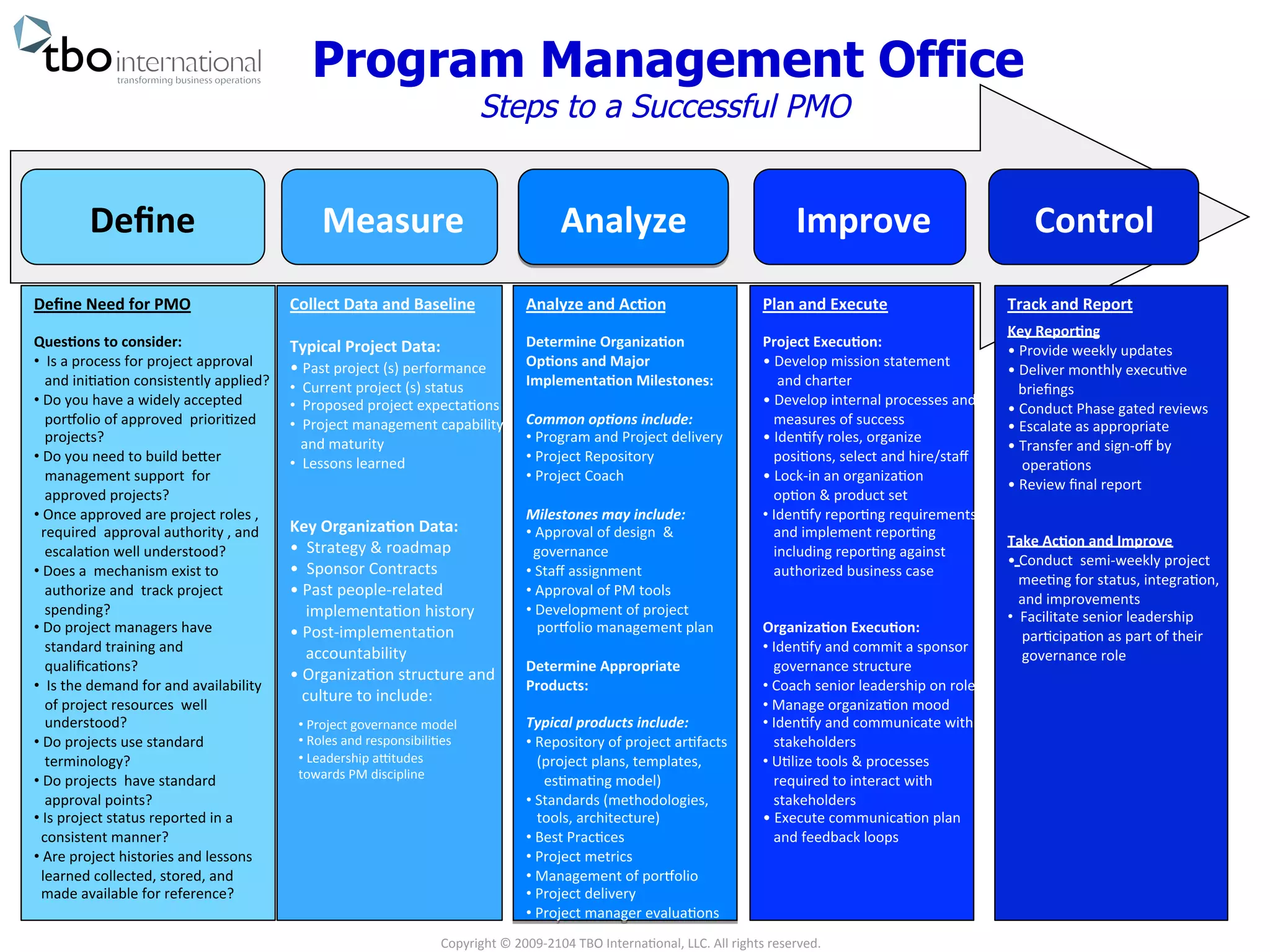
The document outlines the essential steps to establish a successful Program Management Office (PMO), including defining the need, measuring performance, and analyzing organizational capabilities. Key activities involve developing processes for project approval, tracking resources, and maintaining project history while aligning with organizational strategy. It emphasizes continuous improvement through regular reporting and engagement with stakeholders to foster project governance.