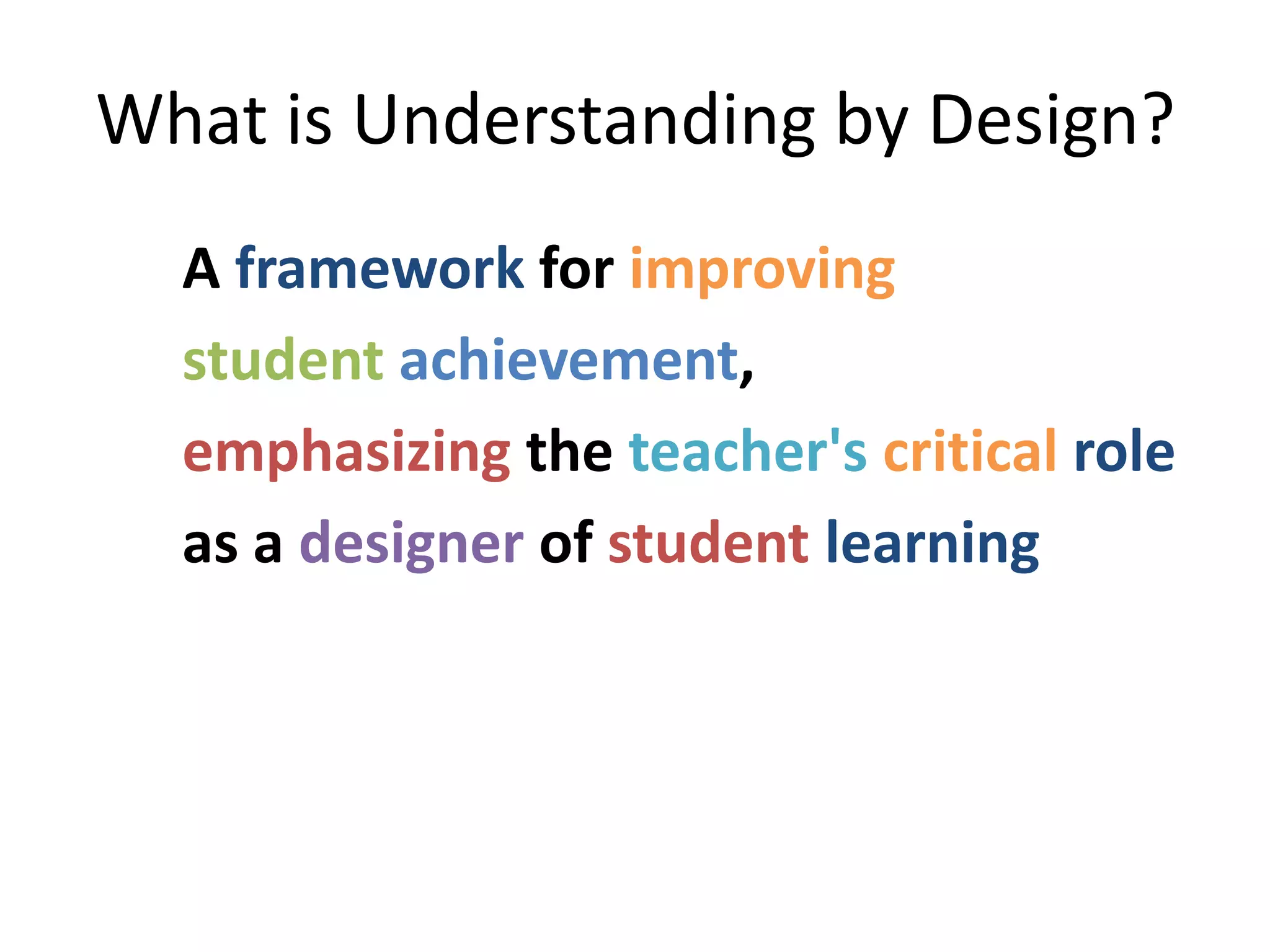
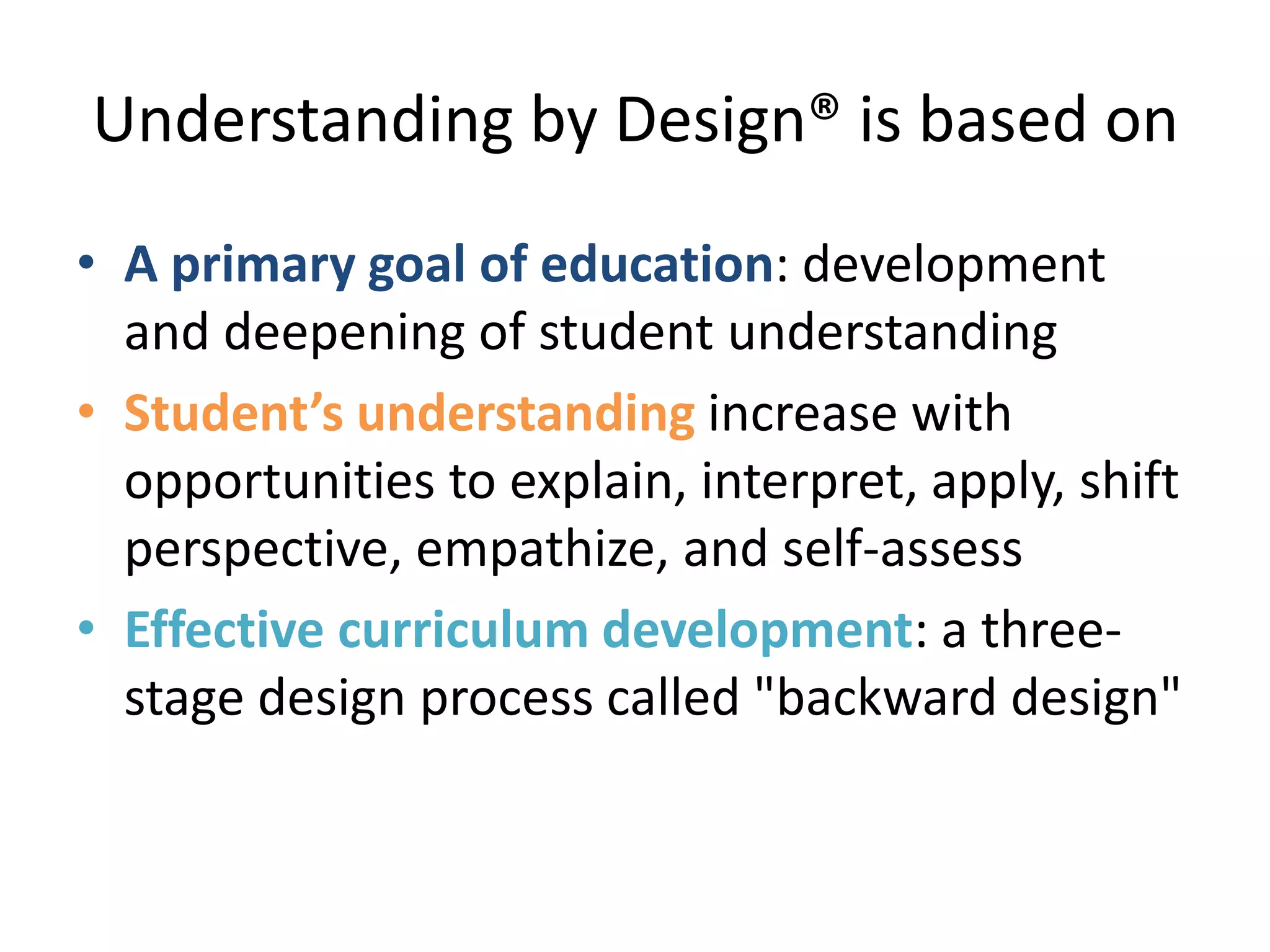
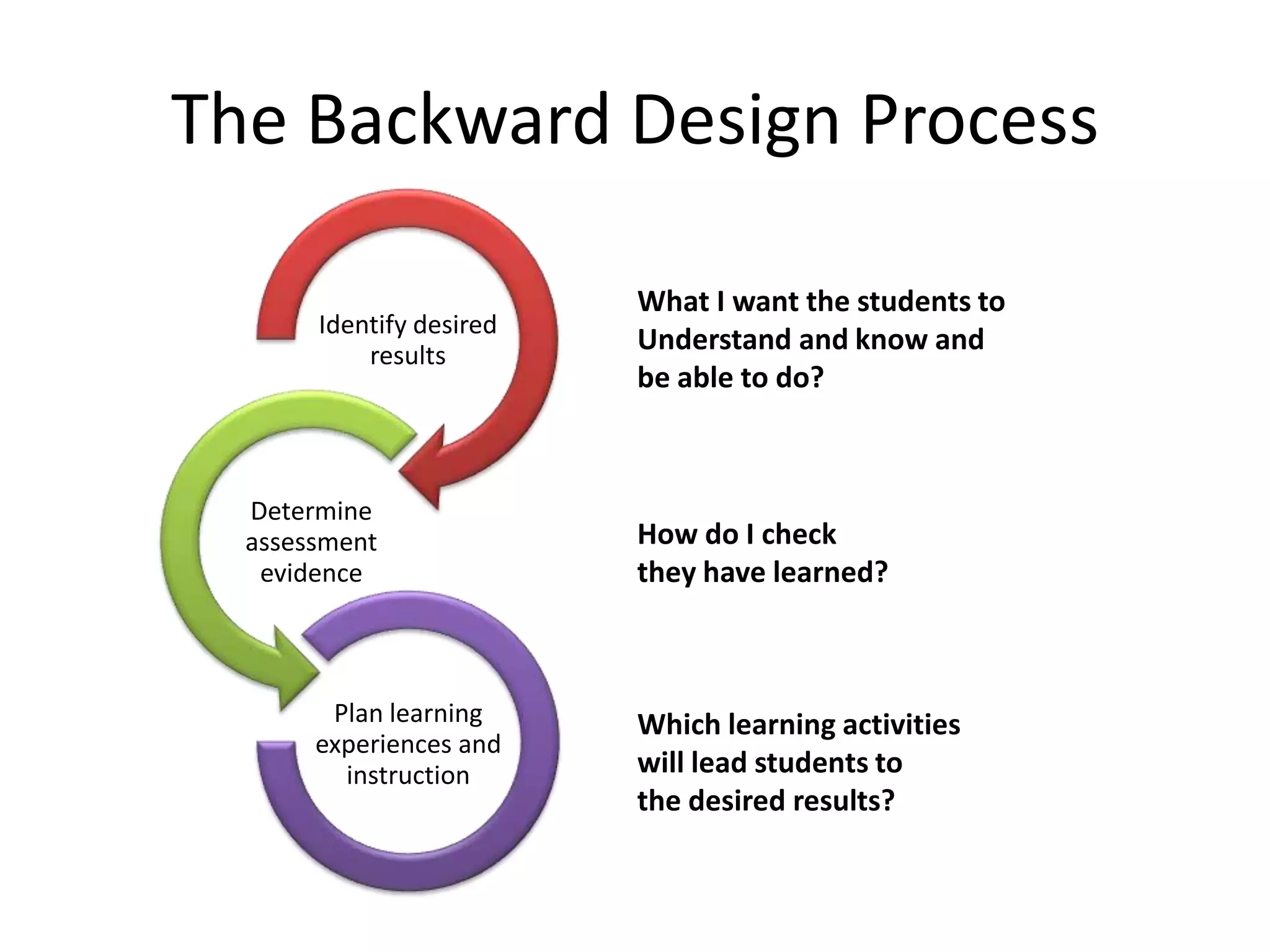
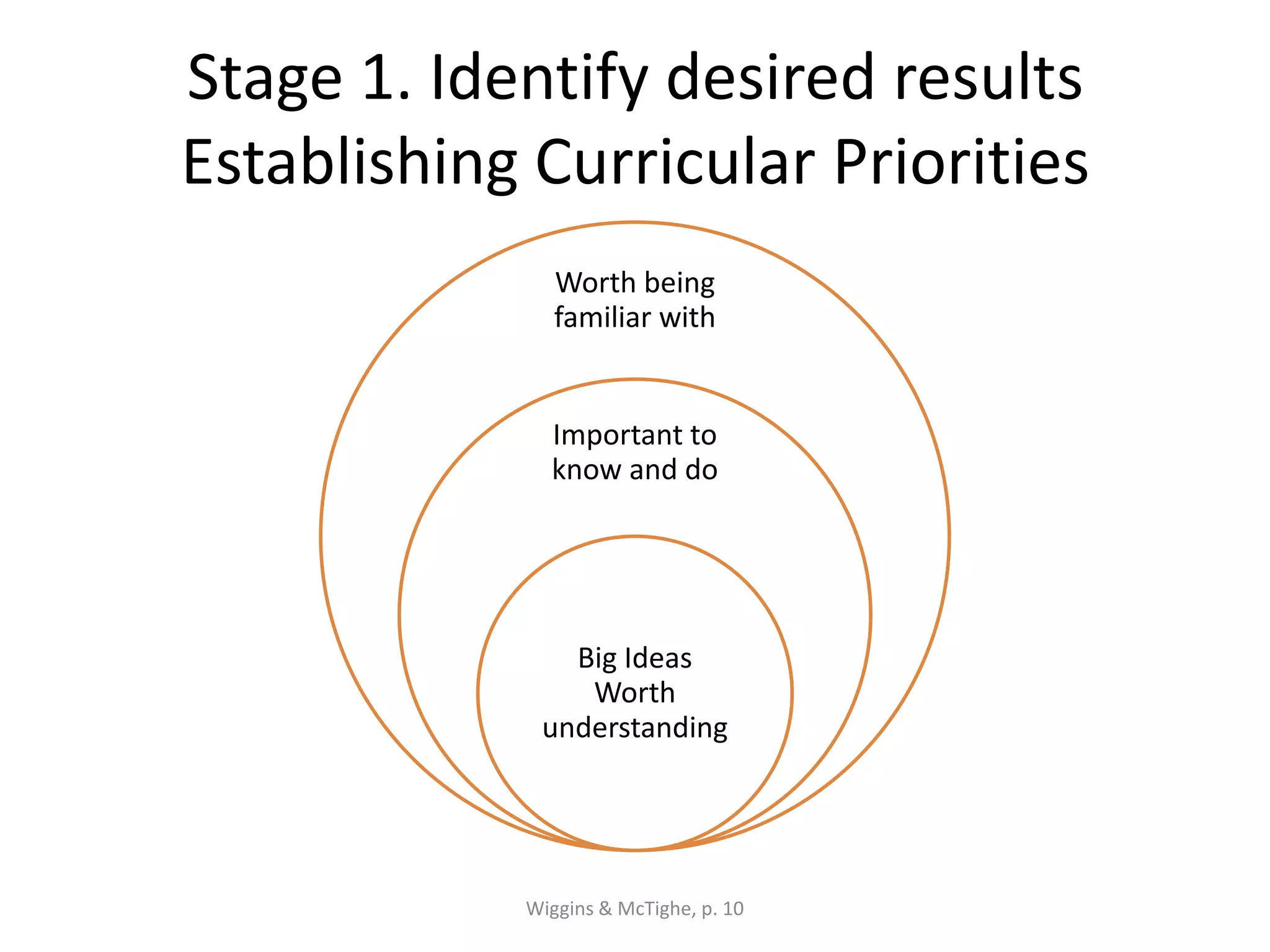
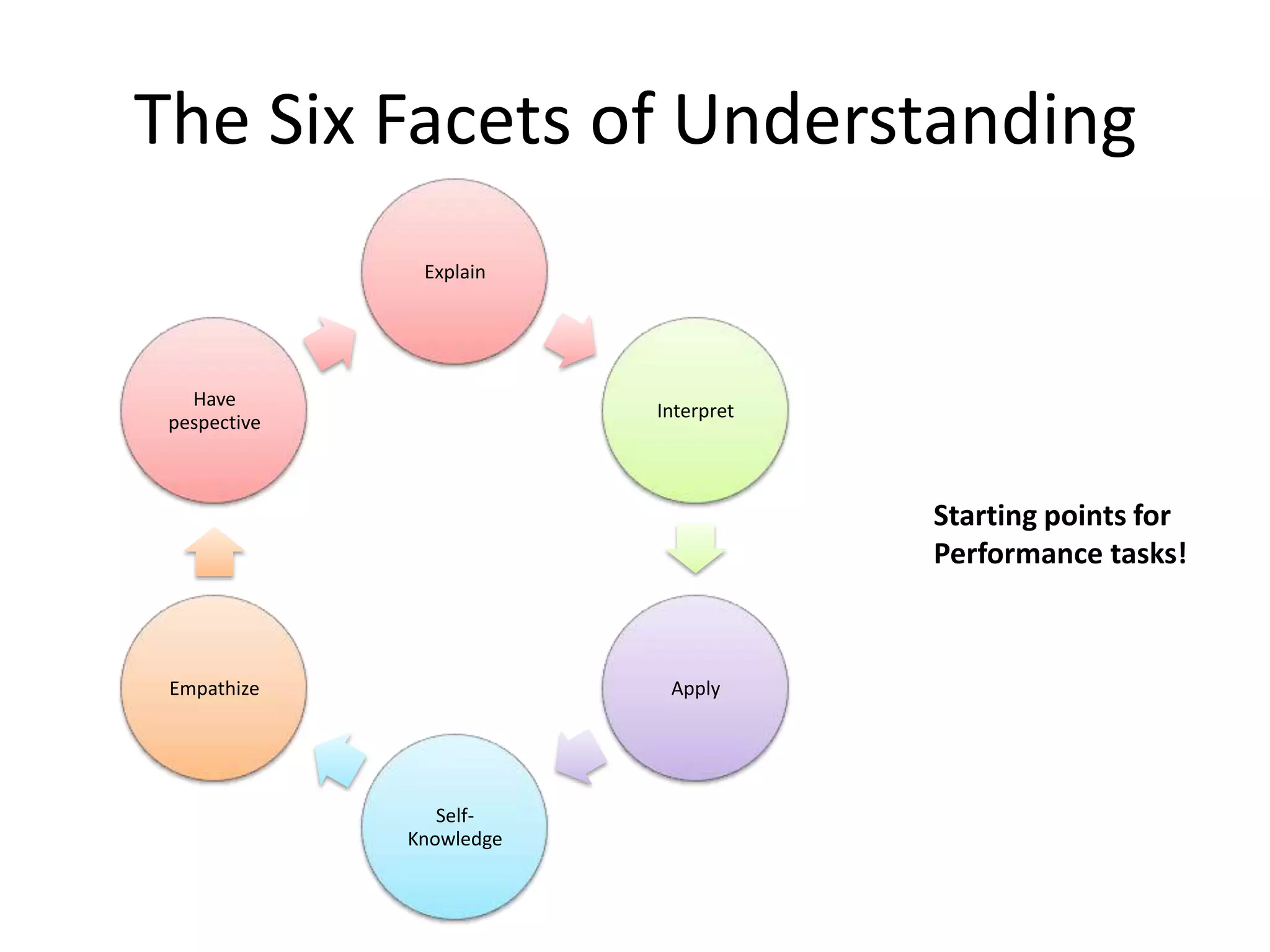
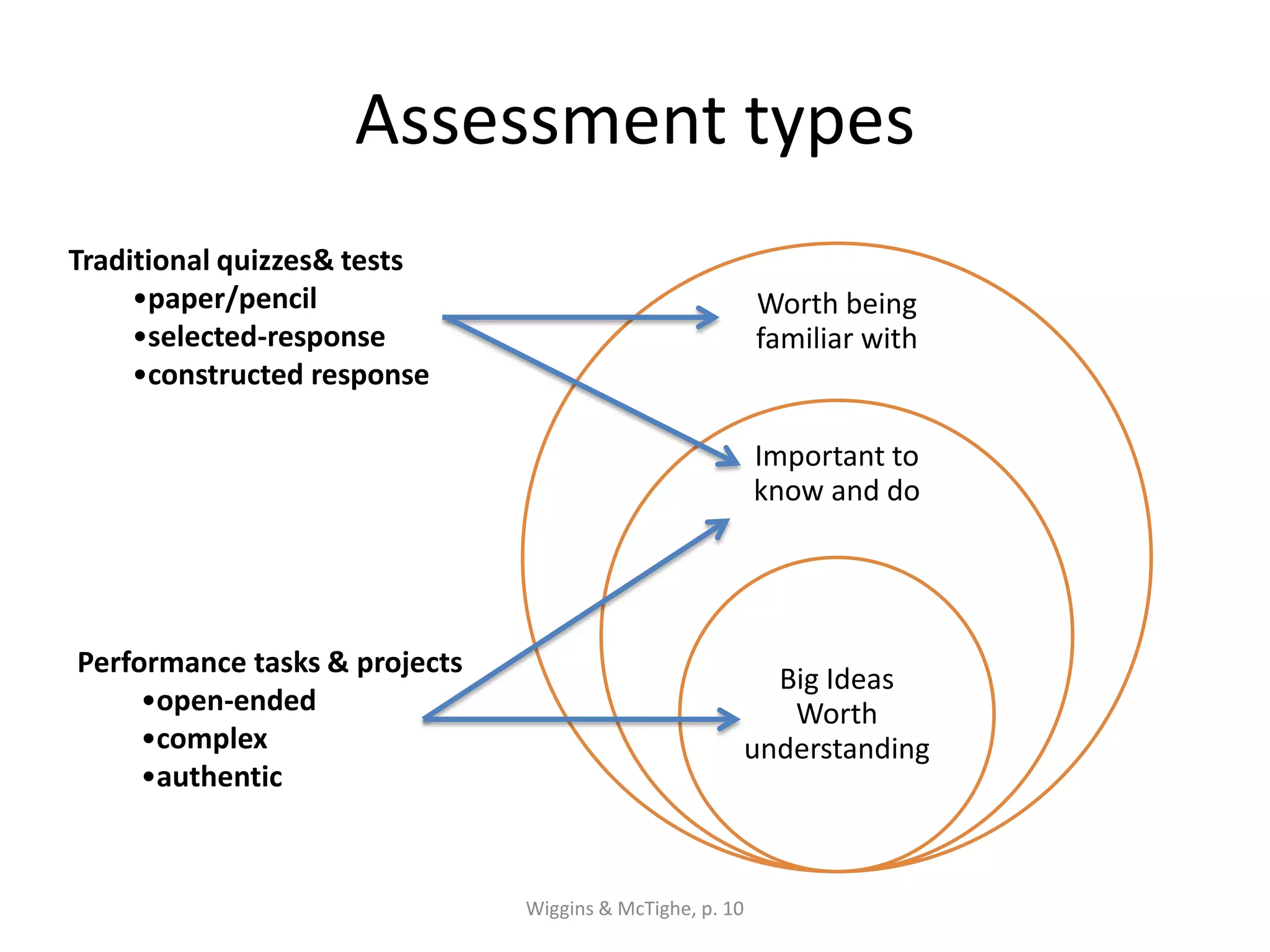
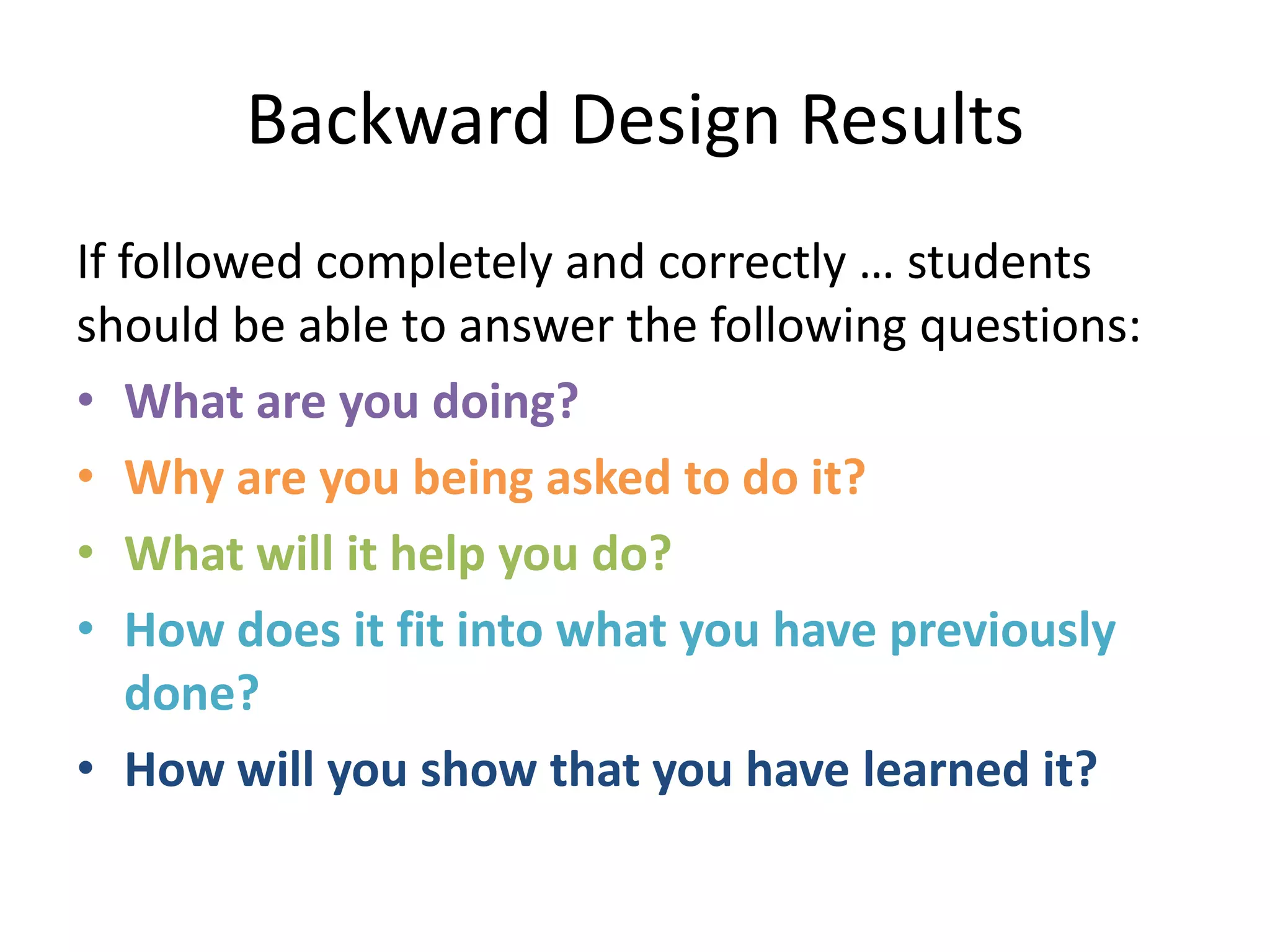
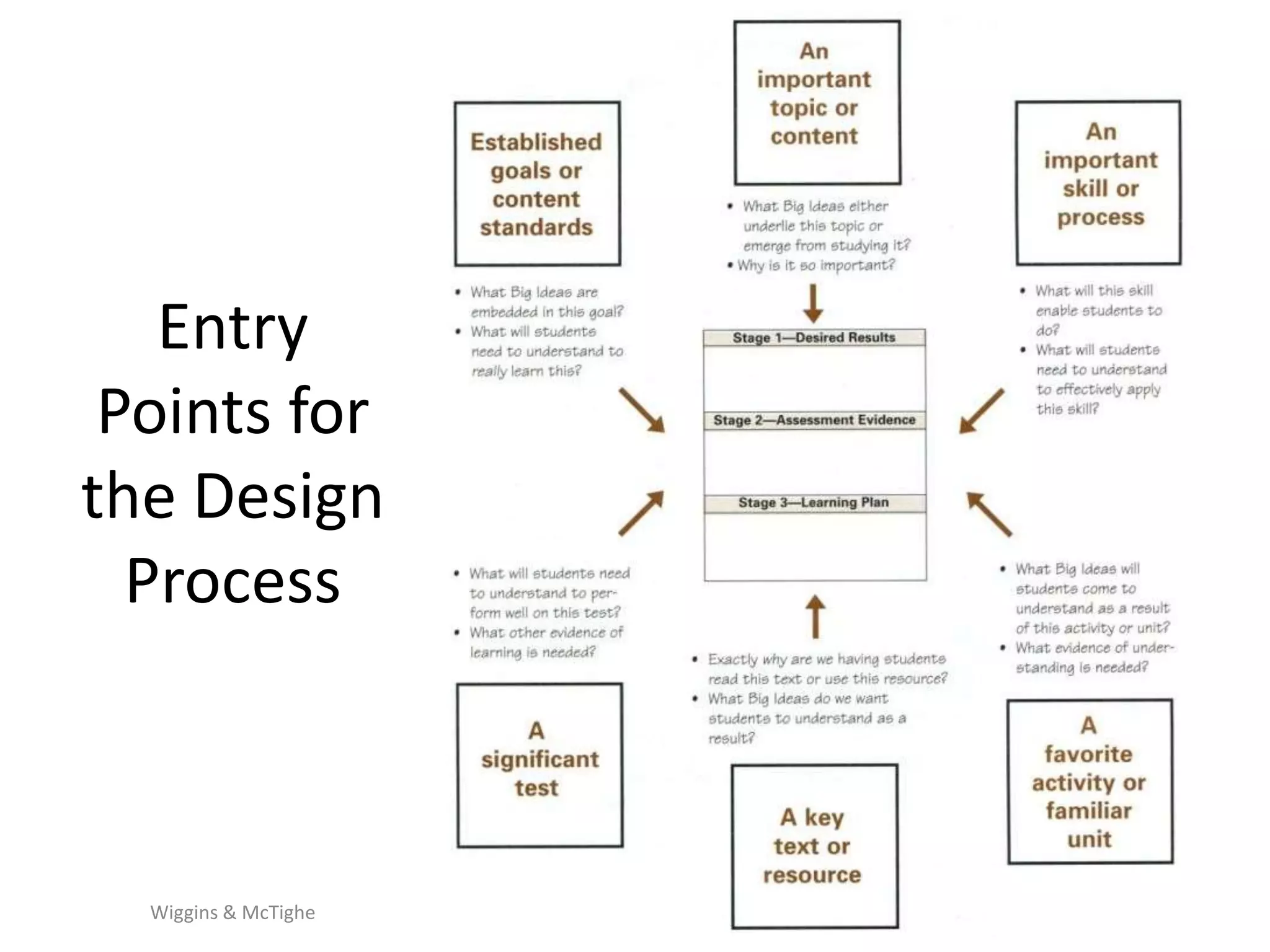
The document outlines the backward design instructional approach, emphasizing the importance of starting with desired learning outcomes to enhance student understanding and achievement. It details a three-stage design process: identifying desired results, determining acceptable evidence, and planning learning experiences and instruction. The framework encourages alignment of goals, assessments, and activities while fostering inquiry through essential questions.