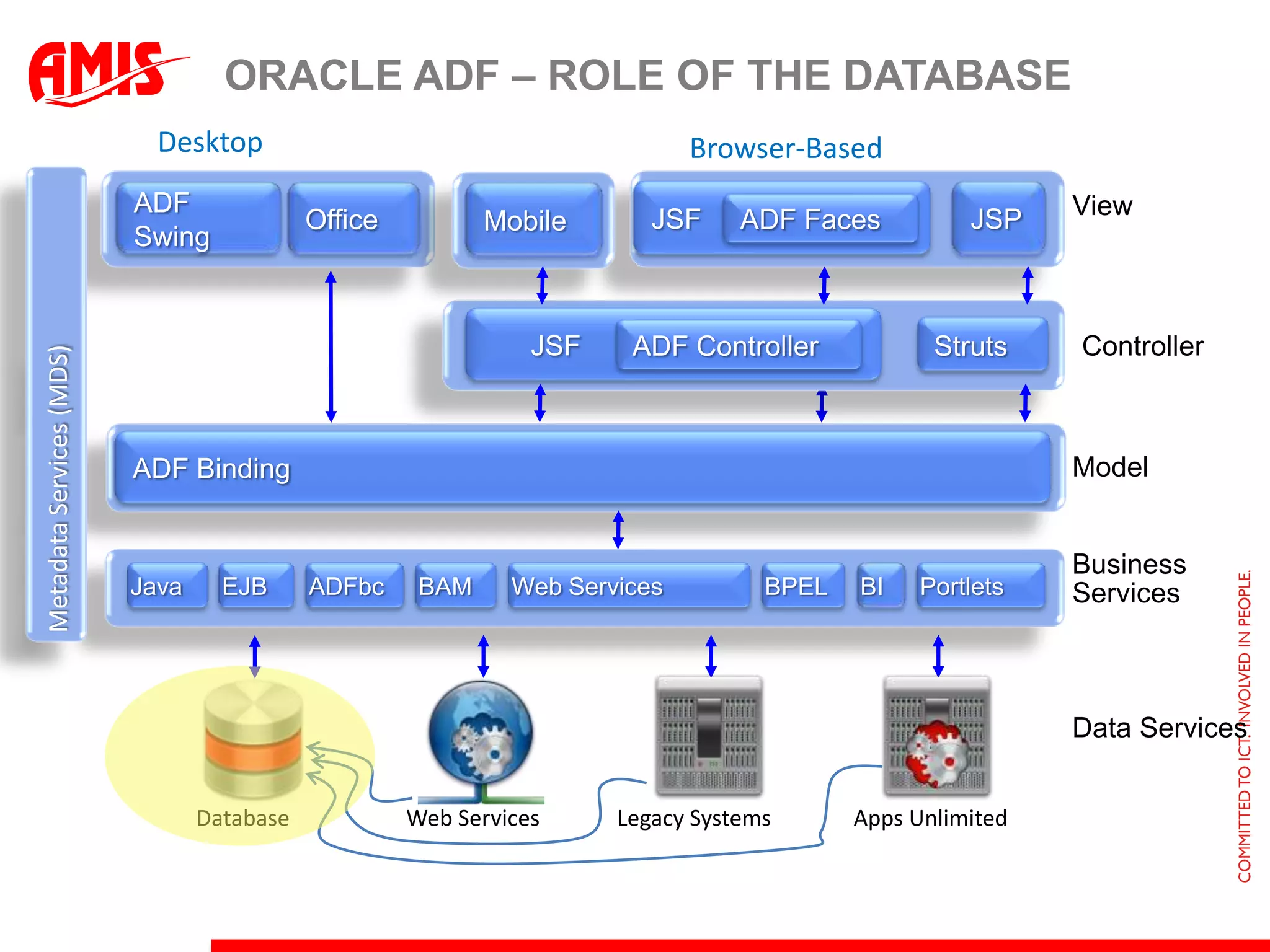
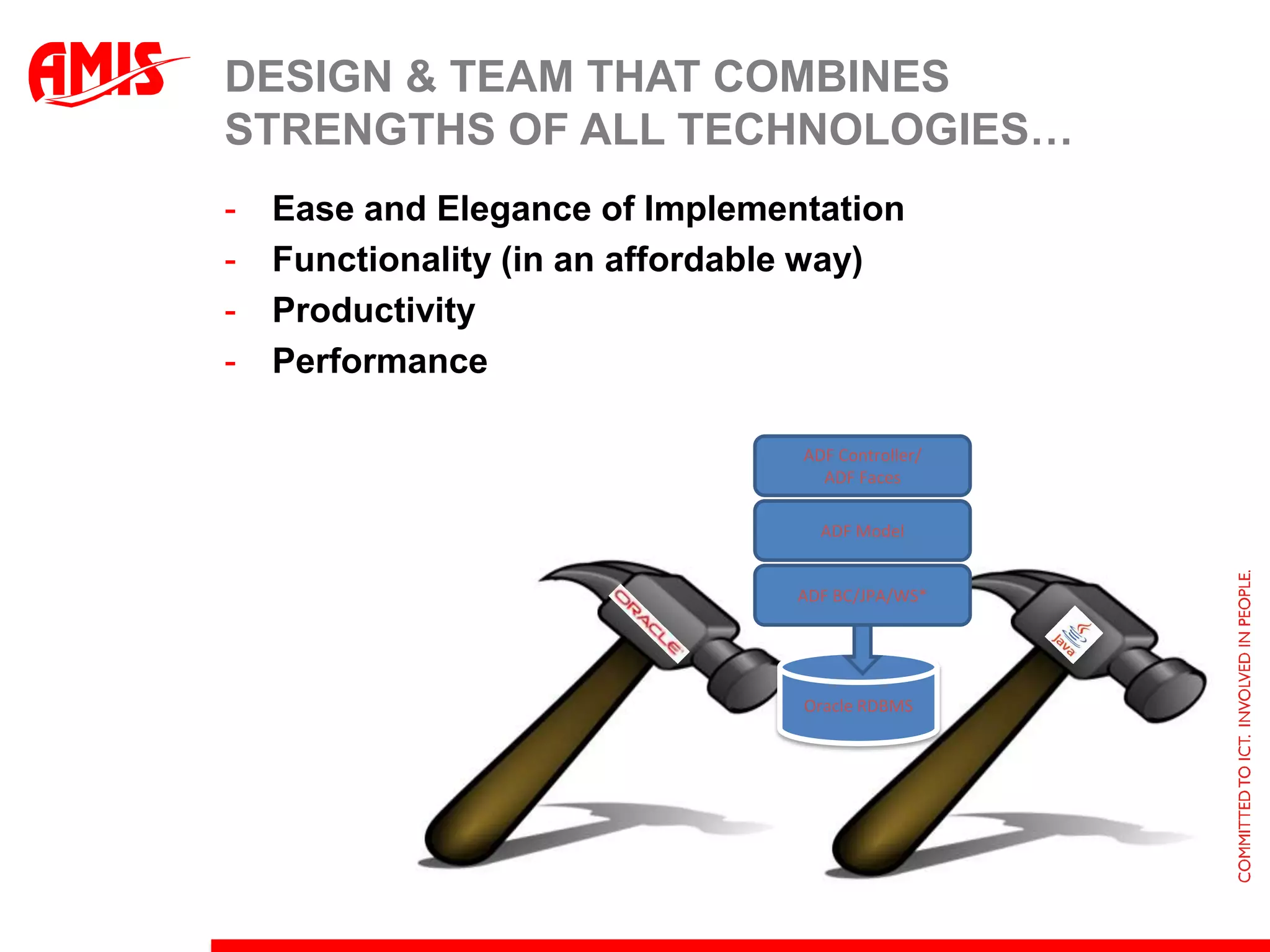
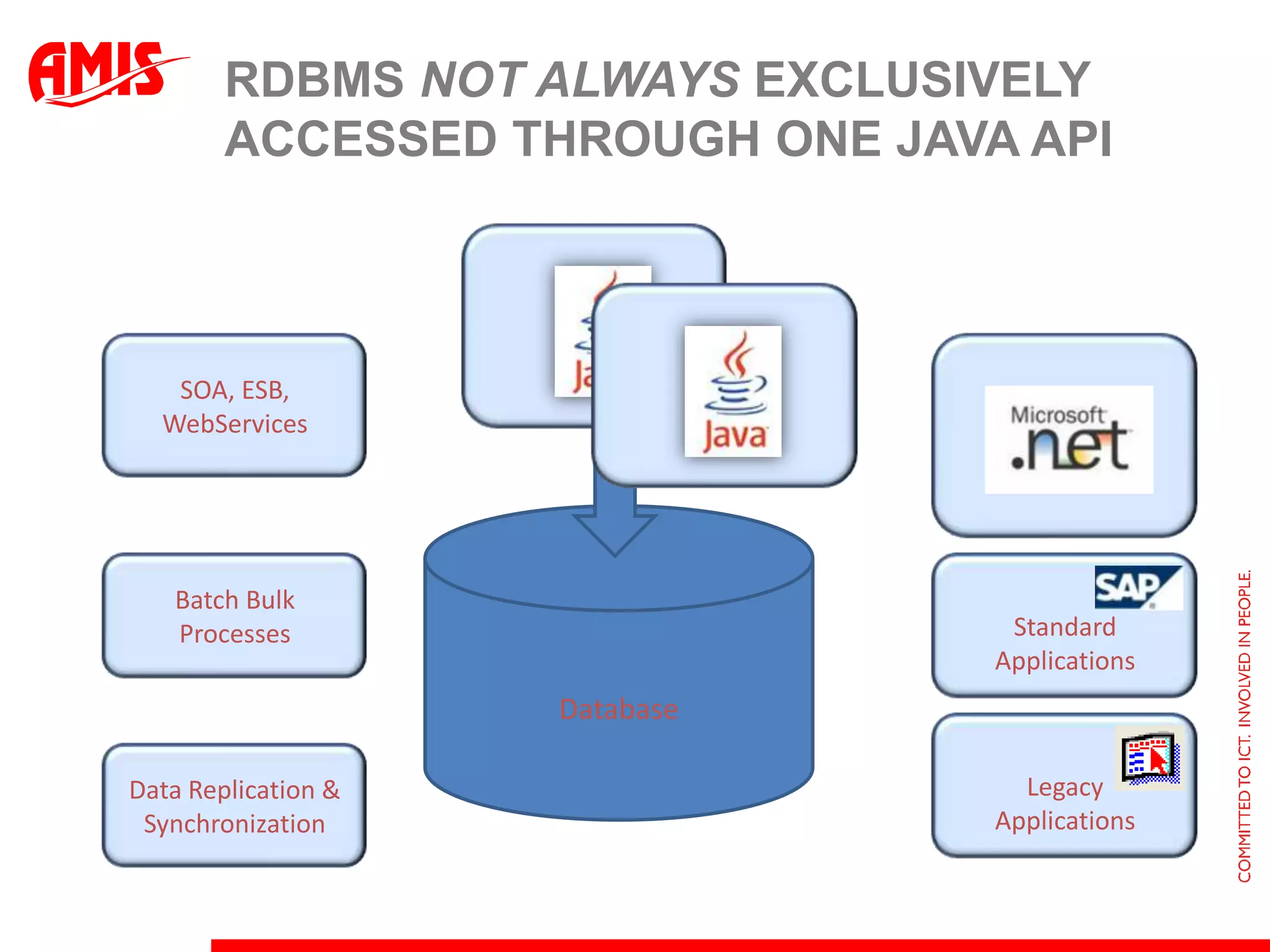
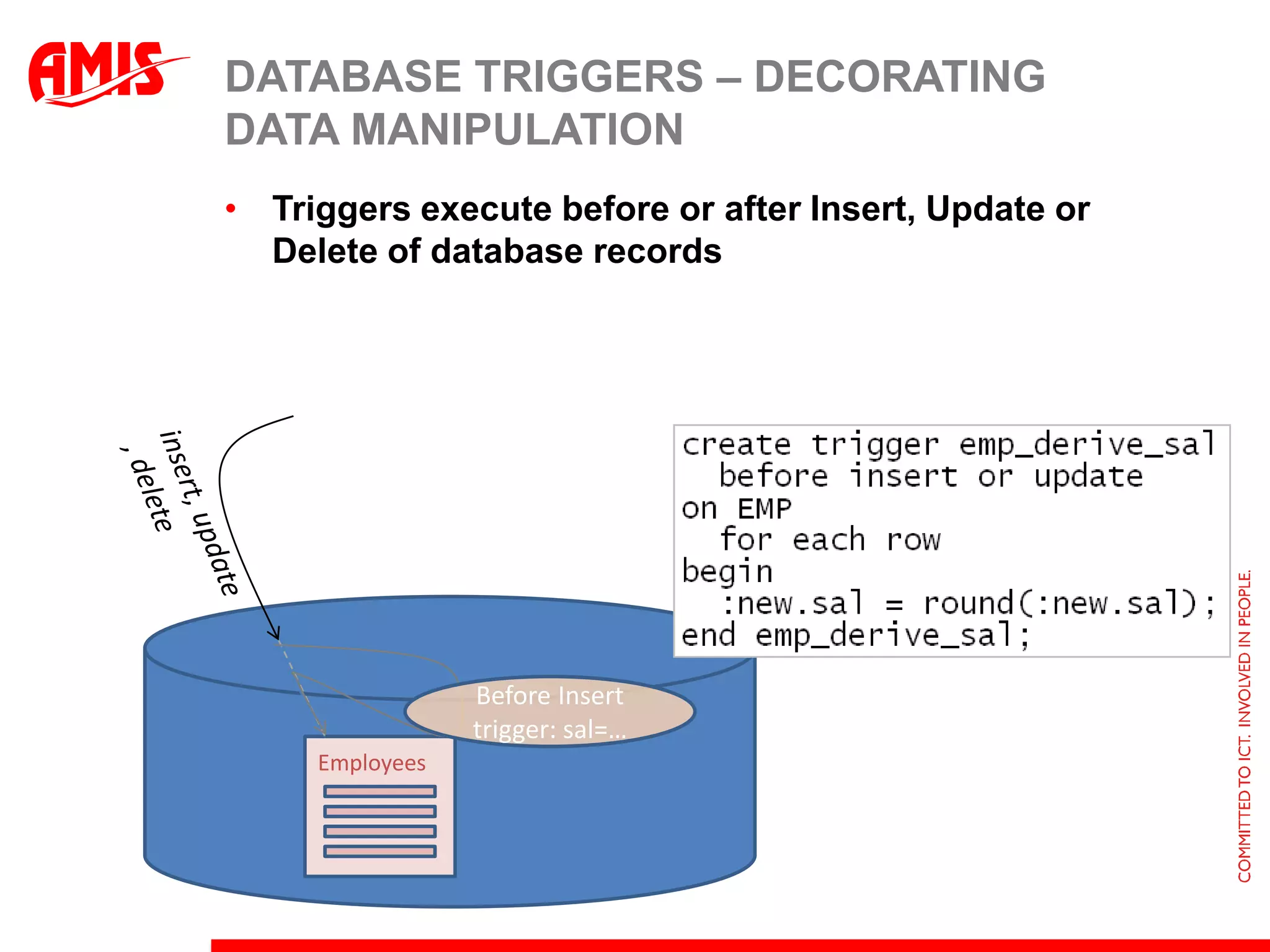
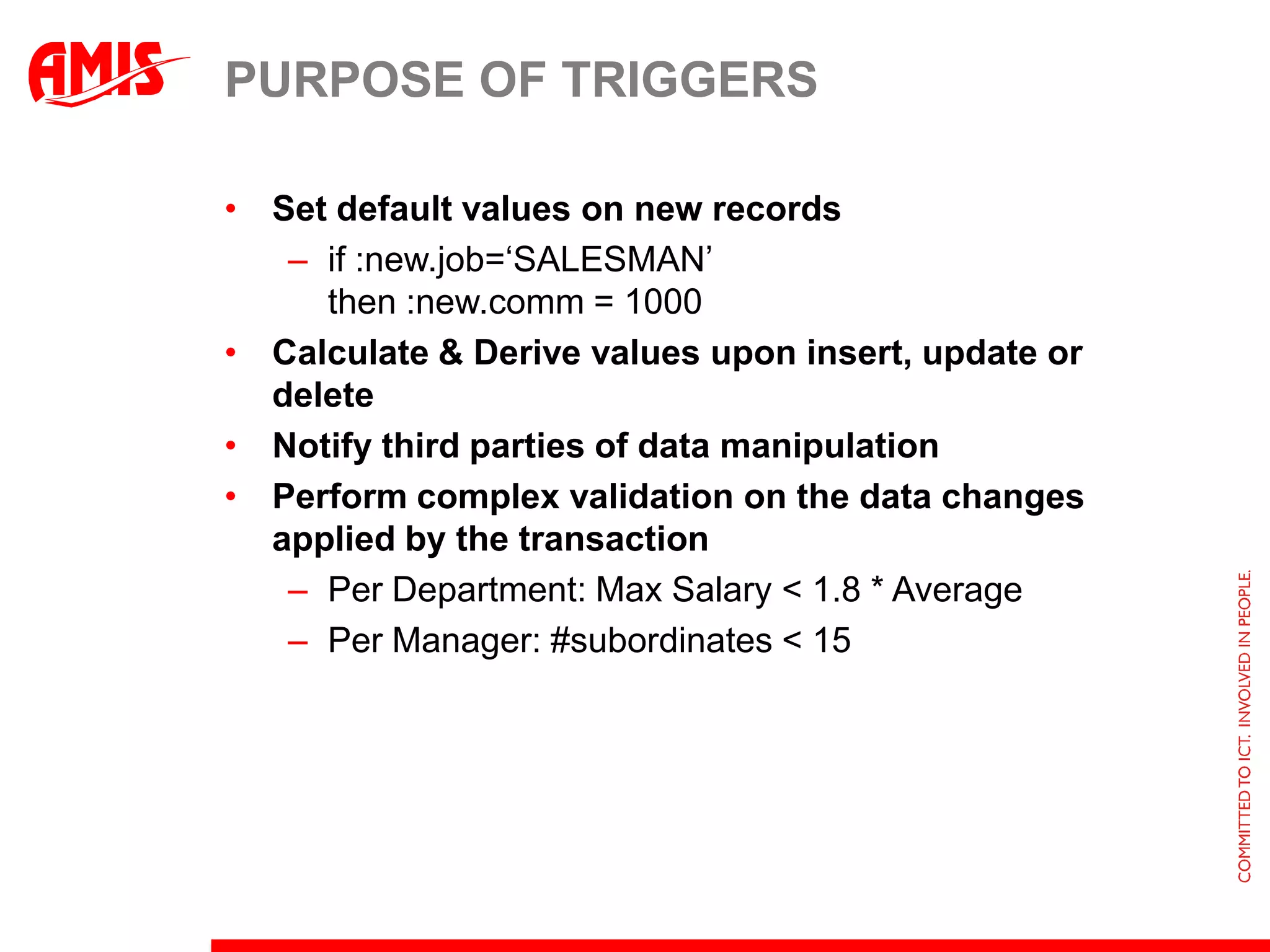
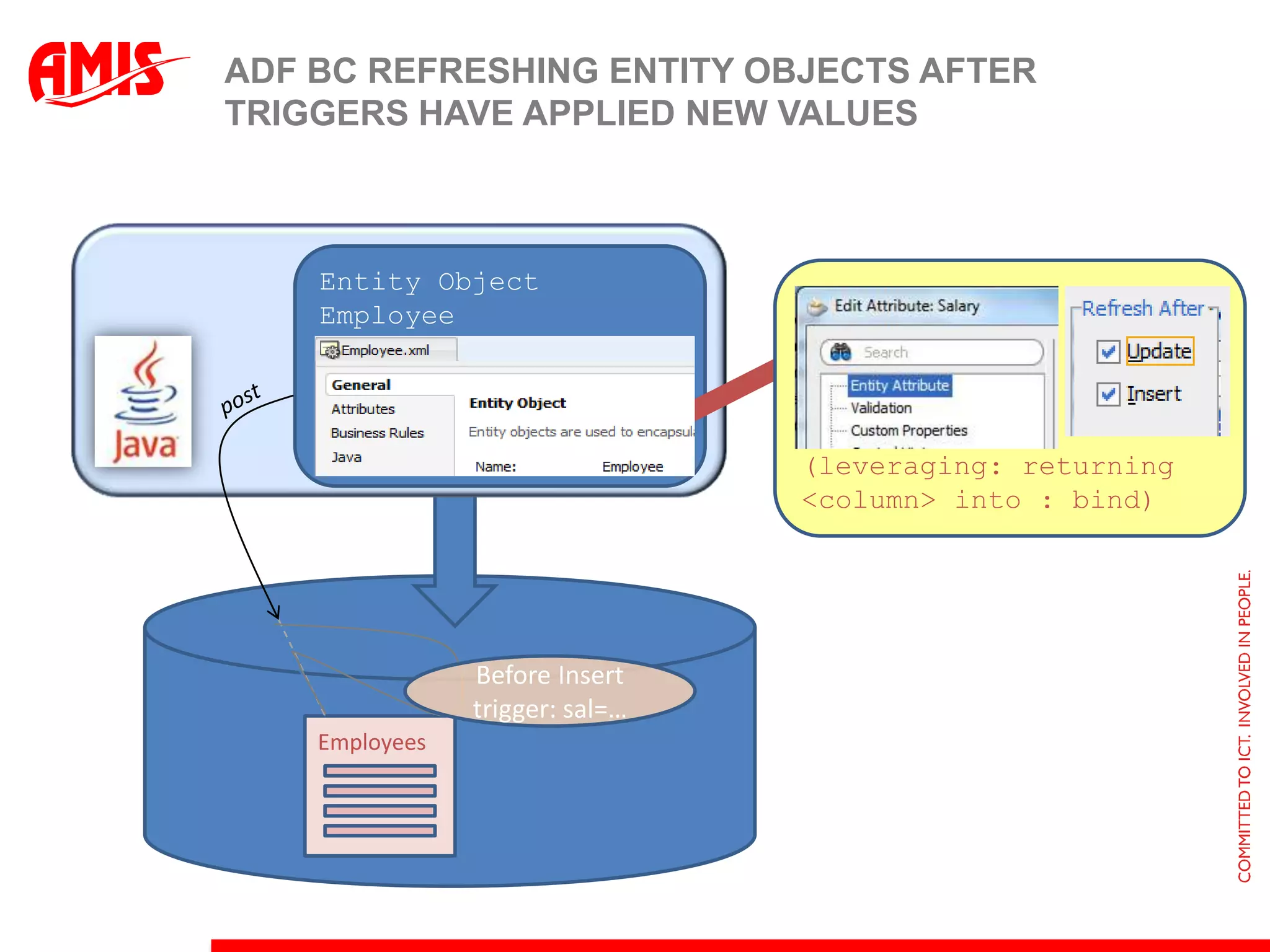
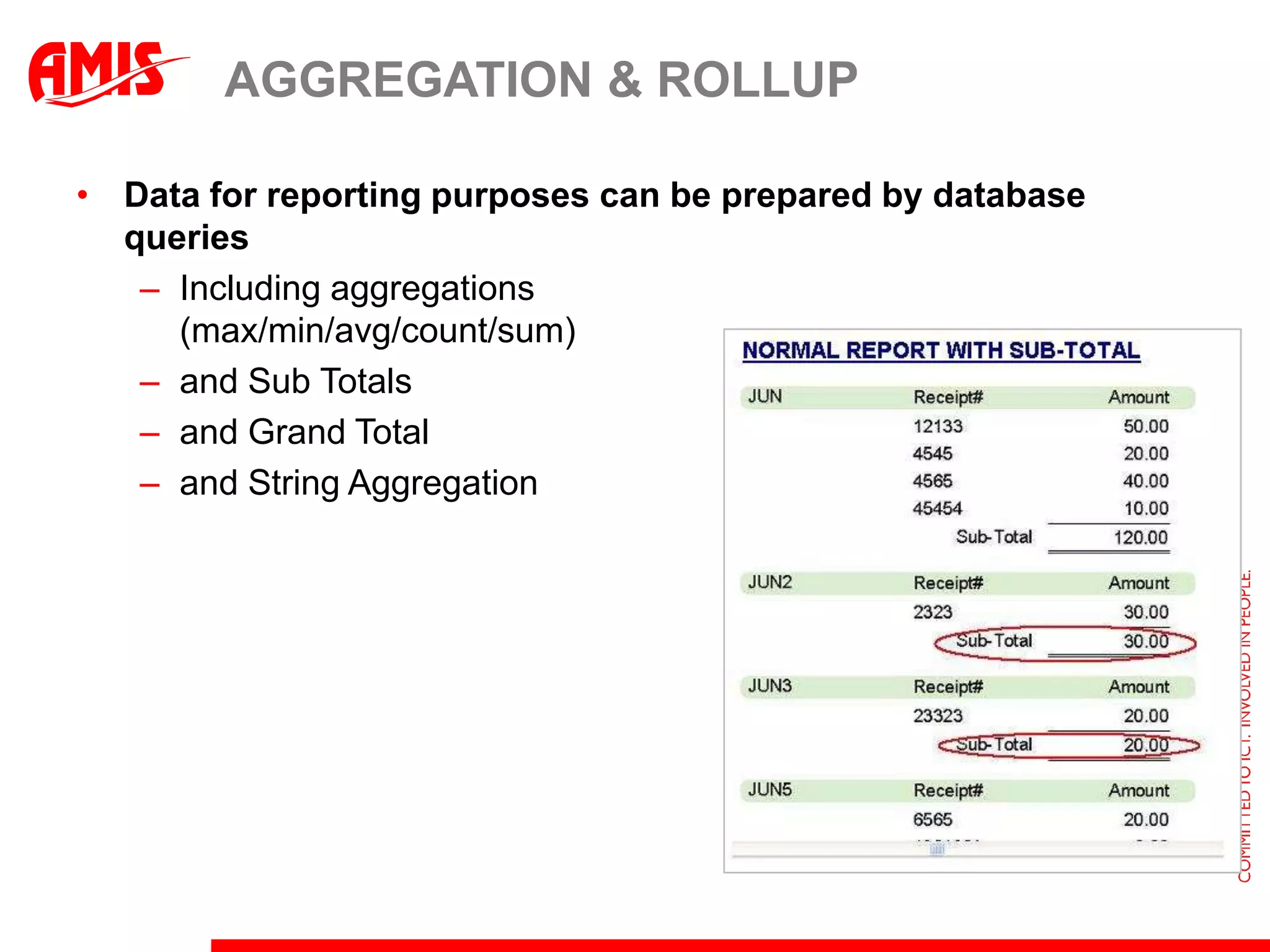
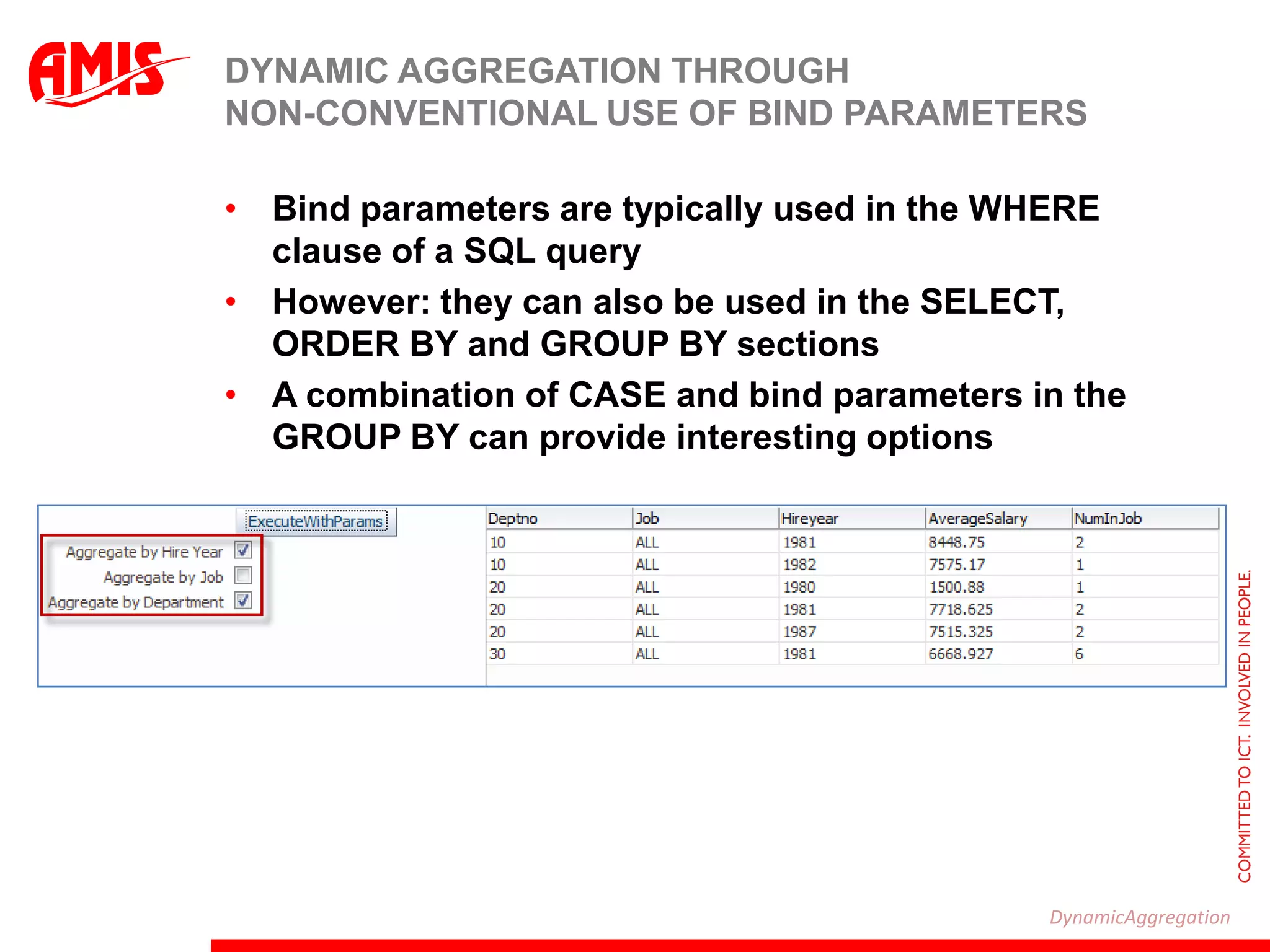
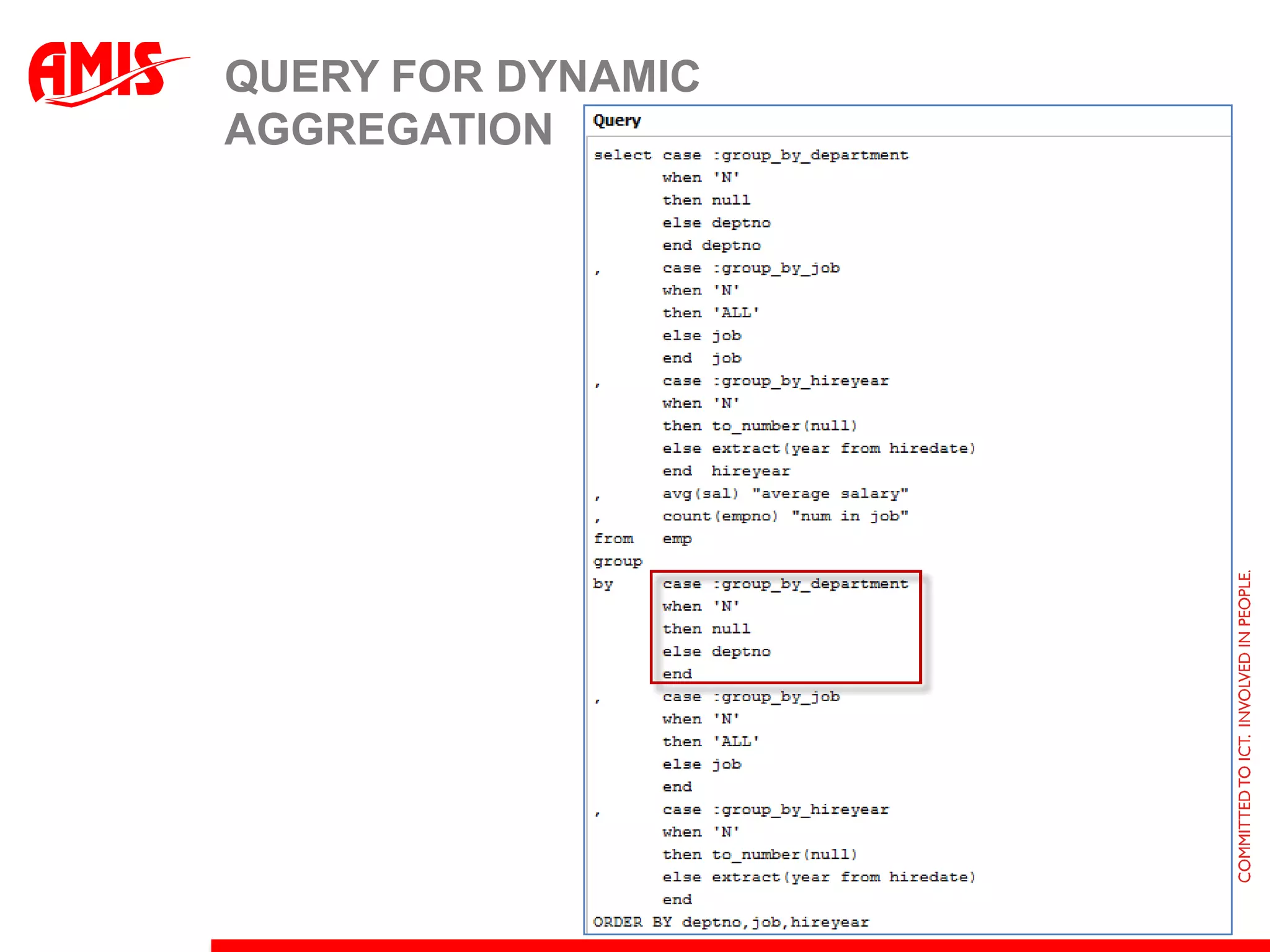
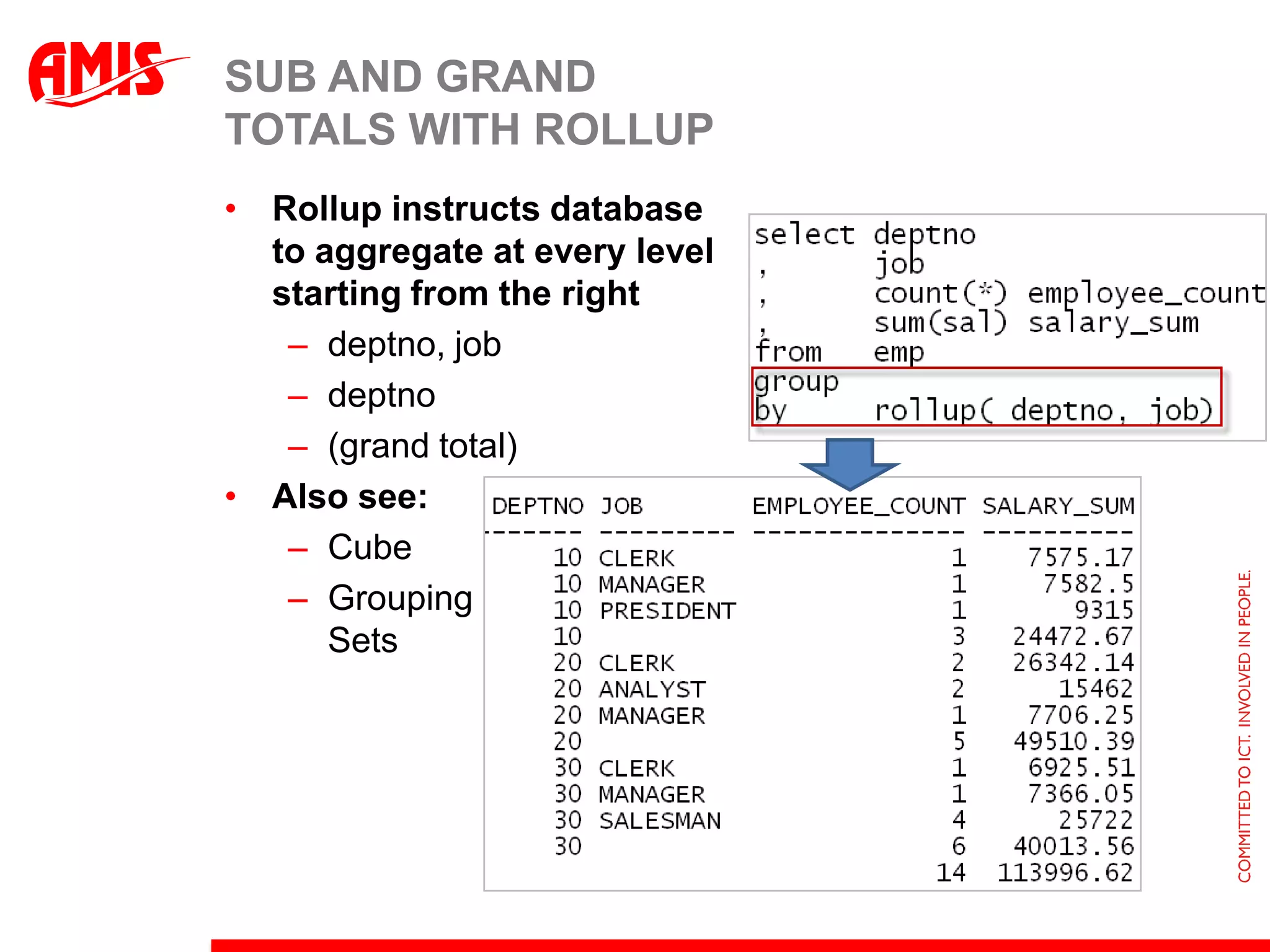
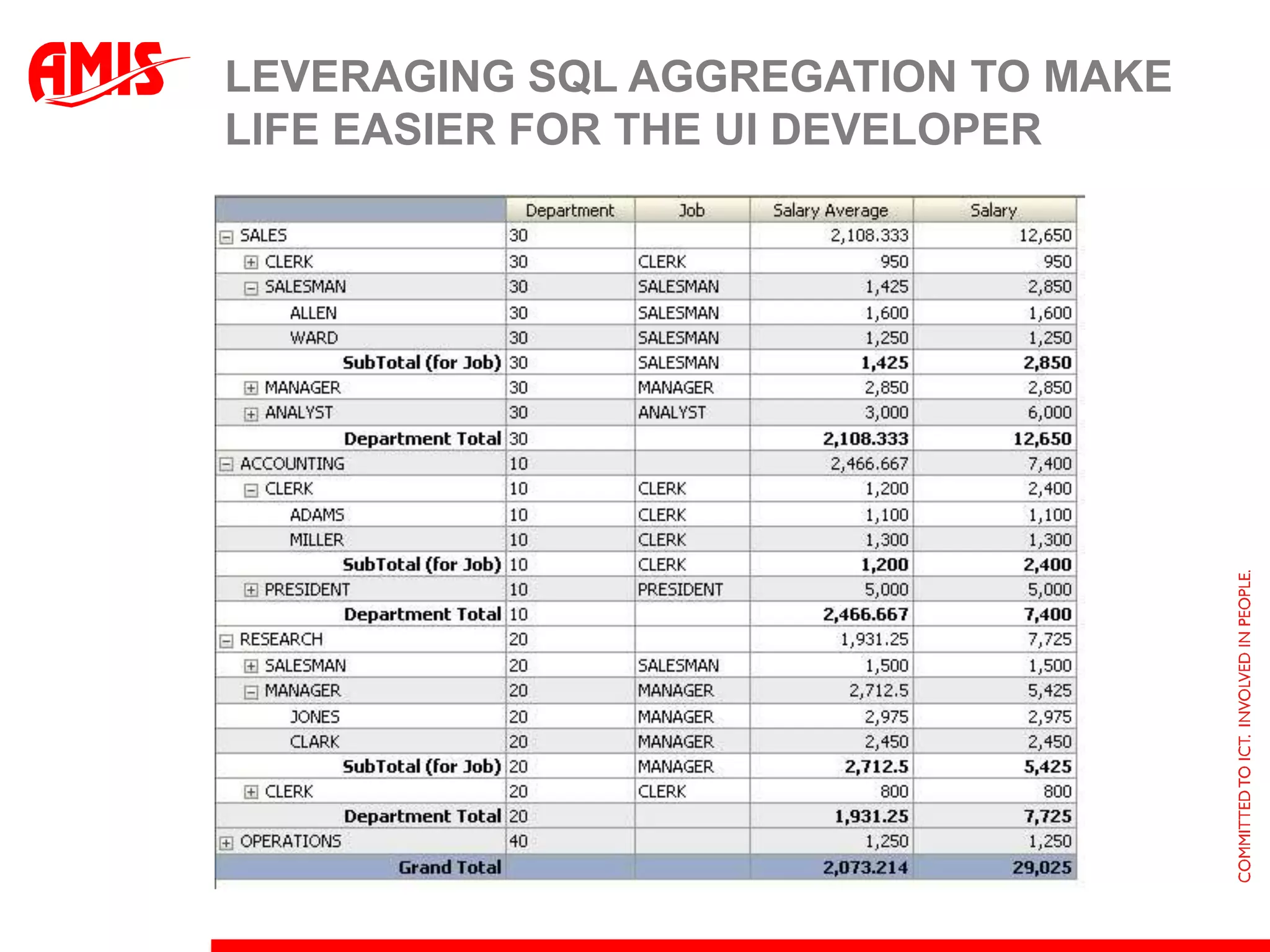
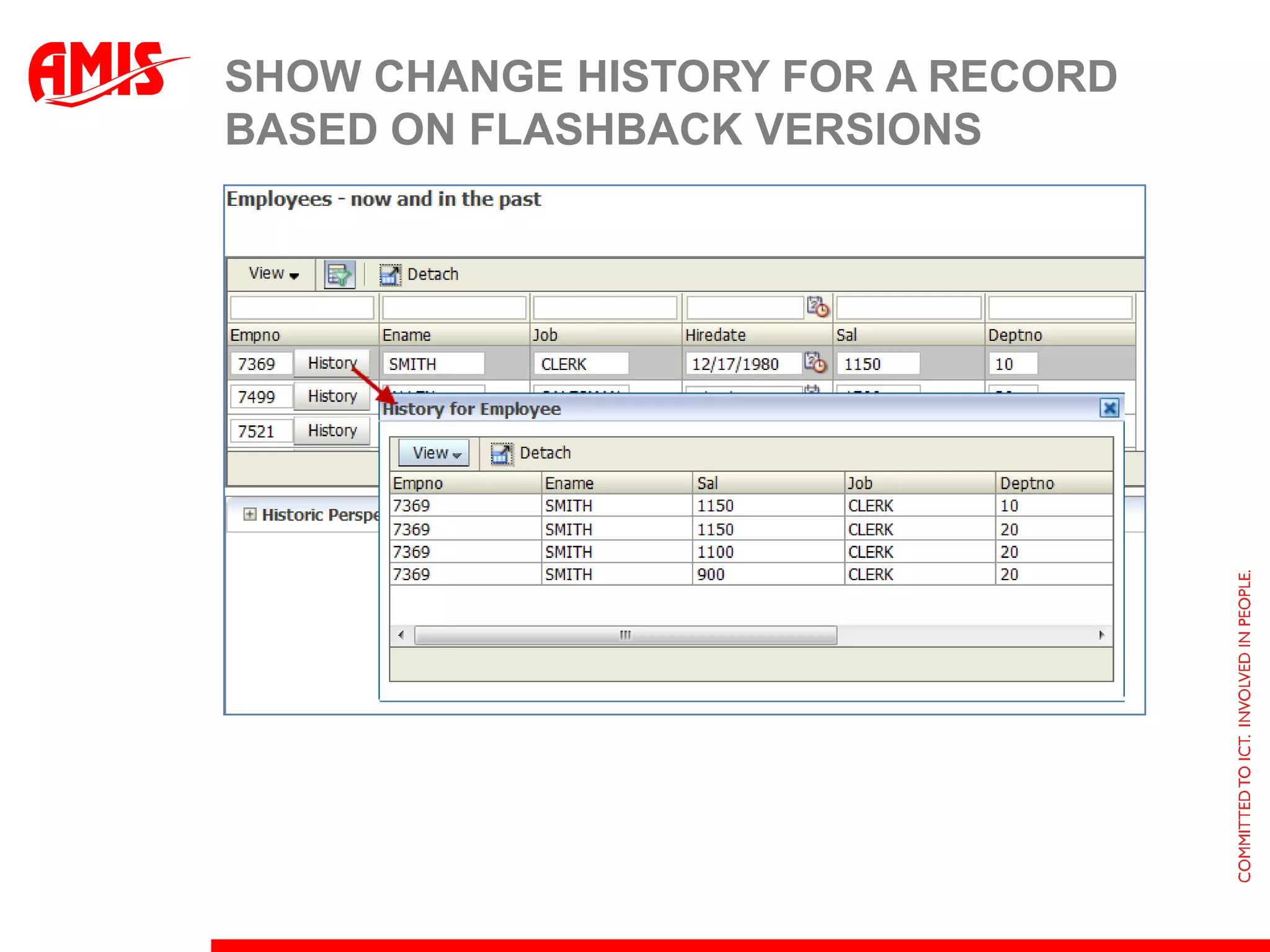
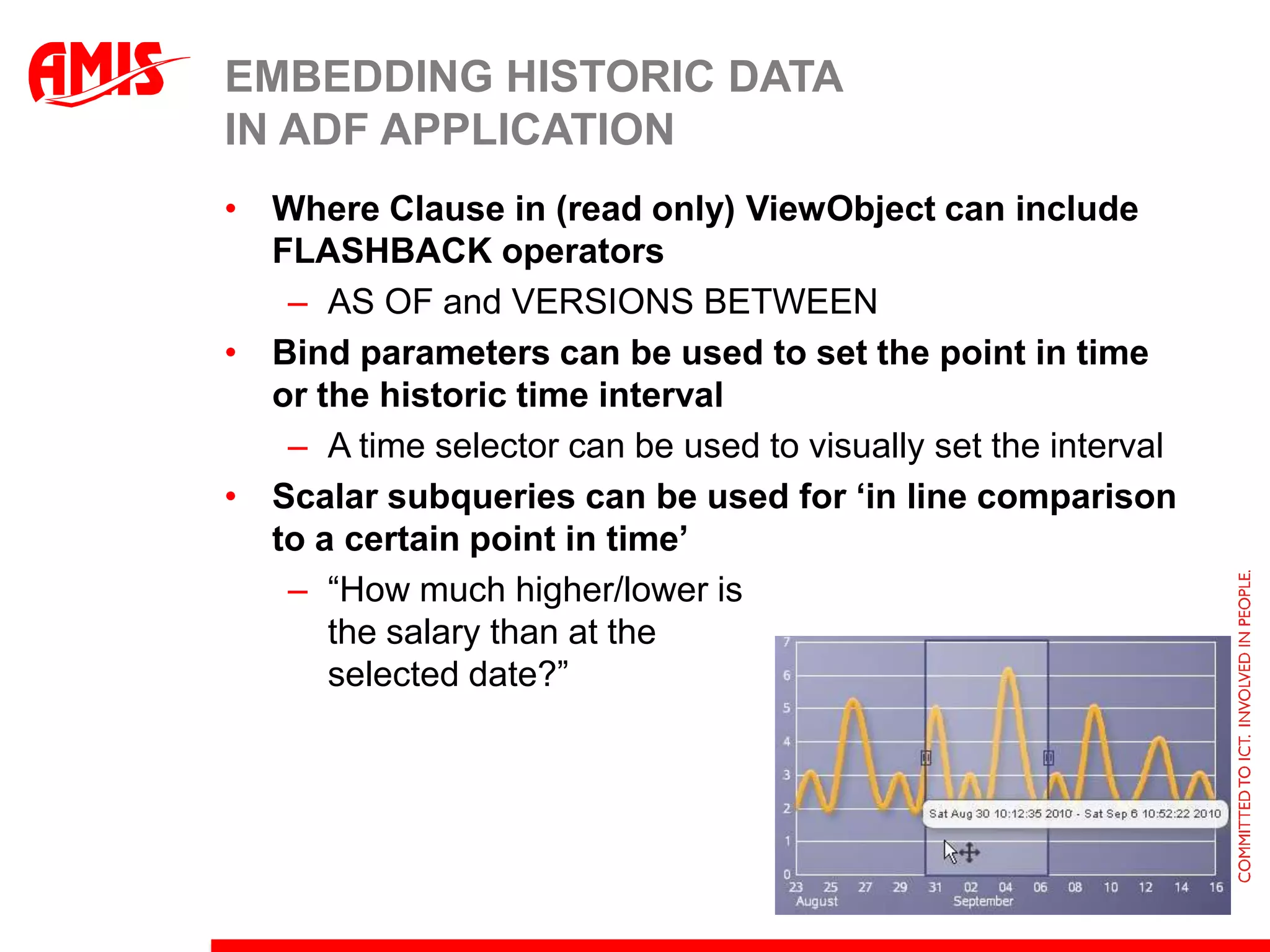
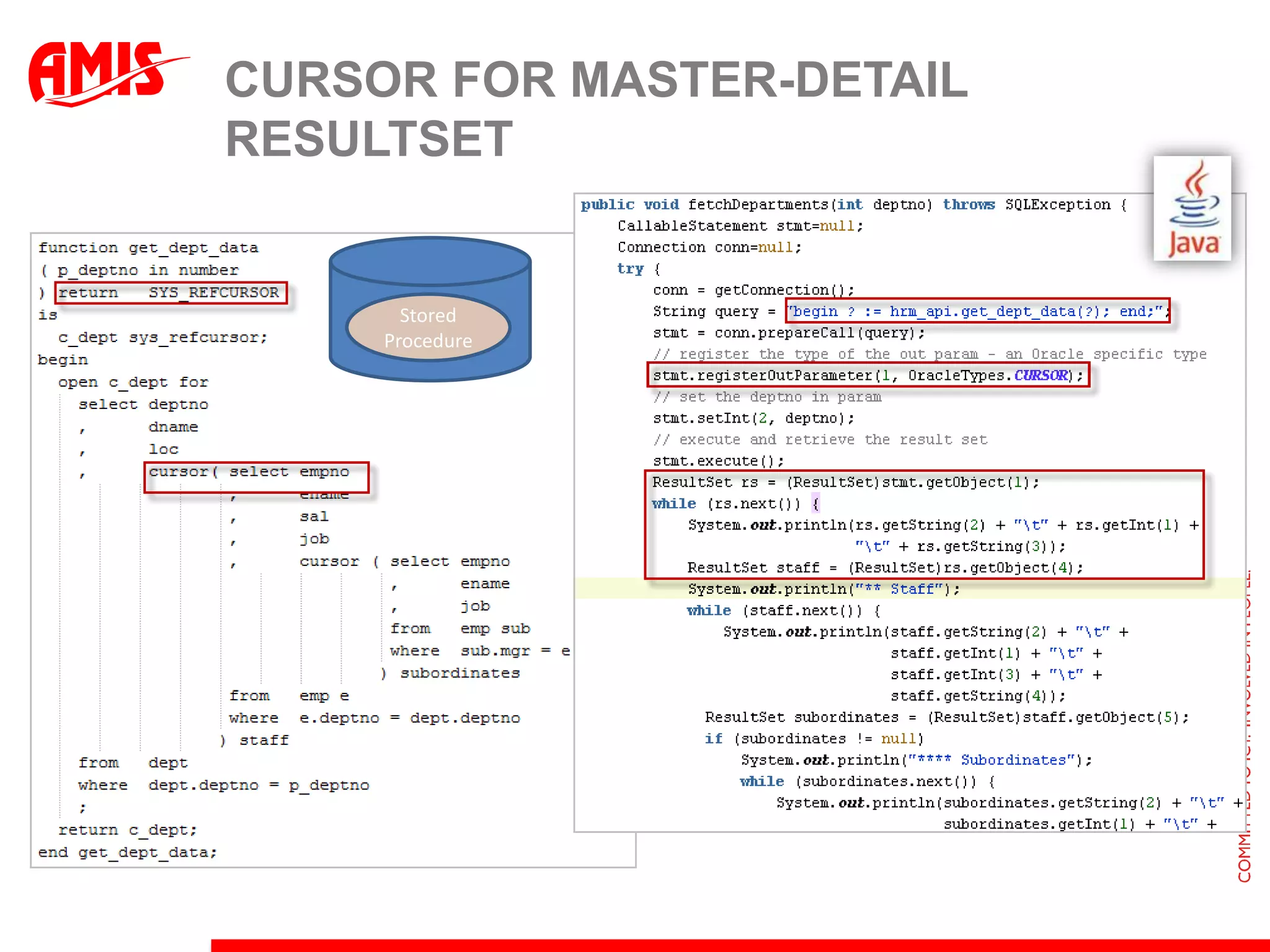
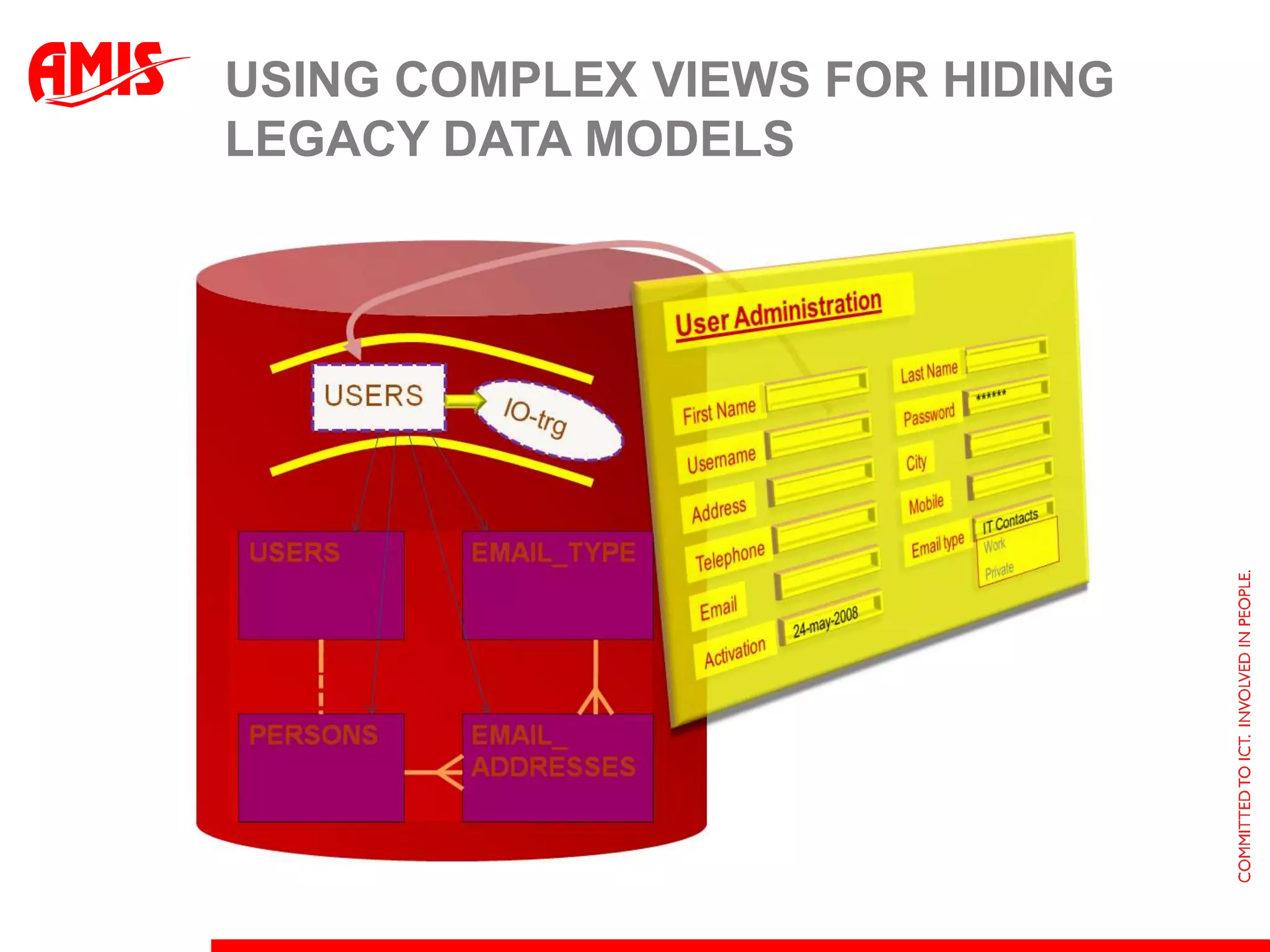
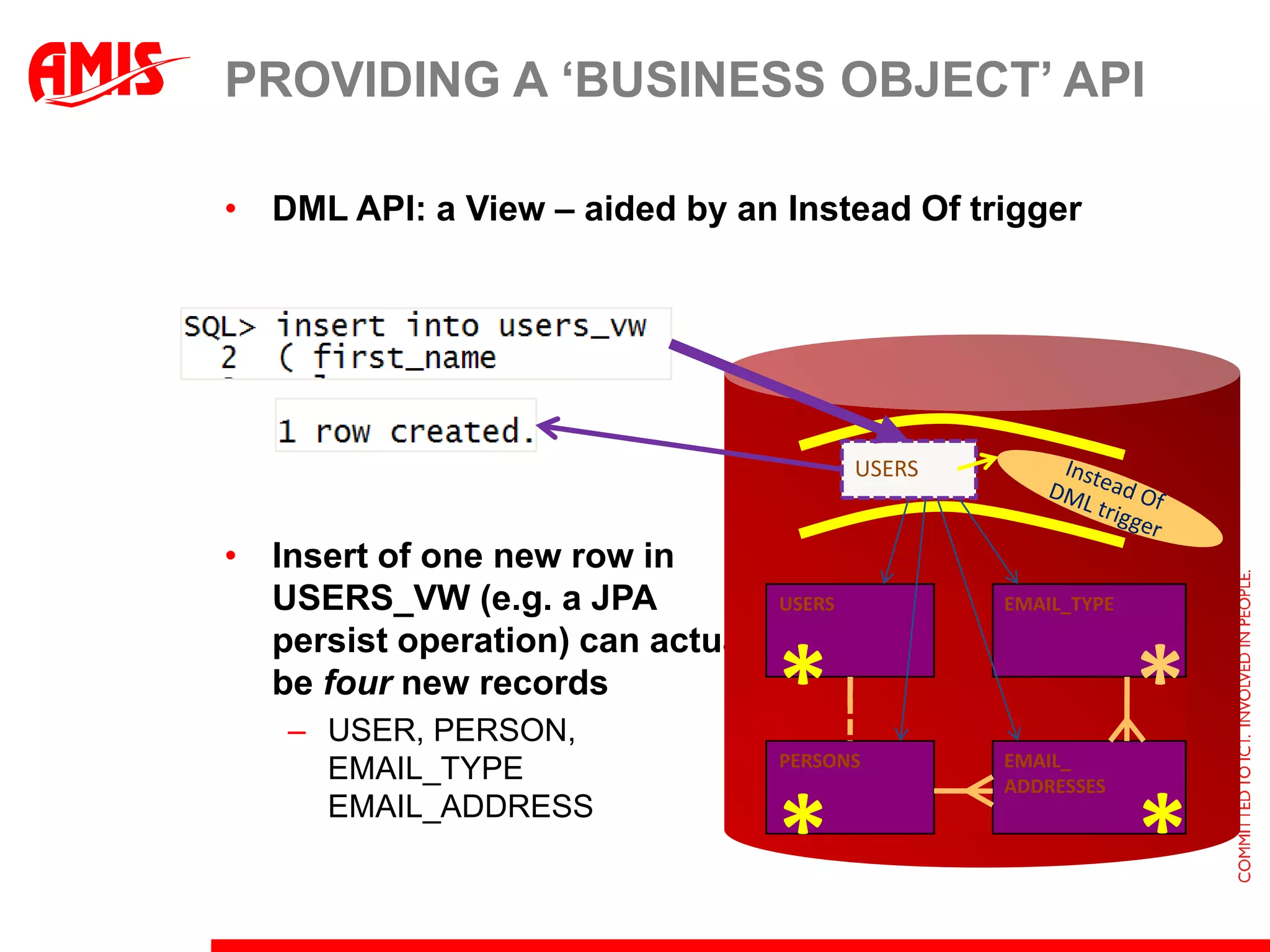
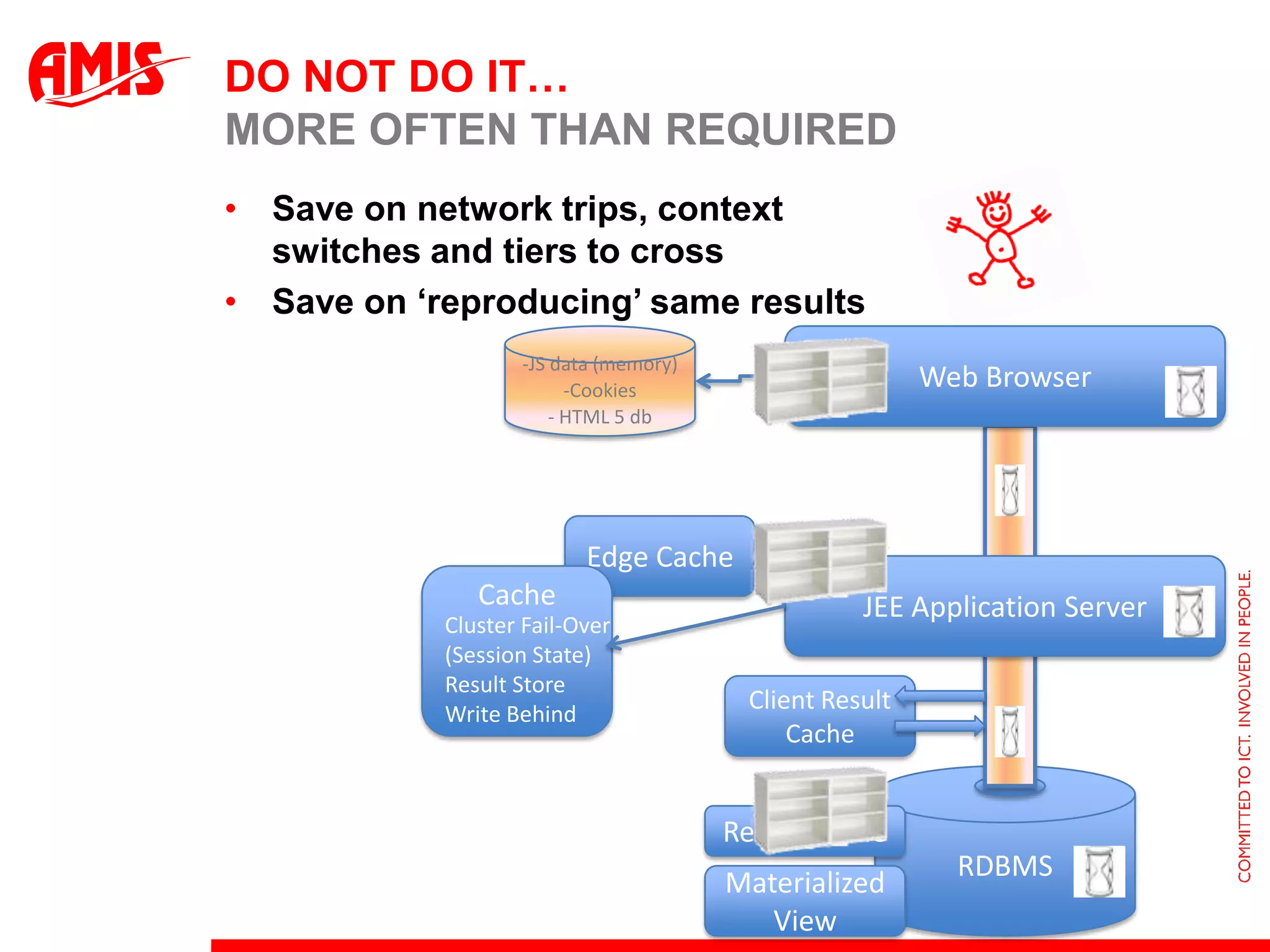
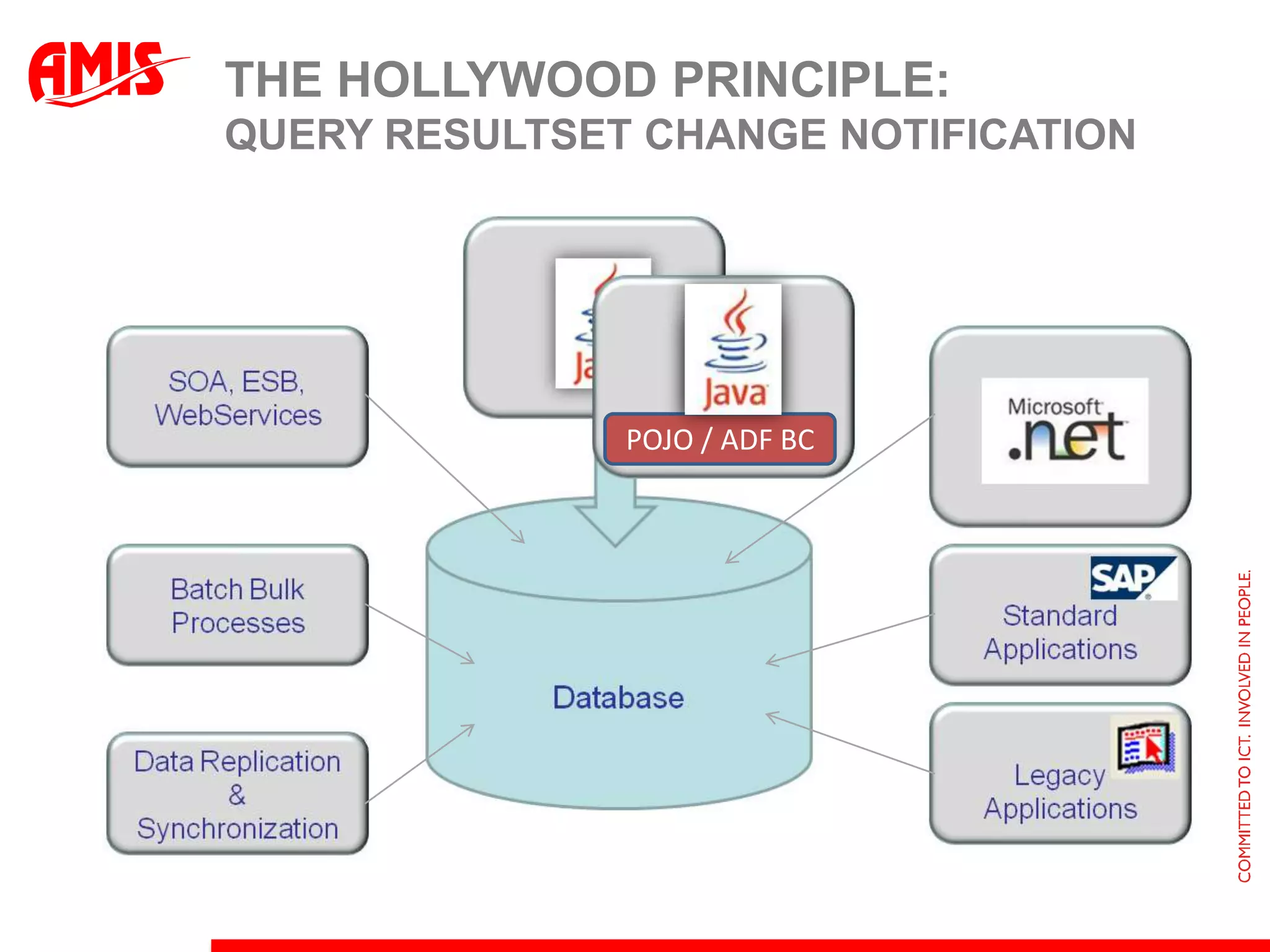
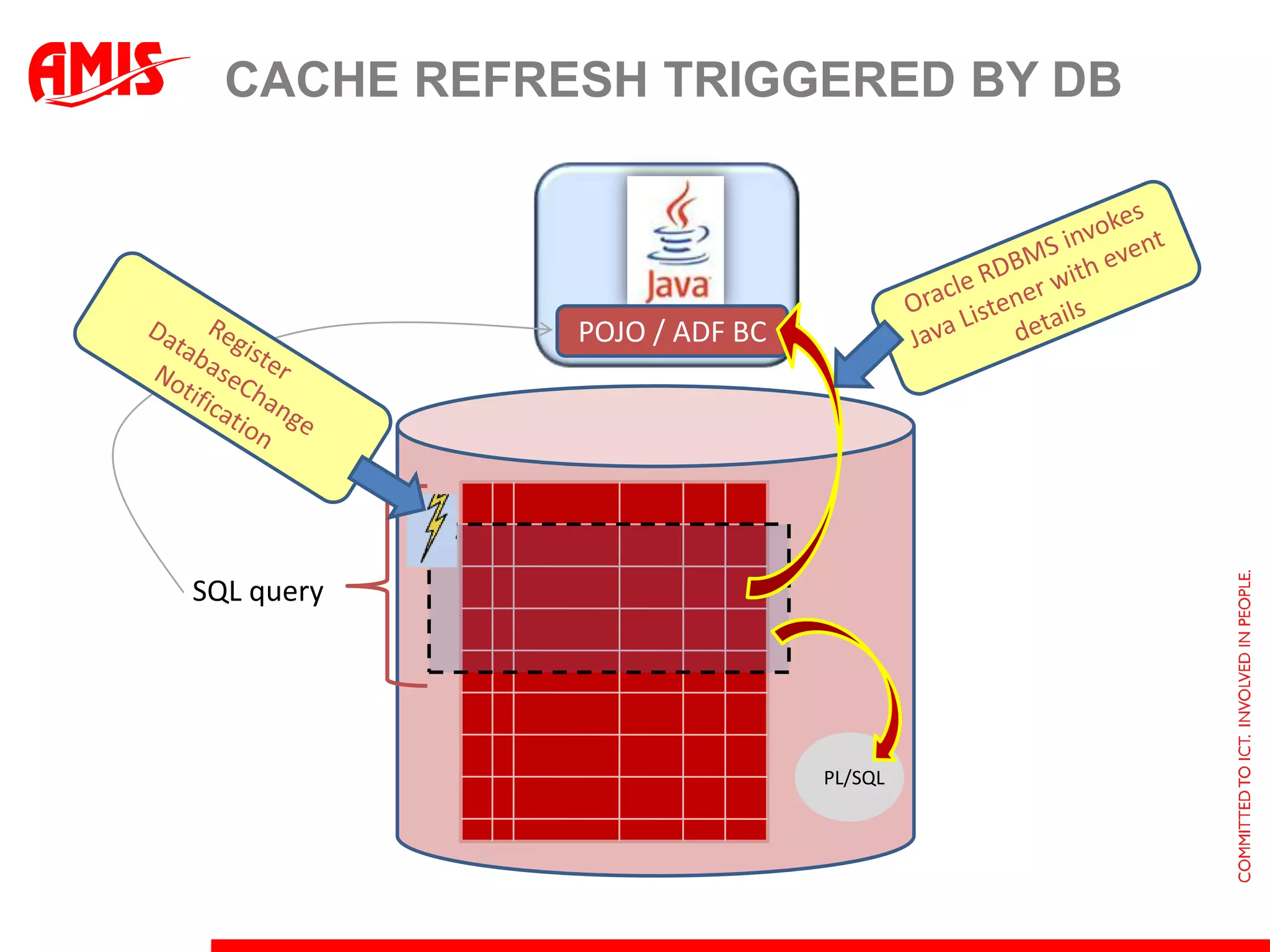
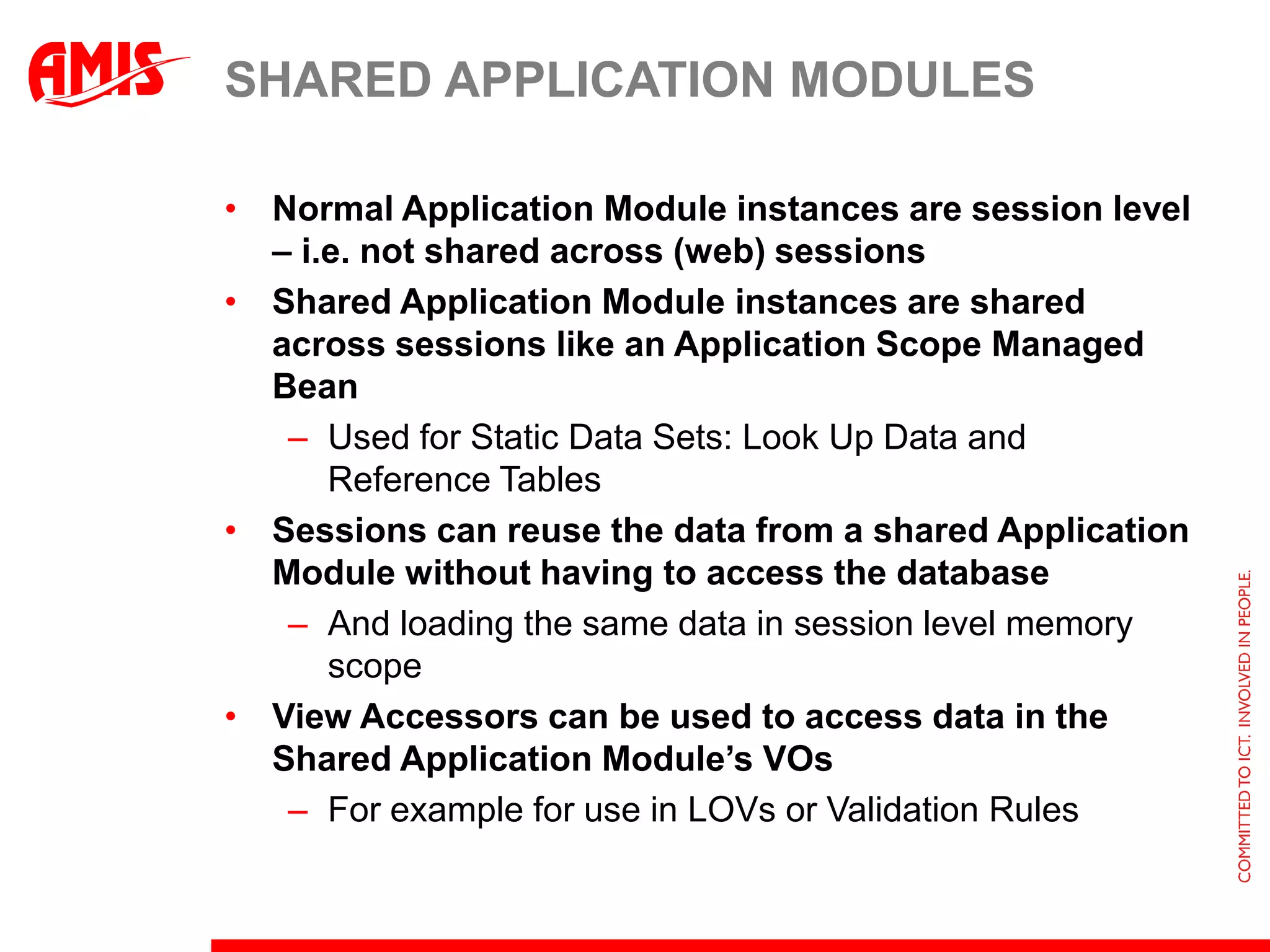
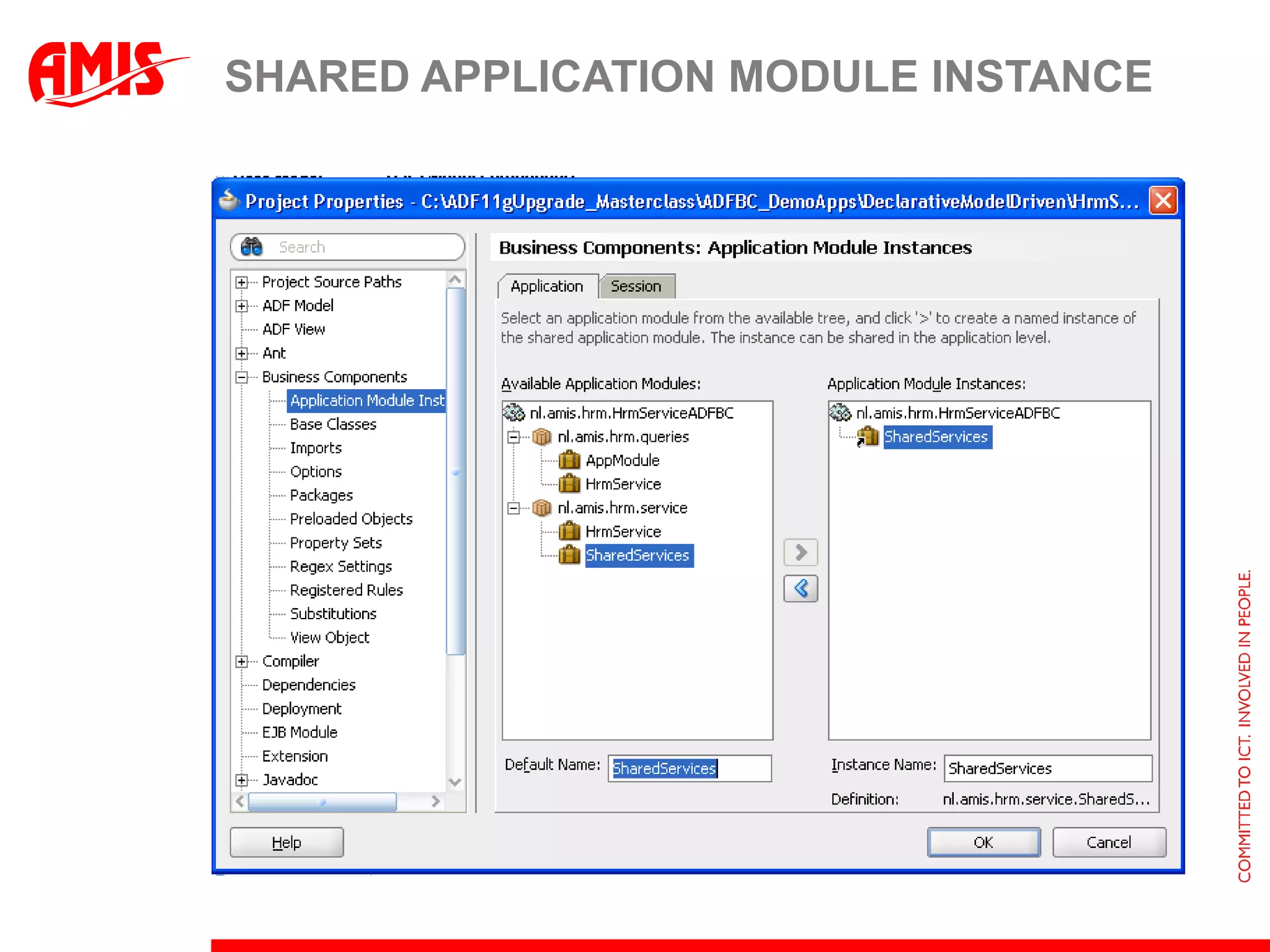
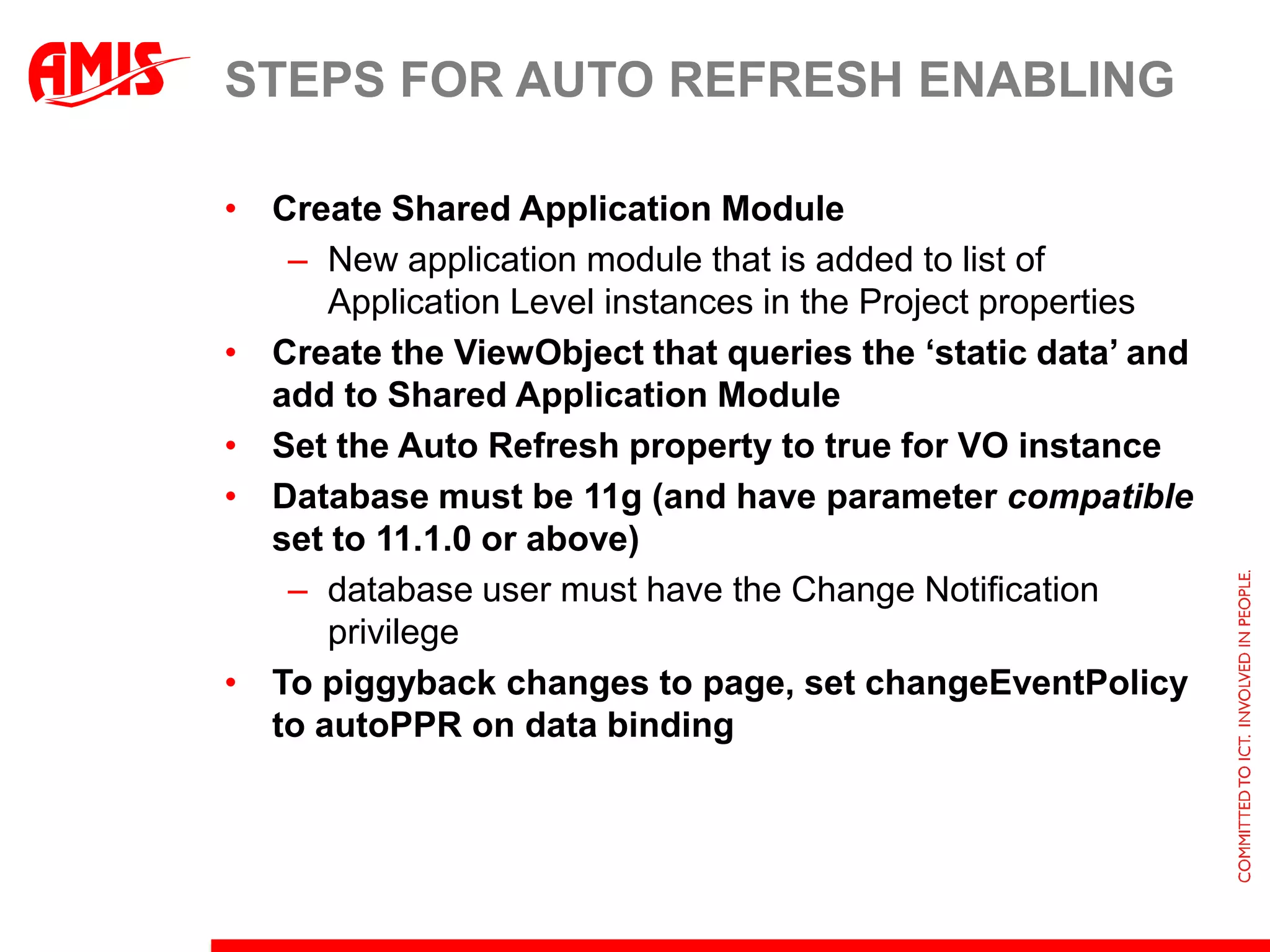
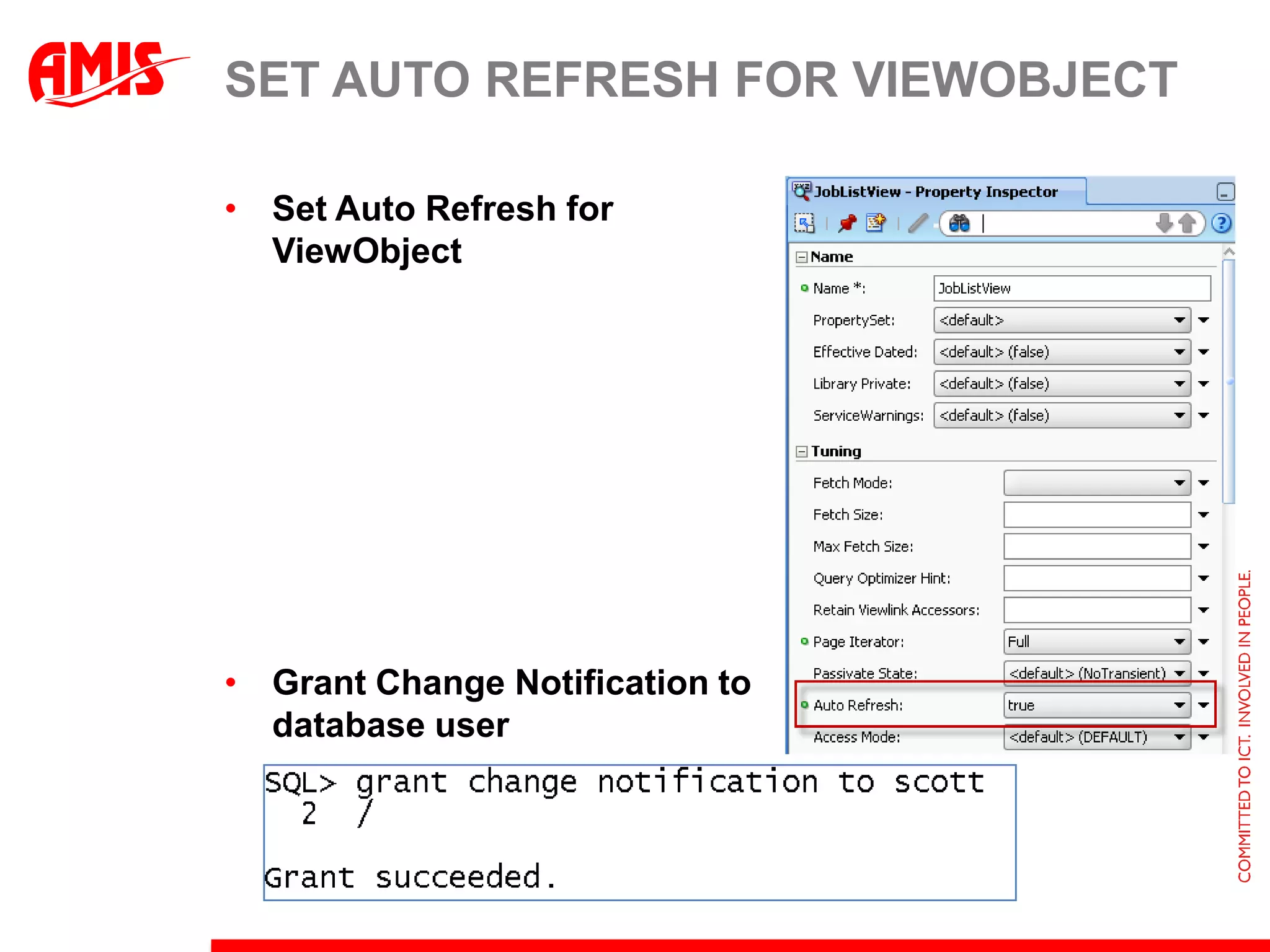
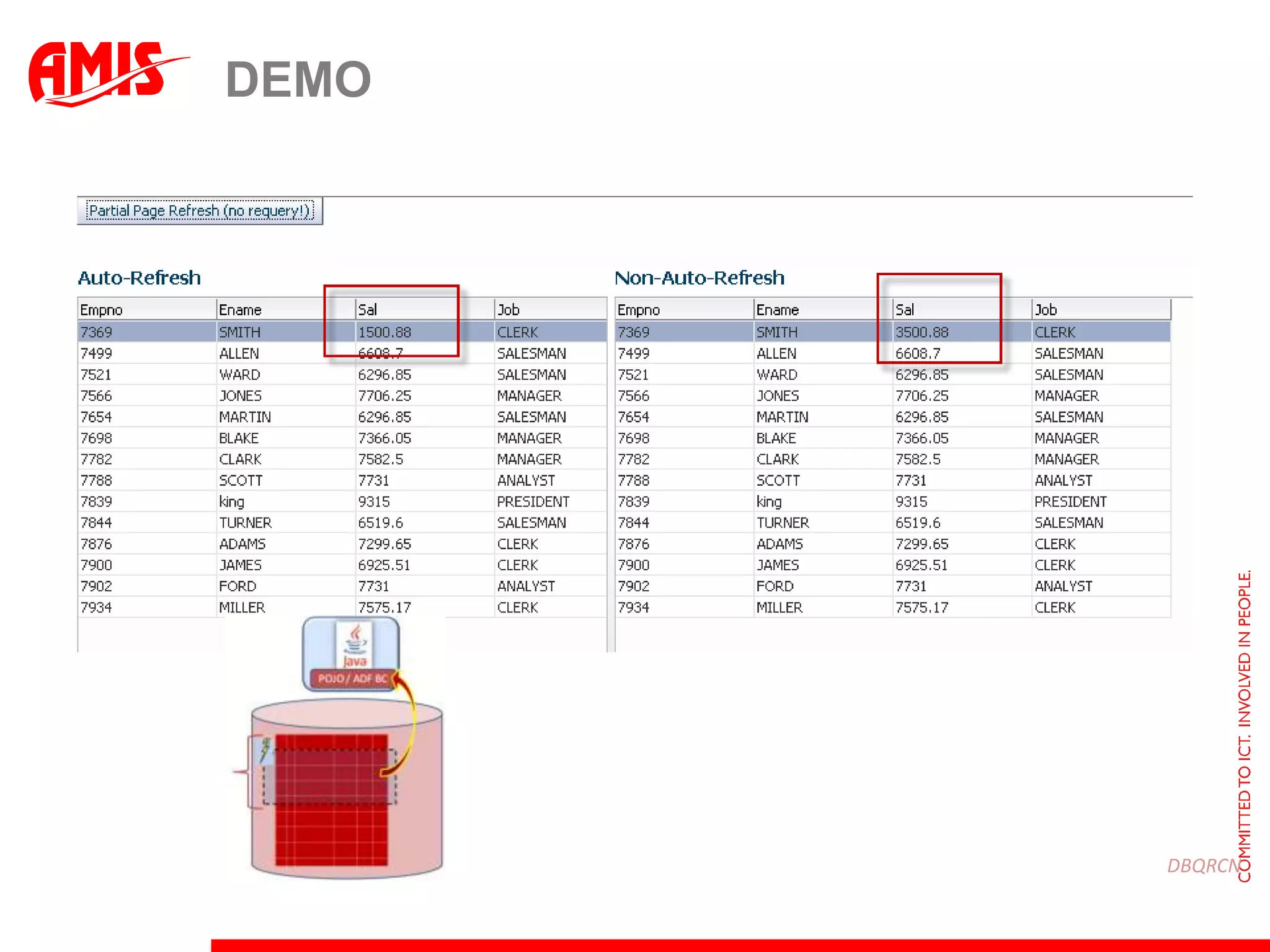
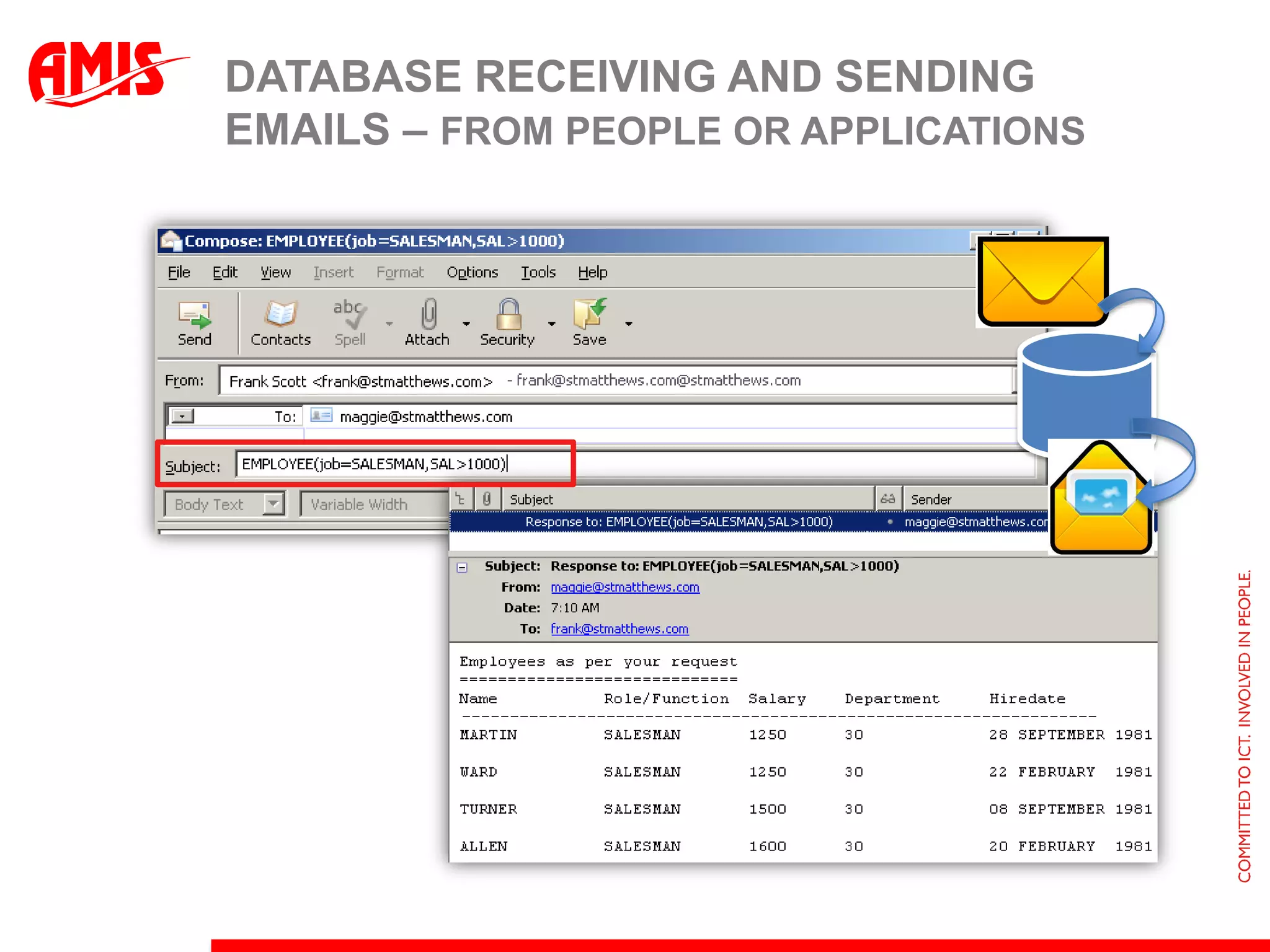
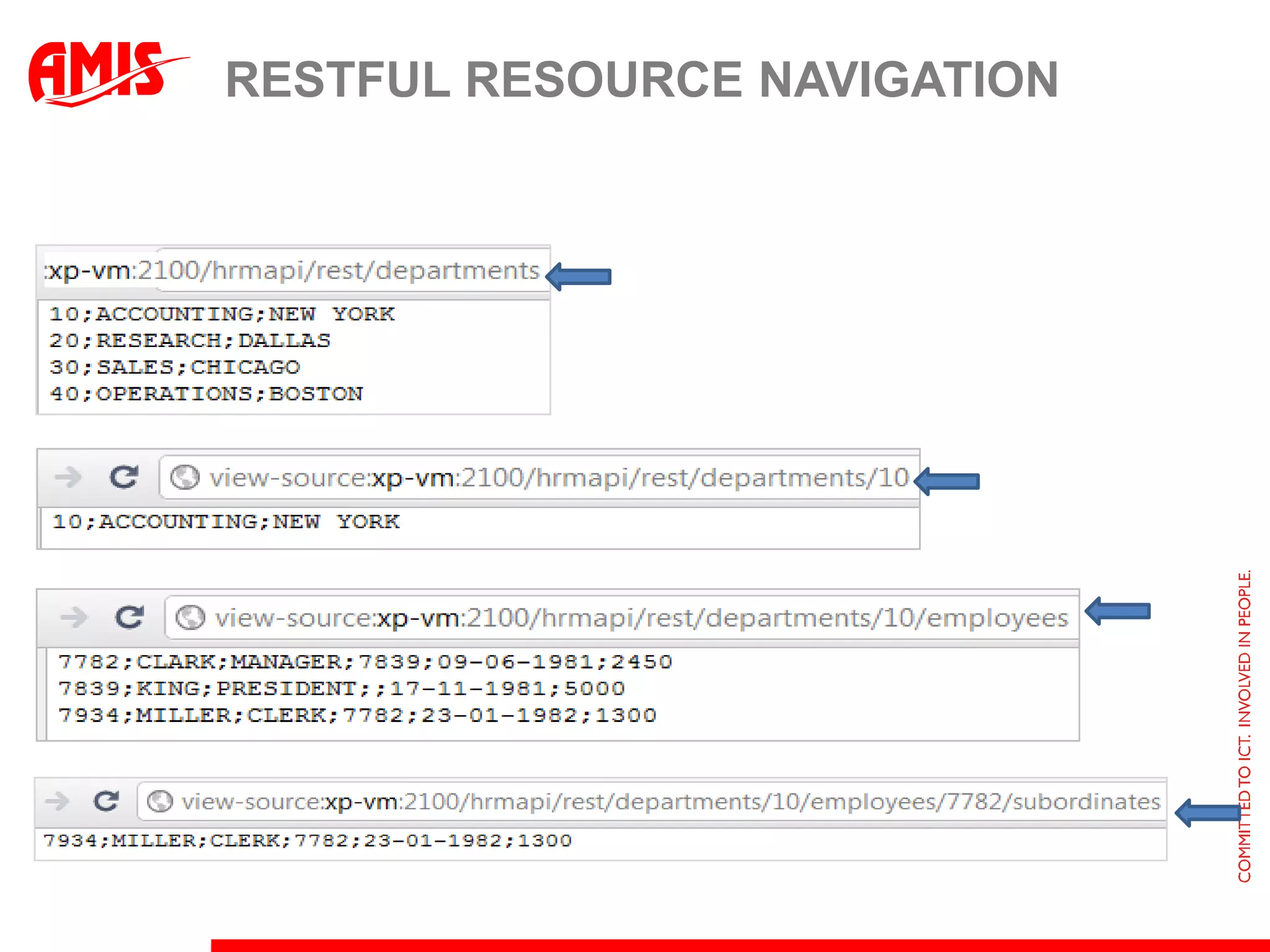
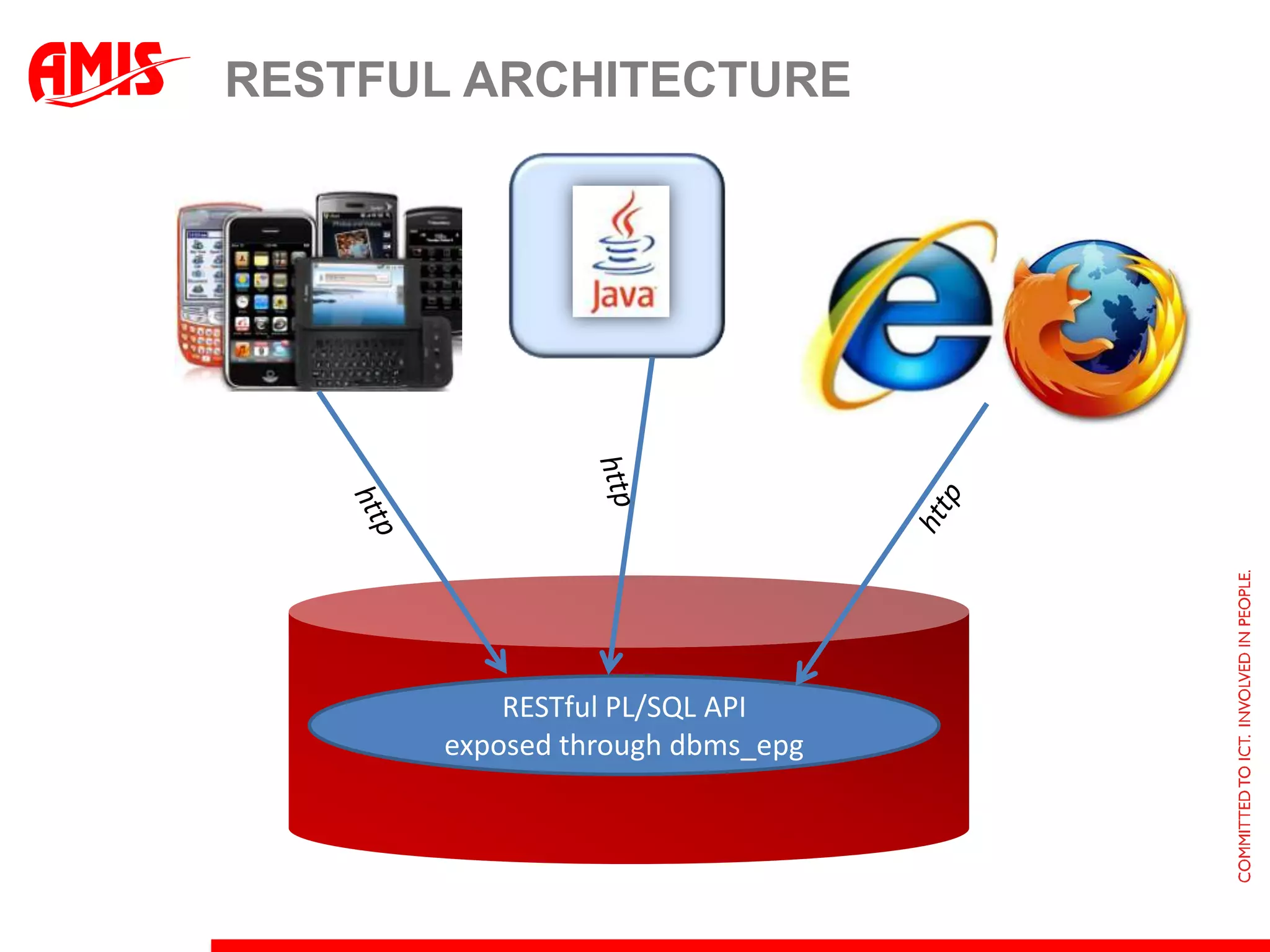
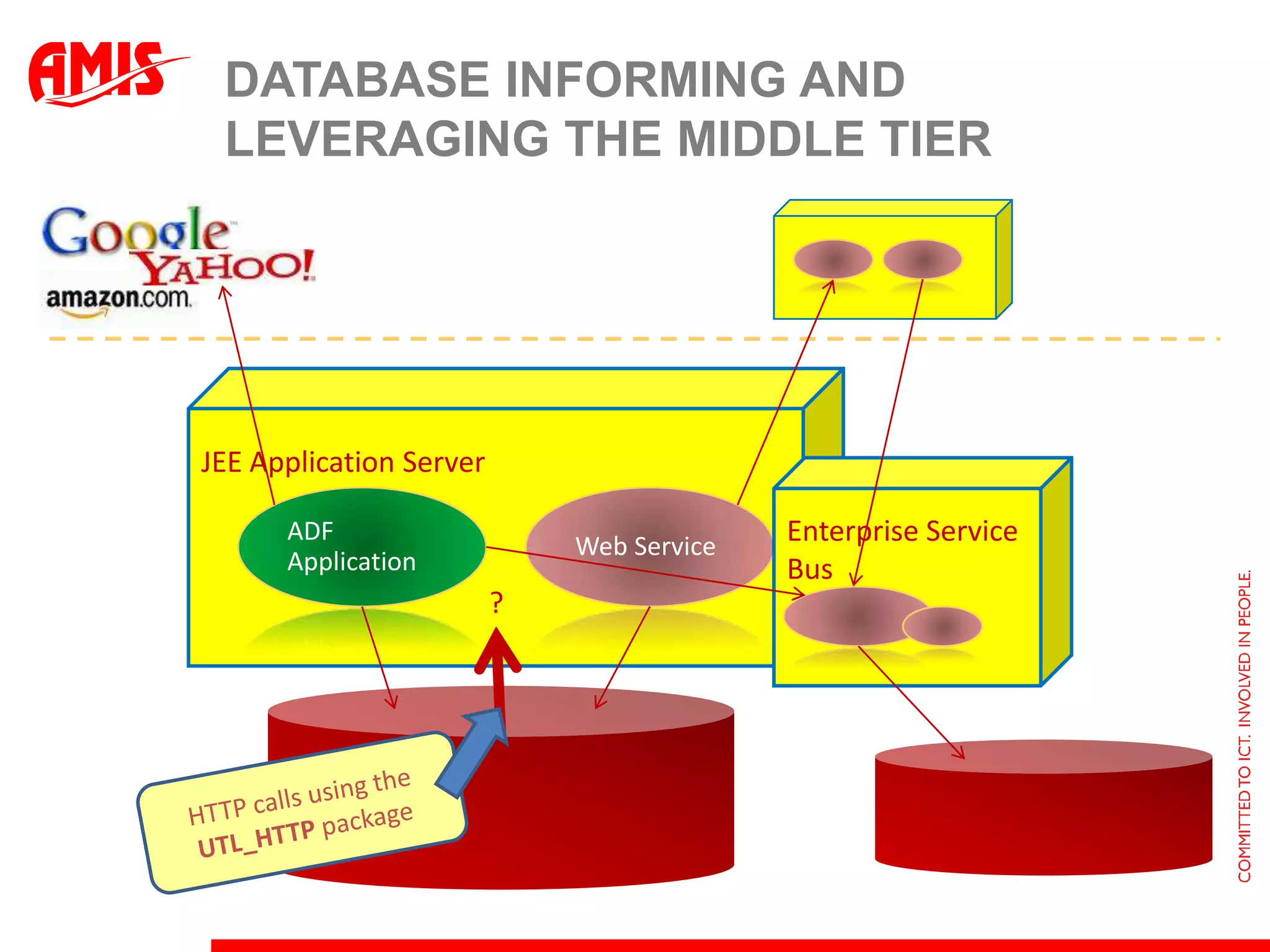
The document discusses various ways that Oracle ADF applications can leverage capabilities of the Oracle database. It describes how database features like triggers, aggregations, analytical functions, and change notification can be used. It emphasizes finding the right balance between what the database and application layers each handle to maximize performance, functionality and productivity.