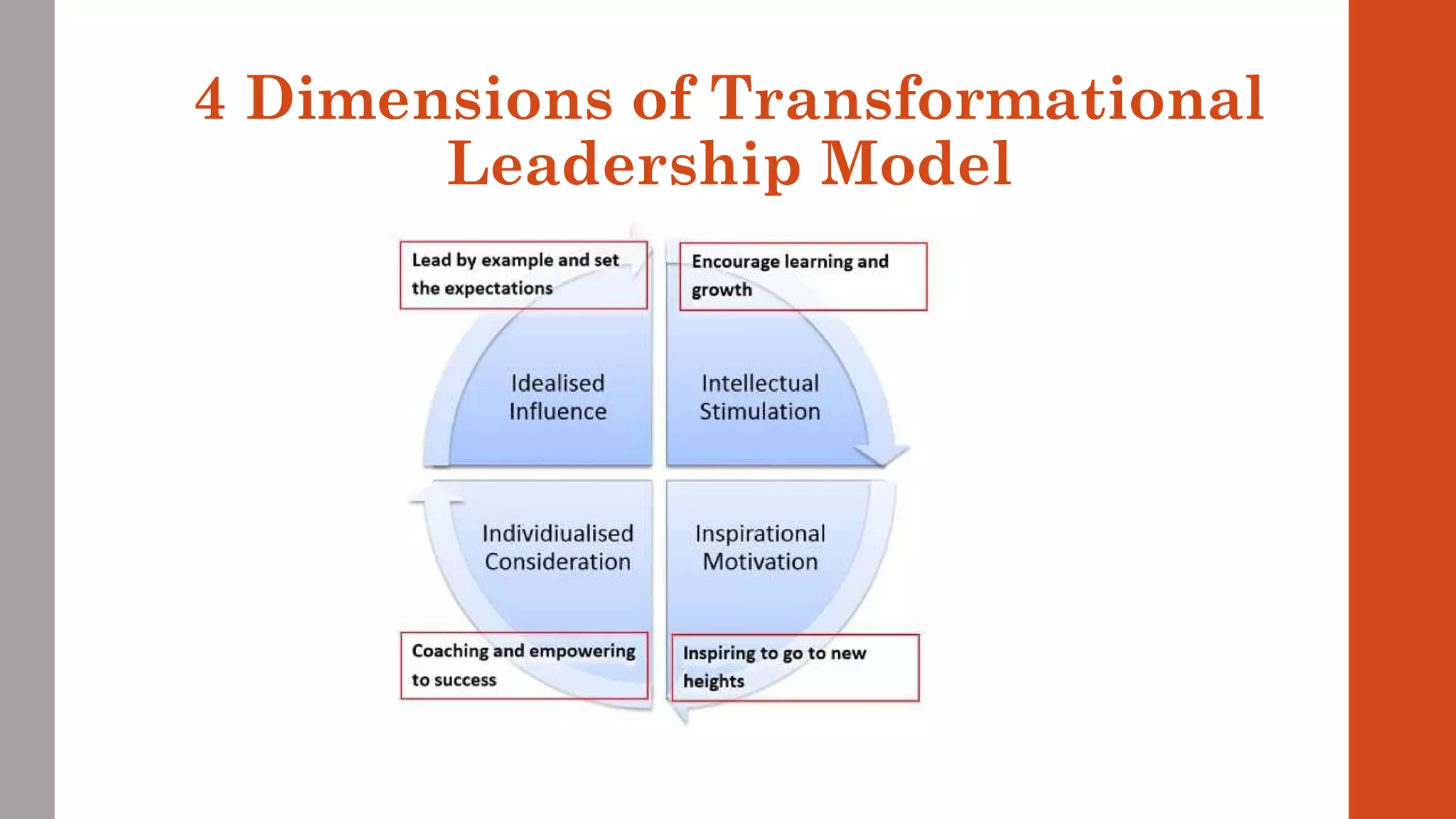
The document discusses transformational leadership theory. It describes transformational leadership as enhancing follower motivation by being a role model, challenging followers, and understanding individual strengths. It outlines four dimensions of transformational leadership: idealized influence, inspirational motivation, individualized consideration, and intellectual stimulation. It also discusses related theorists like Burns and Bass, who developed models of transformational leadership and the Multifactor Leadership Questionnaire assessment.