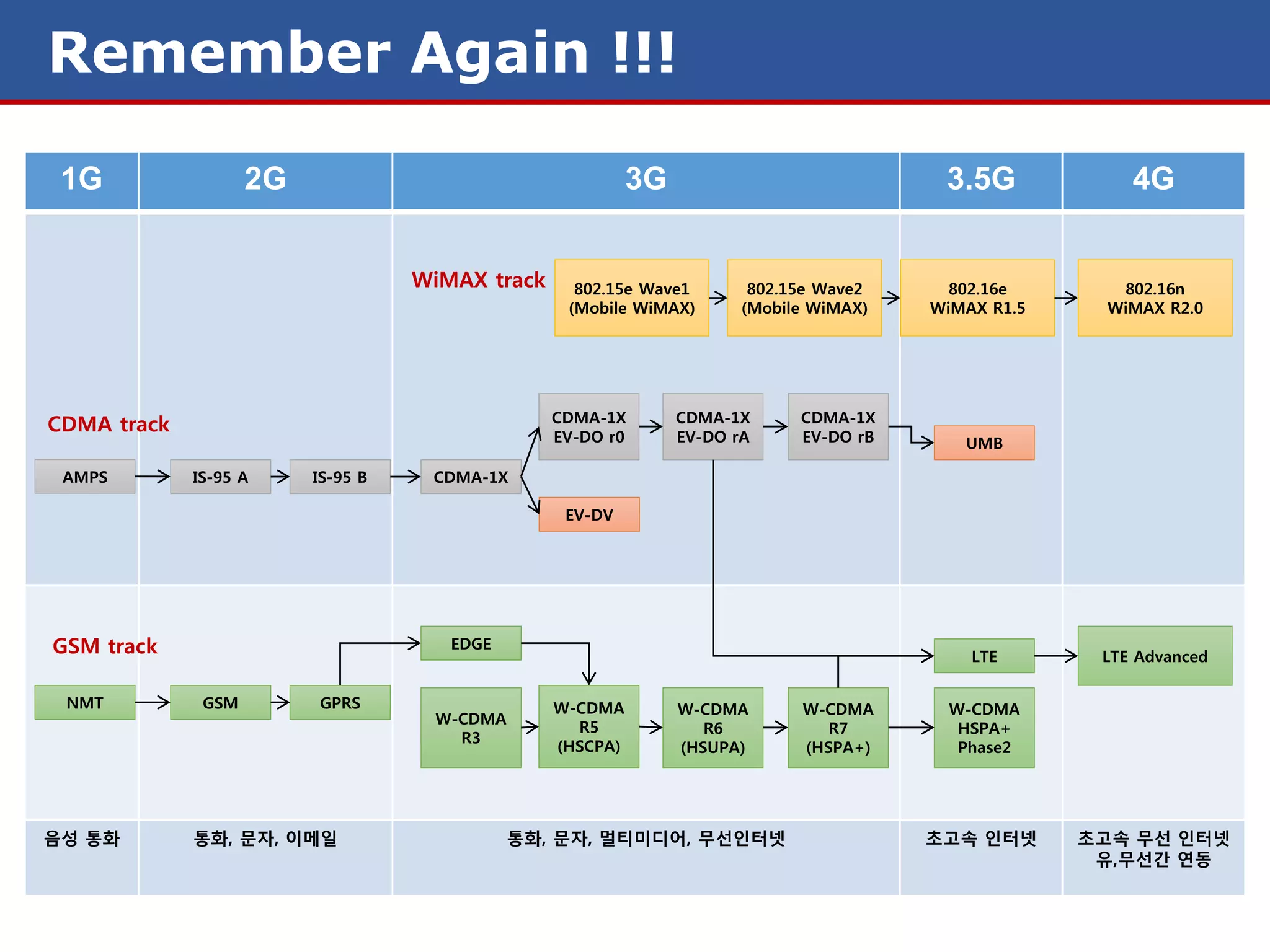
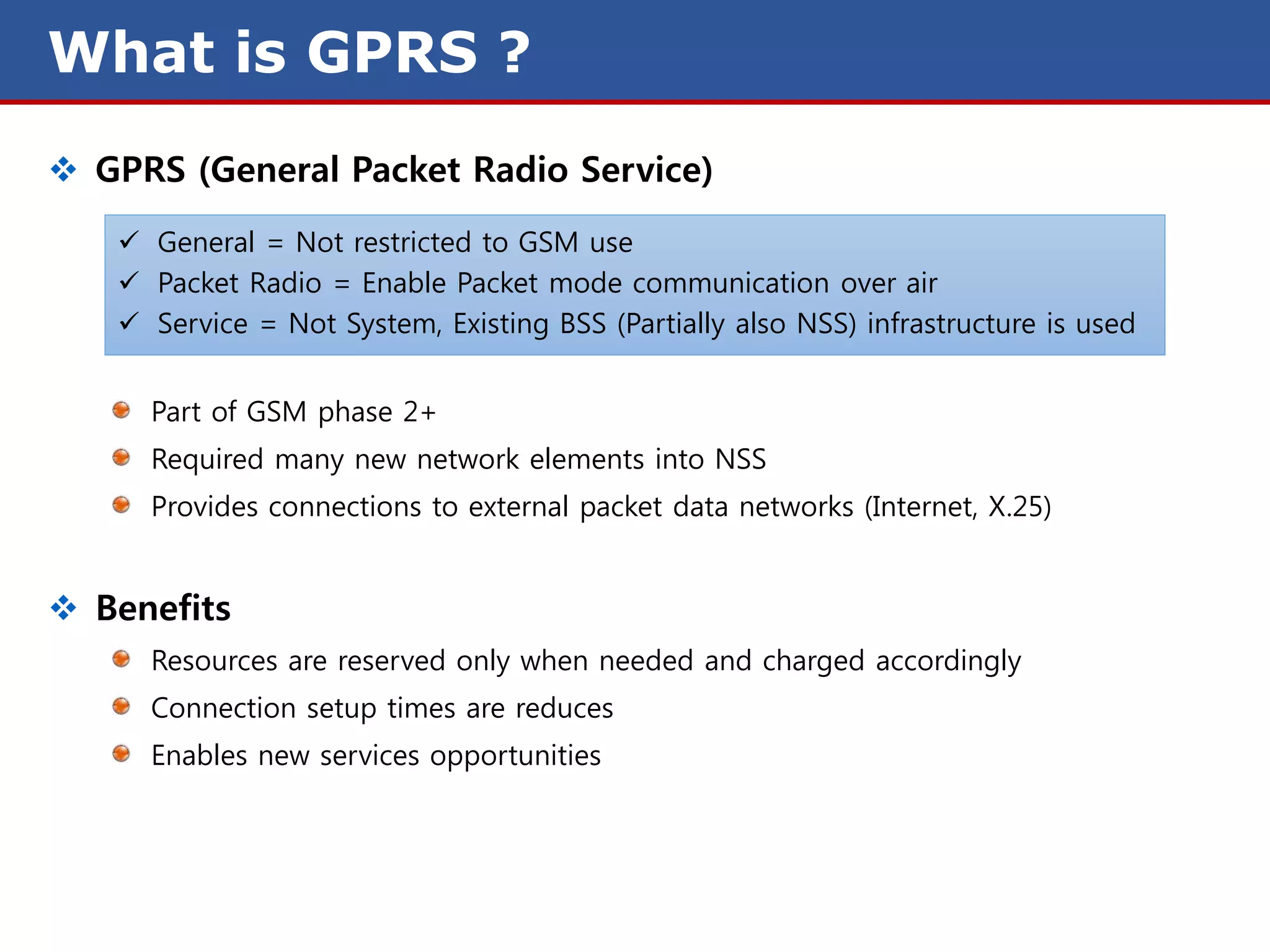
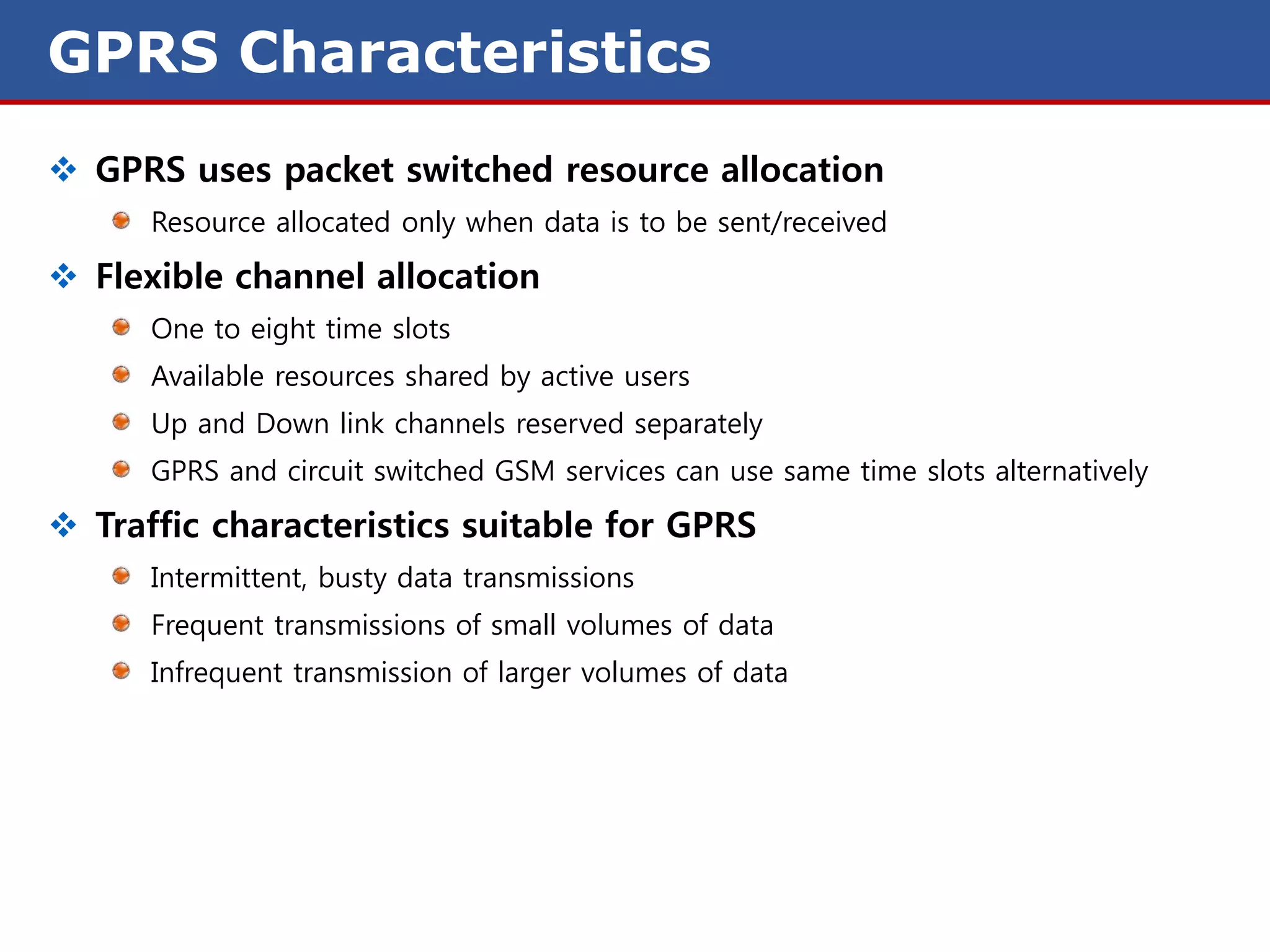
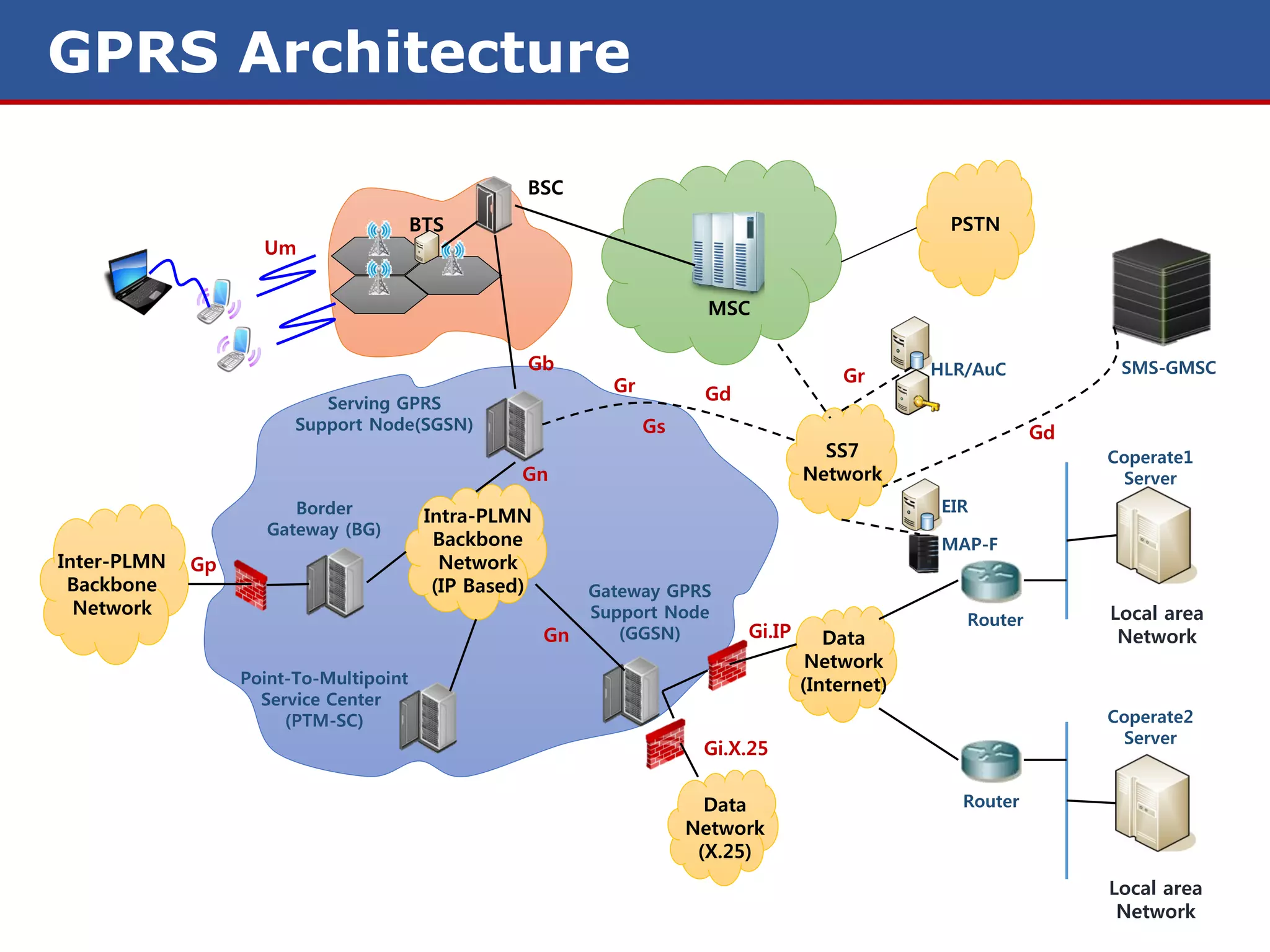
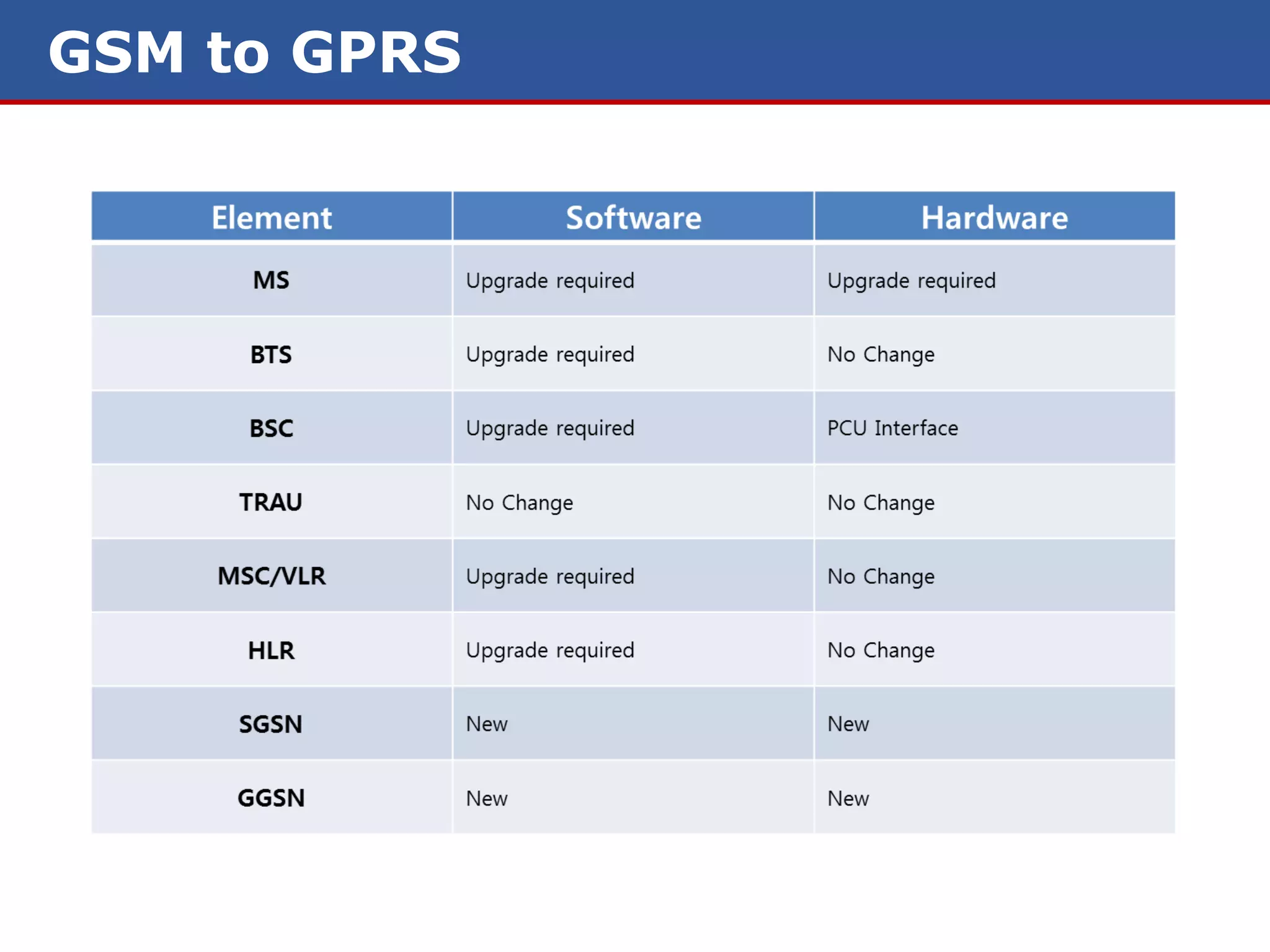
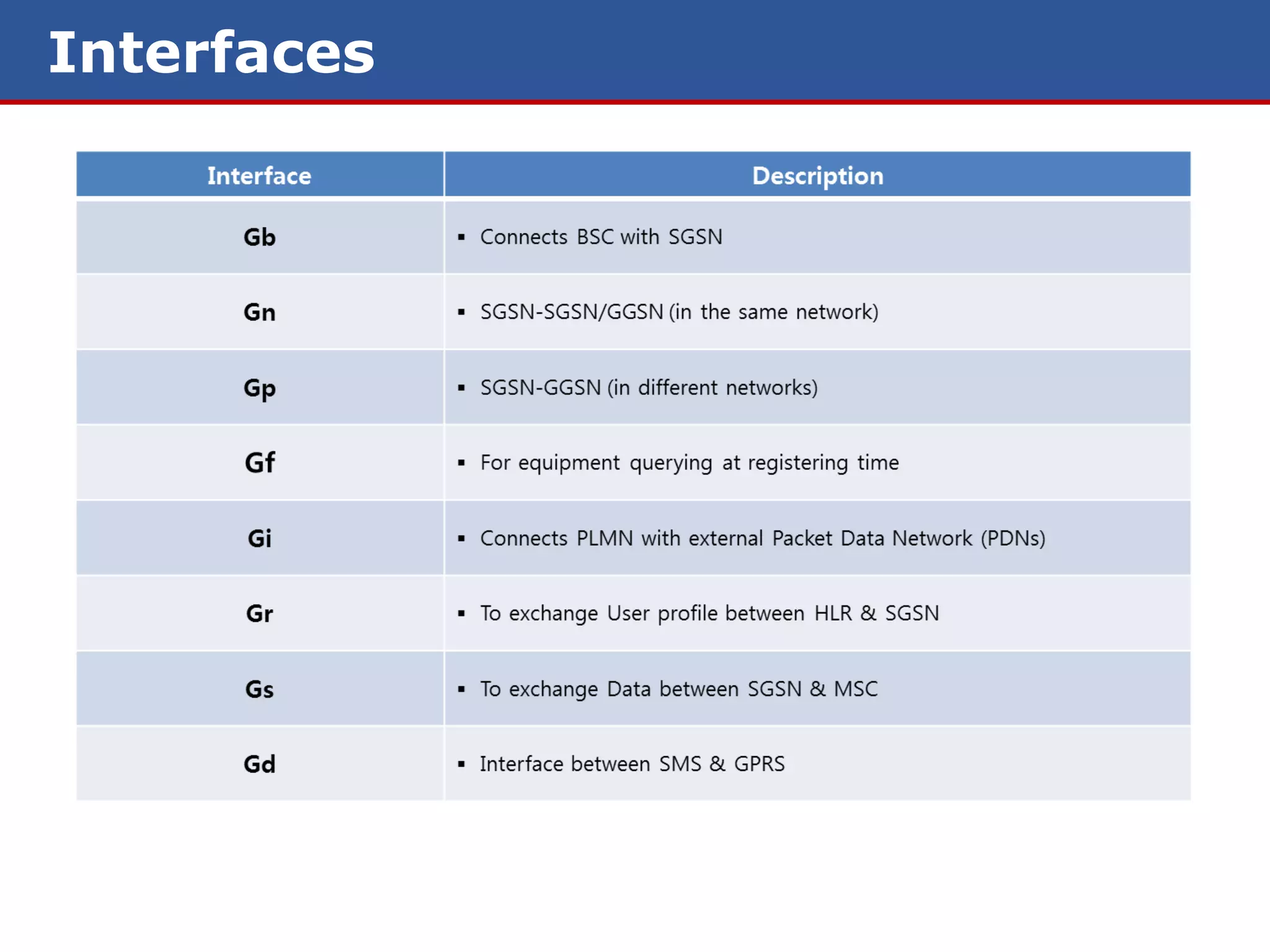
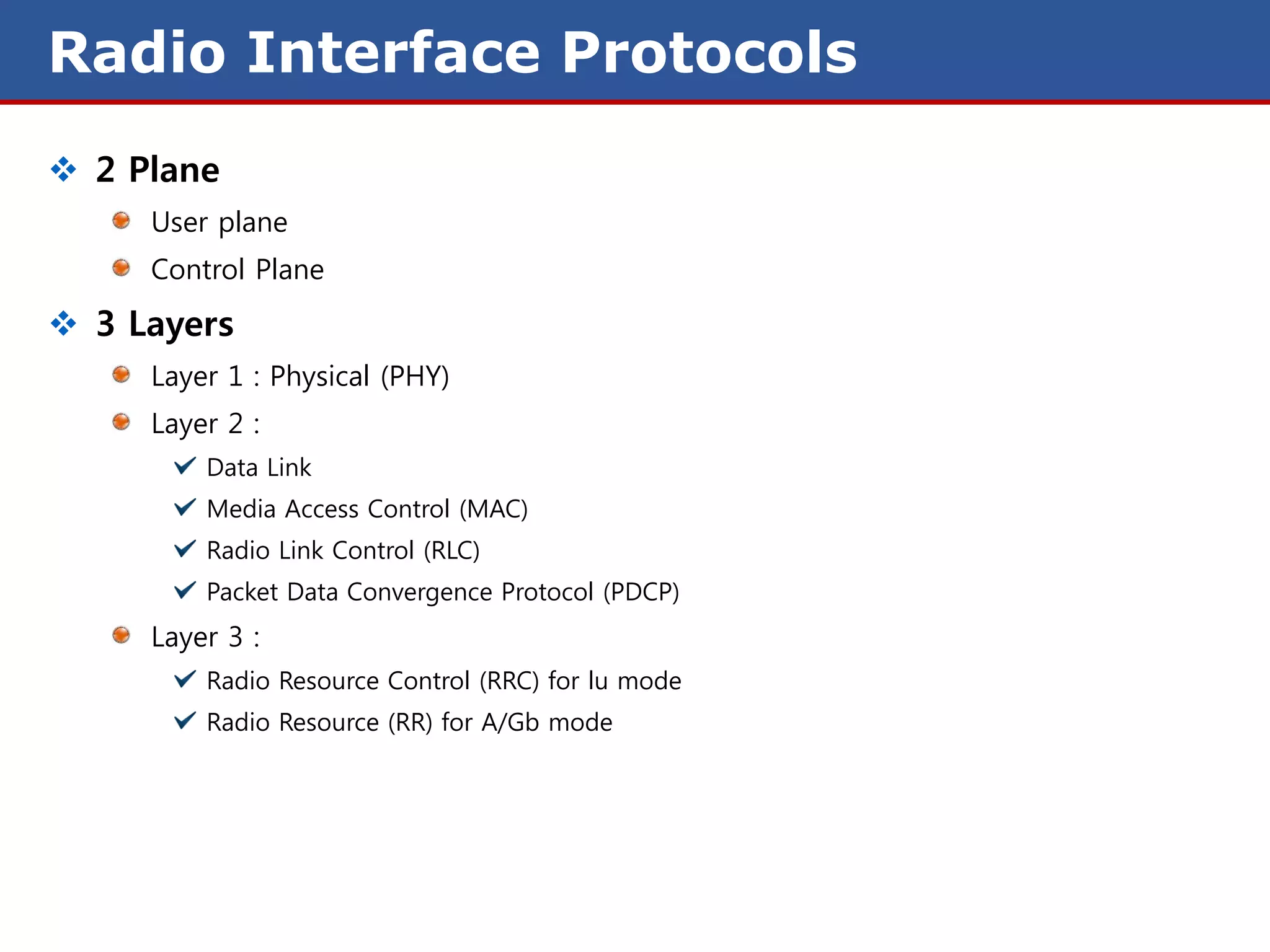
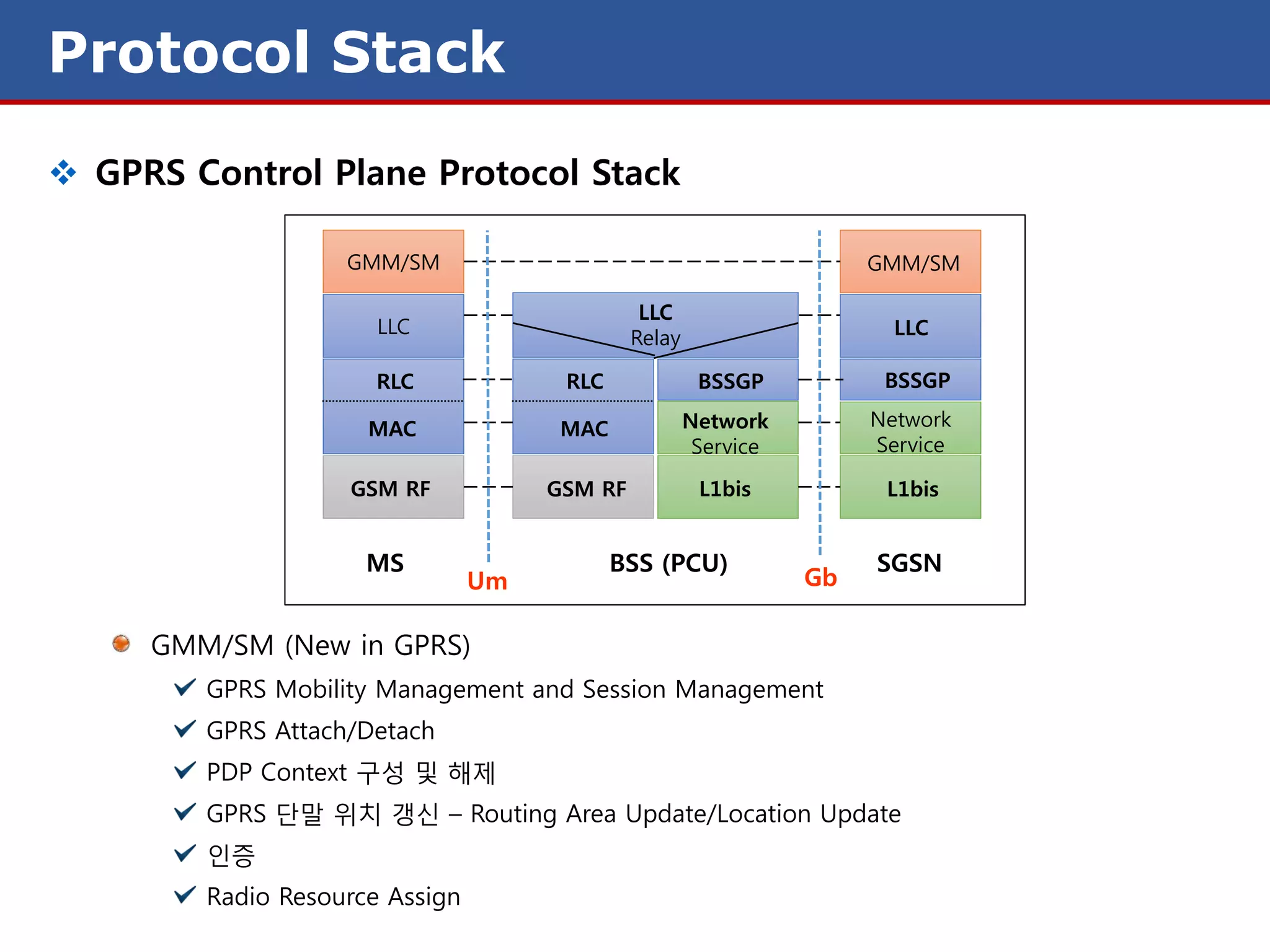
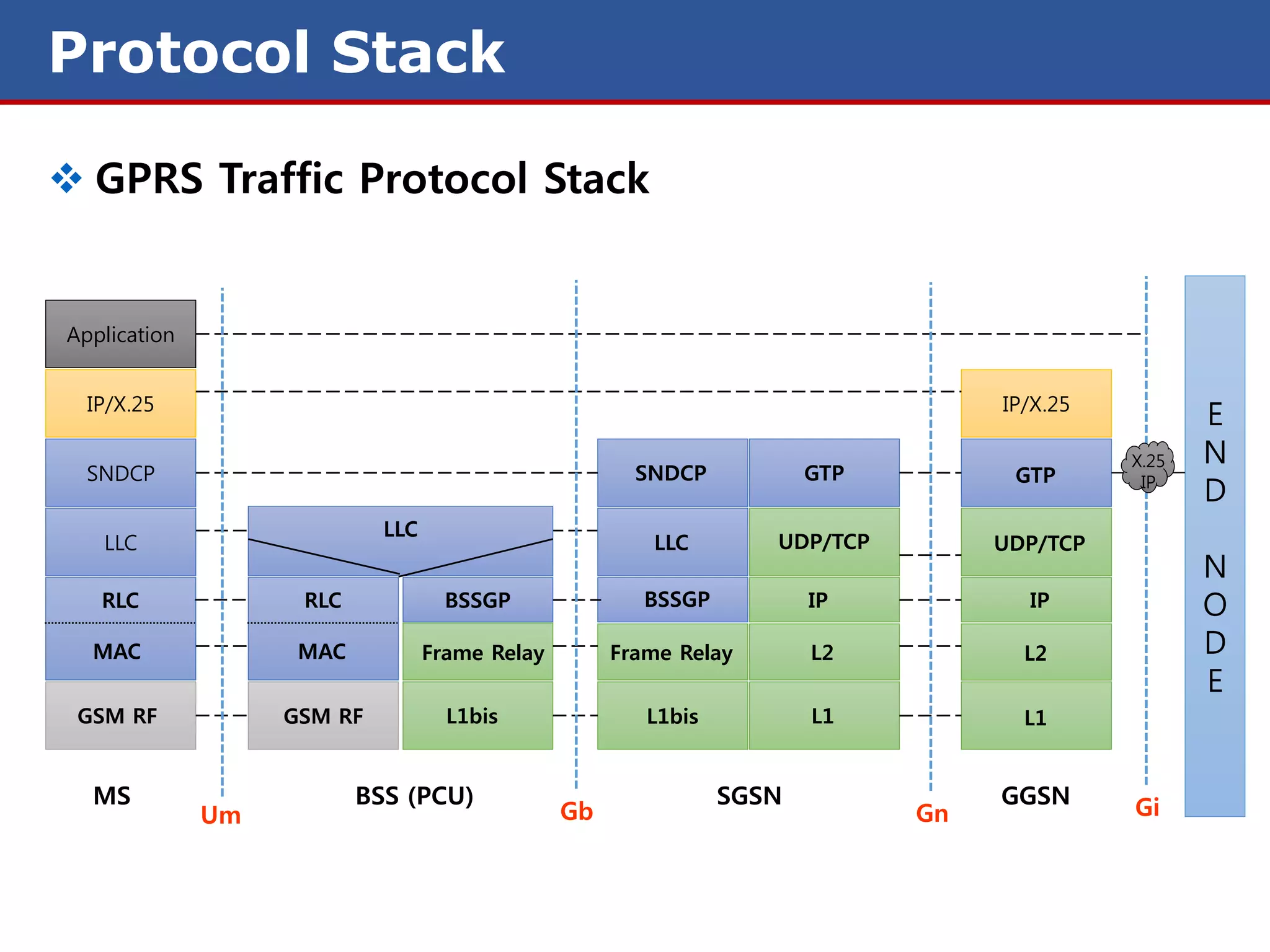
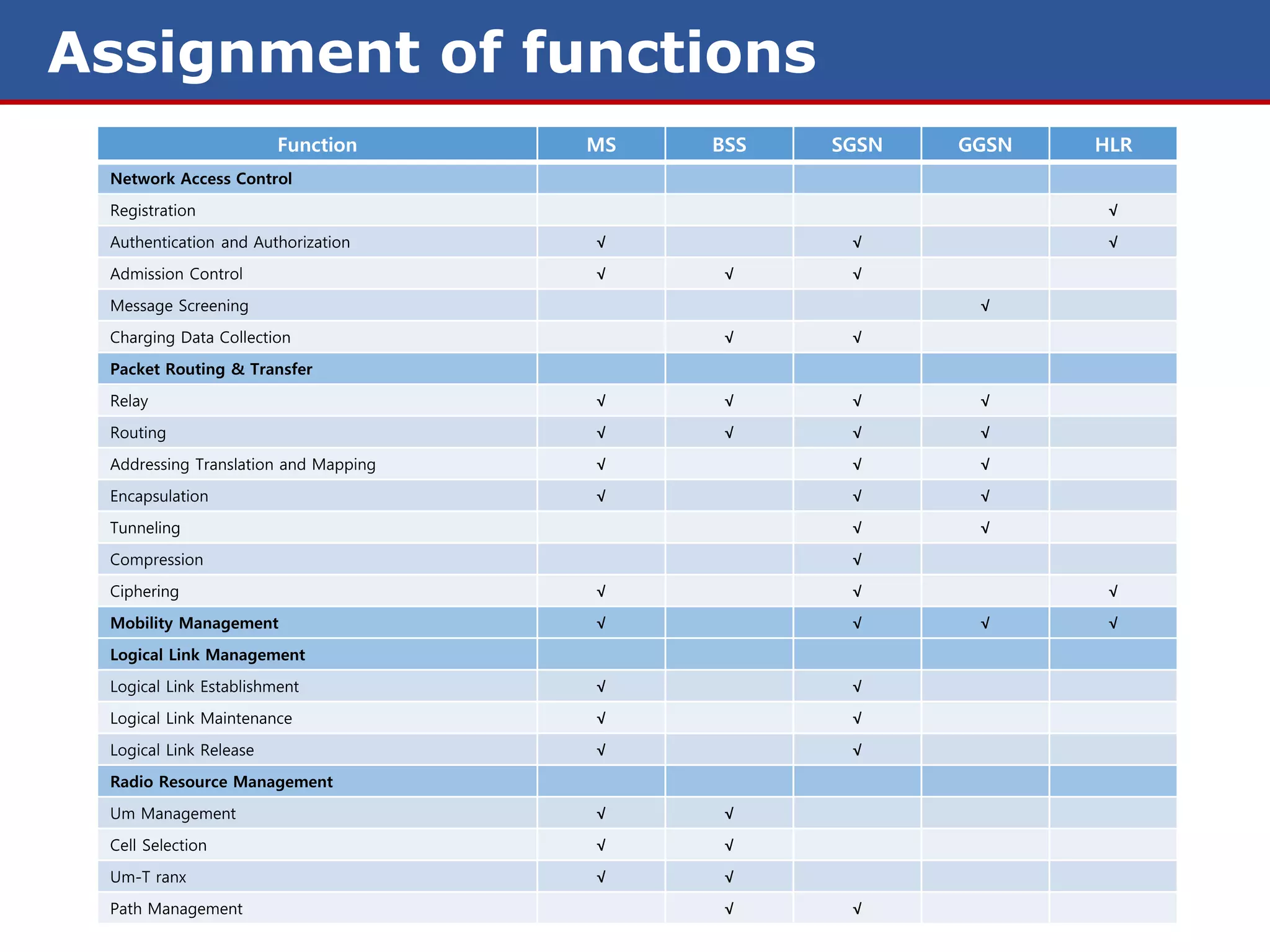
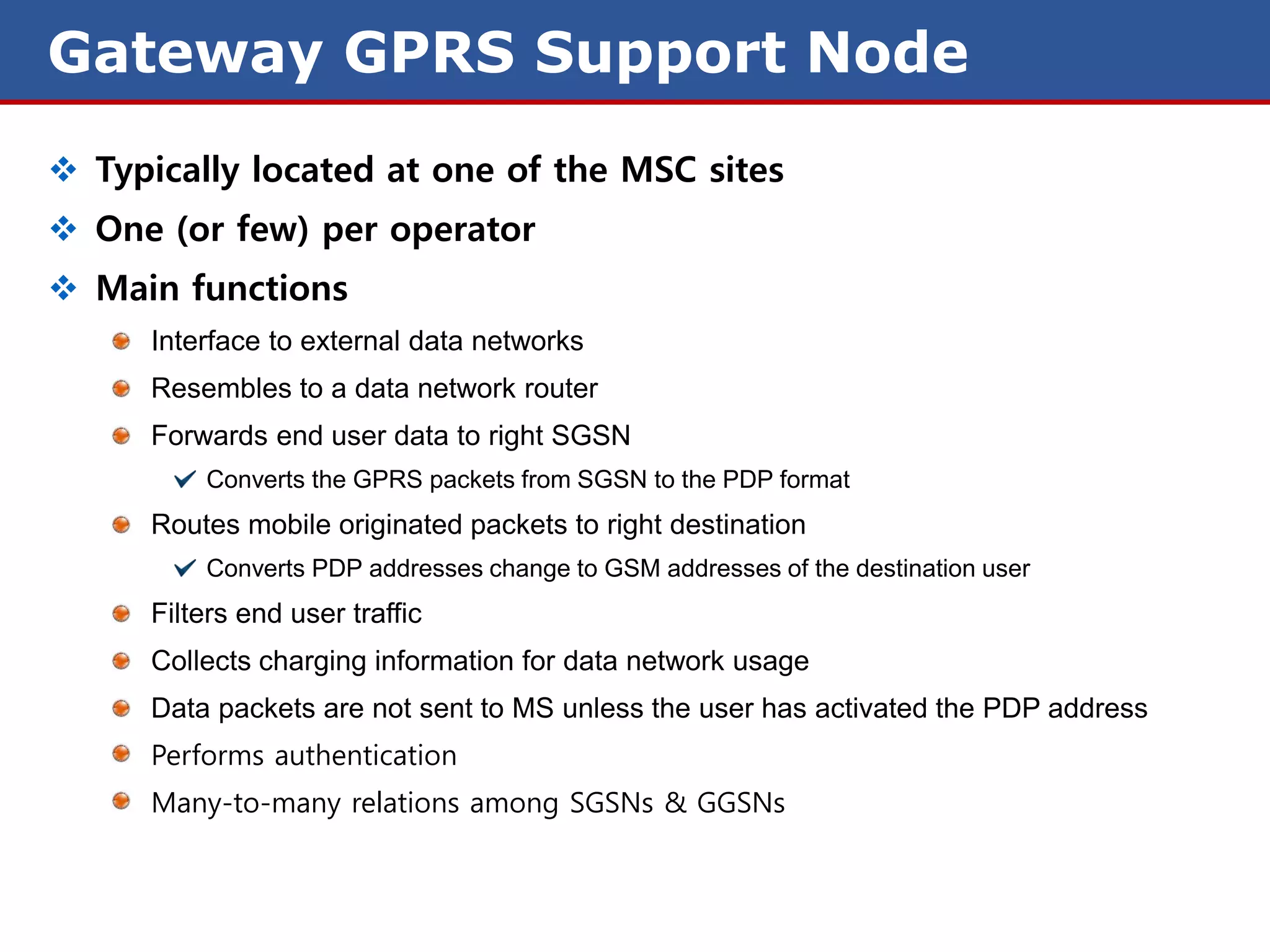
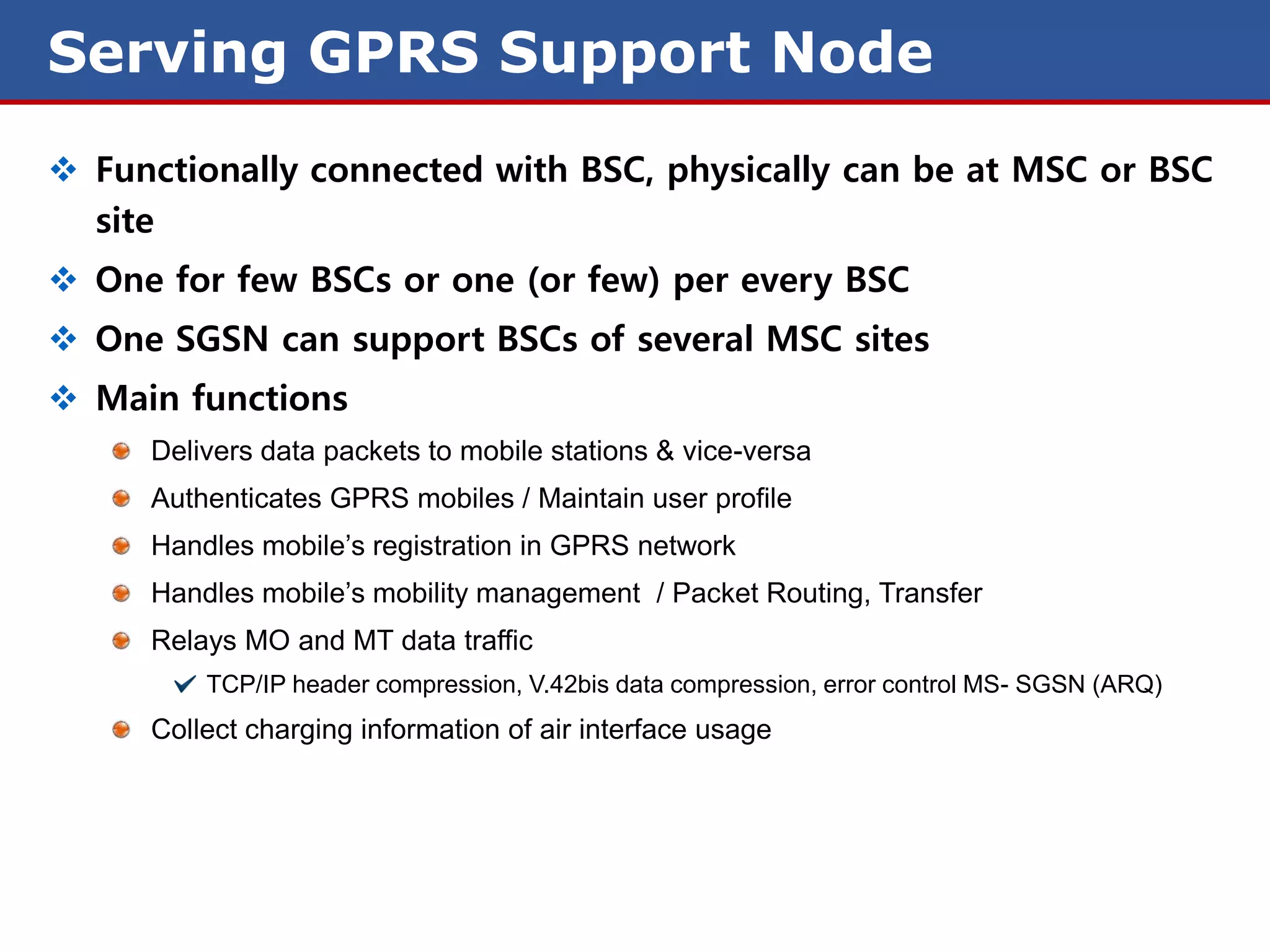
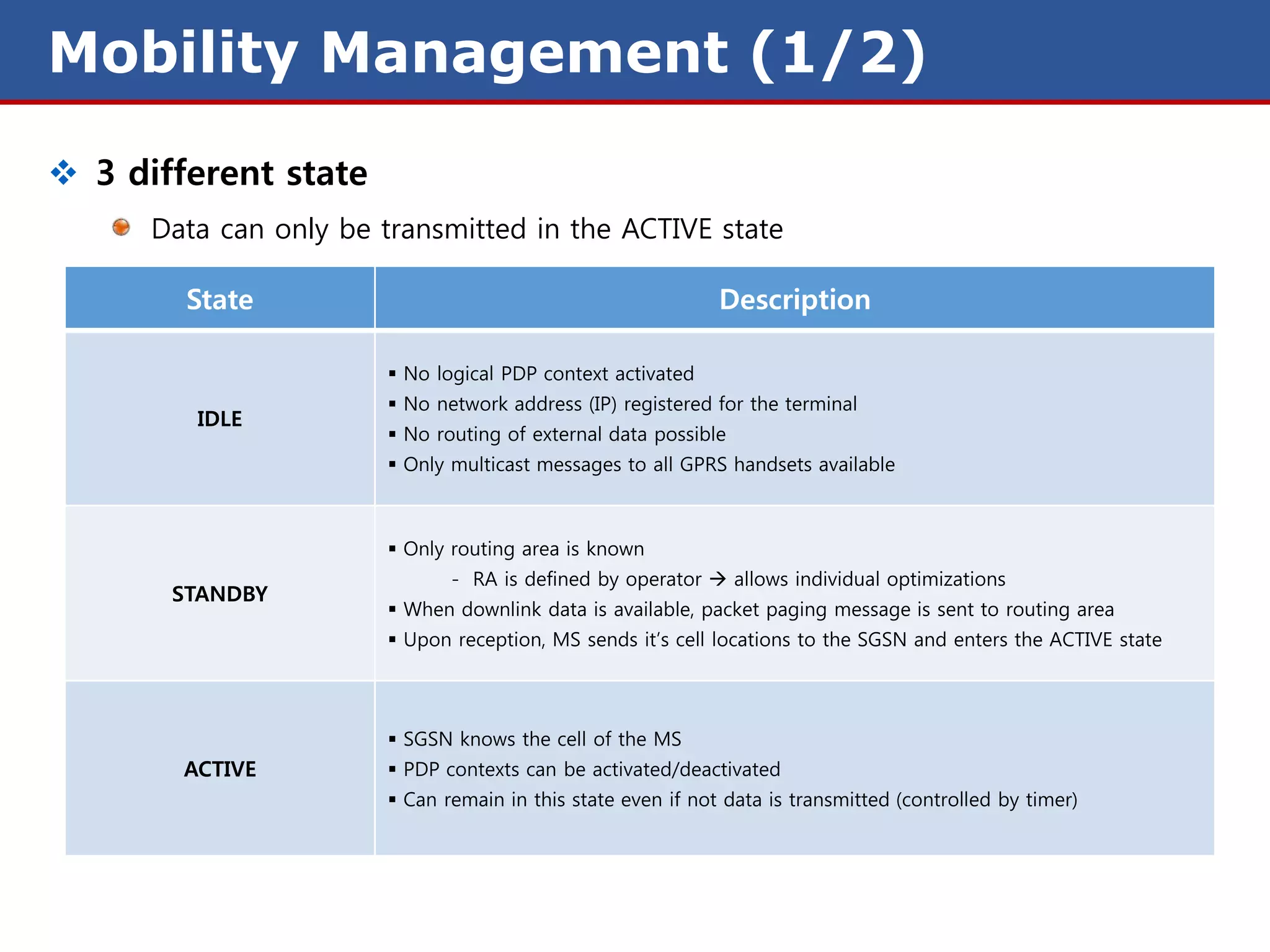
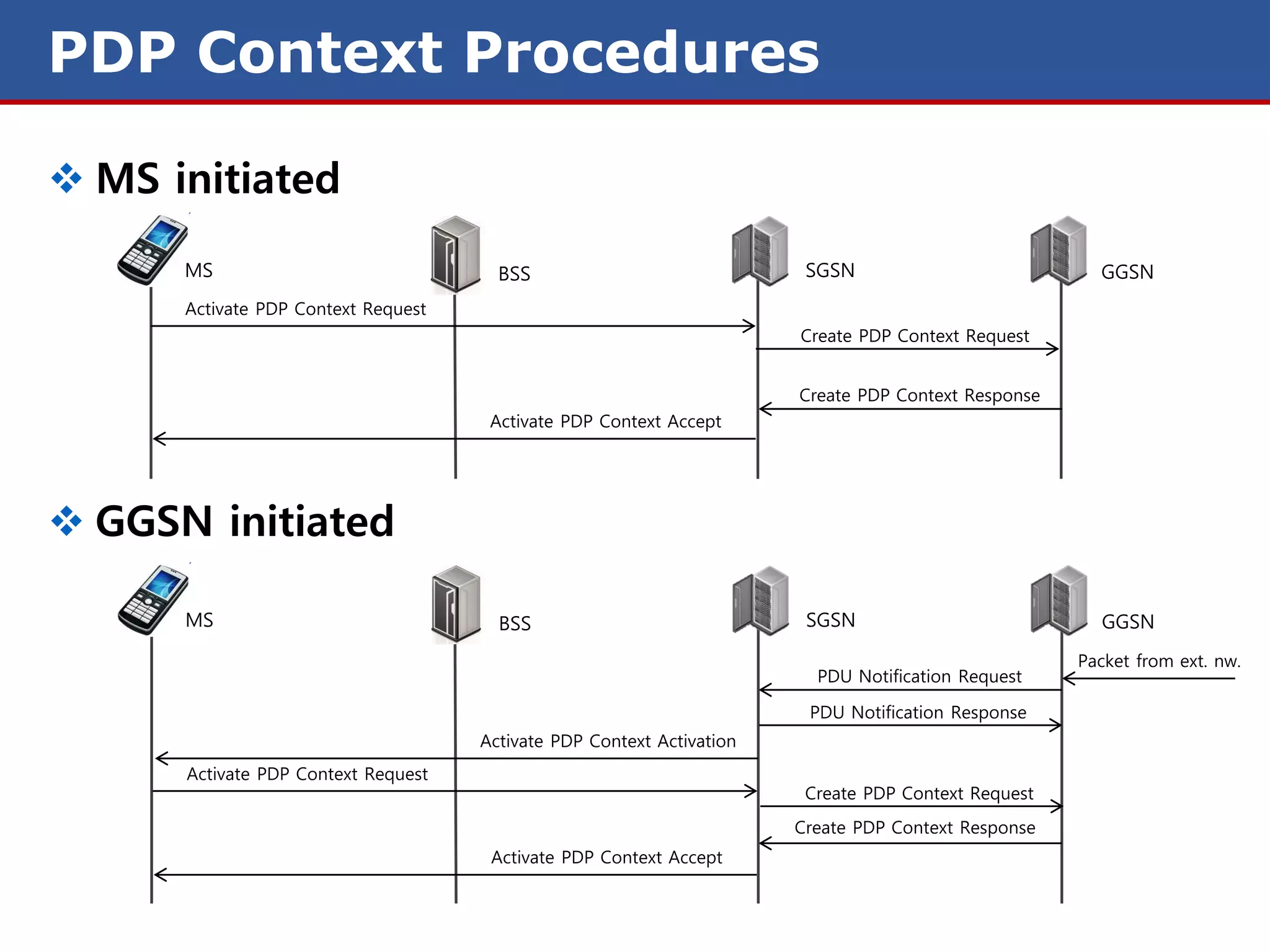
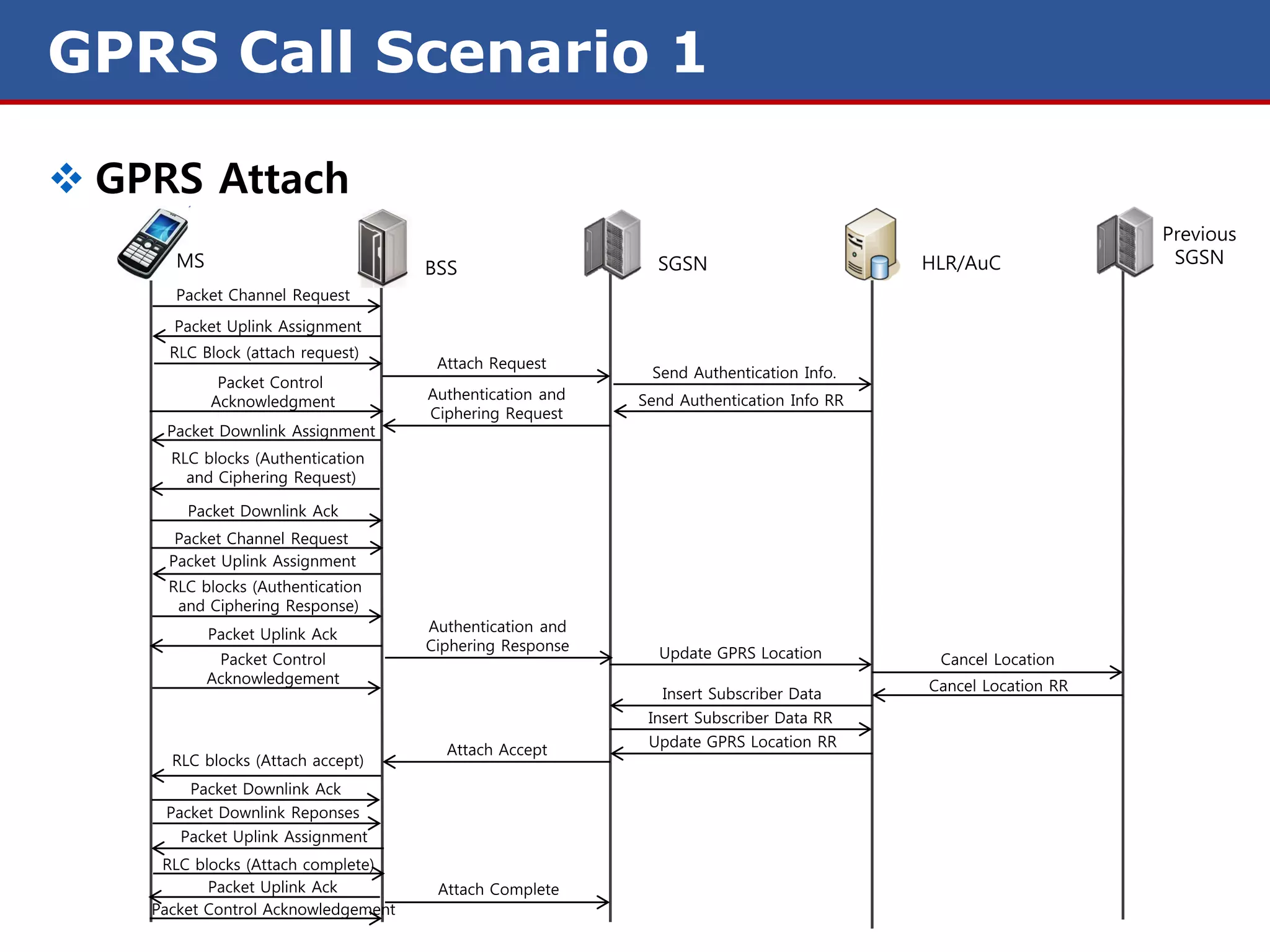
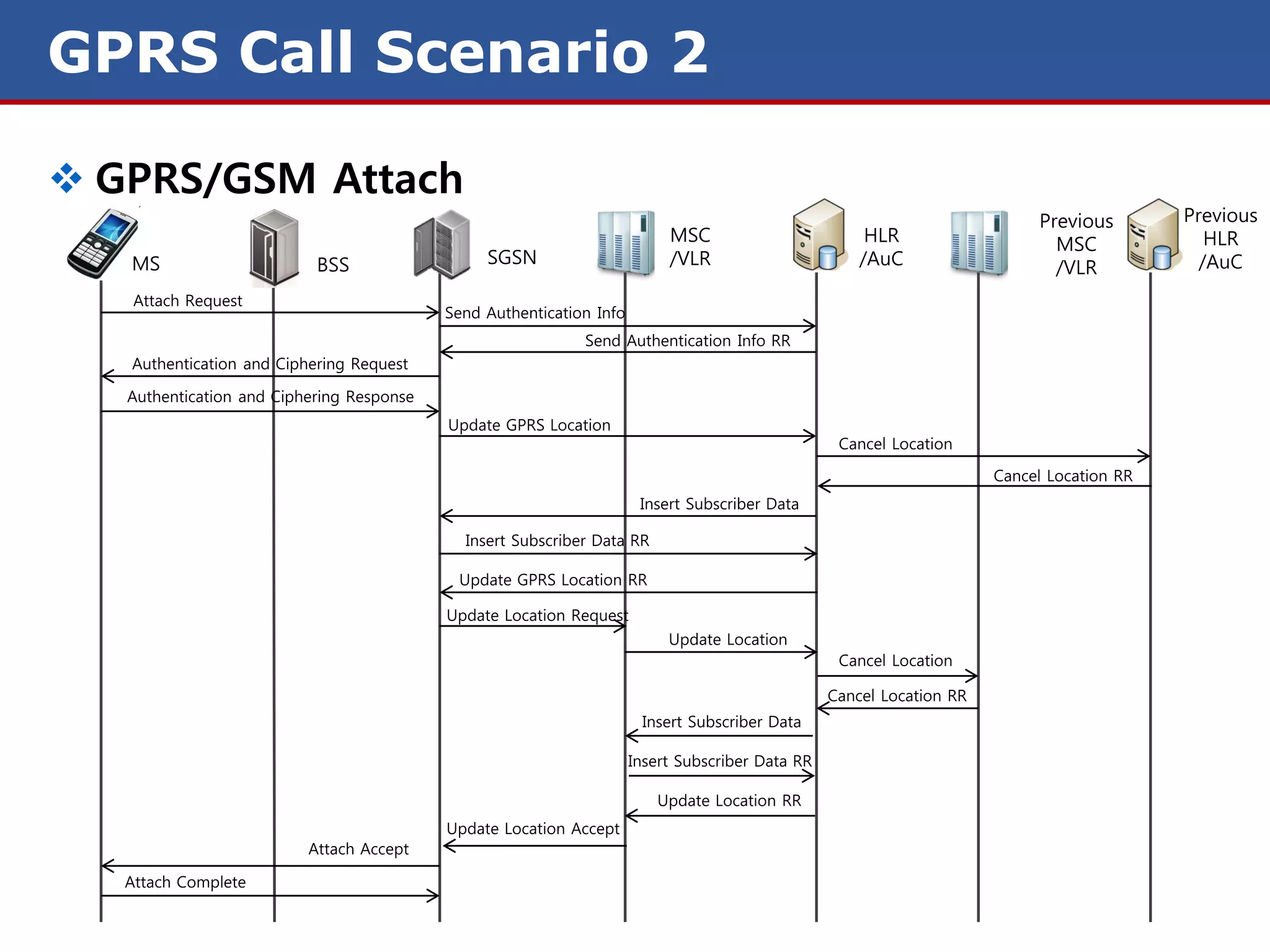
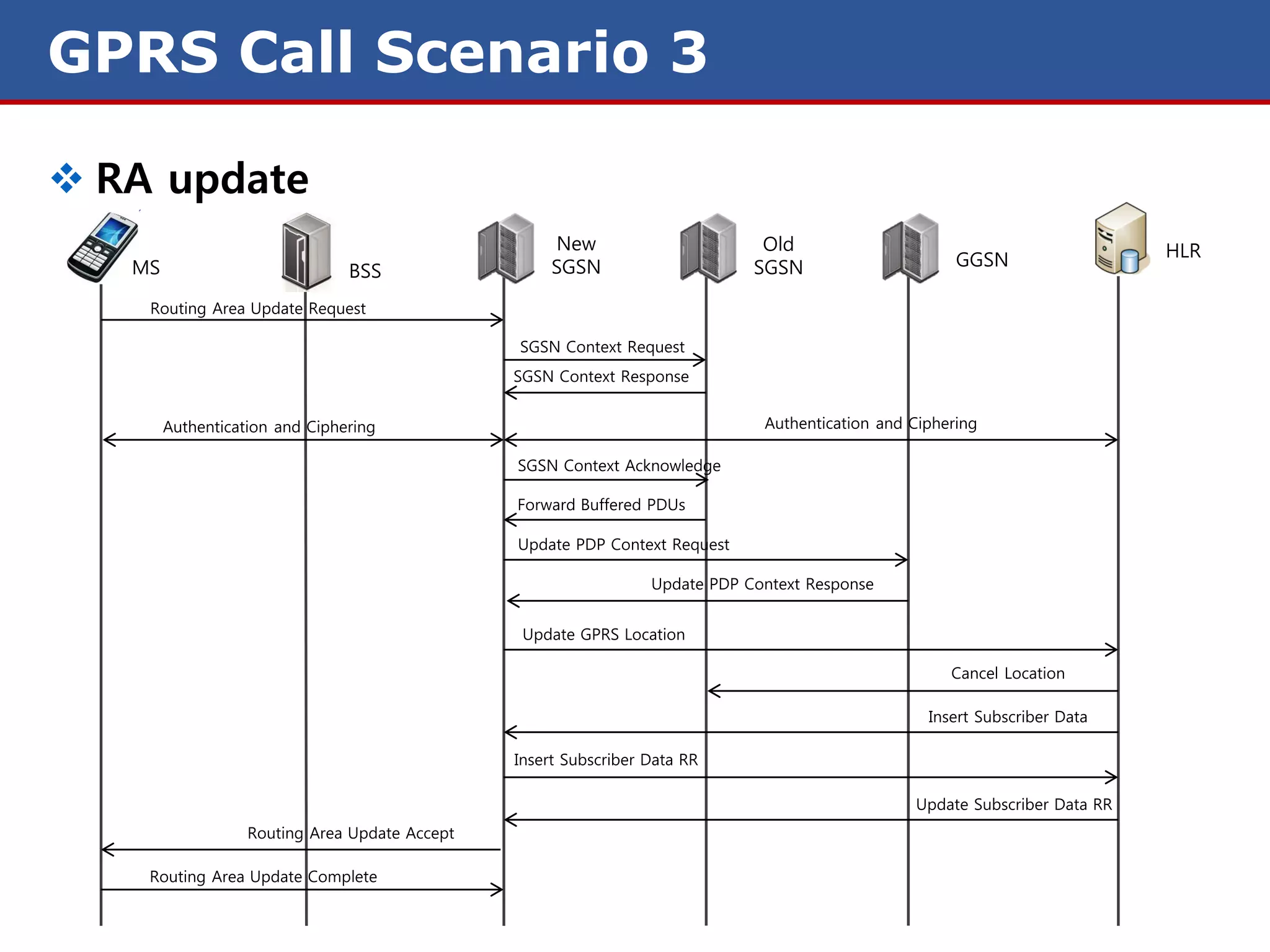
The document discusses GPRS (General Packet Radio Service) networks. It provides an overview of the evolution of mobile network generations from 1G to 4G. It then describes the key components and protocols of GPRS networks, including the GPRS architecture, interfaces, radio interface protocols, protocol stacks, and functions of network elements like the SGSN and GGSN.

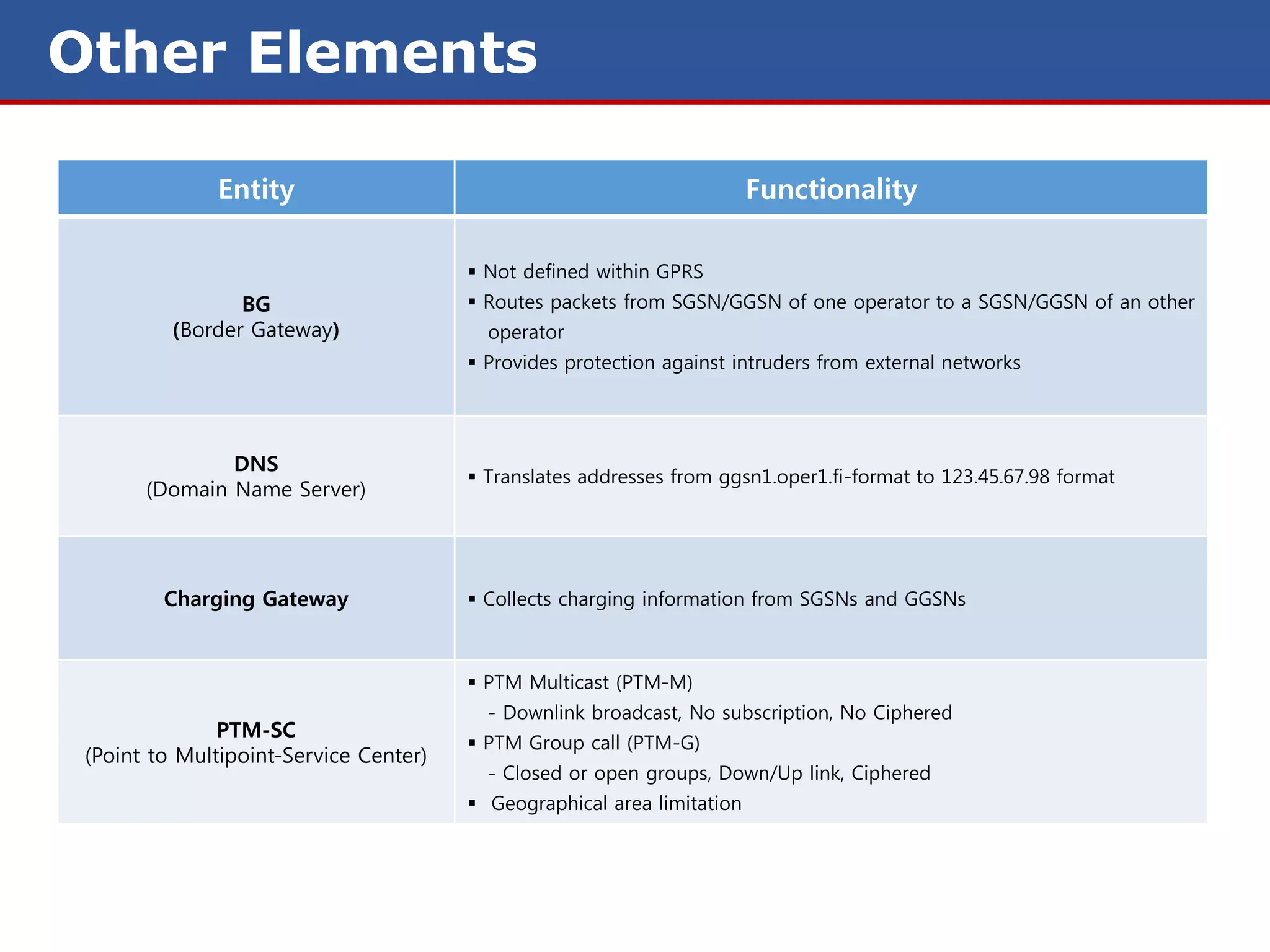


![Logical Channels
Mapped by the MAC to physical channels
Control channels for control, synchronization and signaling
Common/Dedicated/Broadcast
Packet Traffic Channels
Encoded speech/Encoded data
Packet Data Logical Channels
Traffic Channels
Control Channels
PCCCH PBCCH PDCCH PDTCH
PTCCH/U PTCCH/U PTCCH/D PACCH PBCCH PTCCH/U PTCCH/D PACCH PDTCH/H PDTCH/D
[Up] [Down] [Down] [Down] [Down] [Up/Down] [Down] [Up] [Up] [Down]
PCCCH = Packet Common Control Channel PPCH = Packet Paging Channel Up = Uplink Direction
PBCCH = Packet Broadcast Control Channel PAGCH = Packet Access Grant Channel Down = Downlink Direction
PDCCH = Packet Dedicated Control Channel PNCH = Packet Notification Channel
PDTCH = Packet Traffic Channel PACCH = Packet Associated Control Channel
PRACH = Packet Random Access Channel PTCCH = Packet Timing Advance Control
Channel](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/gprsnetwork-130307073627-phpapp01/75/Gprs-network-17-2048.jpg)


![[별첨] GSM vs. GPRS
Email via GSM Email via GPRS
Auth. Auth.
Server Server
GSM PSTN Internet GPRS Internet
Email Email
User Modem Modem Server Virtual Authenticated Server
GPRS Path to Email
Data Tunnel Server
Initial Call Process Time (s) Initial Call Process Time (s)
GSM Call 4 GPRS Call 4
Train Model 30 Login and Authenticate 11
Login and Authenticate 11 Download mail 180
Download mail 180 Total 3min 45s
Total 3min 45s Subsequent Call
Subsequent Call Not applicable – Permanent Virtual
0
Repeat Above 3min 45s Circuit](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/gprsnetwork-130307073627-phpapp01/75/Gprs-network-29-2048.jpg)
