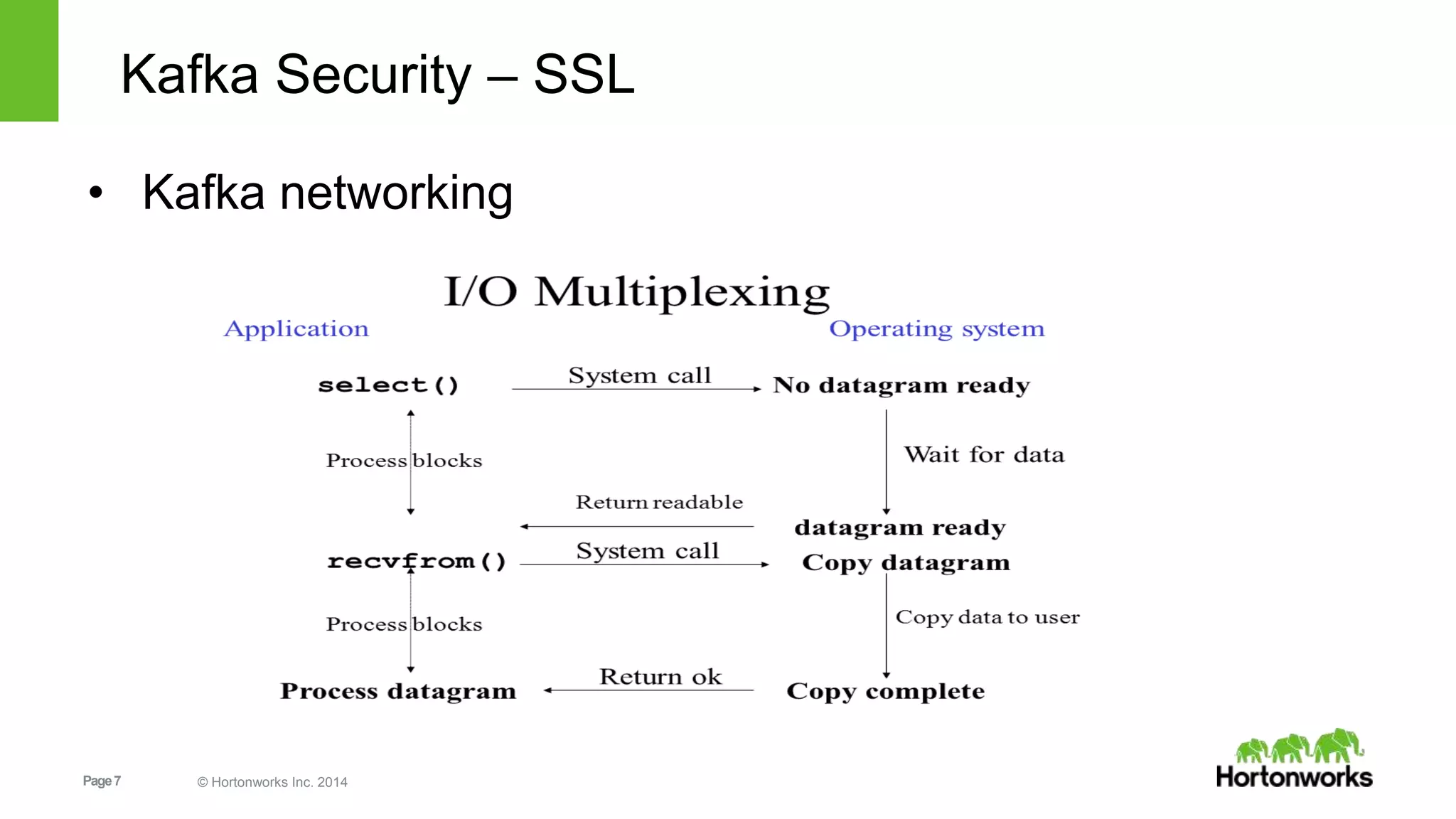
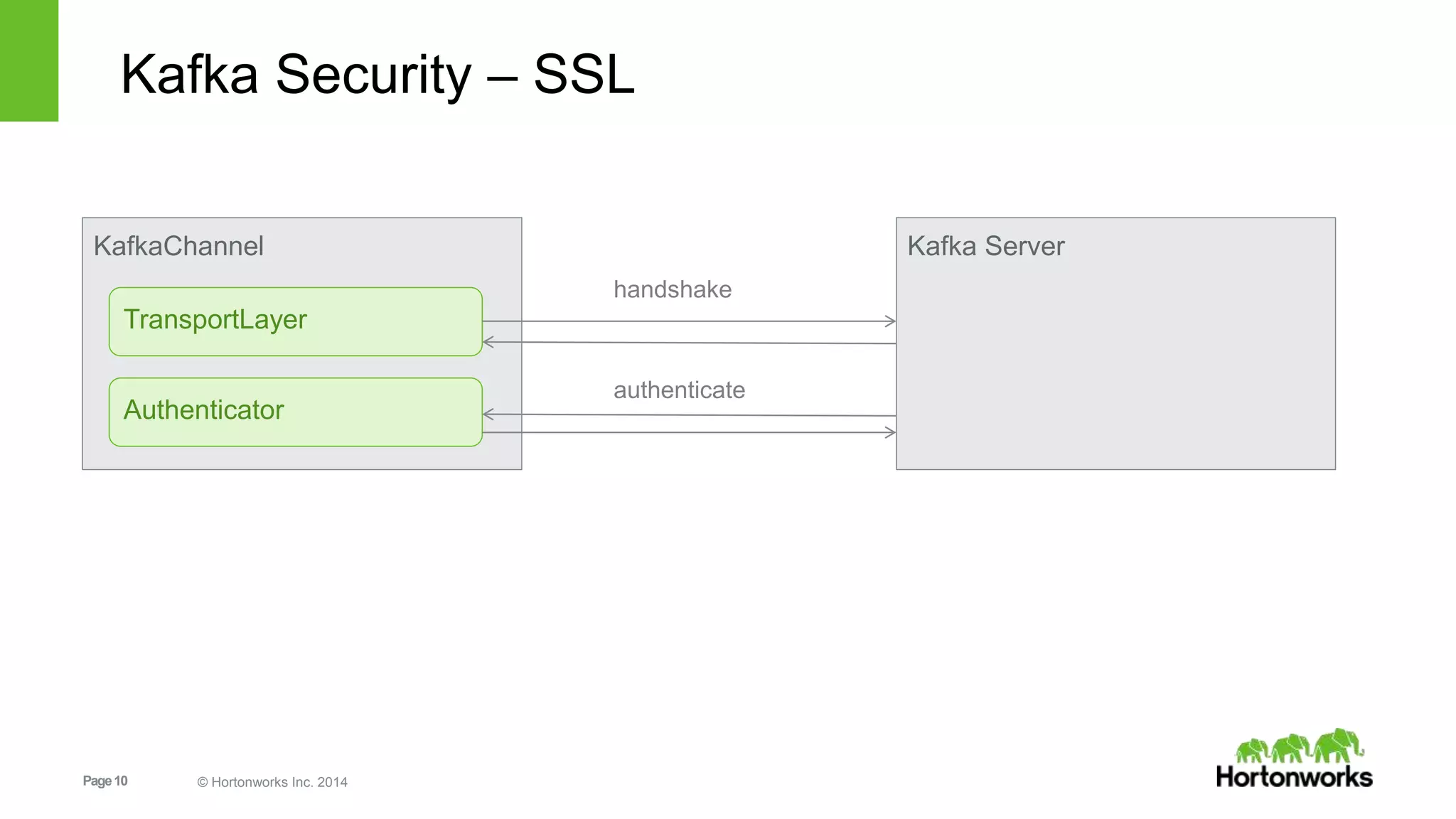
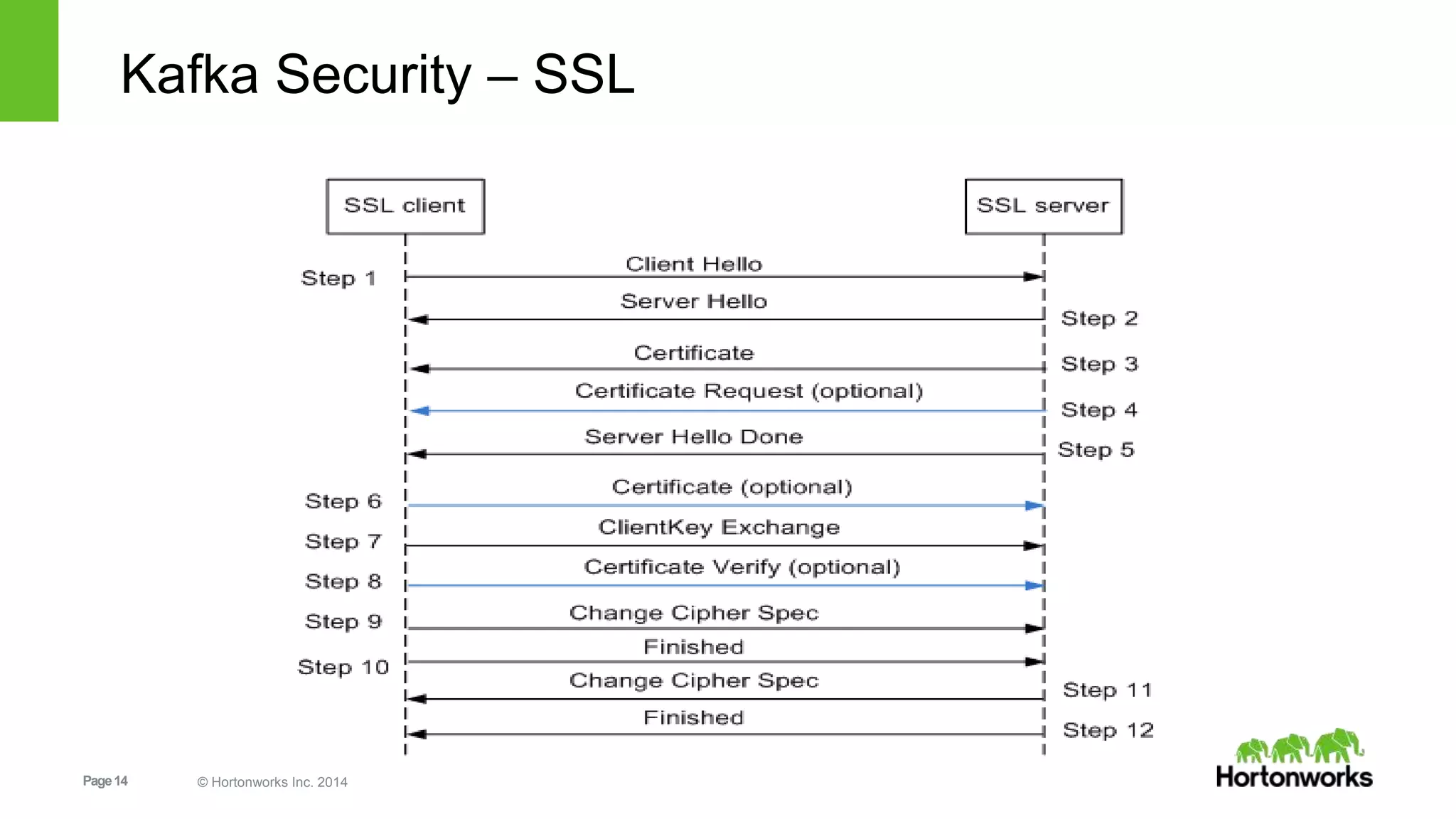
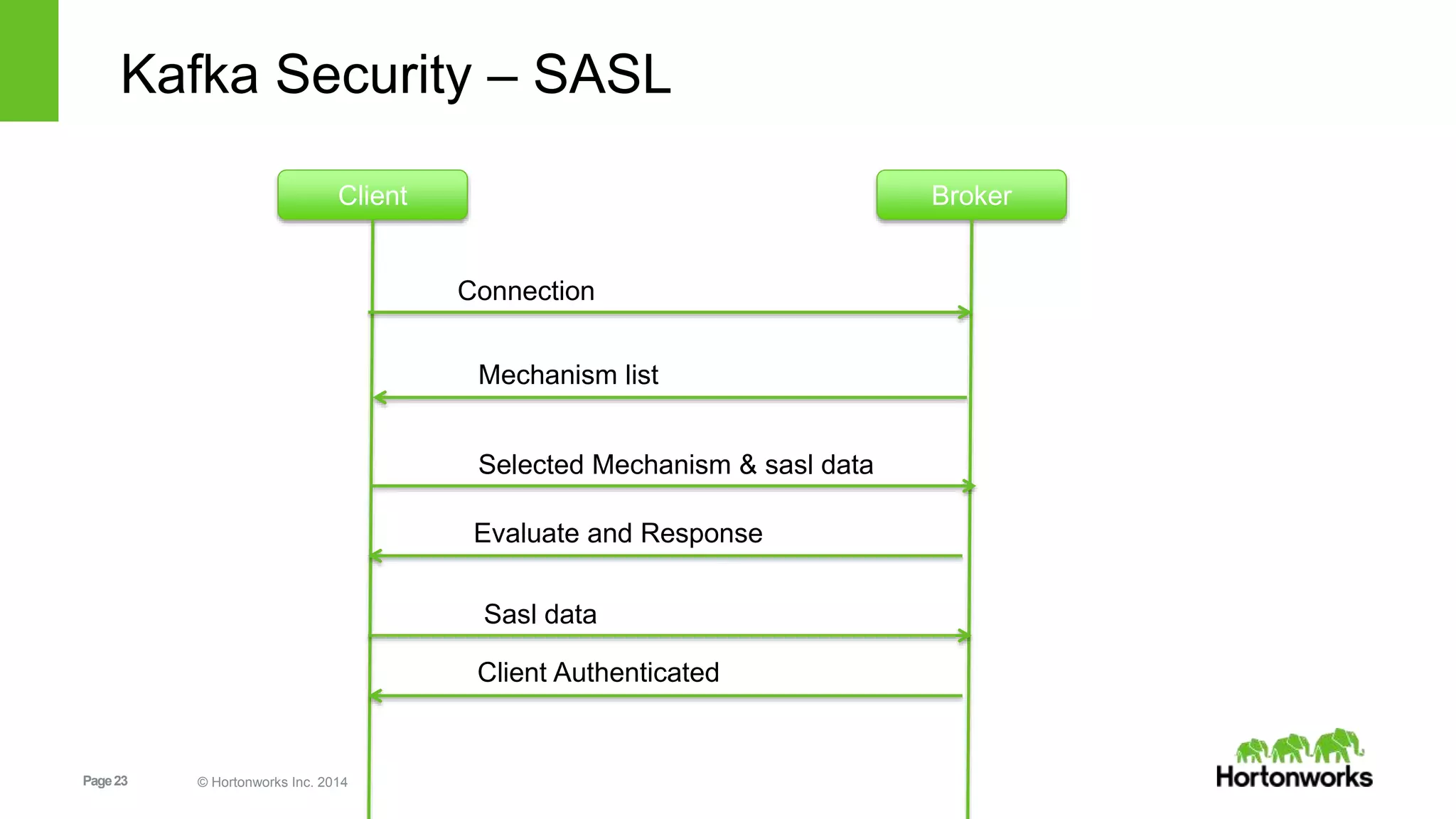
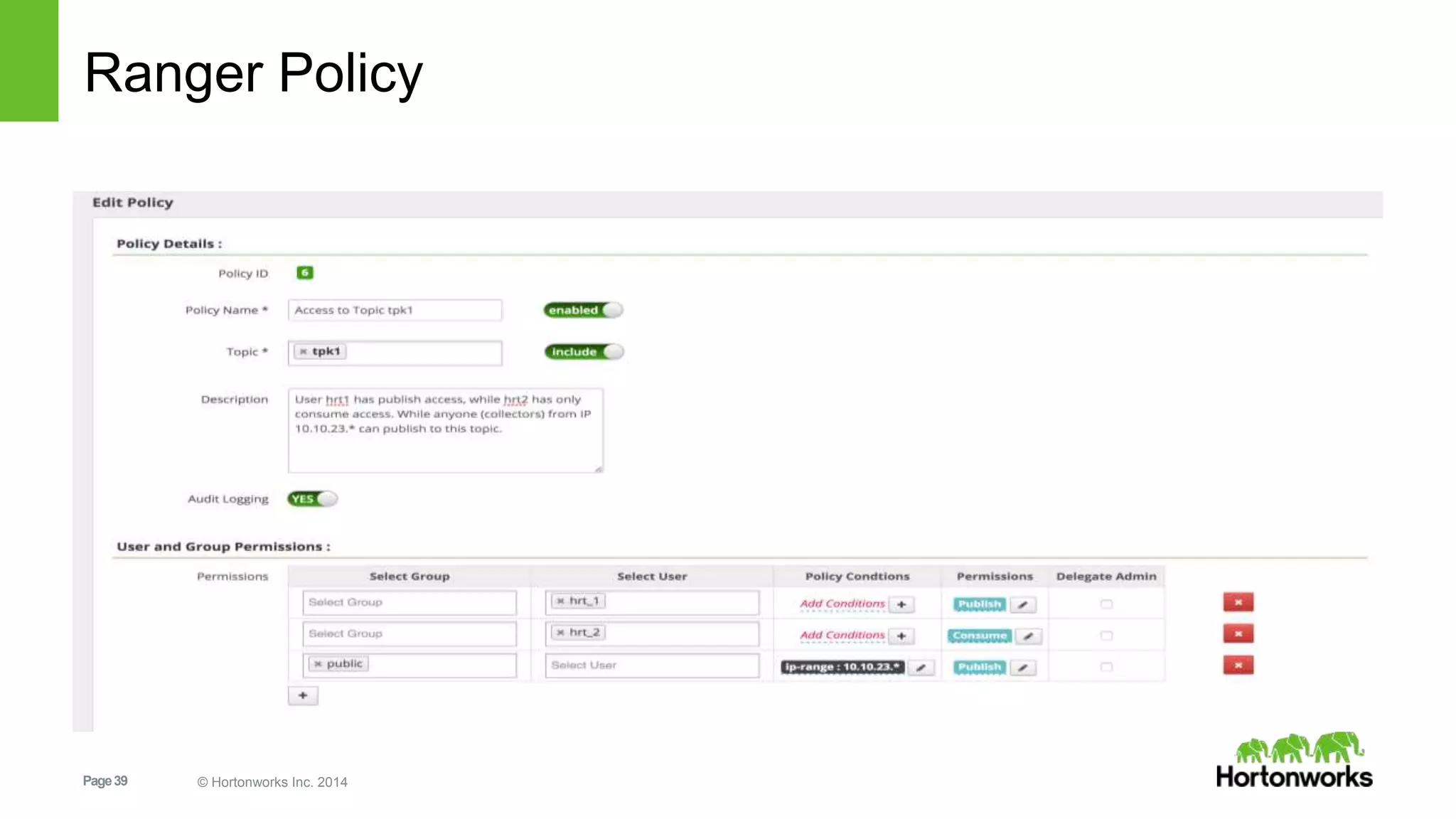
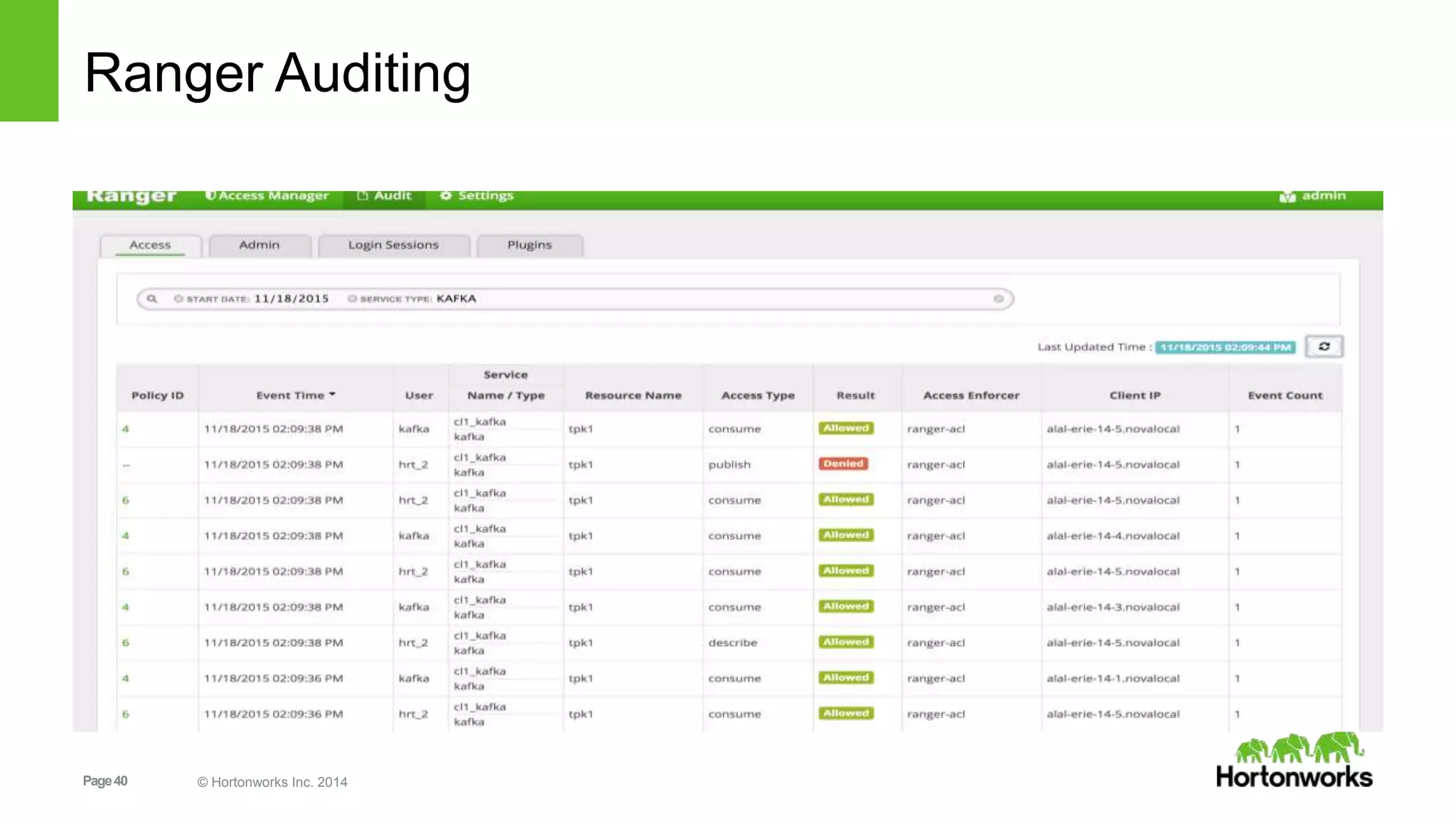
Kafka security includes SSL for wire encryption, SASL (Kerberos) for authentication, and authorization controls. SSL uses certificates for encryption during network communication. SASL performs authentication using Kerberos credentials. Authorization is provided by pluggable authorizers that define access control lists controlling permissions for principals to perform operations on resources and hosts. Securing Zookeeper with ACLs and SASL is also important as Kafka stores metadata there.