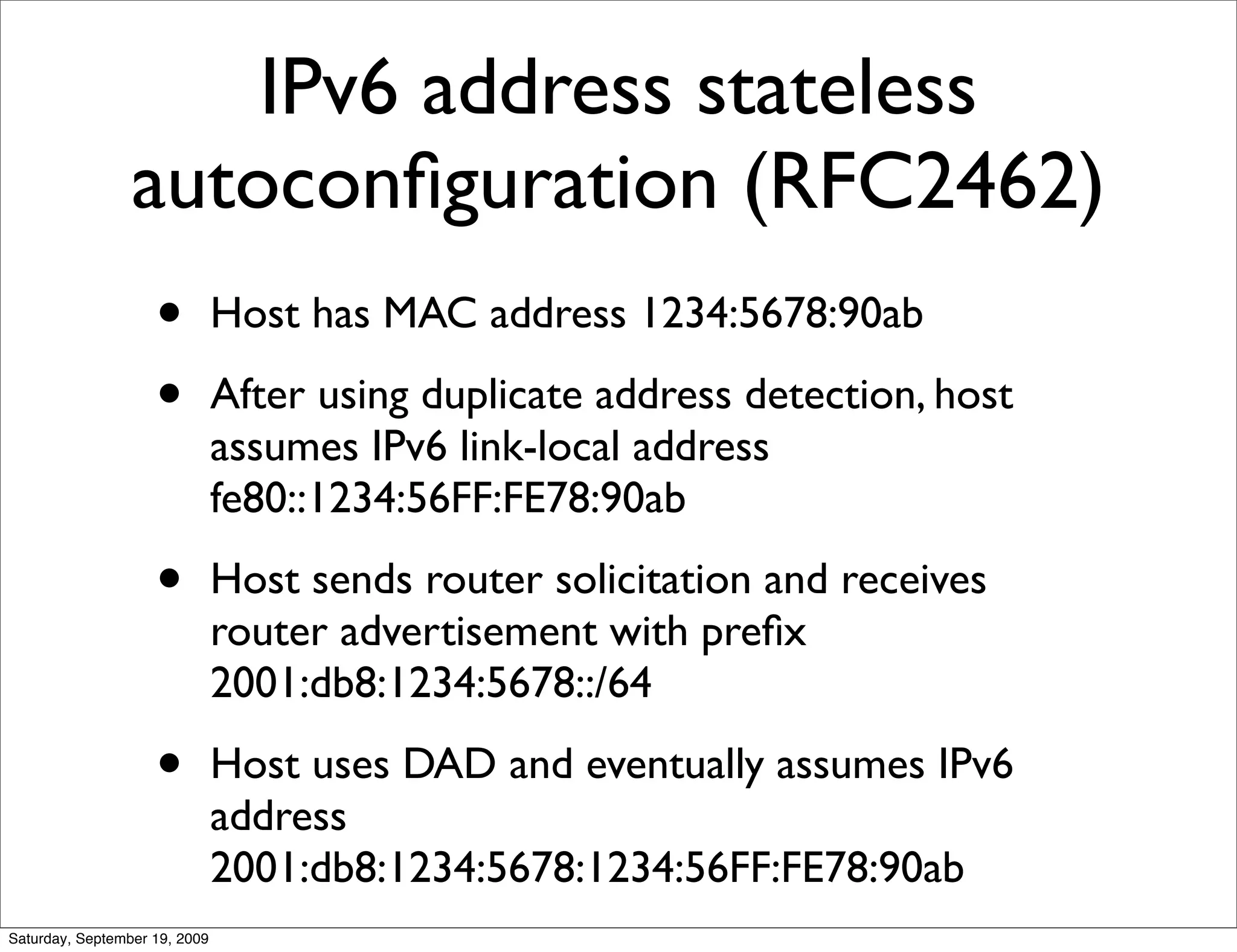
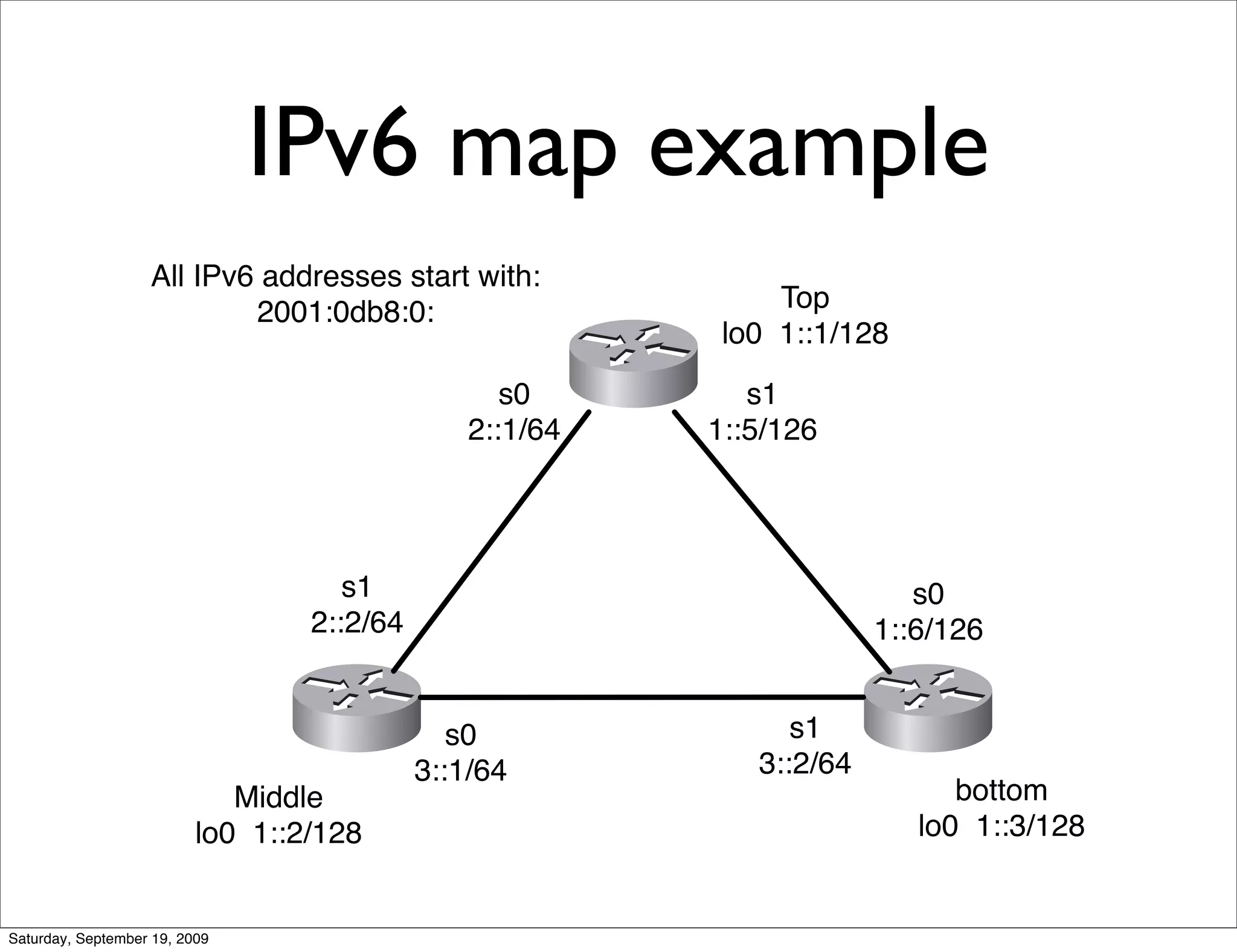
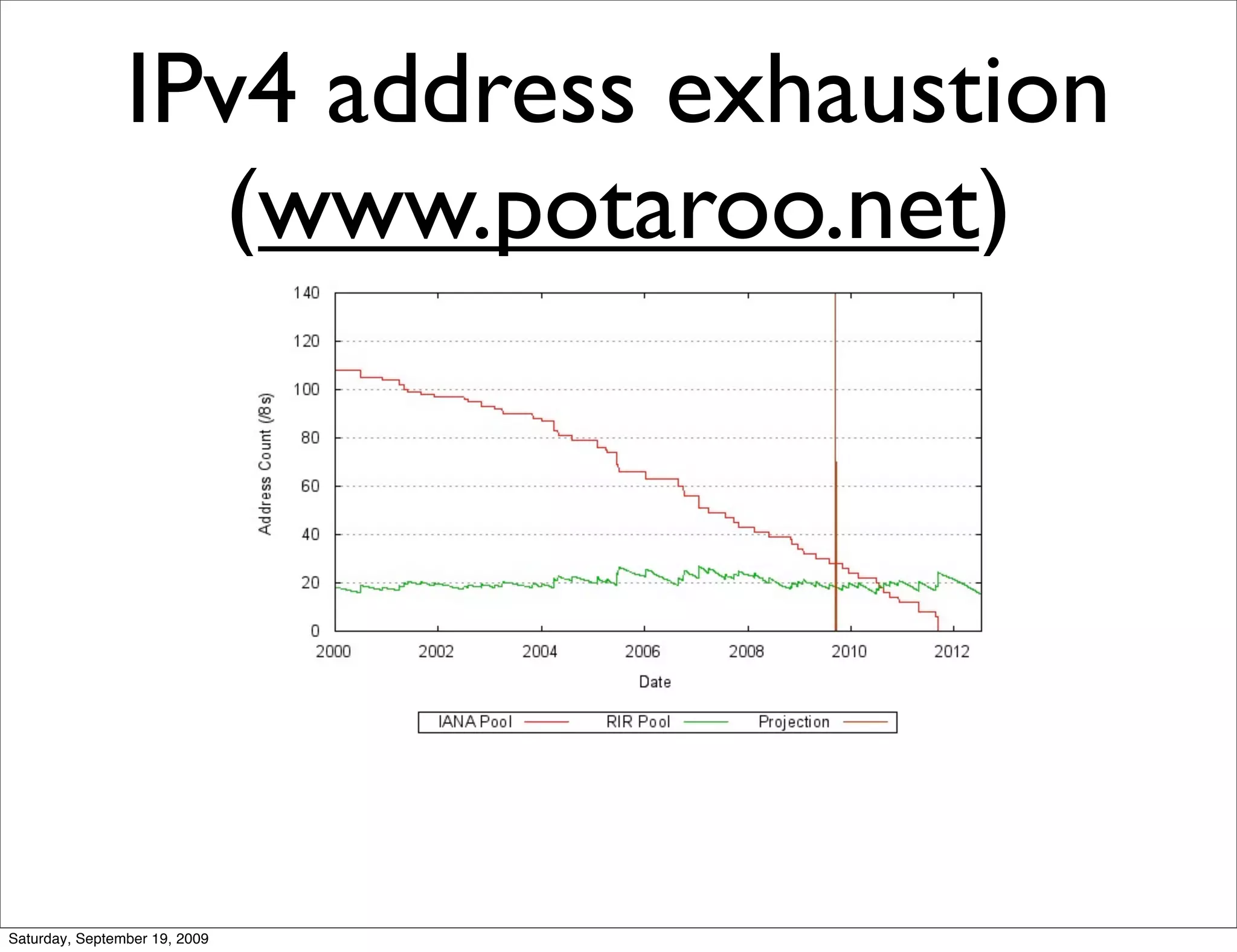
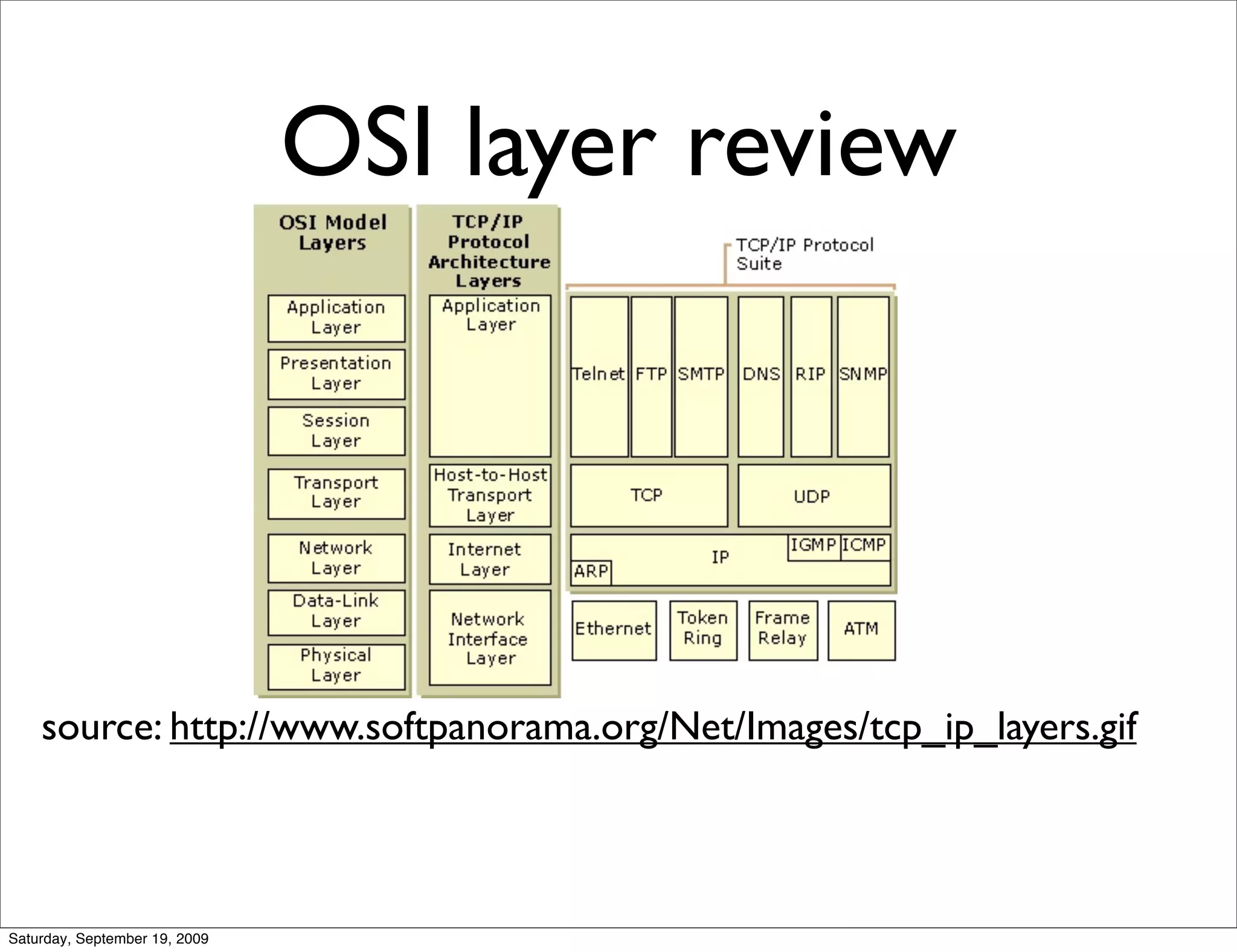
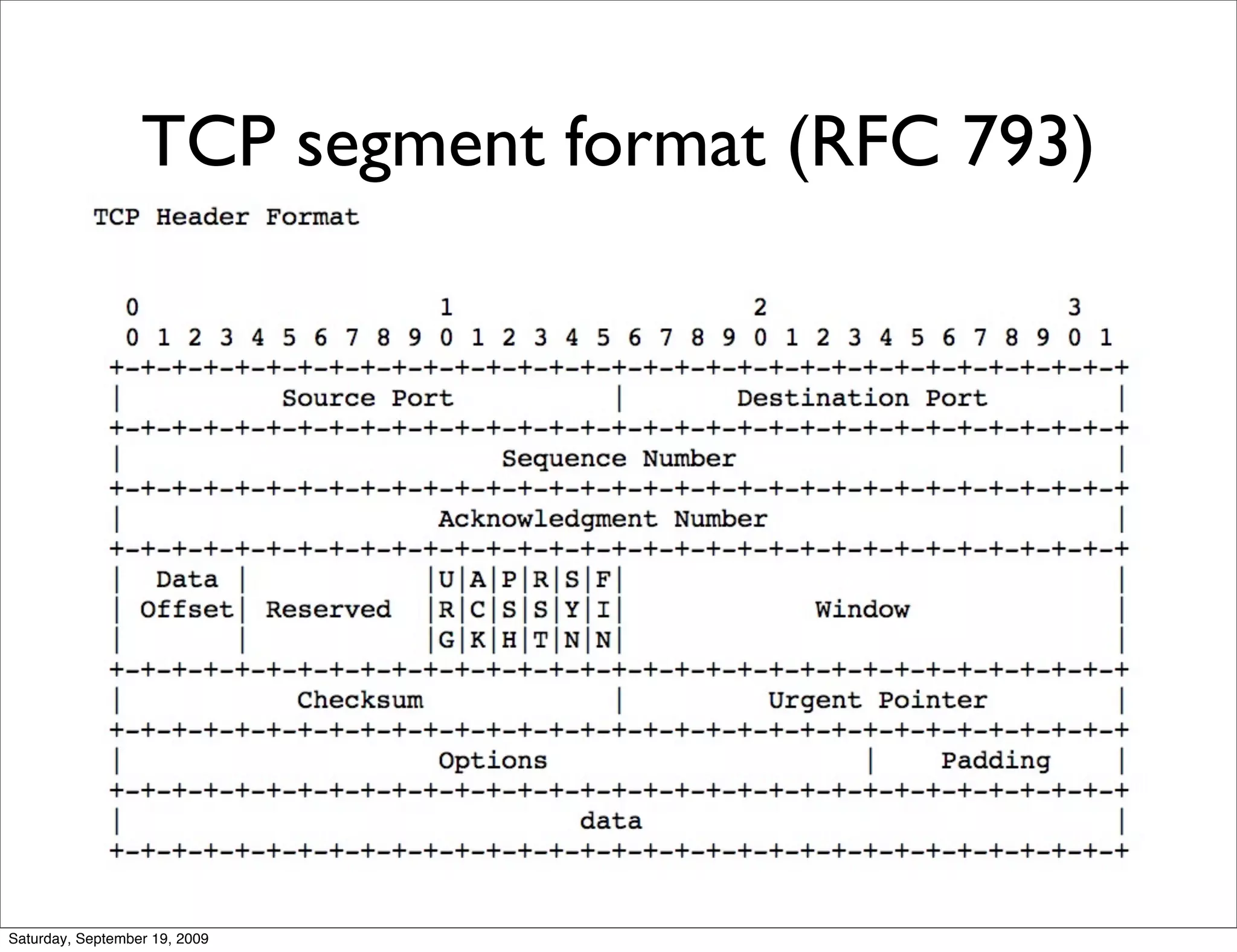
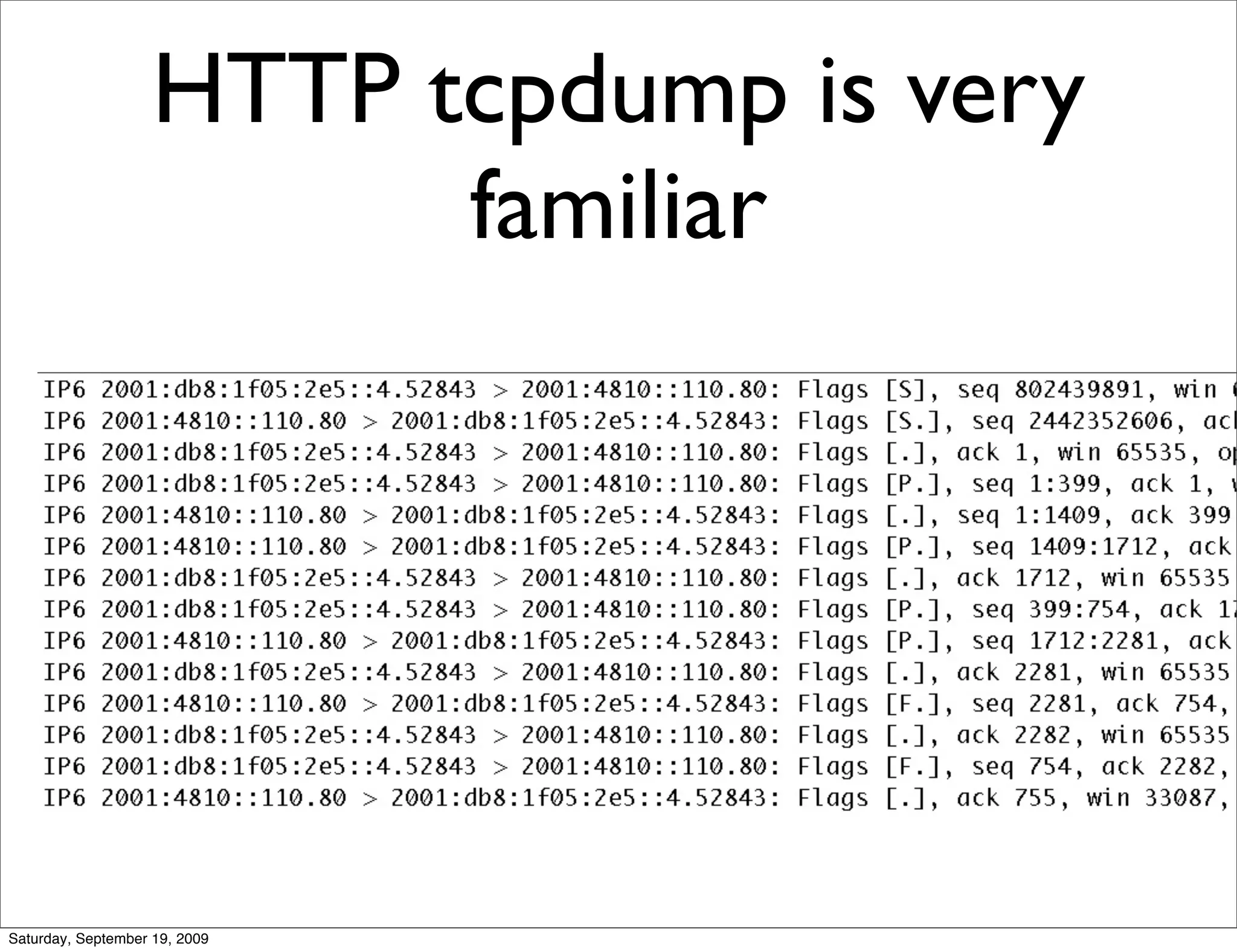
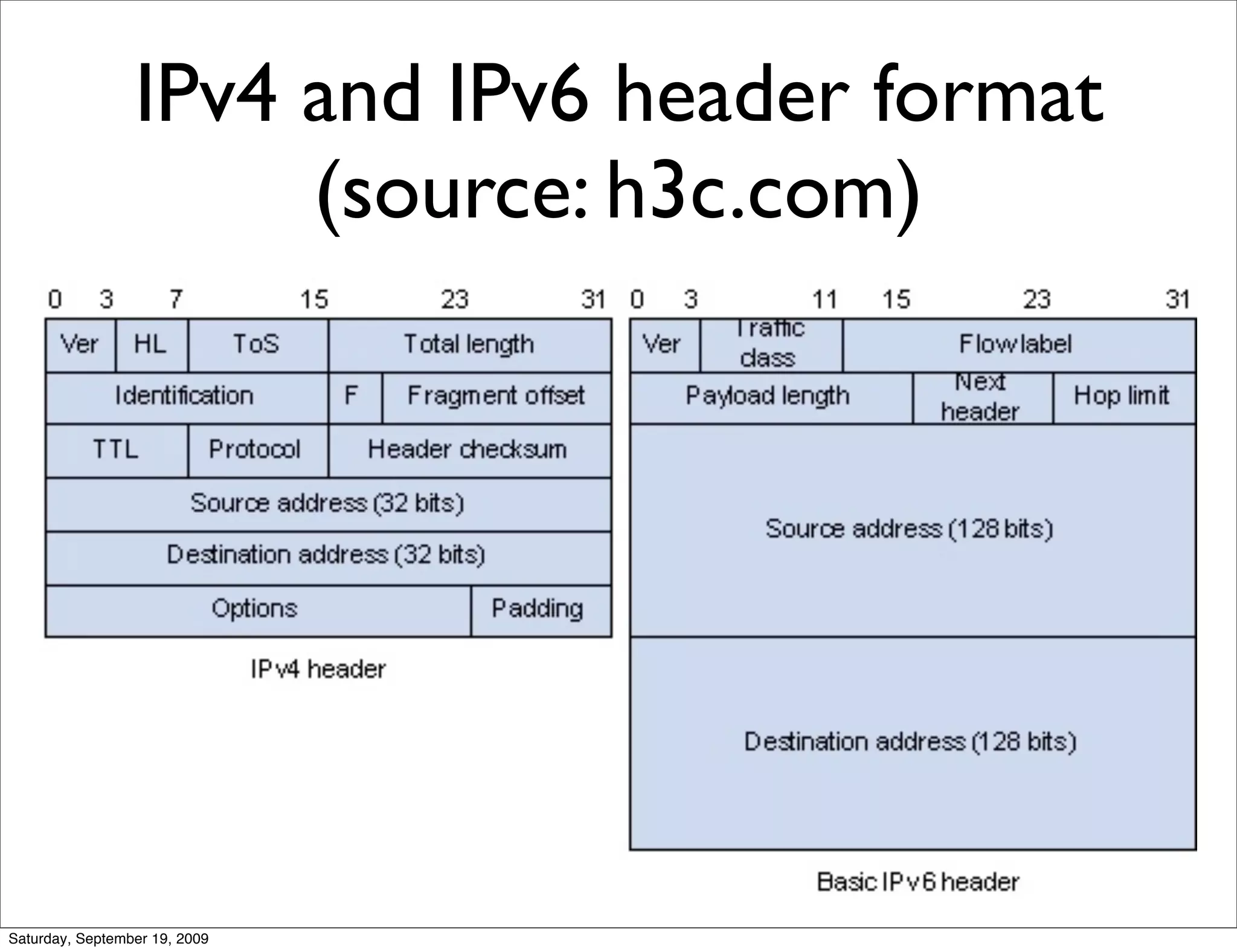
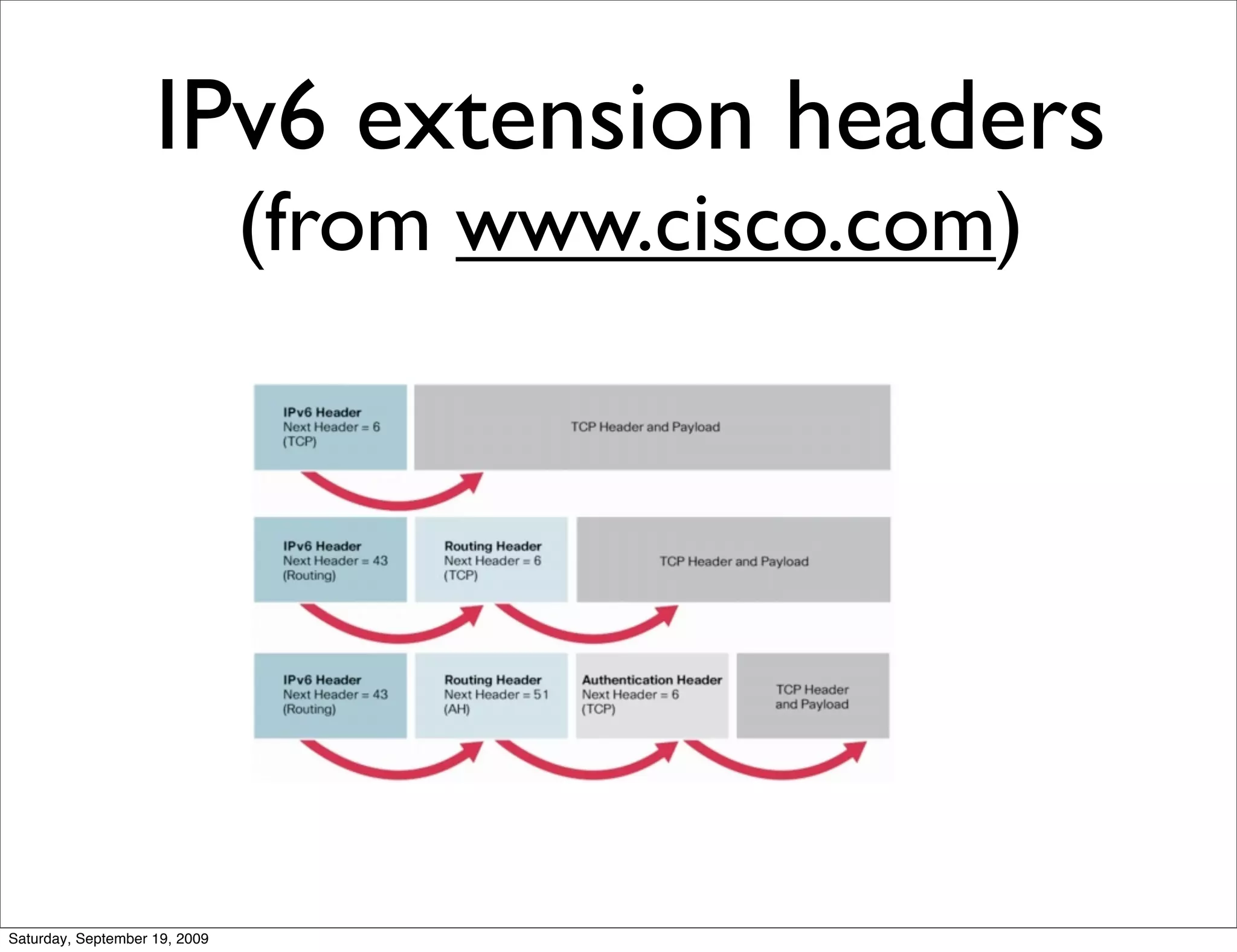
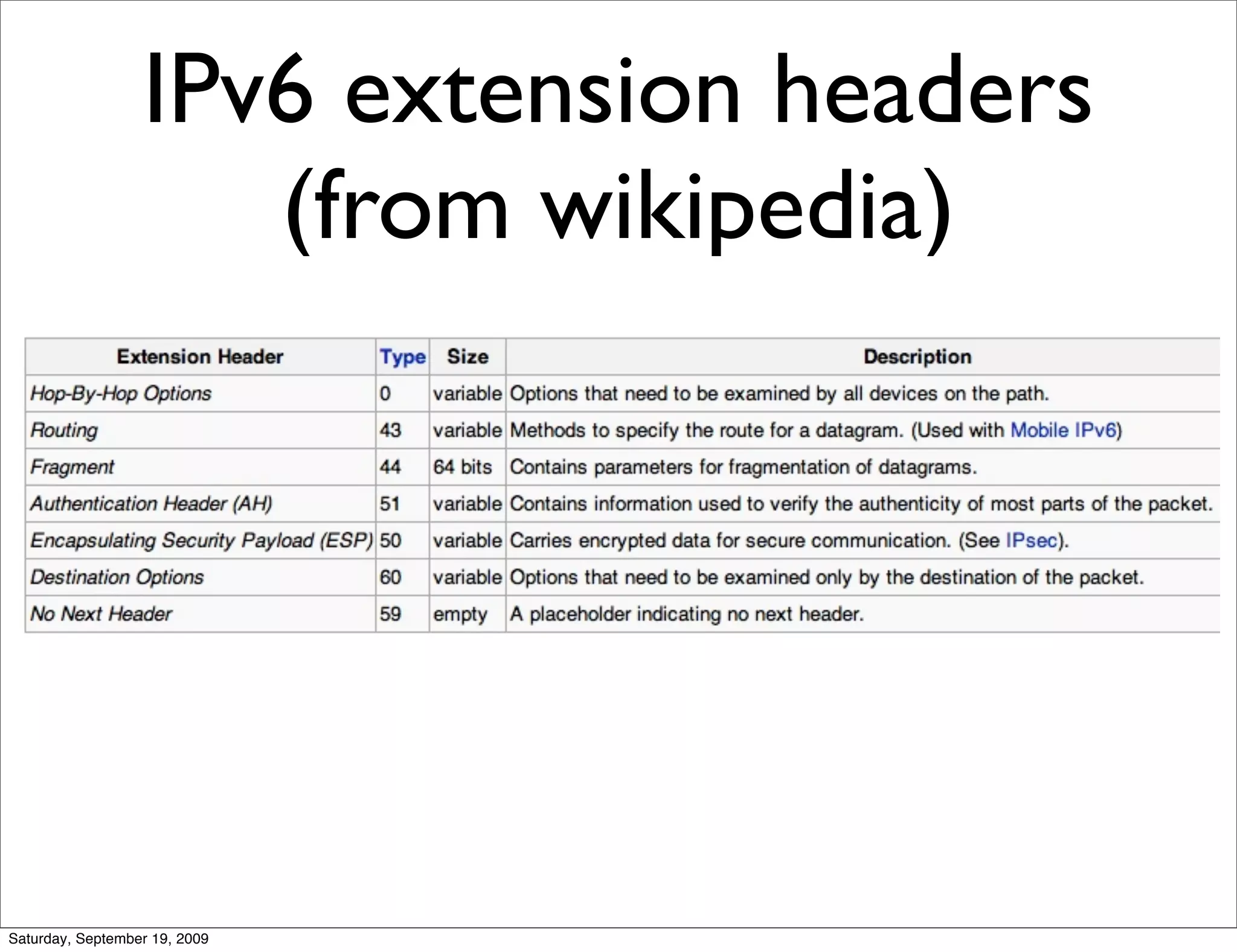
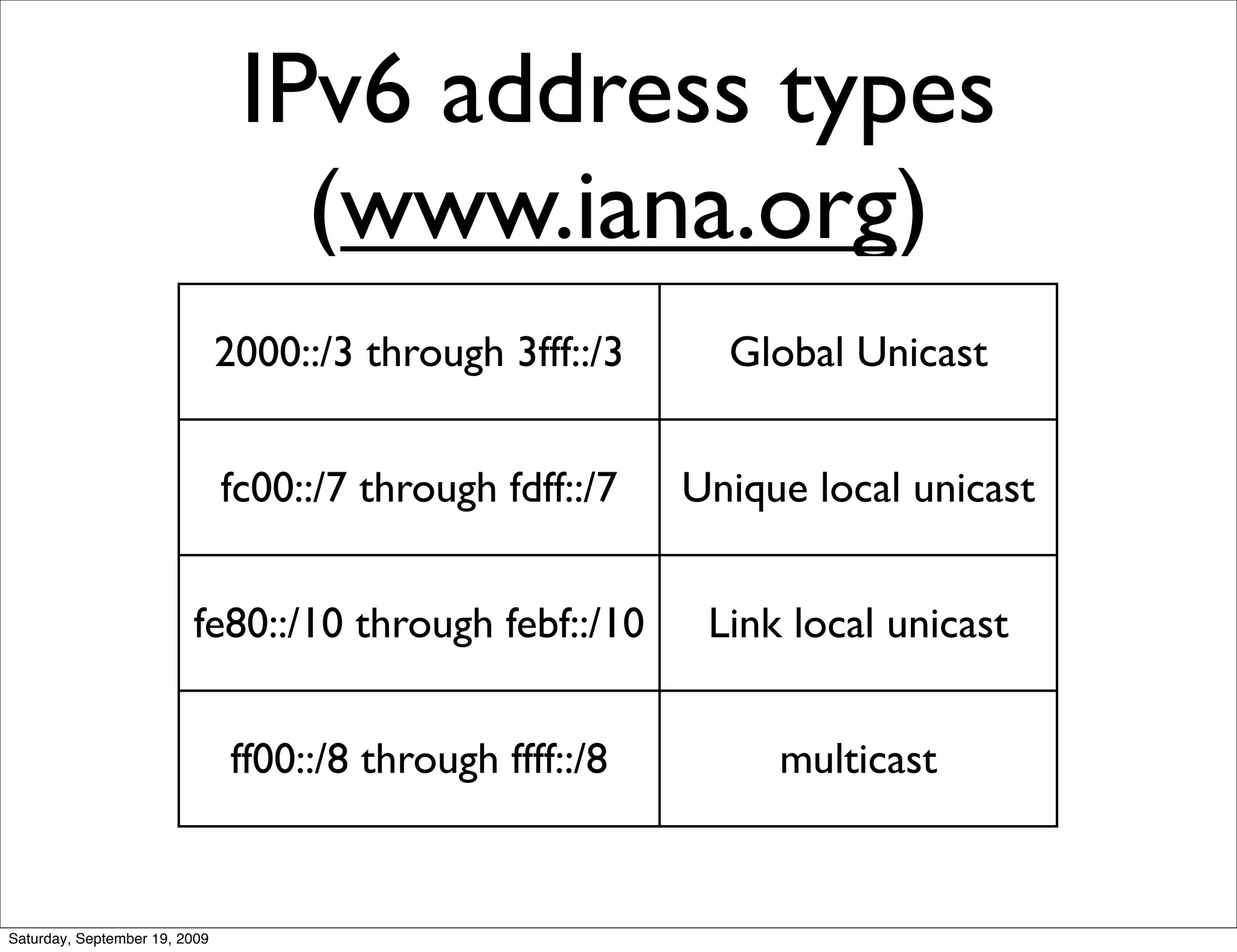
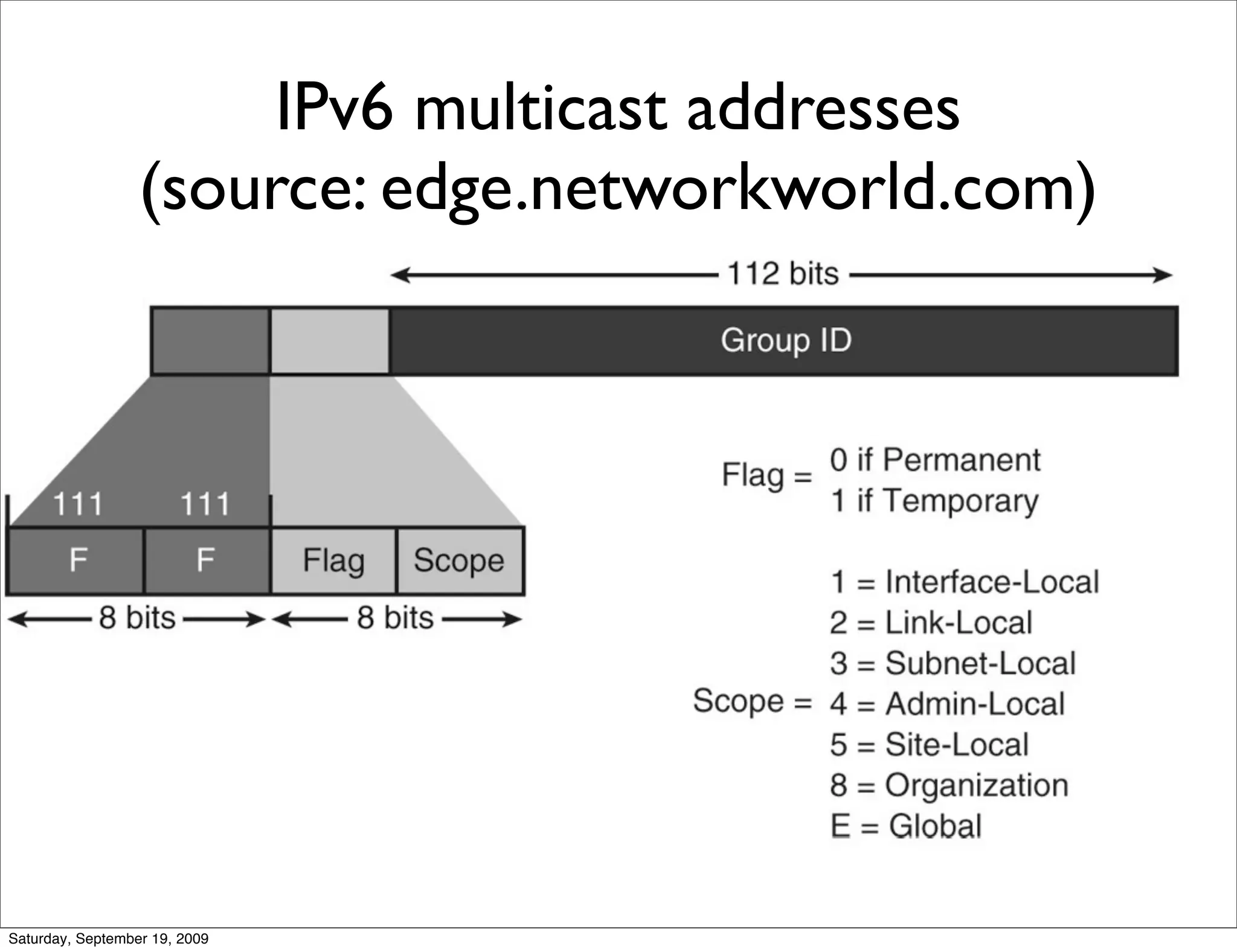
This document summarizes a training presentation on IPv6 theory. It includes sections on IPv4 address exhaustion, OSI layer review, Ethernet and TCP/IP segment formats, common protocols like HTTP and UDP, IPv4 and IPv6 header formats, IPv6 extension headers, IPv6 addressing including examples and shorthand, subnetting and netmasks, address types and scopes, multicast addressing, neighbor discovery, router advertisements, stateless address autoconfiguration, IPv6 support in Cisco IOS, and an example IPv6 network map and configuration.










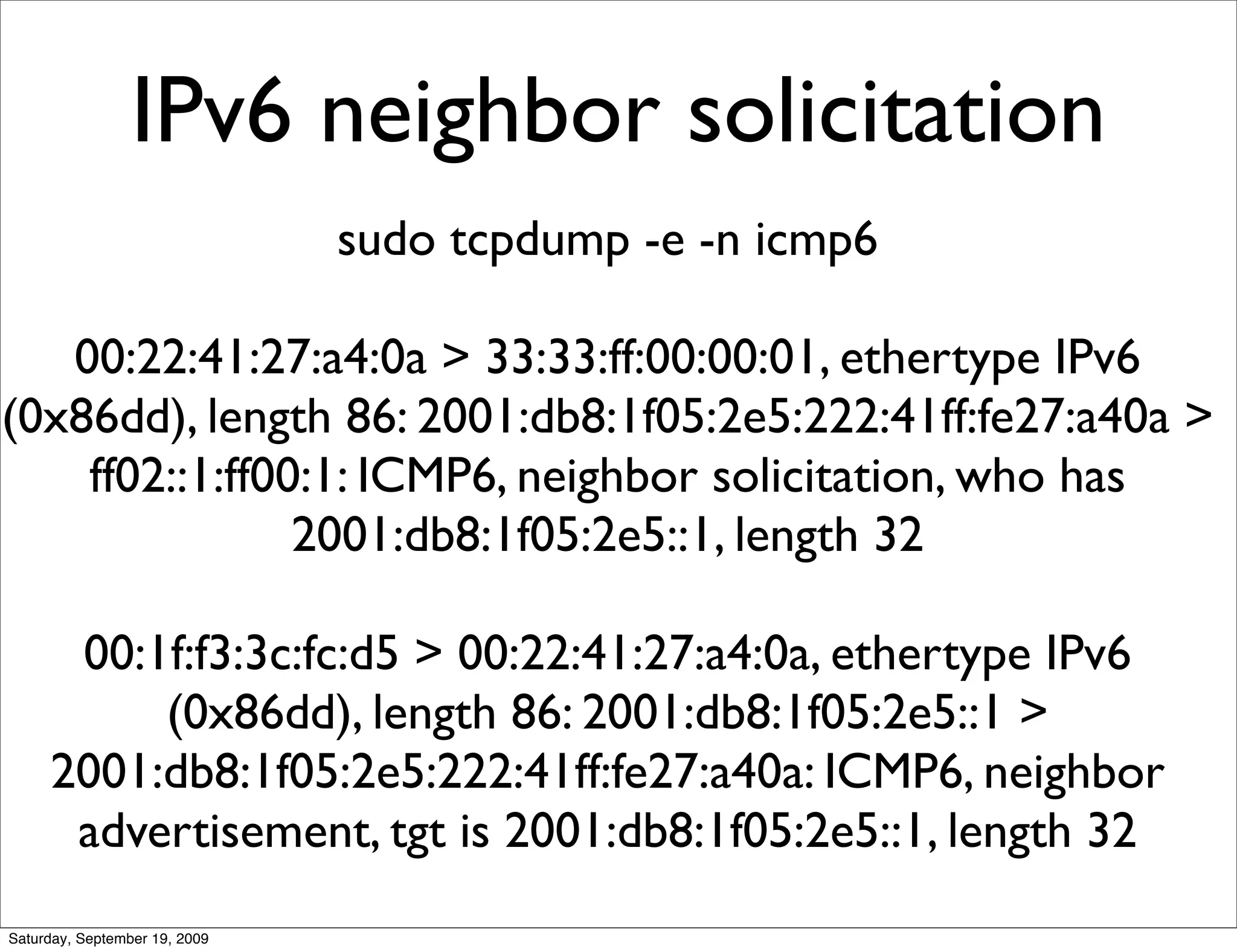

![IPv6 router
advertisements
00:1f:f3:3c:fc:d5 > 33:33:00:00:00:01, ethertype IPv6 (0x86dd),
length 110: (hlim 255, next-header ICMPv6 (58) payload length:
56) fe80::21f:f3ff:fe3c:fcd5 > ff02::1: [icmp6 sum ok] ICMP6, router
advertisement, length 56
hop limit 64, Flags [none], pref medium, router lifetime 1800s,
reachable time 0s, retrans time 0s
source link-address option (1), length 8 (1): 00:1f:f3:3c:fc:d5
0x0000: 001f f33c fcd5
prefix info option (3), length 32 (4): 2001:db8:1f05:2e5::/64, Flags
[onlink, auto], valid time 2592000s, pref. time 604800s
Saturday, September 19, 2009](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ipv6-theory-100224013242-phpapp02/75/IPv6-Theory-by-Cisco-22-2048.jpg)