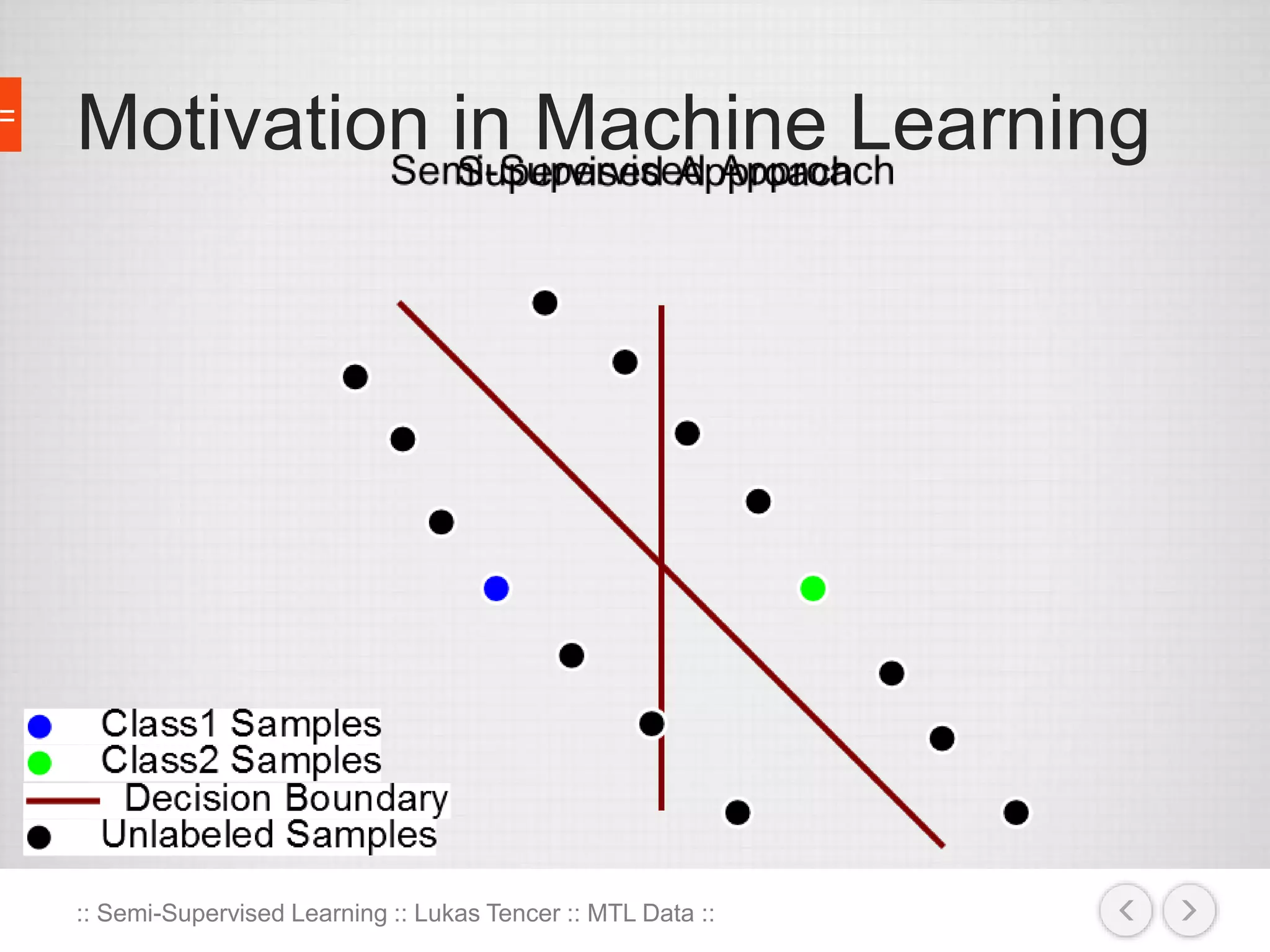
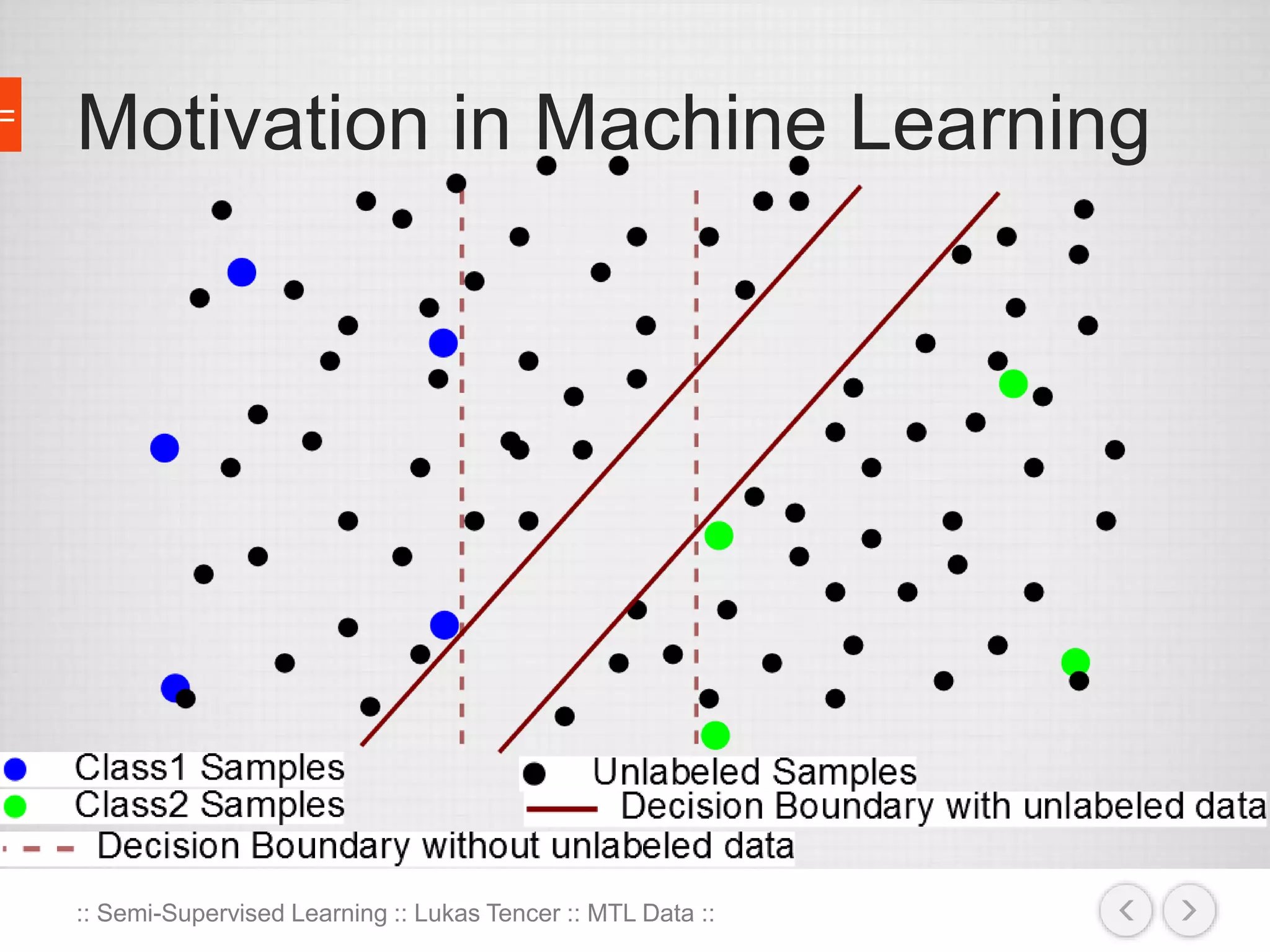
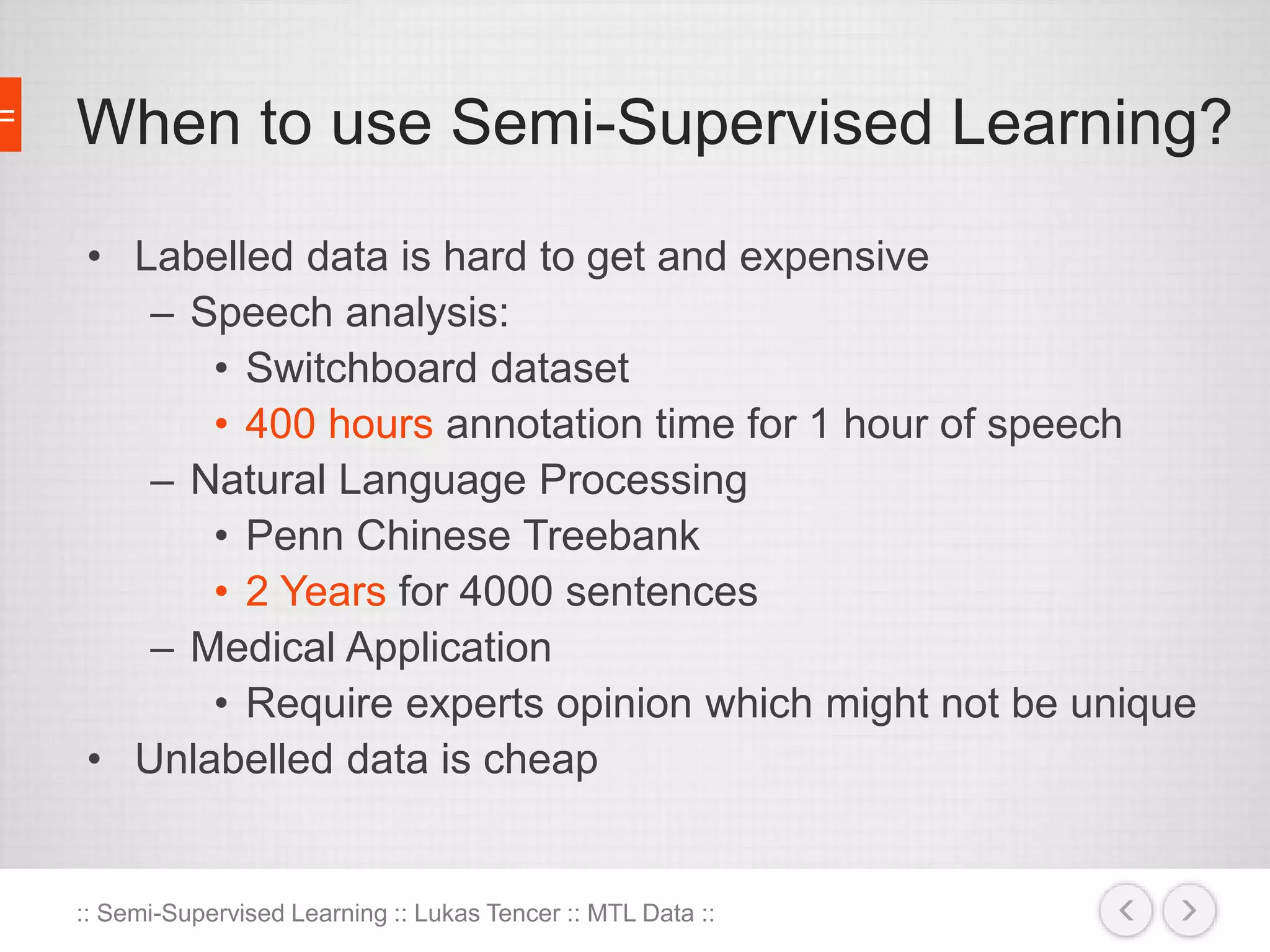
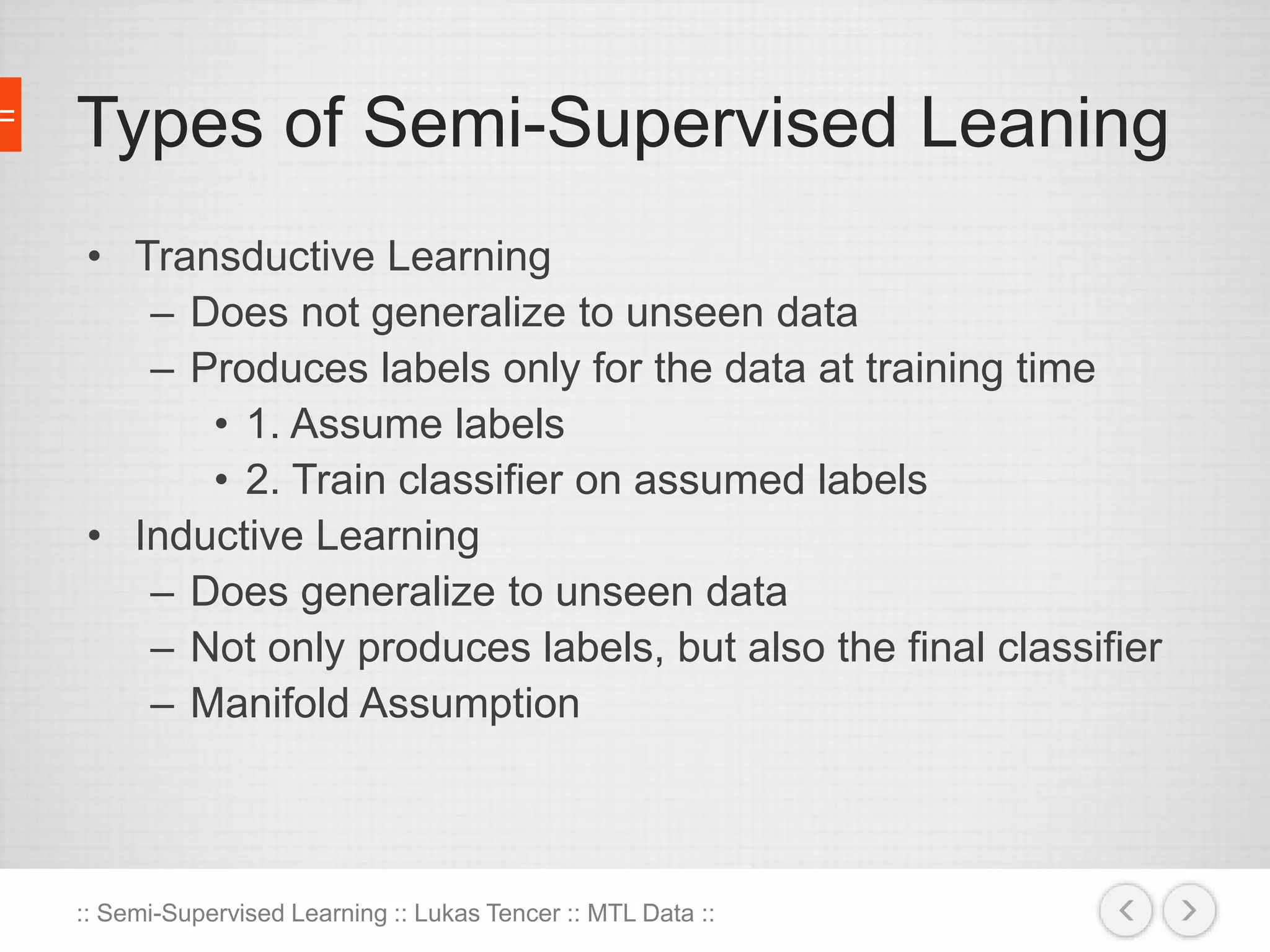
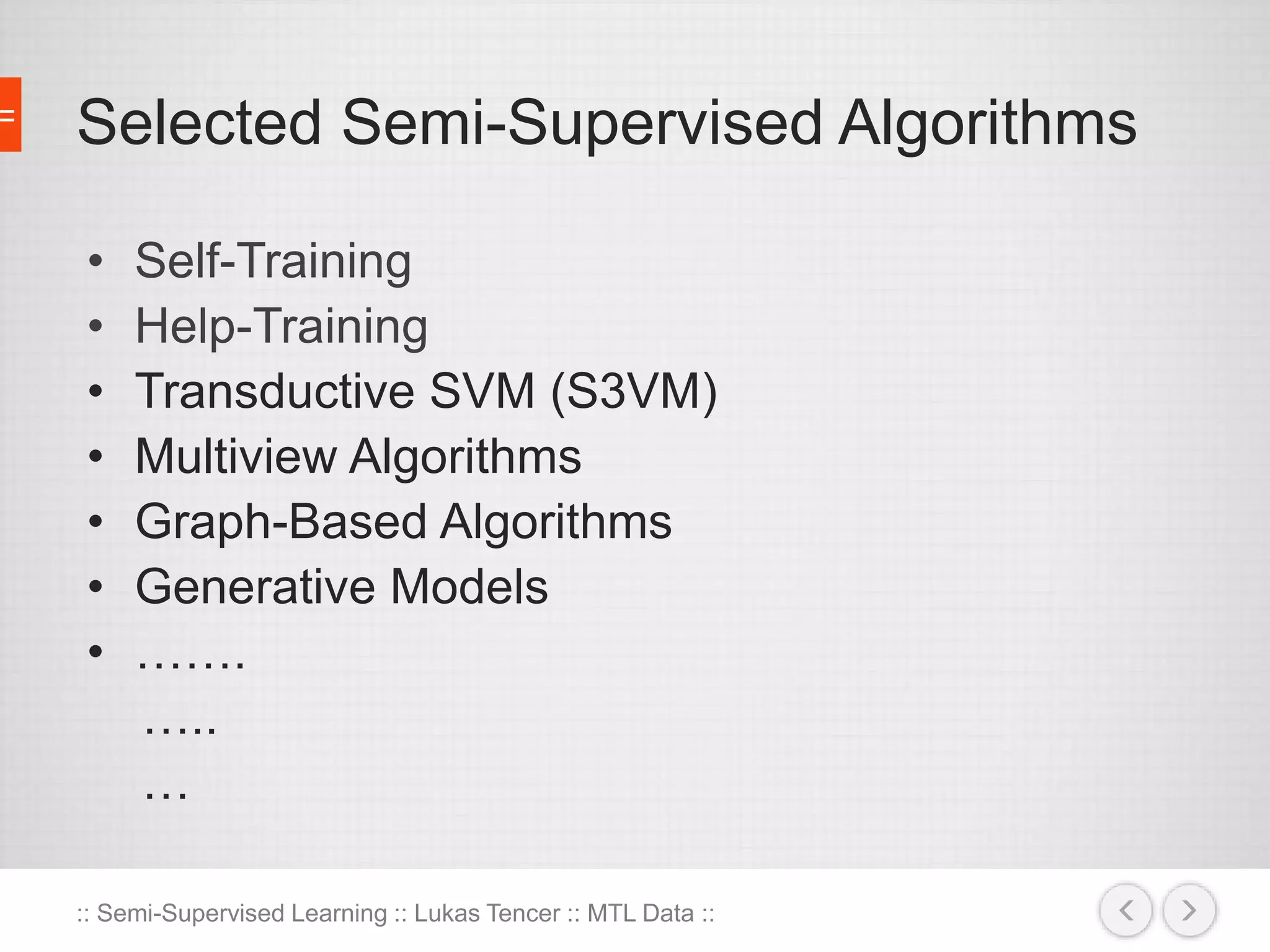
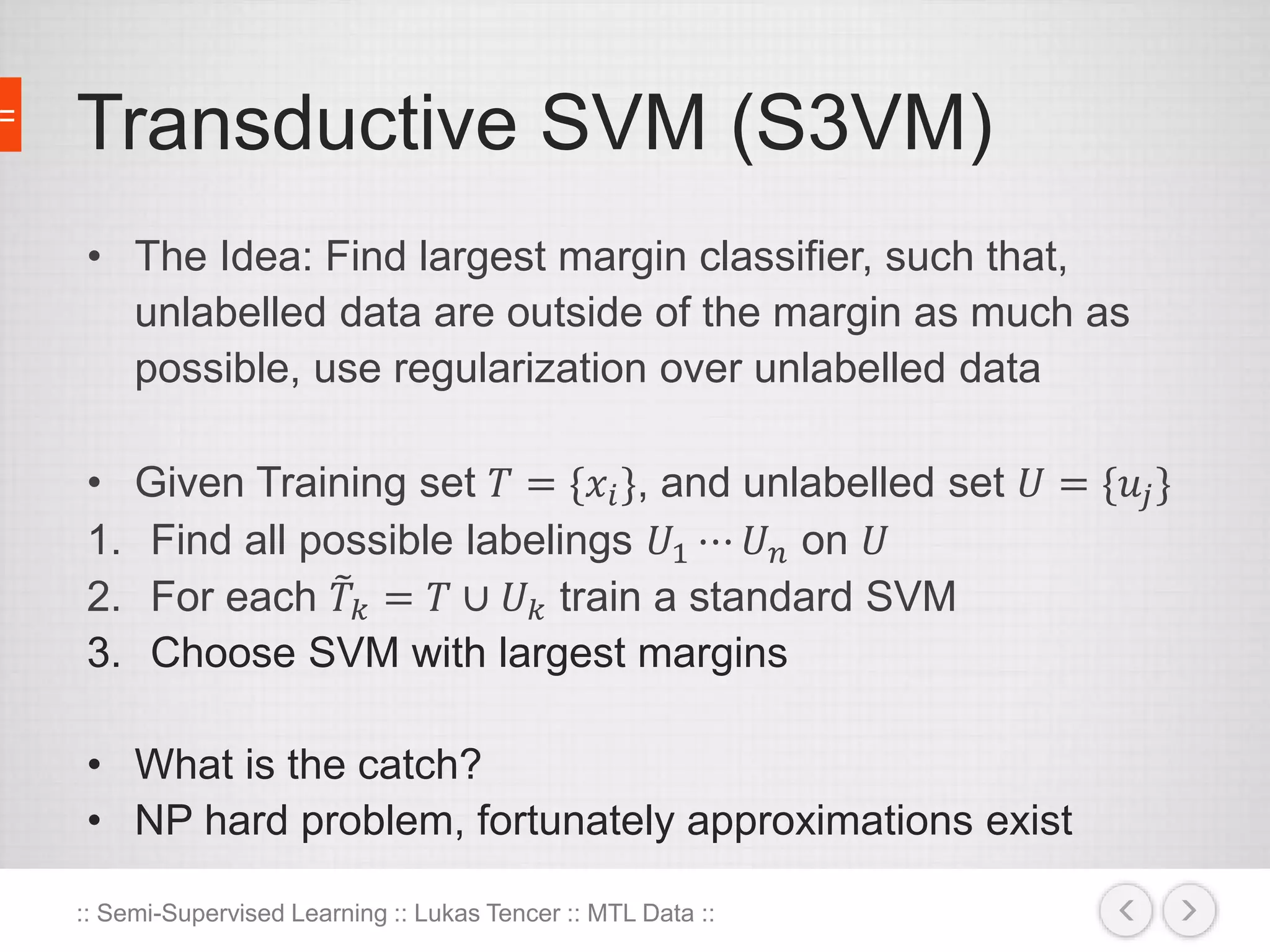
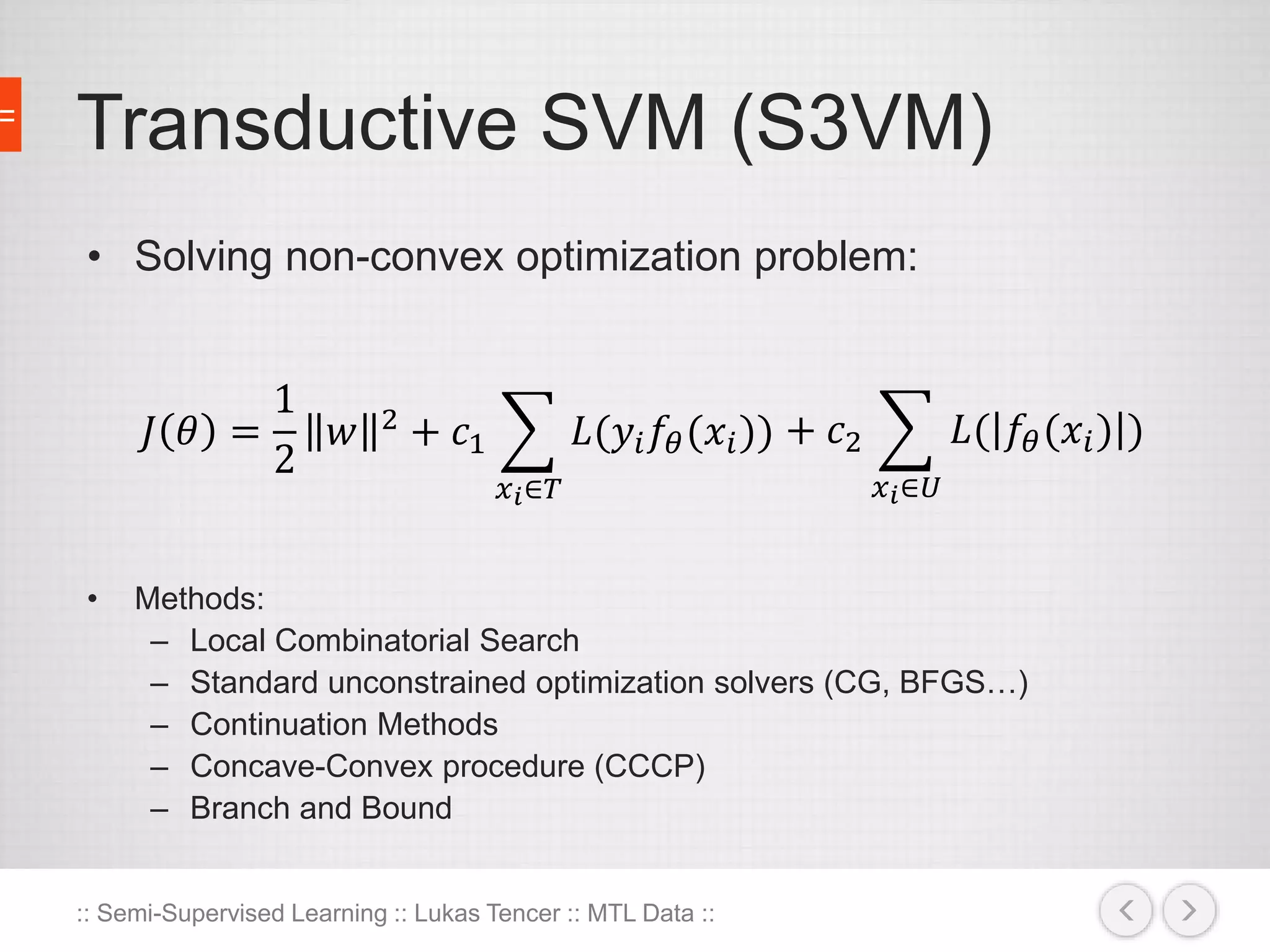
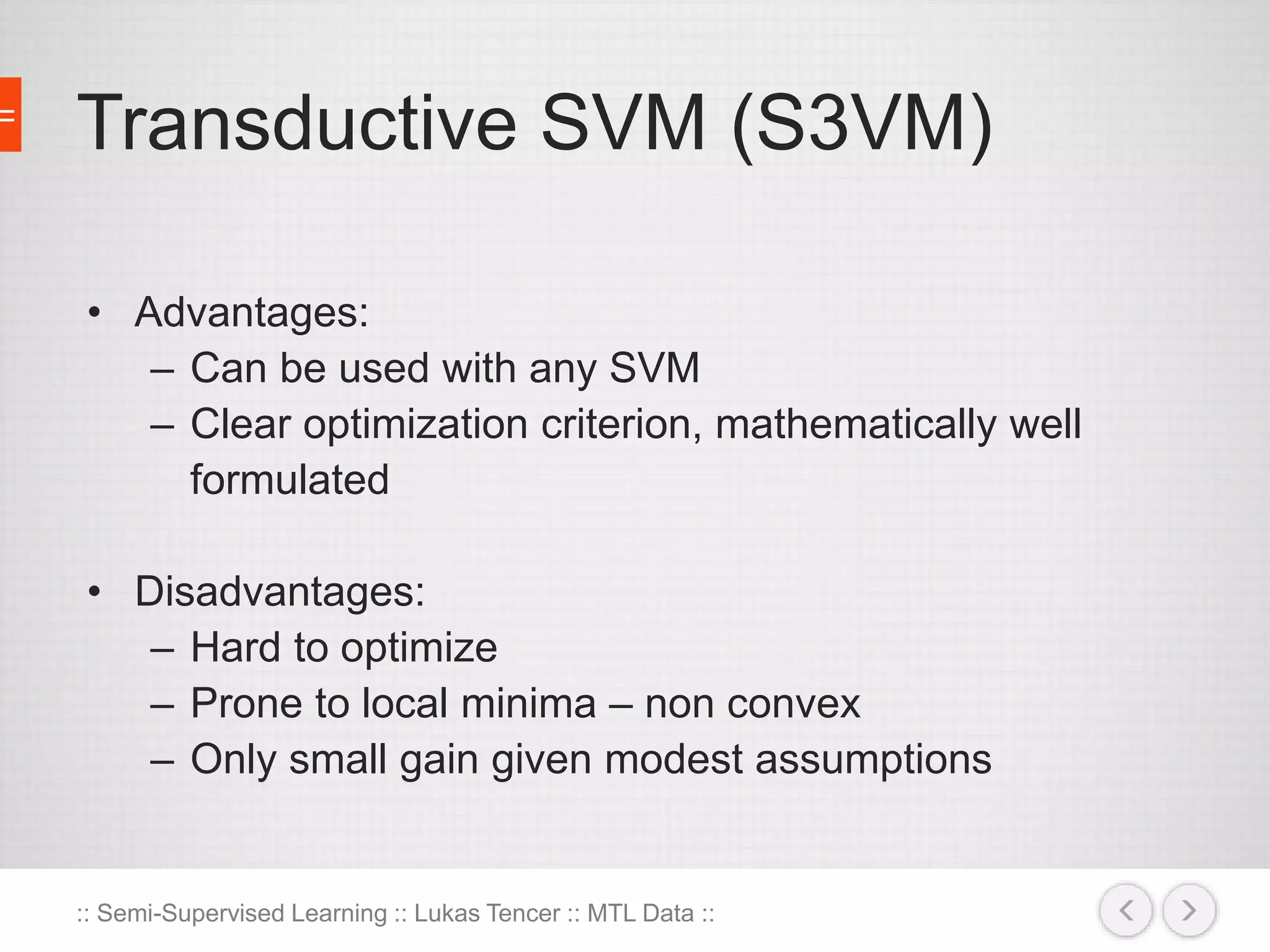
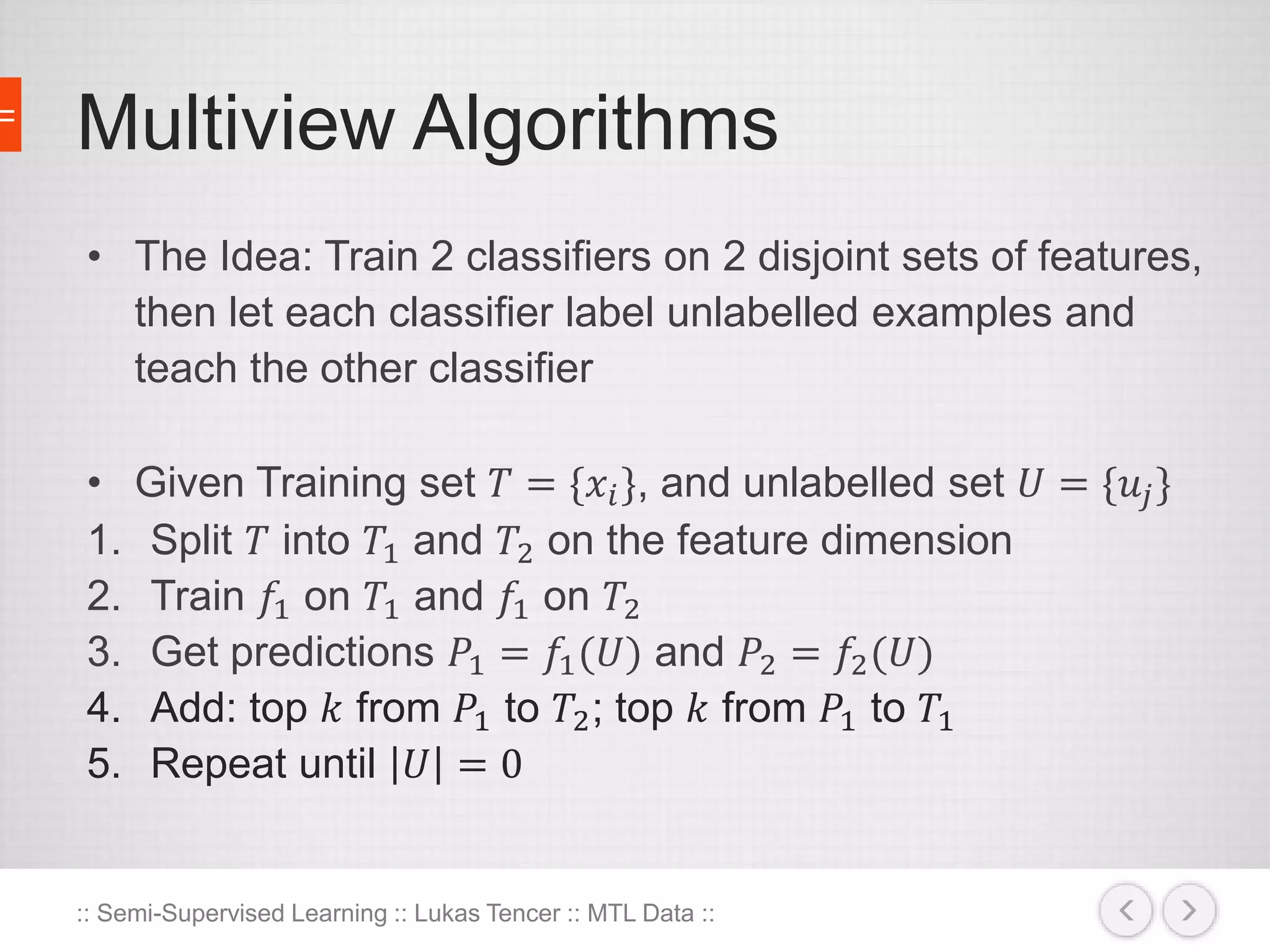
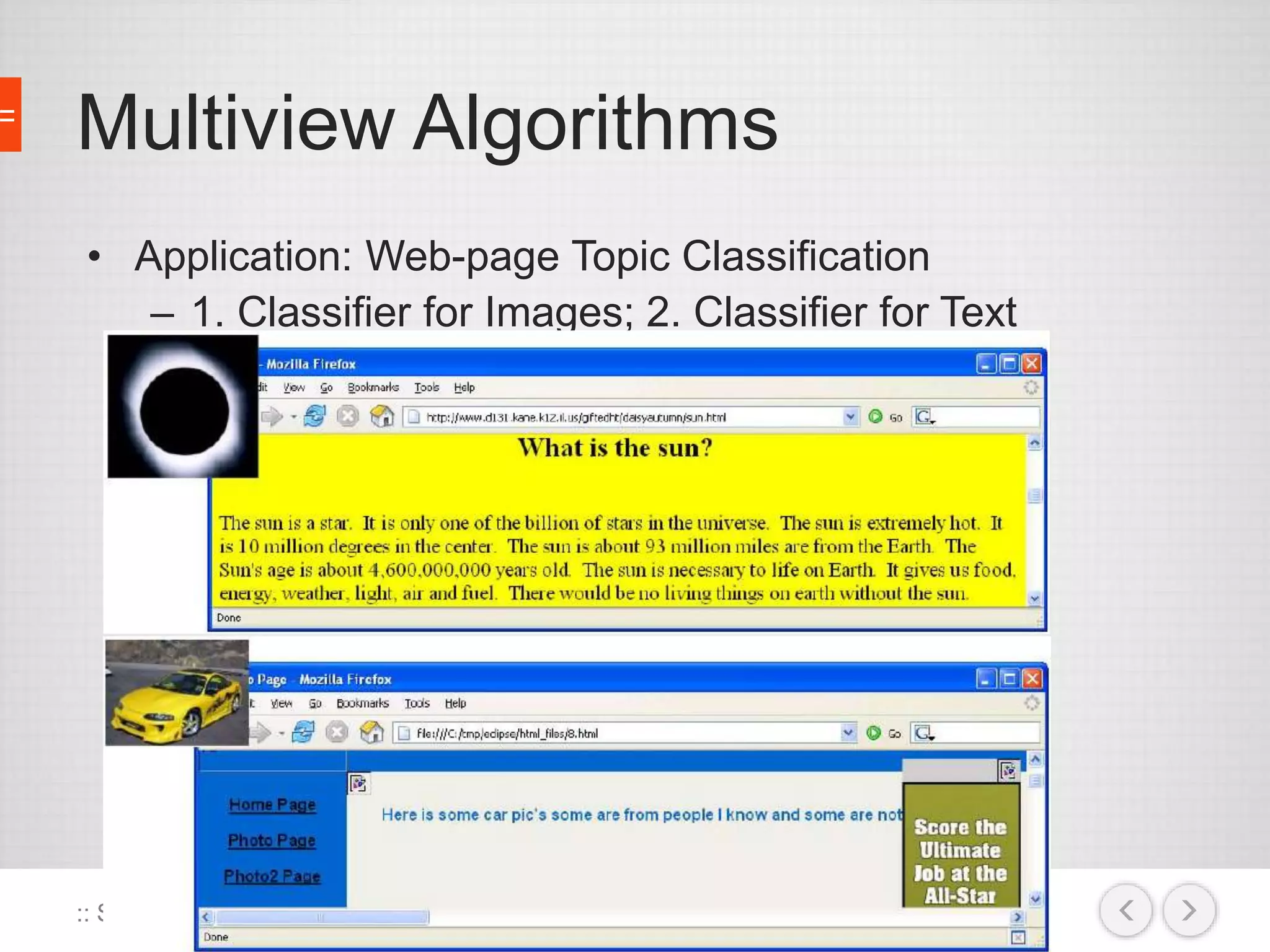
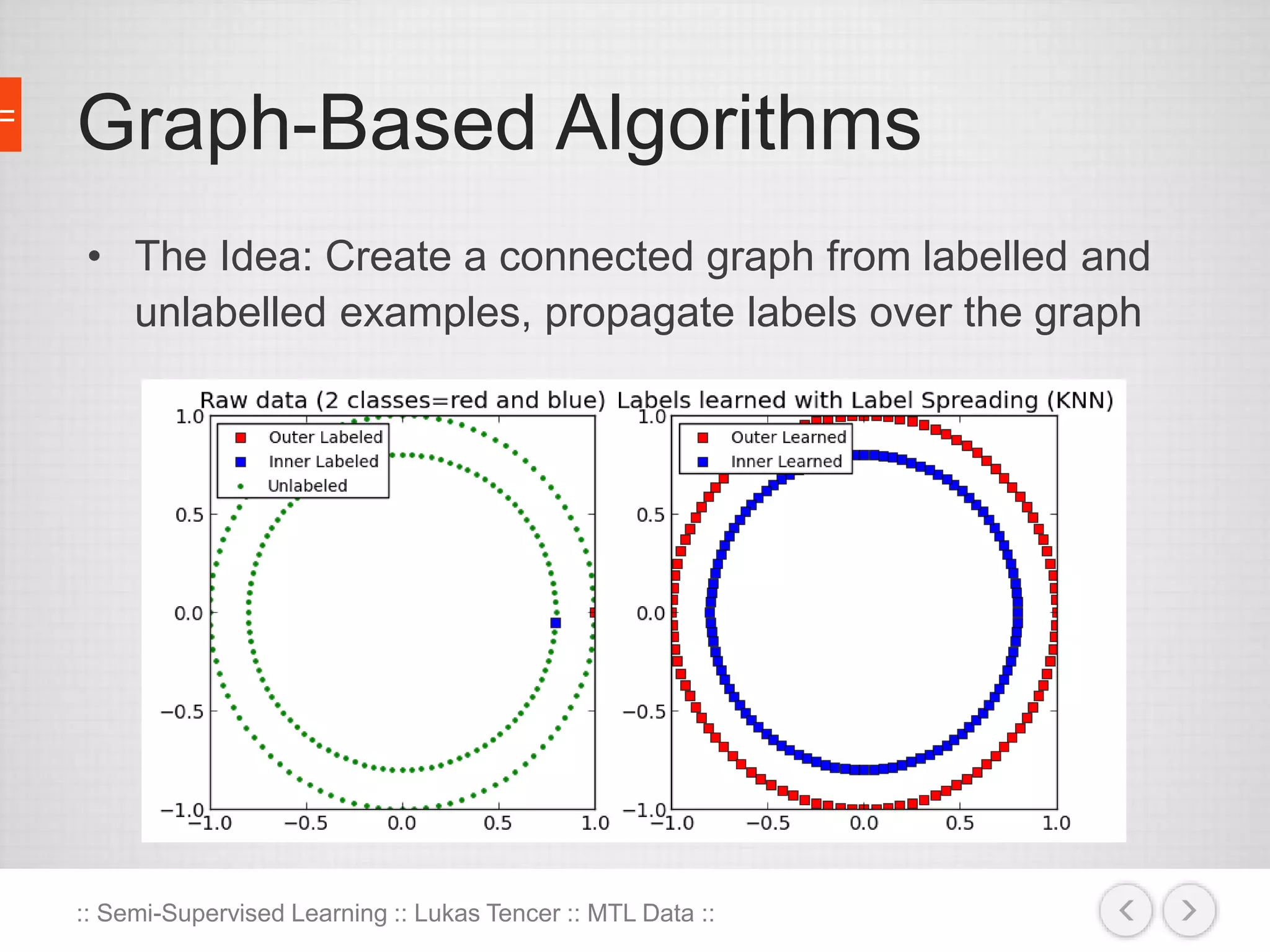
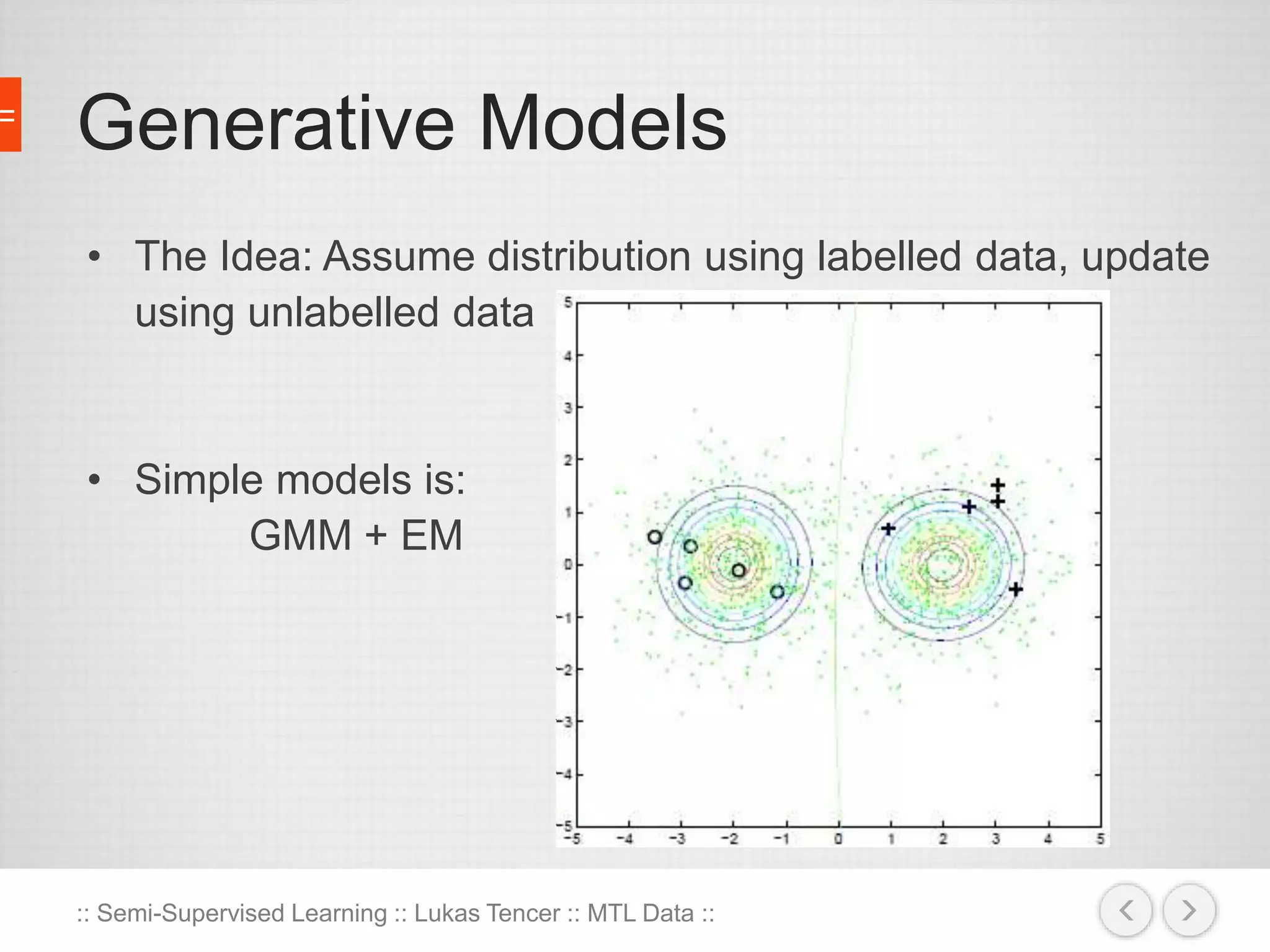
The document discusses the concept of semi-supervised learning, highlighting its importance due to the high cost of labeled data in fields like speech analysis, natural language processing, and medical applications. It details various methods and algorithms used in semi-supervised learning, including self-training, help-training, transductive SVM, multiview algorithms, graph-based algorithms, and generative models, along with their advantages and disadvantages. Additionally, it emphasizes the need for caution in real-world applications and offers resources for further study.