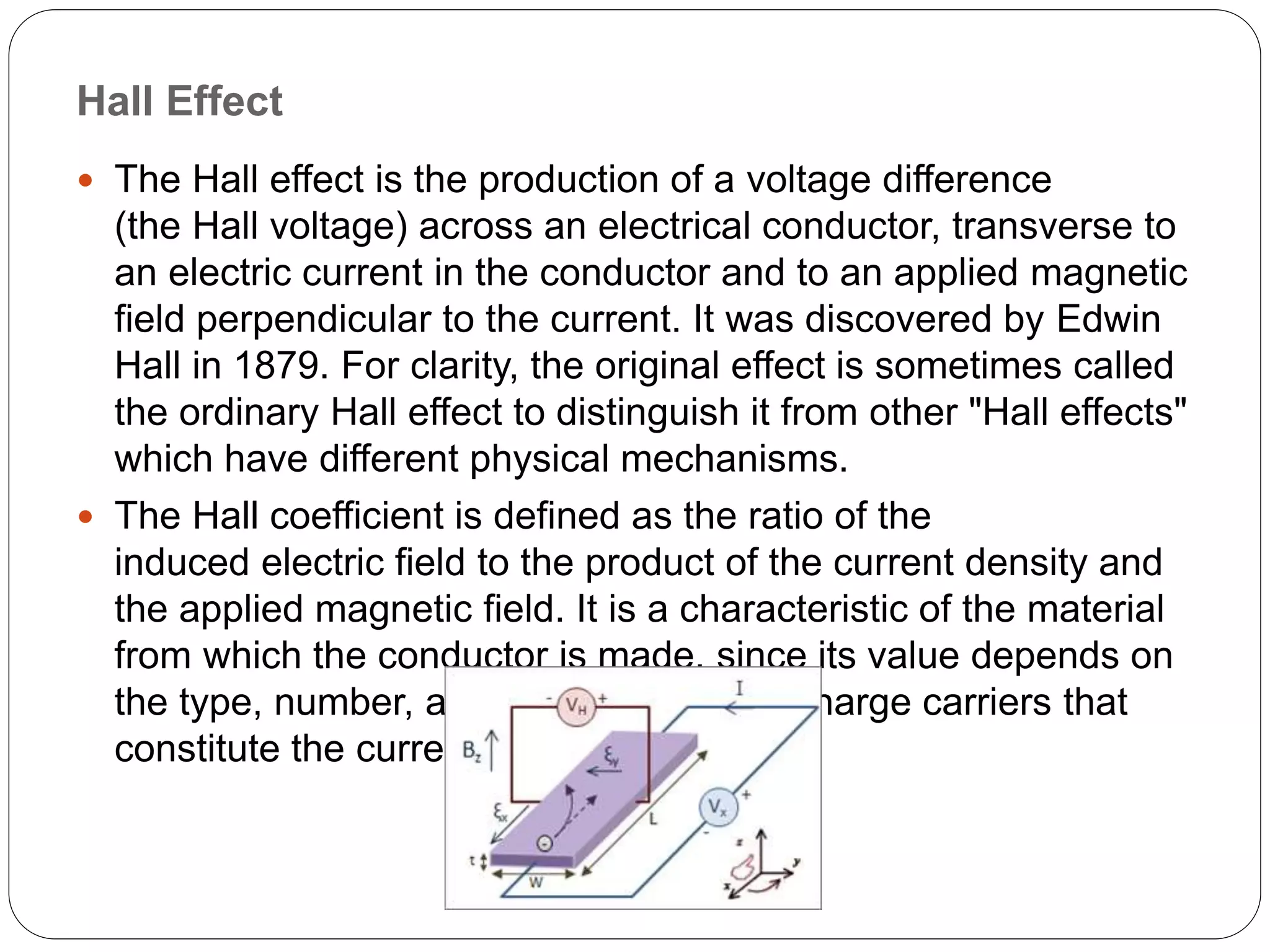
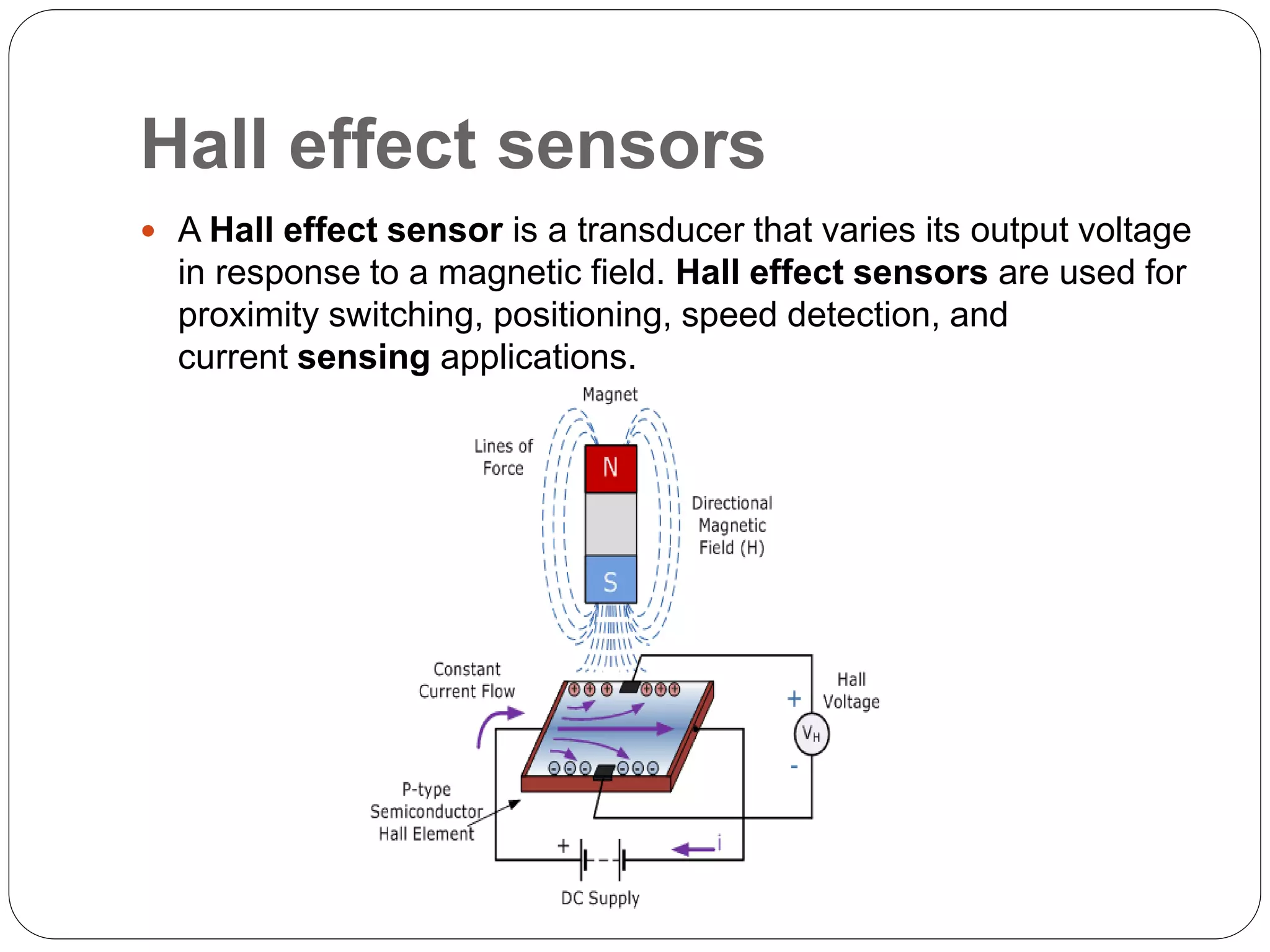
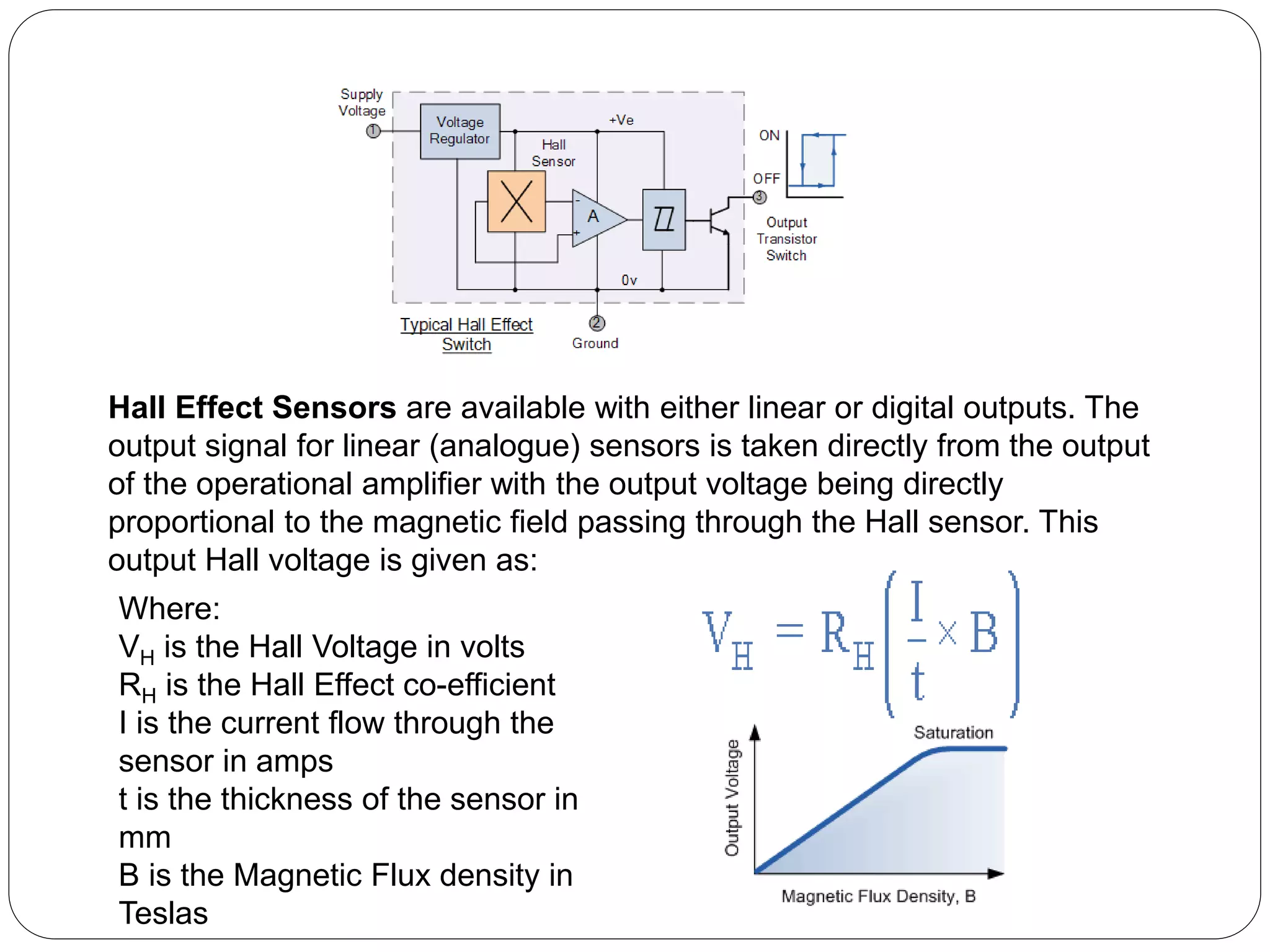
Hall Effect sensors operate based on the Hall effect, where a voltage difference is produced across a conductor when an electric current passes through it and is exposed to a magnetic field. Hall Effect sensors can detect magnetic fields and produce either linear or digital outputs. They are used in applications like current sensing, speed detection, proximity switching, and position sensing. Some advantages are that they are not affected by ambient conditions and do not have contact with mechanical parts. Some disadvantages include limited range and sensitivity to temperature fluctuations and external magnetic fields.