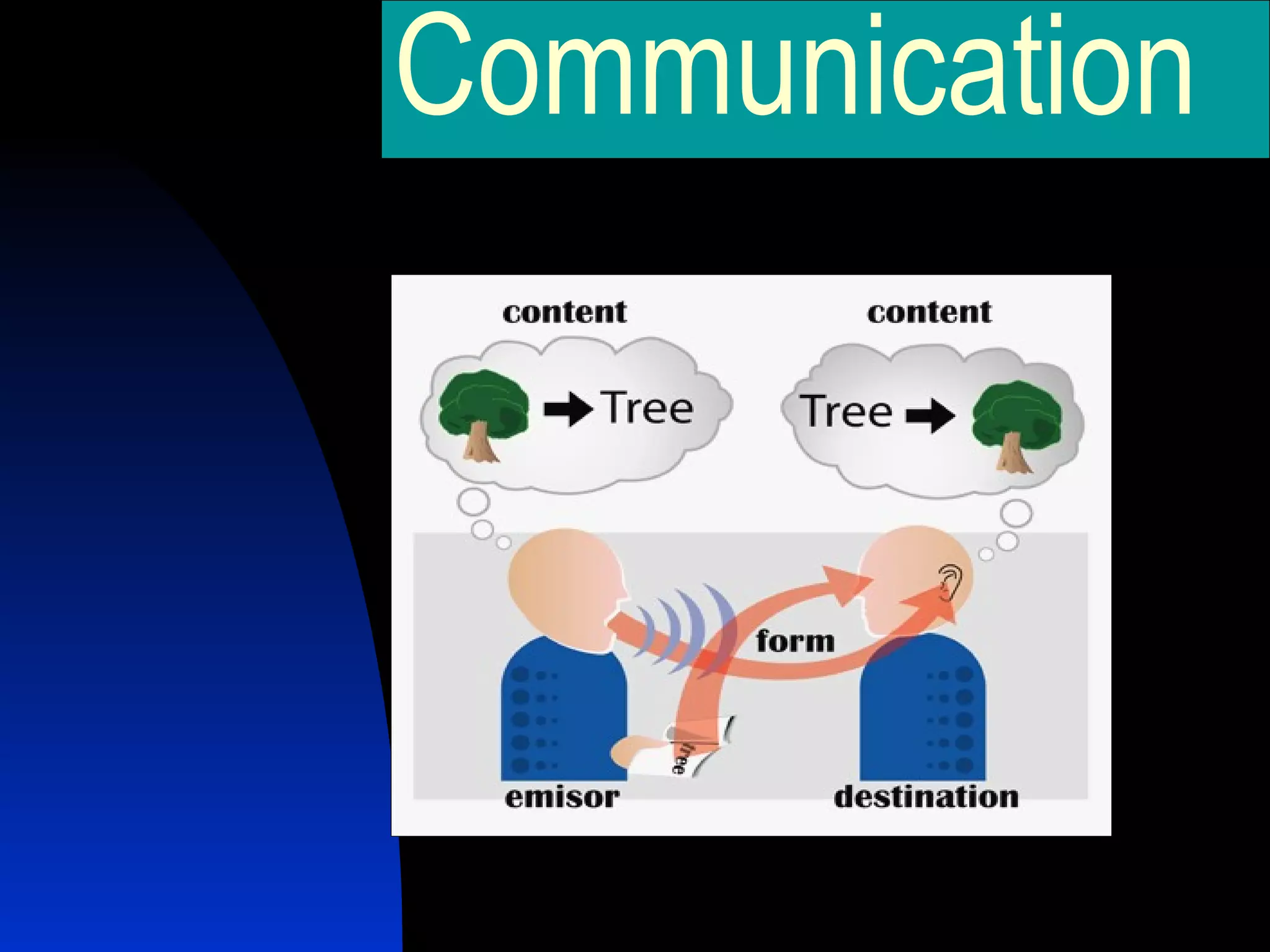
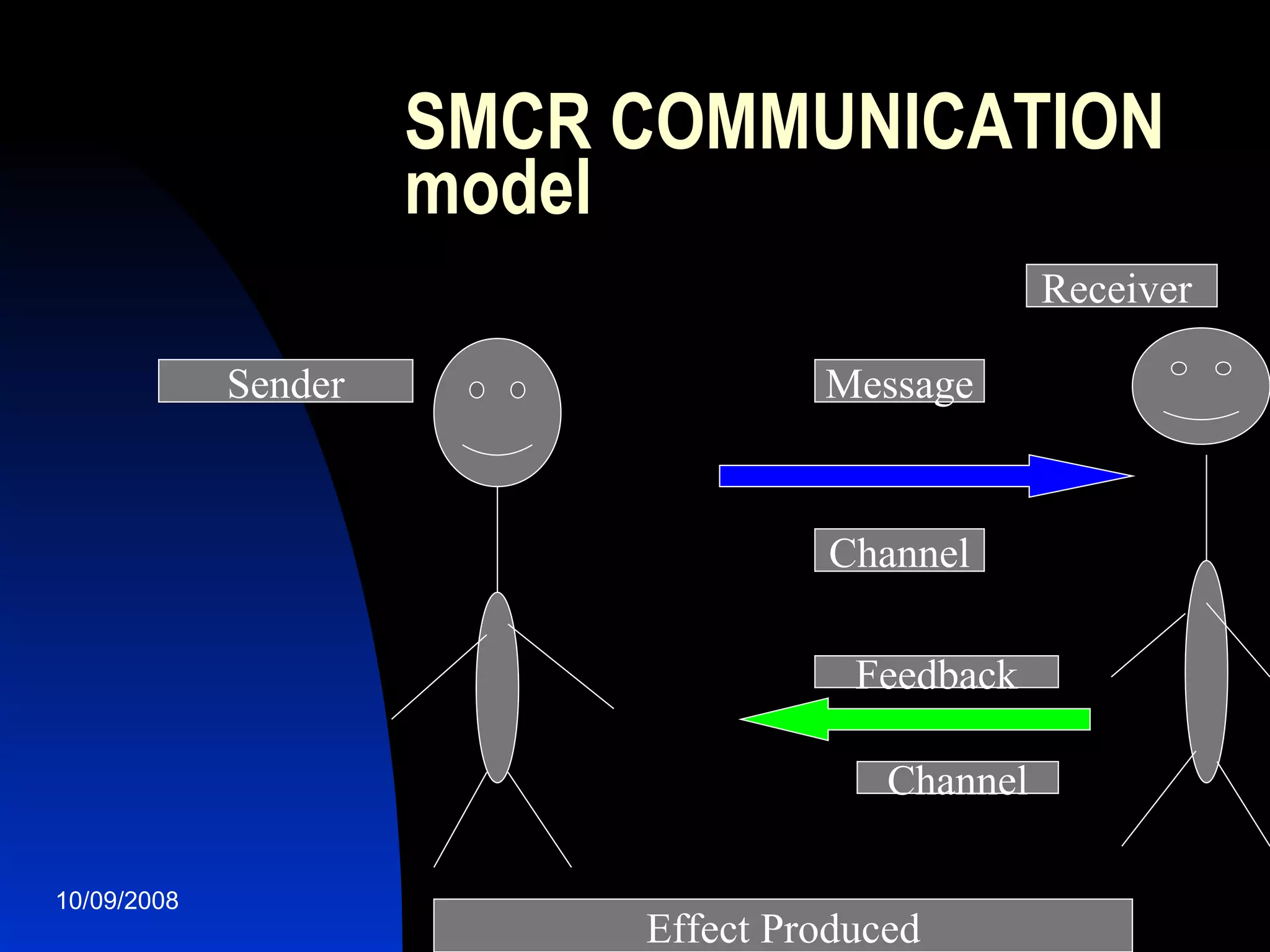
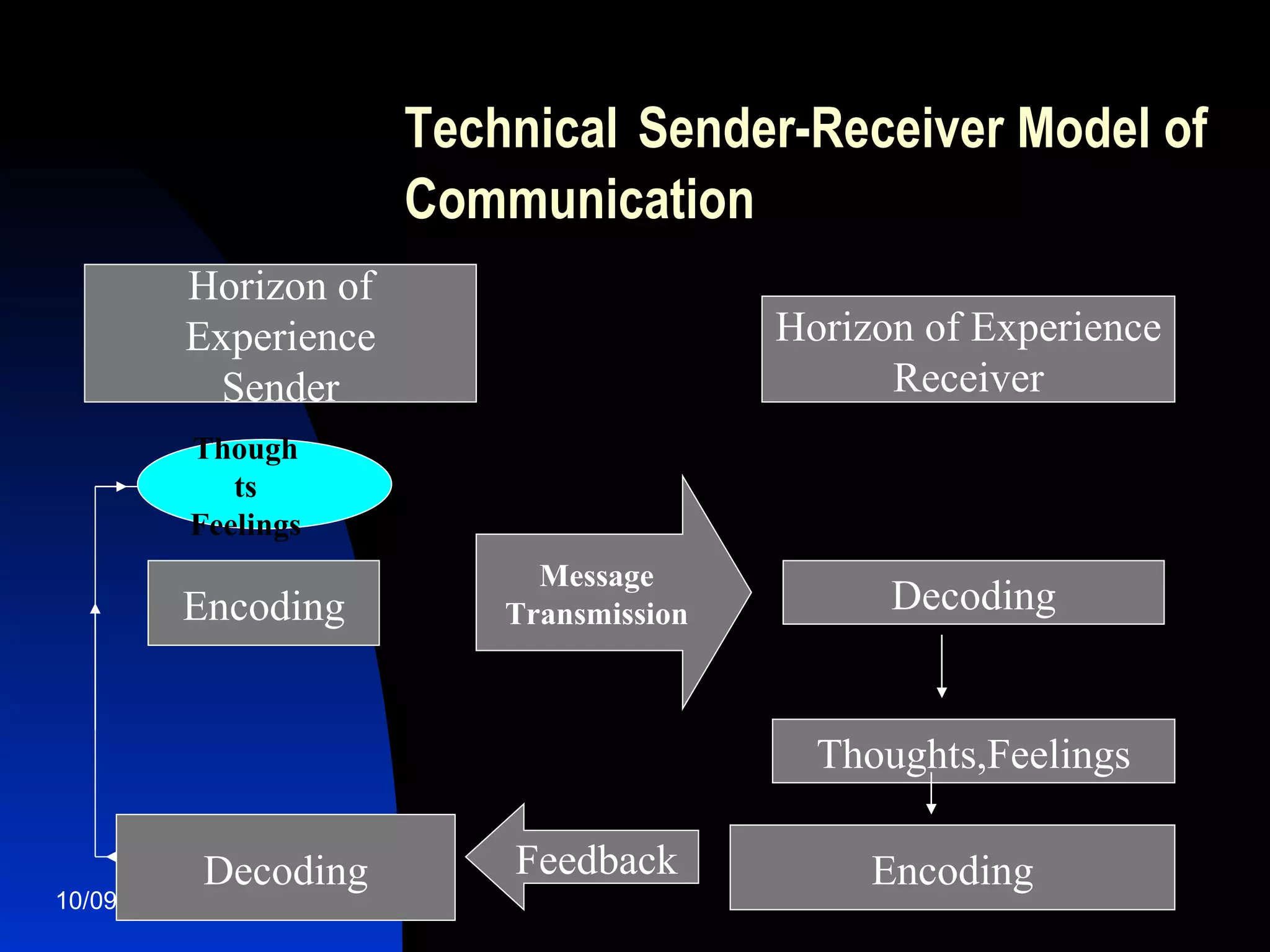
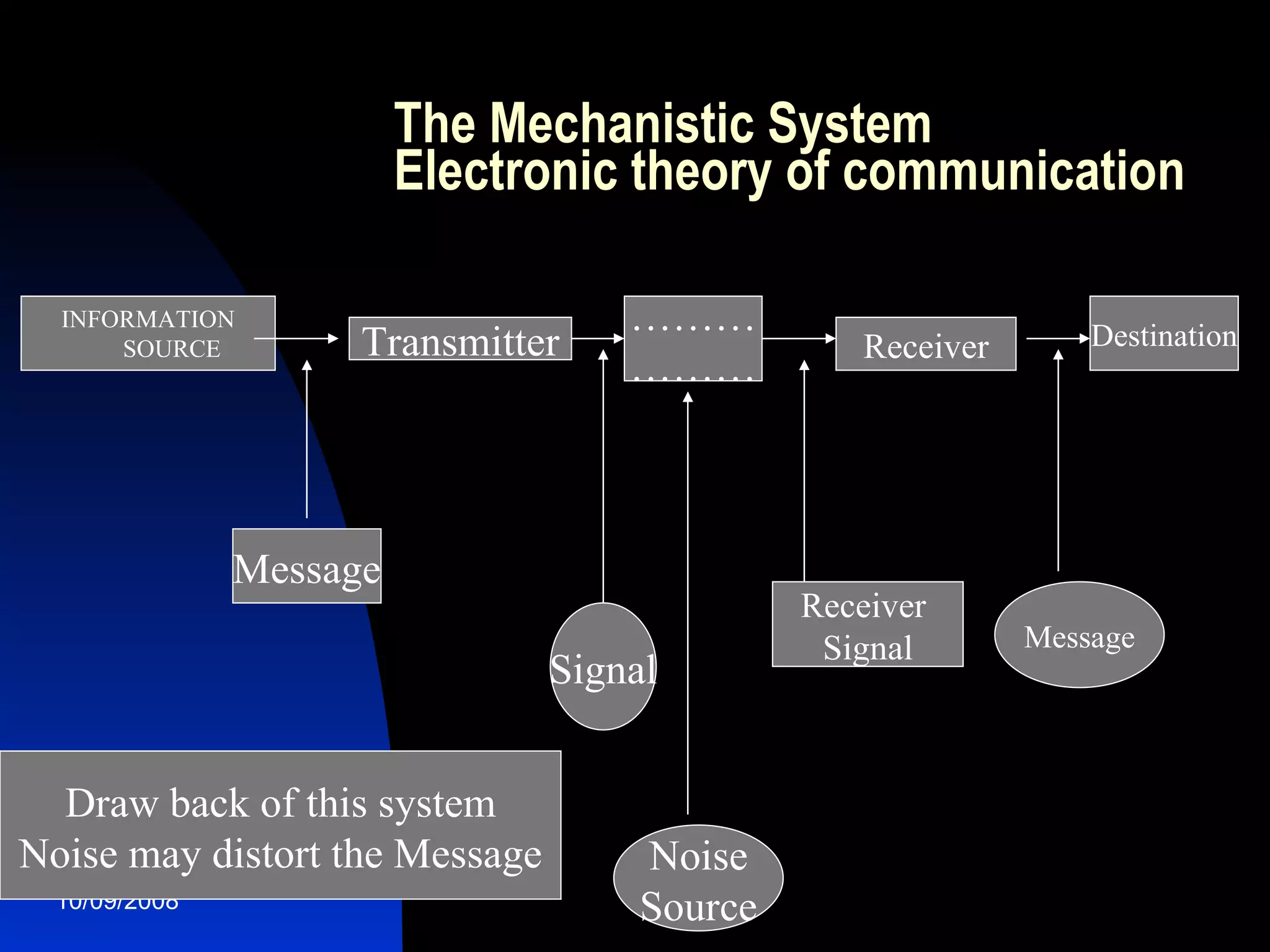
Communication is a dynamic process of exchanging meanings, values, and experiences between two or more people. There are two main theories of communication: the technical theory views it as transmission of information like electronics, while the contextual/social environment theory recognizes human and interpersonal elements like beliefs, attitudes, and nonverbal cues. Effective communication requires understanding different cultural communication styles and overcoming barriers like psychological blocks or improper delivery.