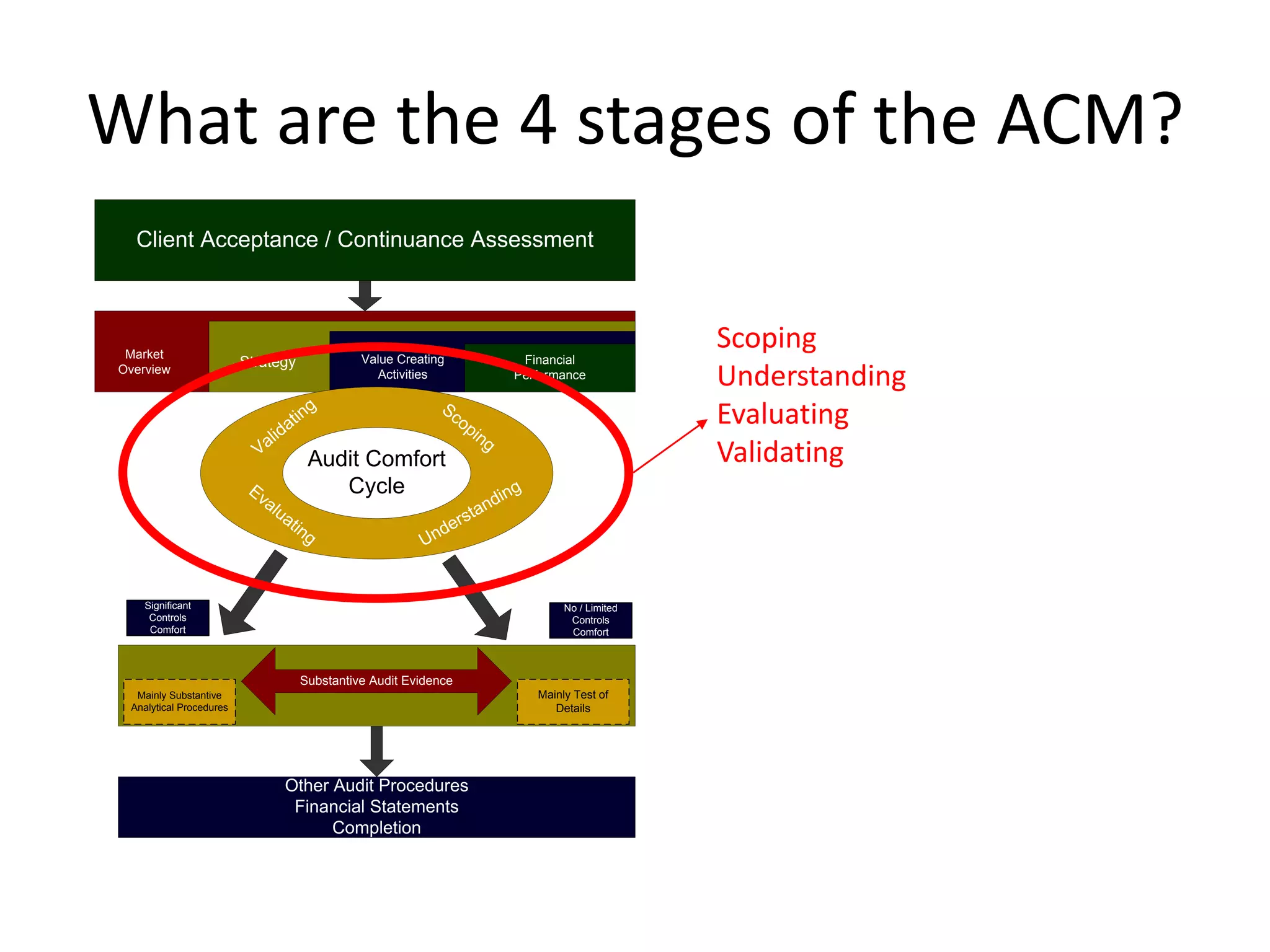
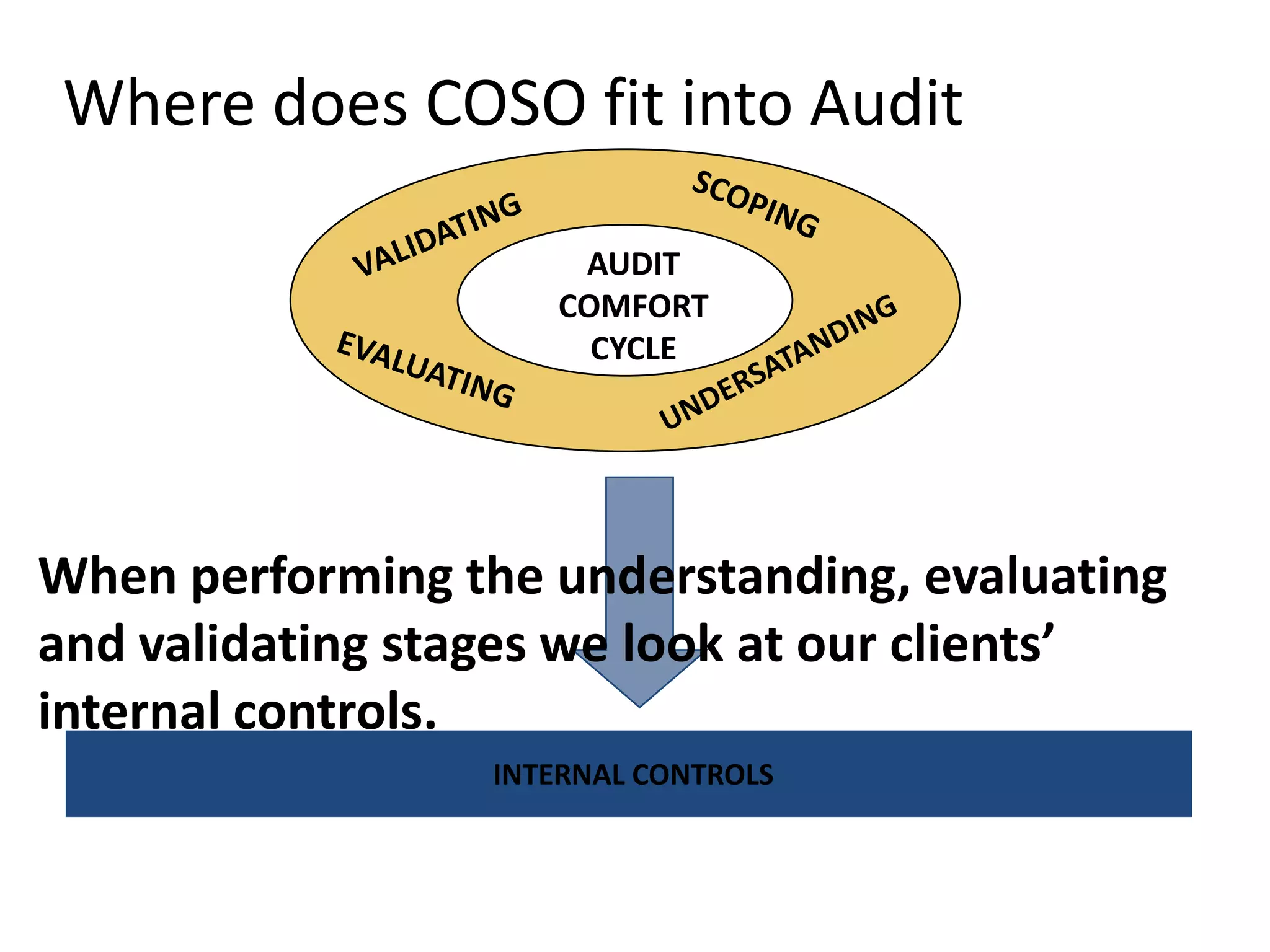
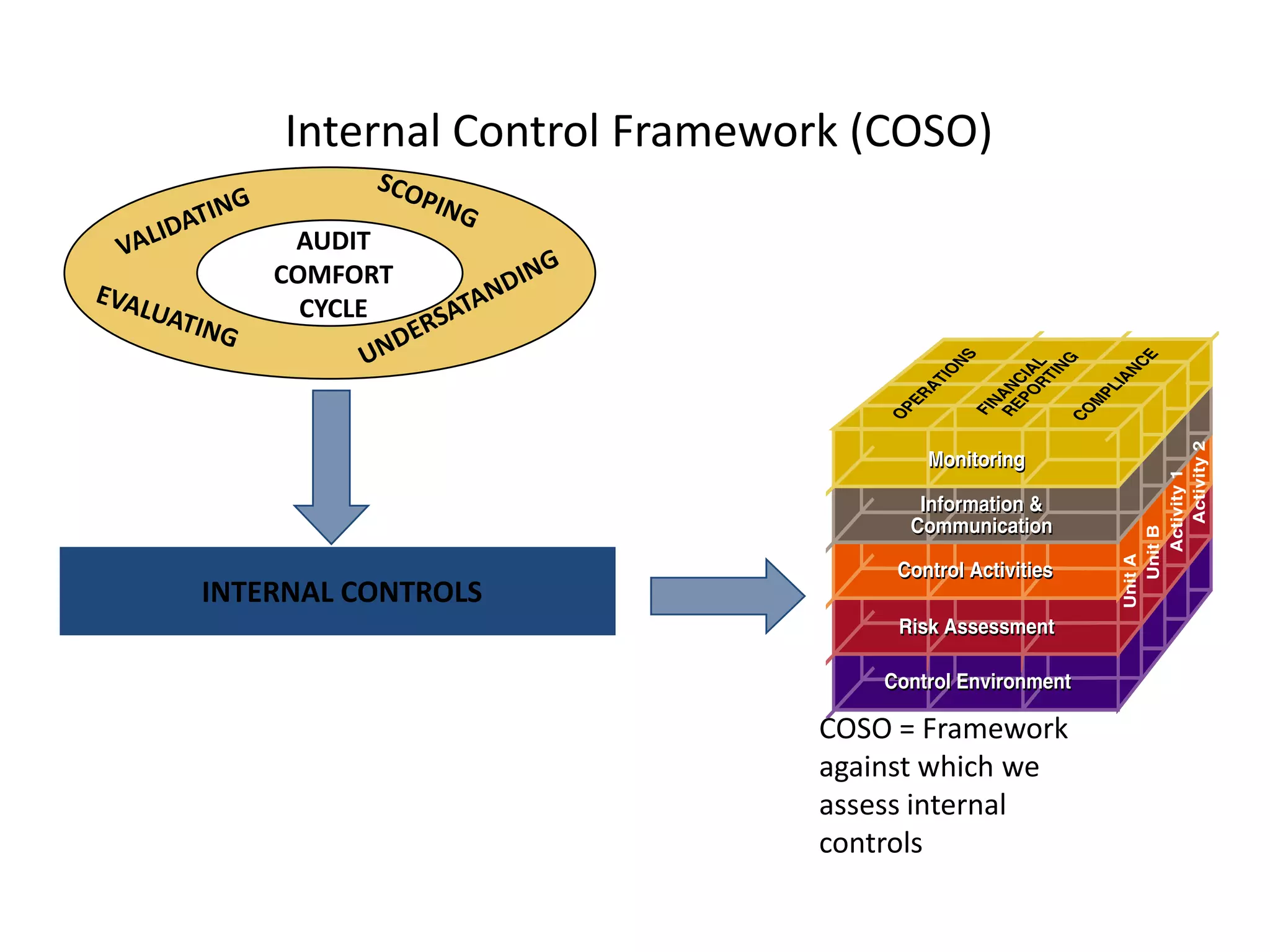
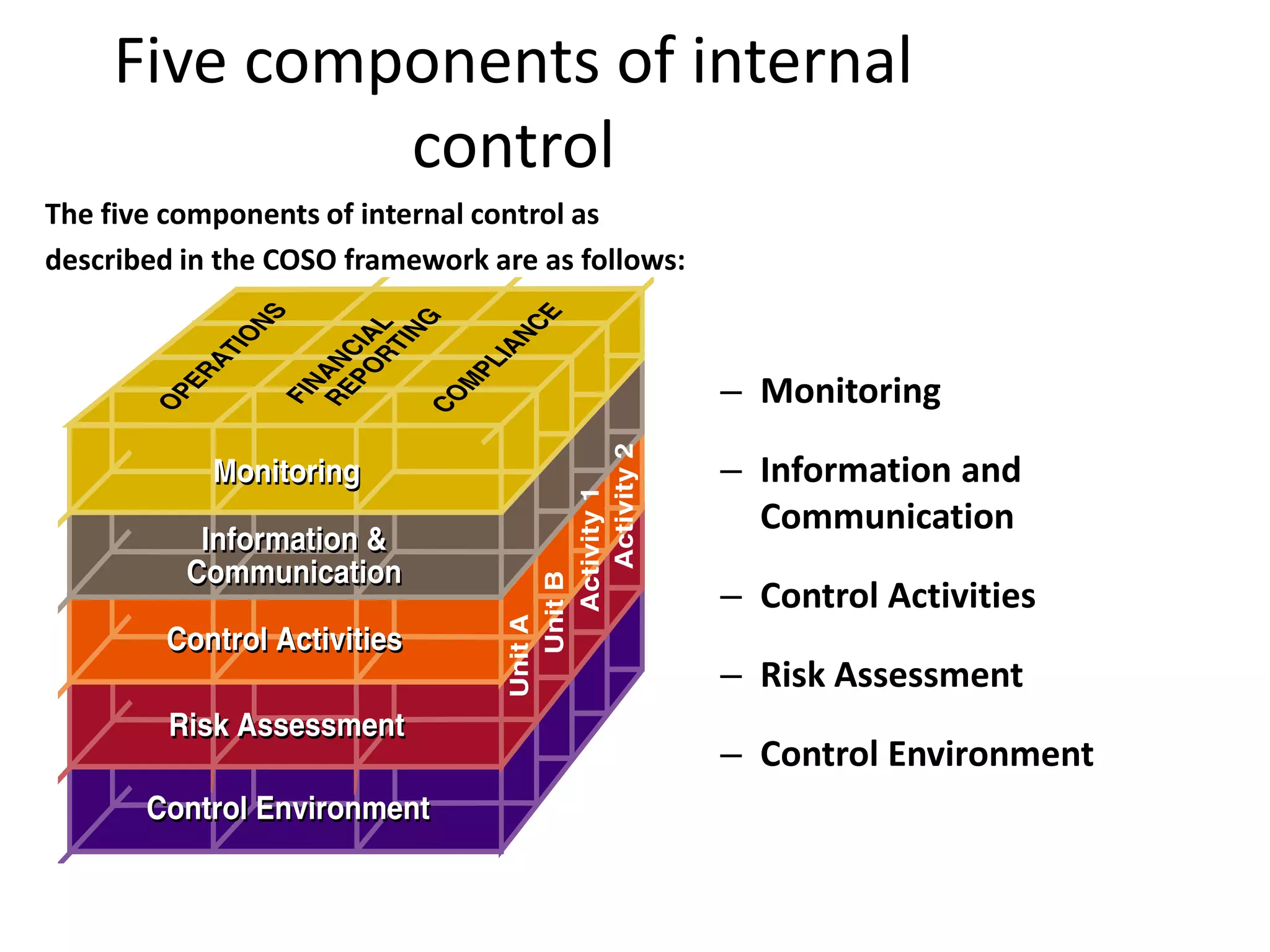
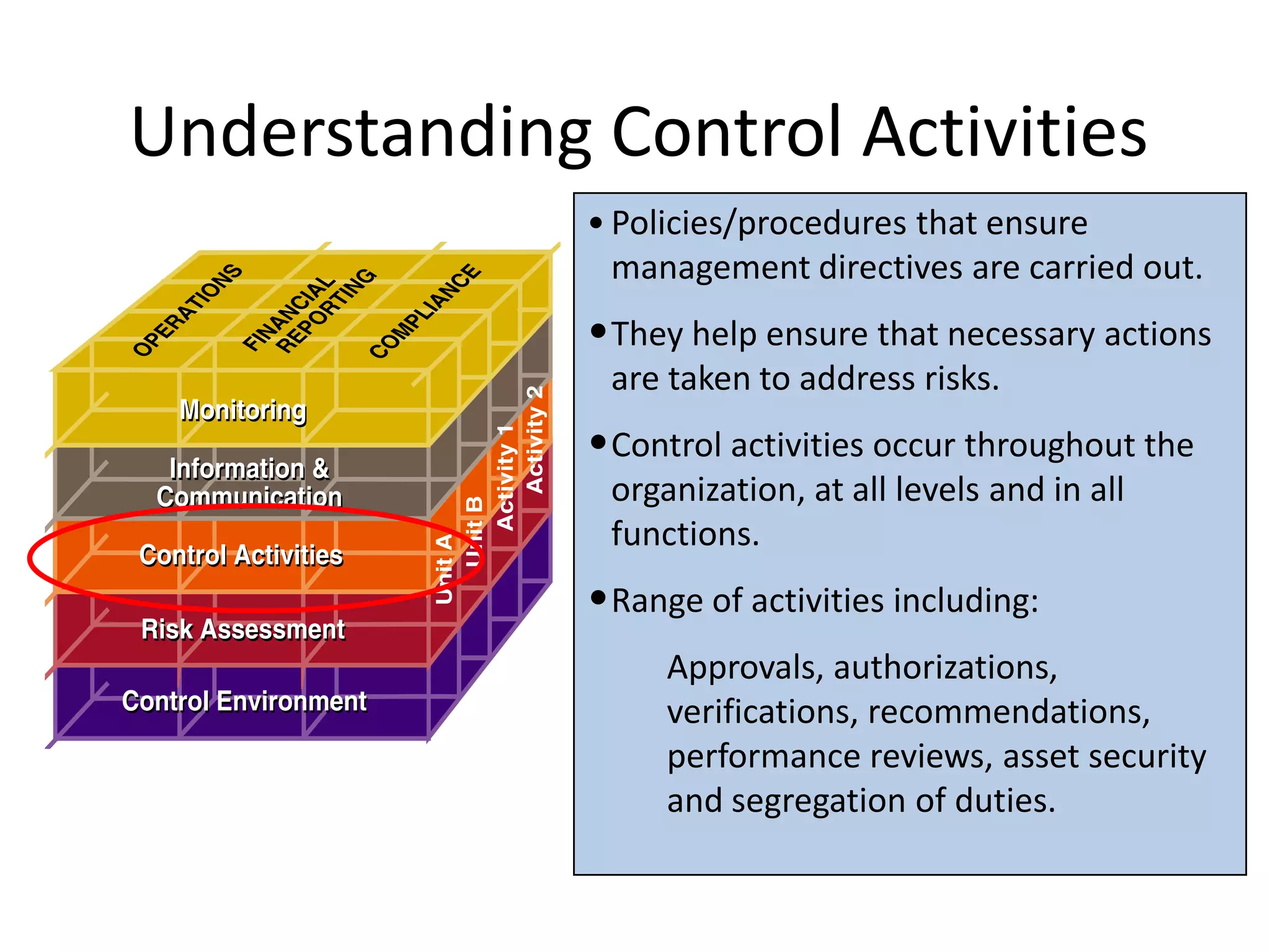
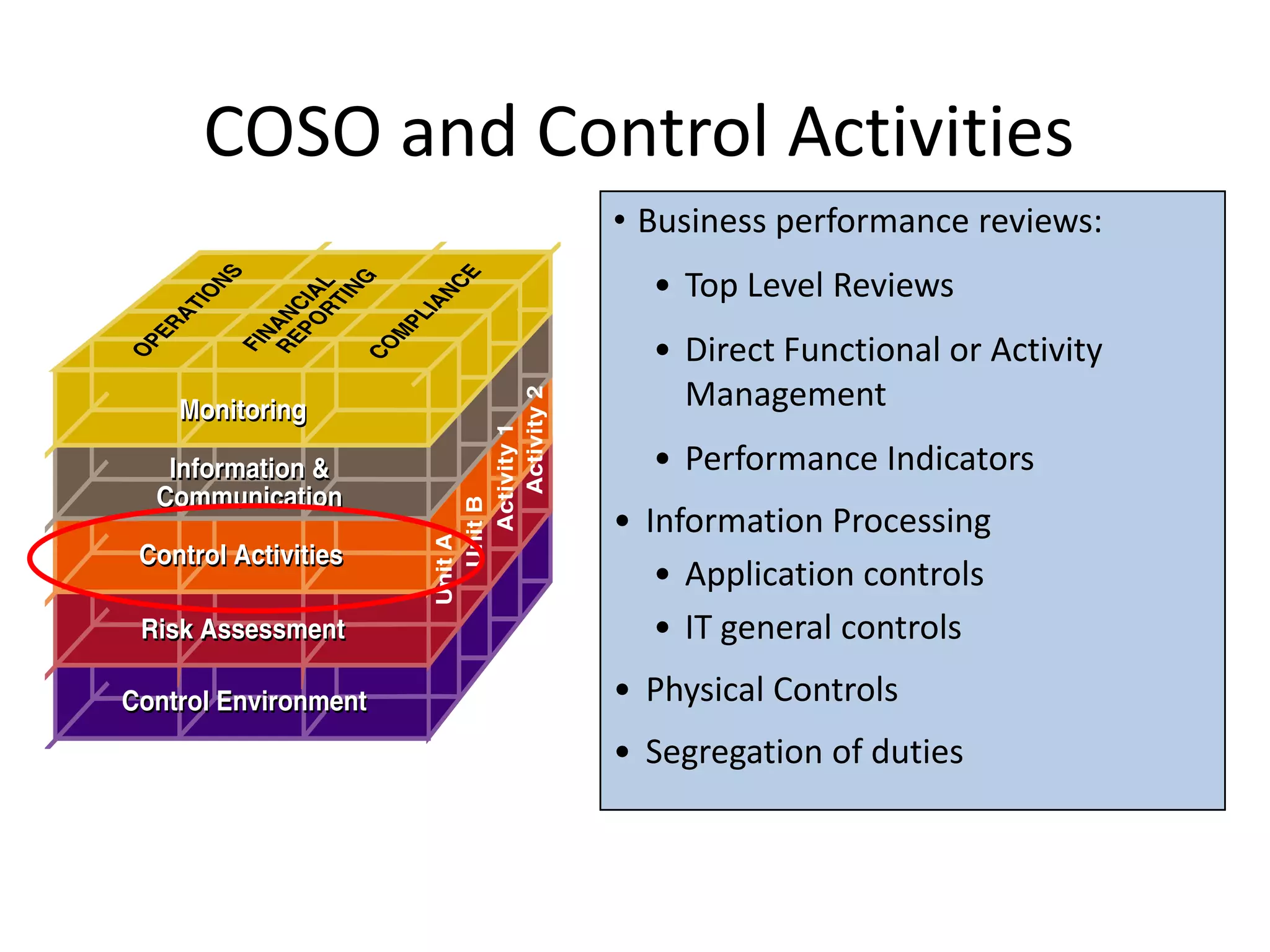
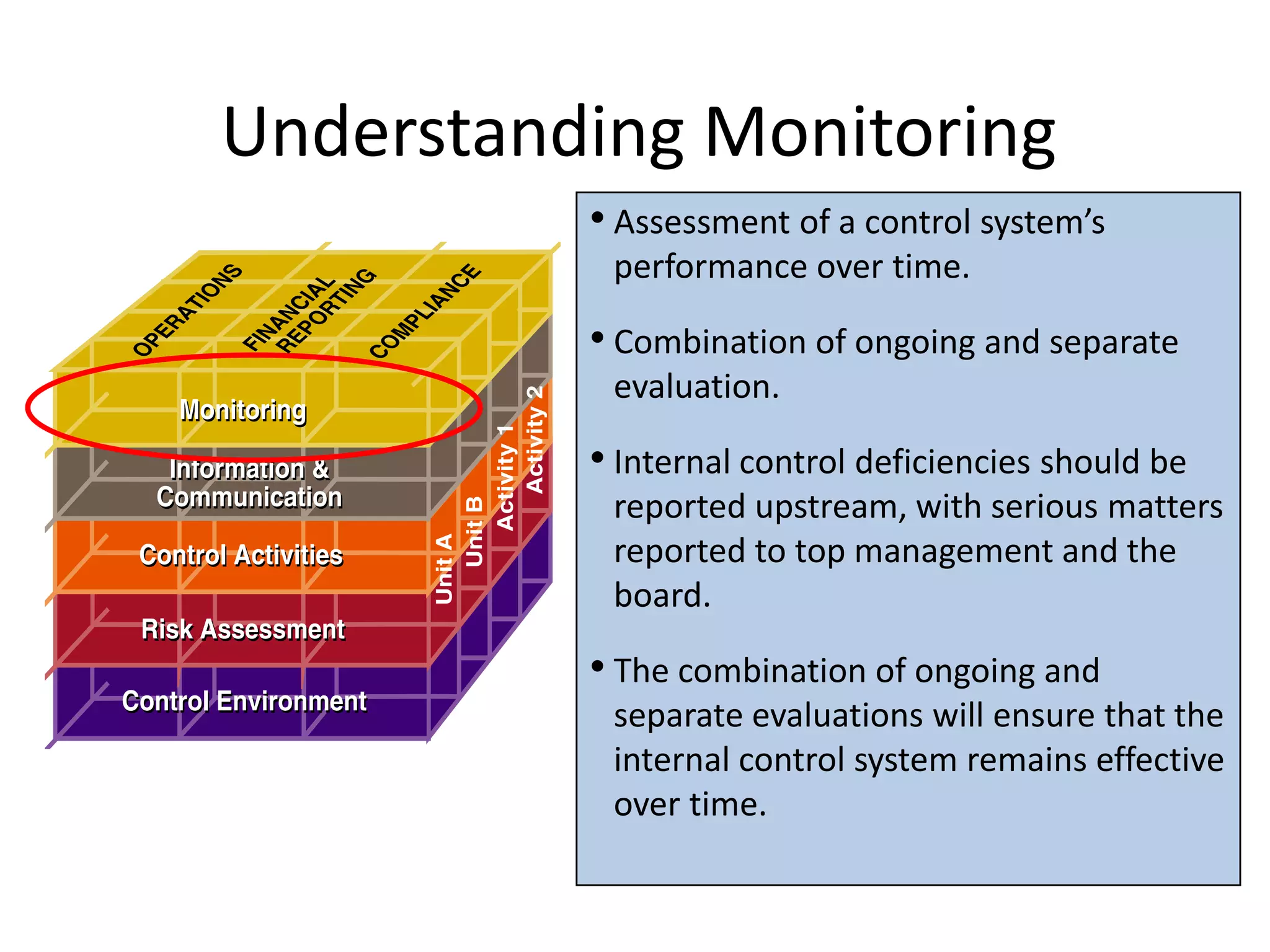
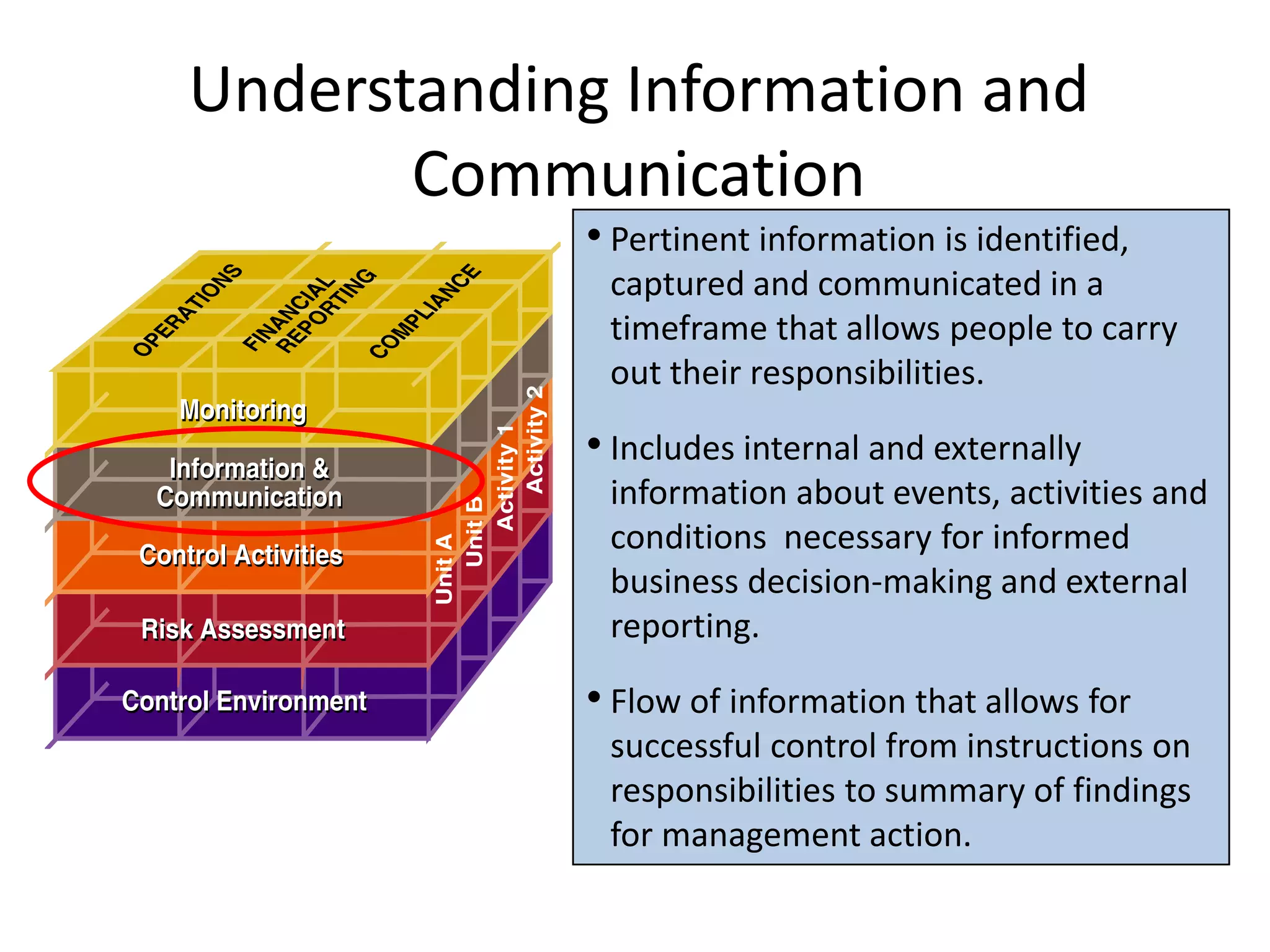
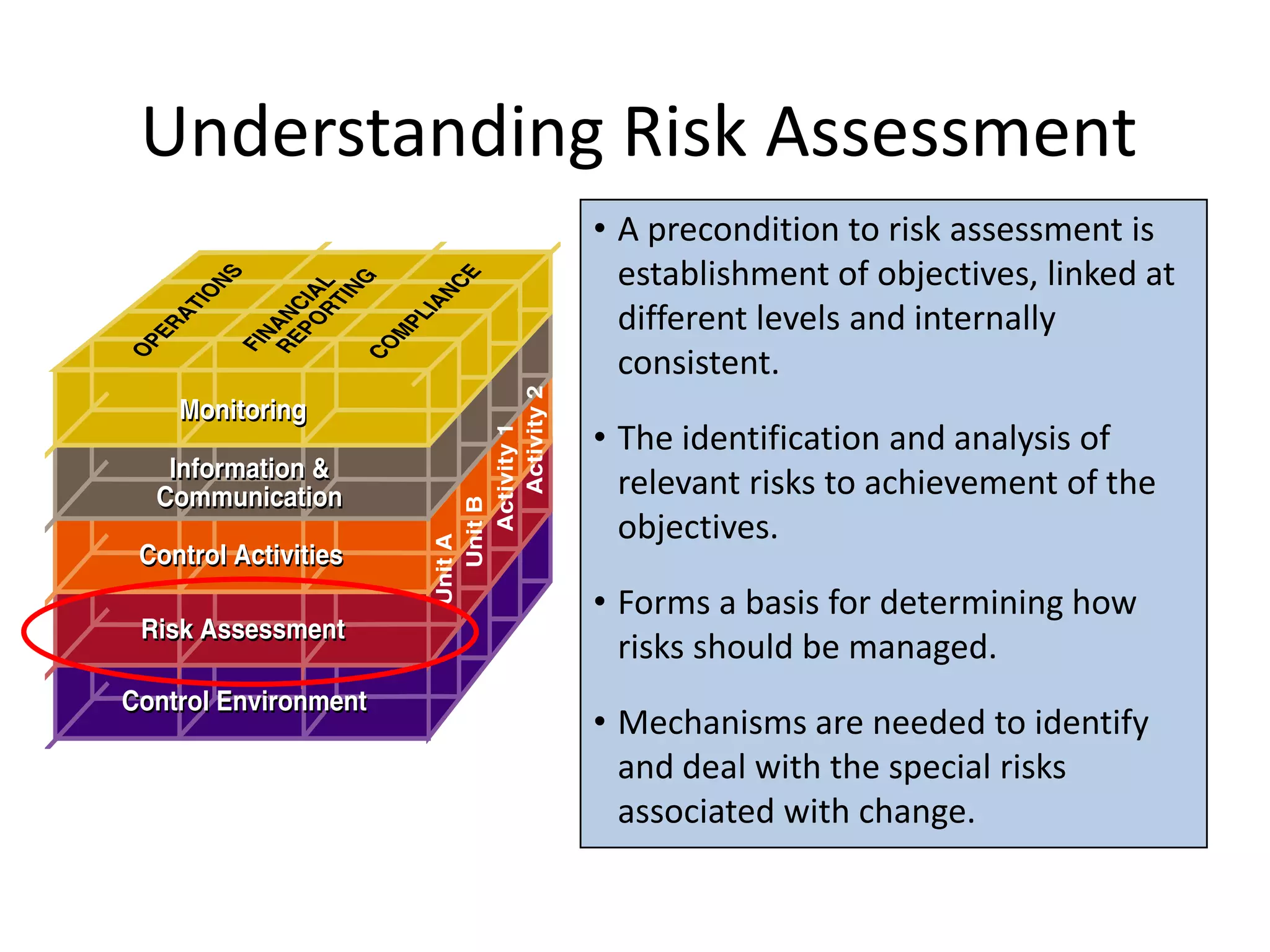
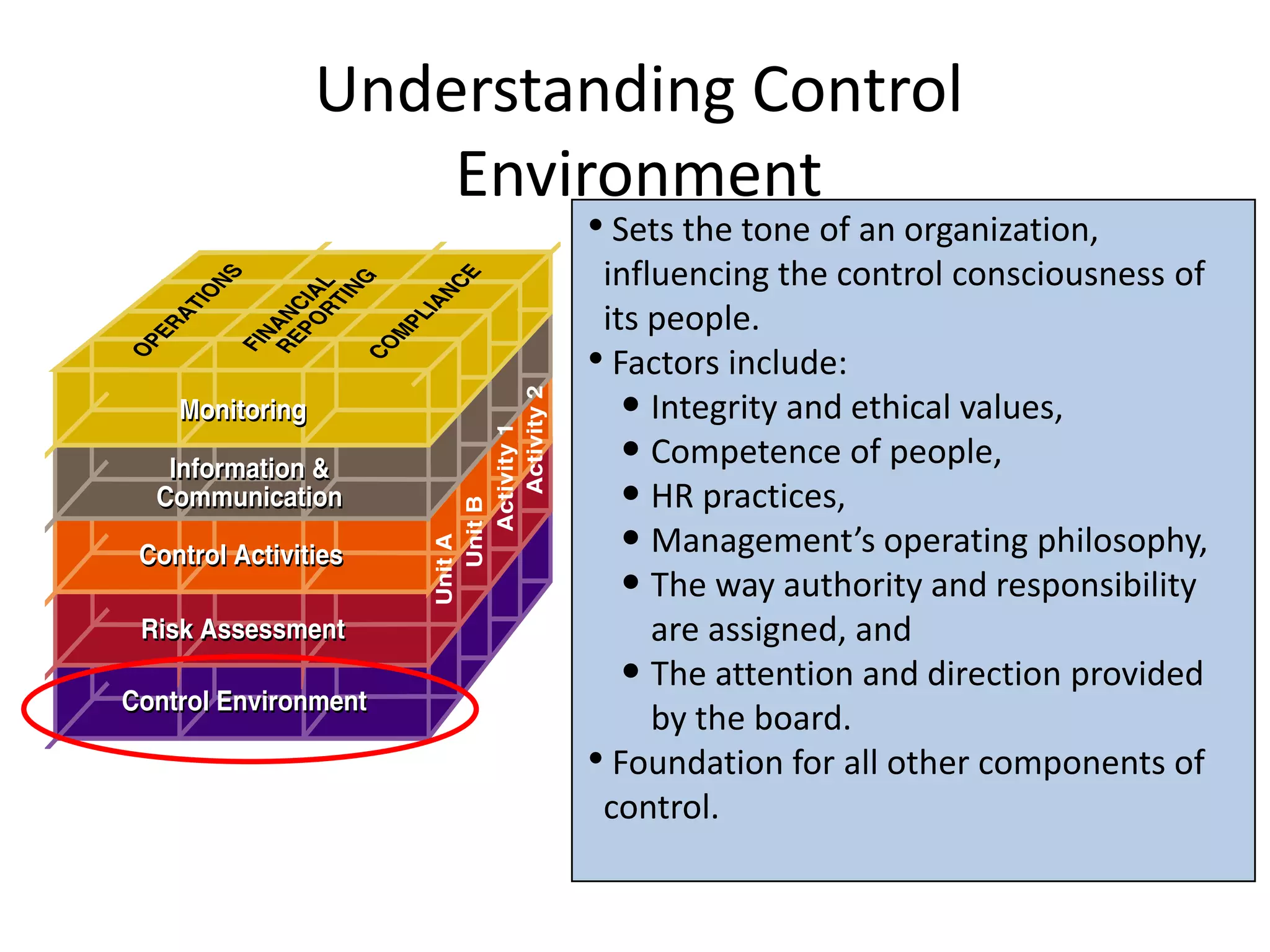
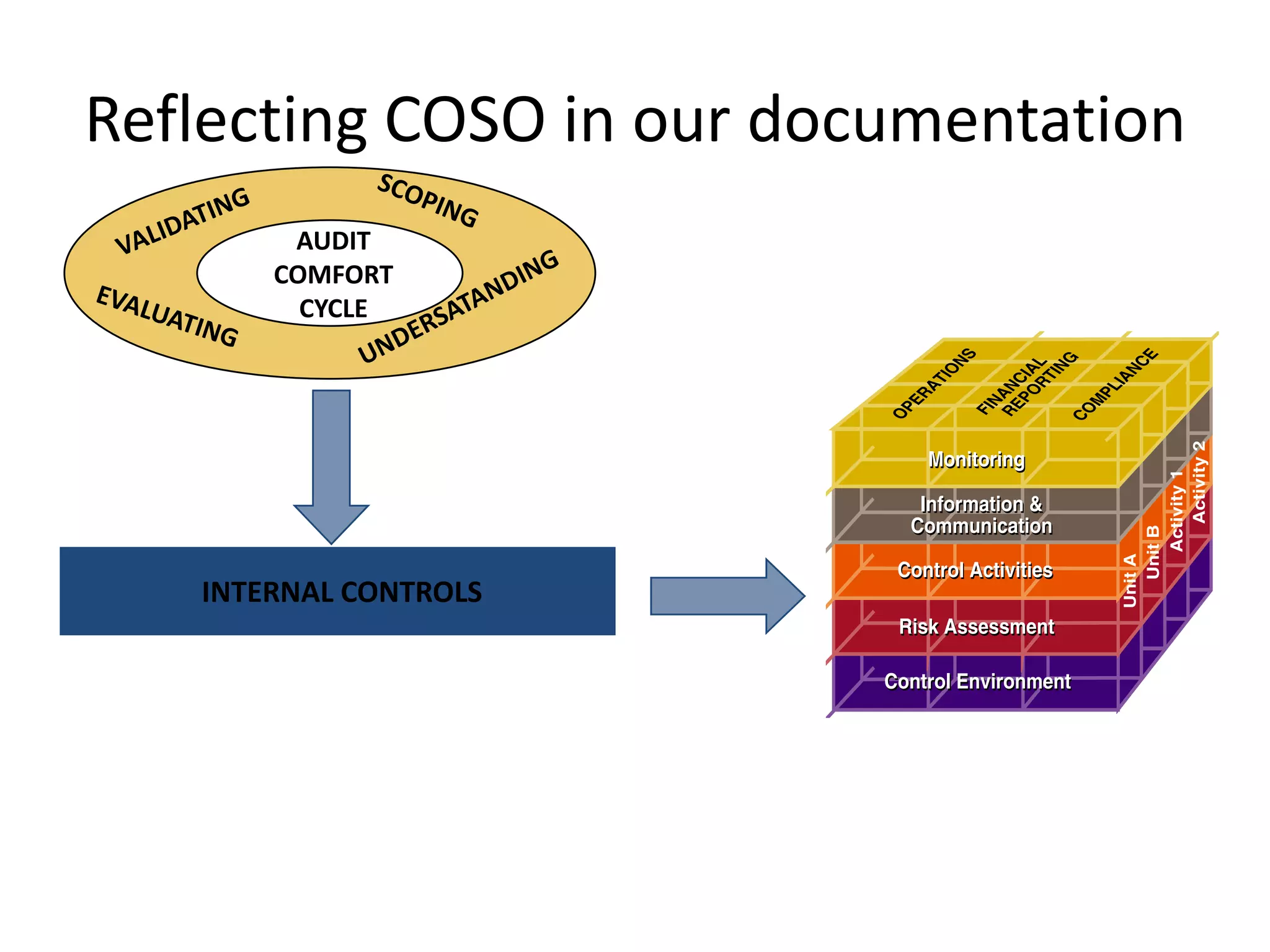
The document discusses COSO (Committee of Sponsoring Organizations of the Treadway Commission), an internal control framework that auditors use to assess clients' internal controls. It describes the five components of COSO - control environment, risk assessment, control activities, information and communication, and monitoring. The document also discusses how COSO fits into the audit process and provides an overview of COSO 2, which incorporates enterprise risk management.