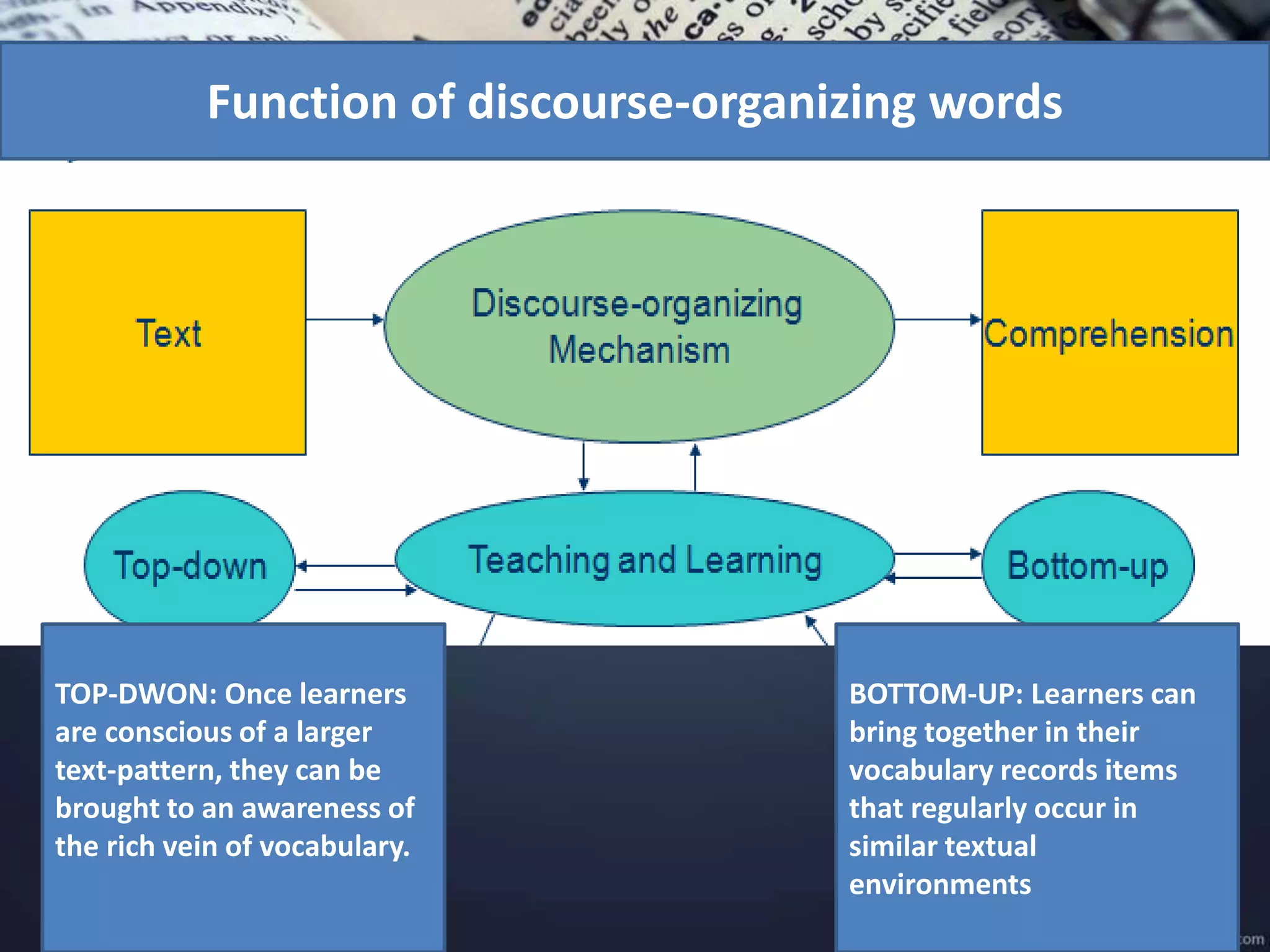
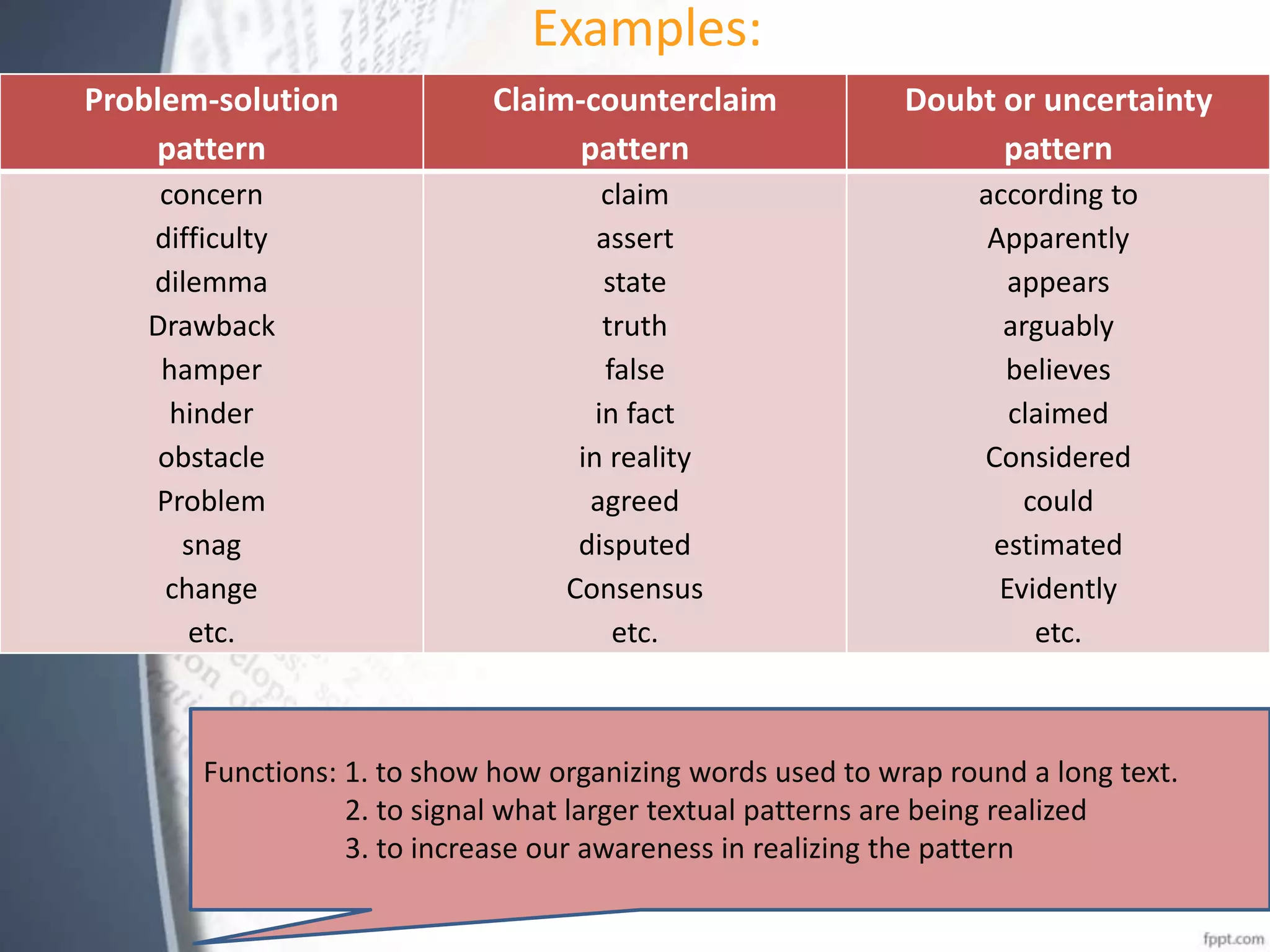
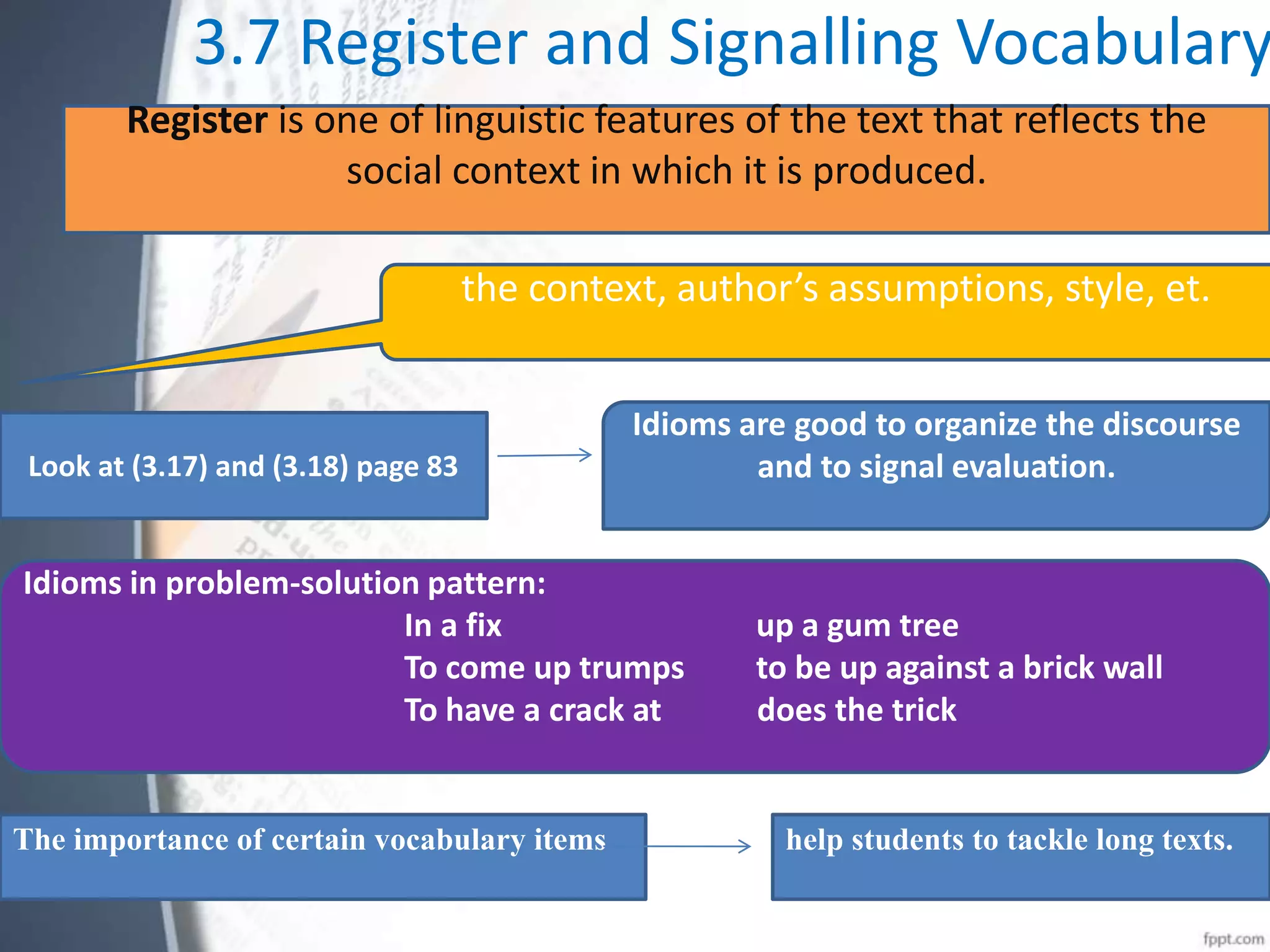
This document discusses discourse analysis and vocabulary. It explains that discourse-organizing words help signal larger textual patterns and parcel up phrases and sentences. Examples of discourse patterns include problem-solution, claim-counterclaim, and doubt/uncertainty. Register and idioms also help organize discourse. Modality expresses certainty, possibility, volition, permission and obligation and conveys stance. Studying vocabulary in discourse looks at patterns across clauses/sentences and how certain words organize structure and register. Collecting vocabulary along discourse-functional lines can motivate word lists beyond traditional semantic fields.