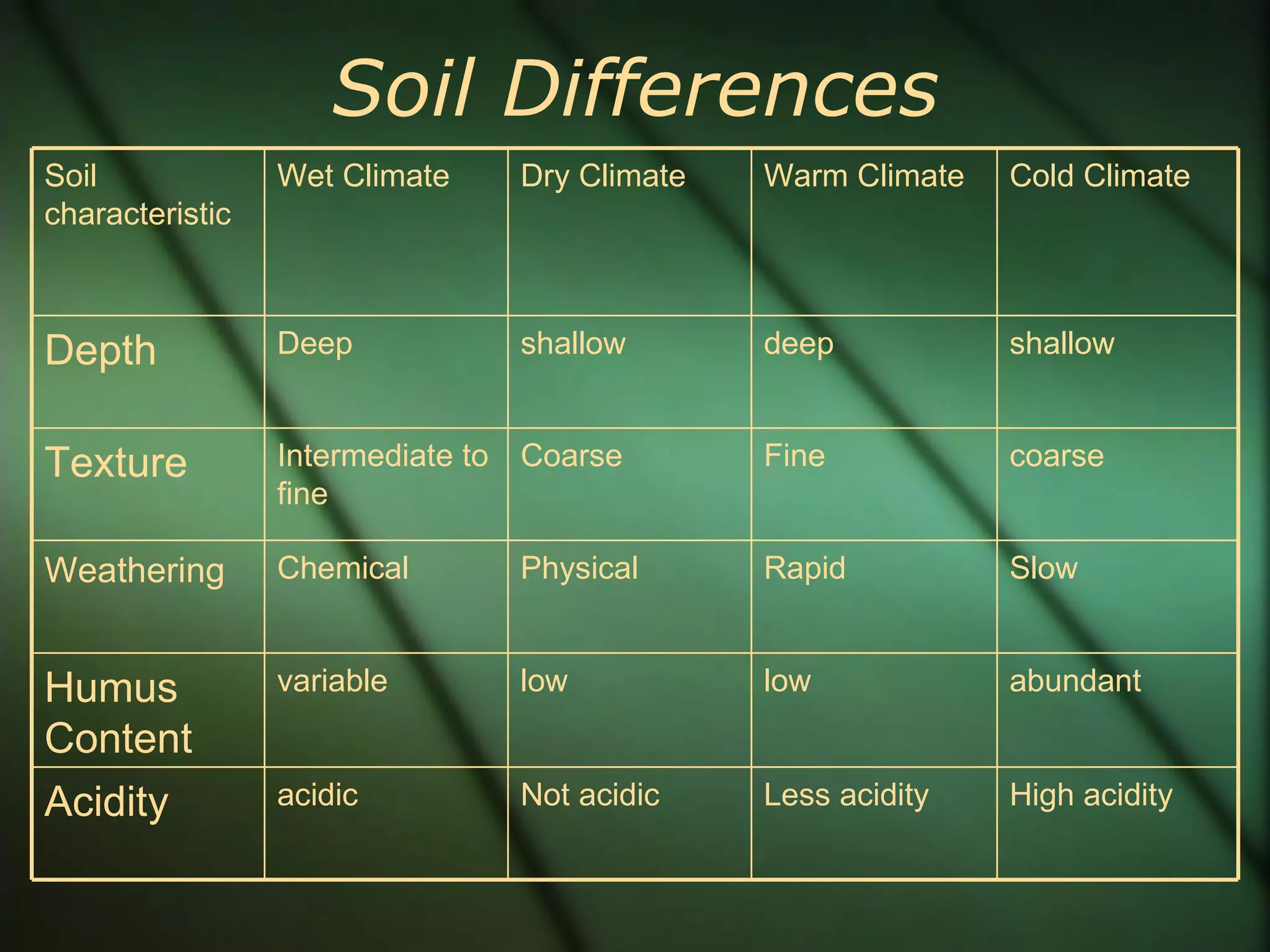
1) The document discusses soil regions and vegetation regions. Soil is a thin layer of weathered rock, humus, air and water that the world's food supply greatly depends on. (2) Humus refers to stable organic matter in soil that lends it a dark color and can remain for centuries. (3) There are typically four main biomes - forest, grassland, desert, and tundra - and the type of vegetation in each region depends on the climate and soil characteristics.