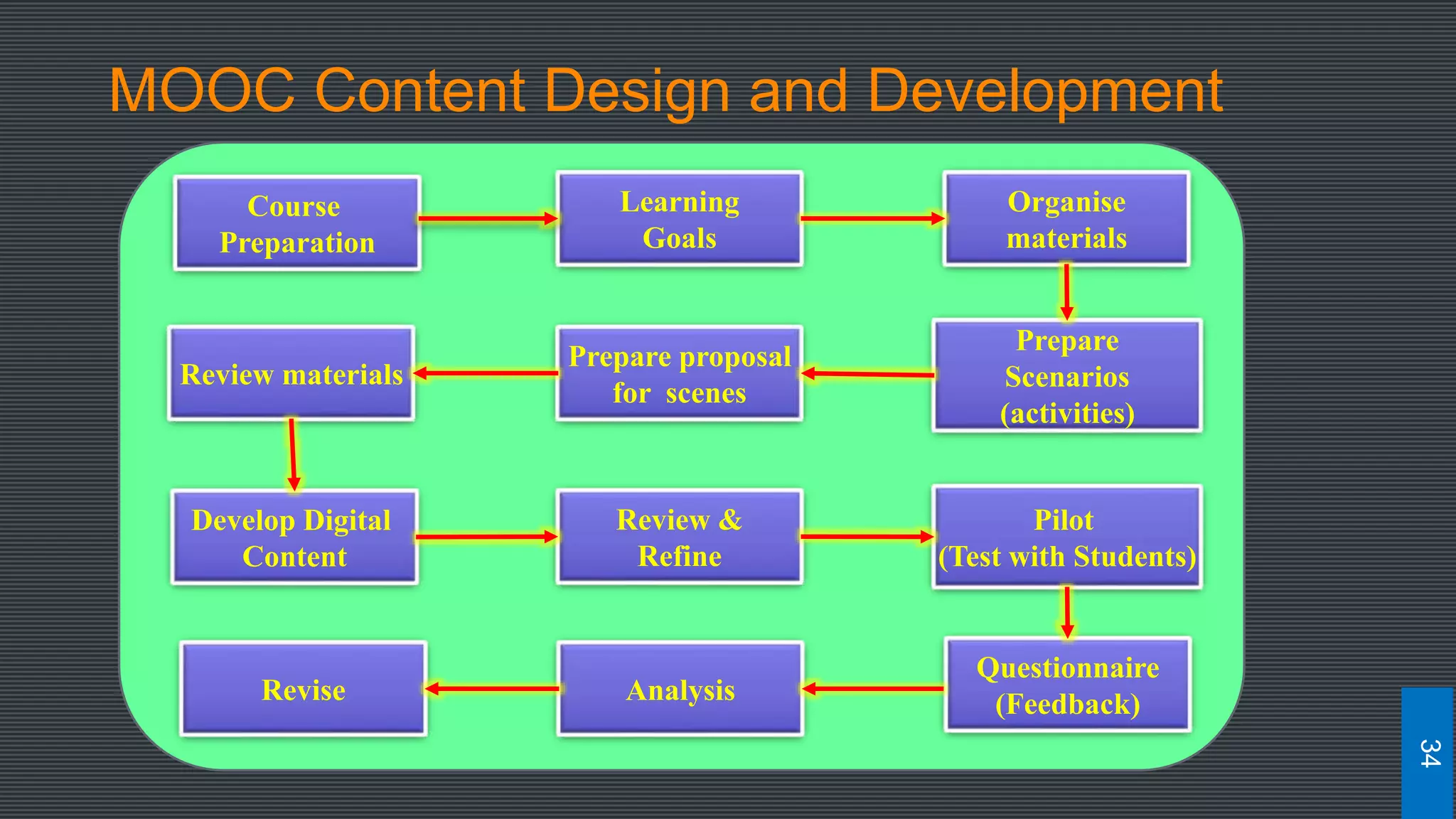
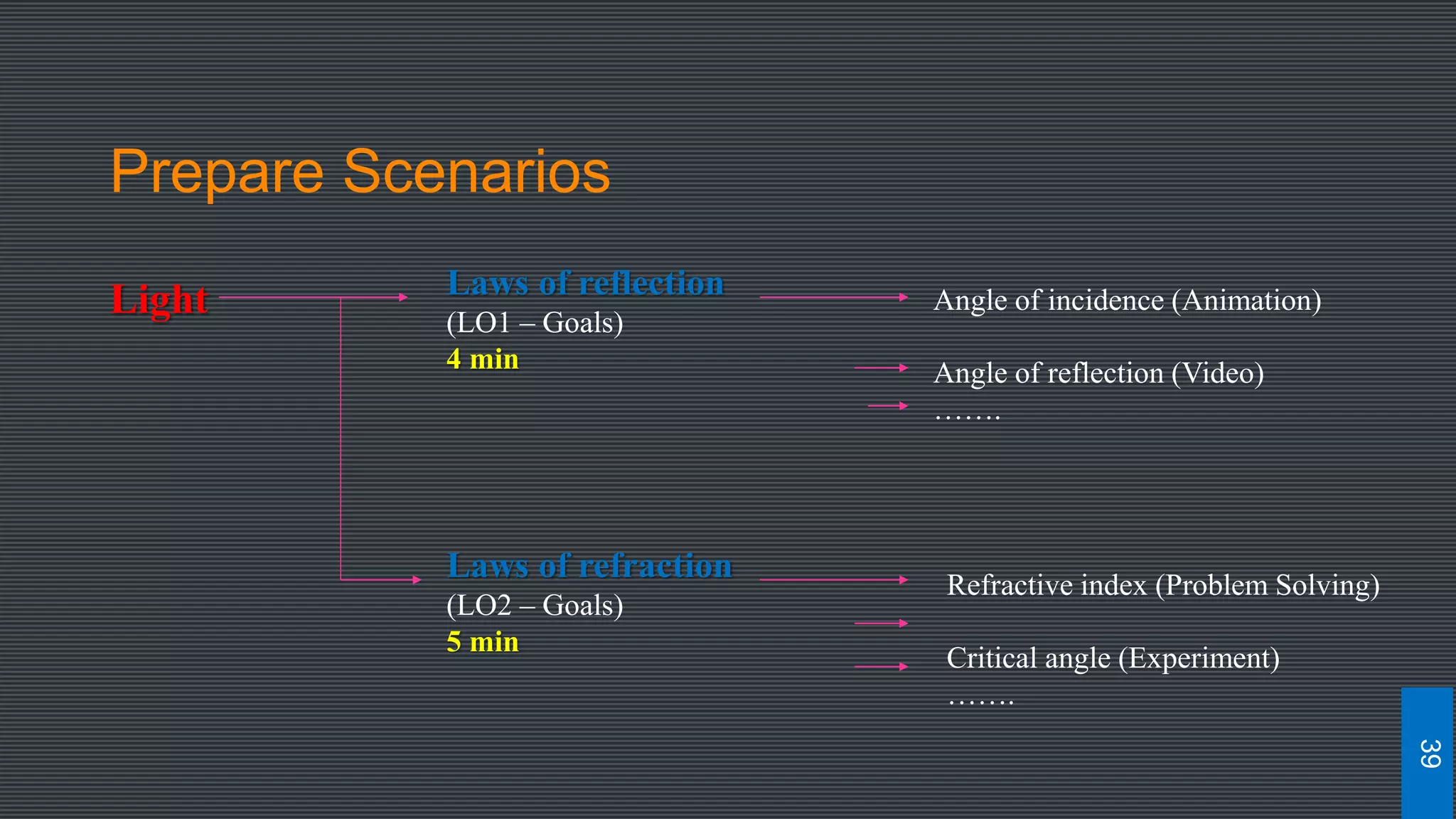
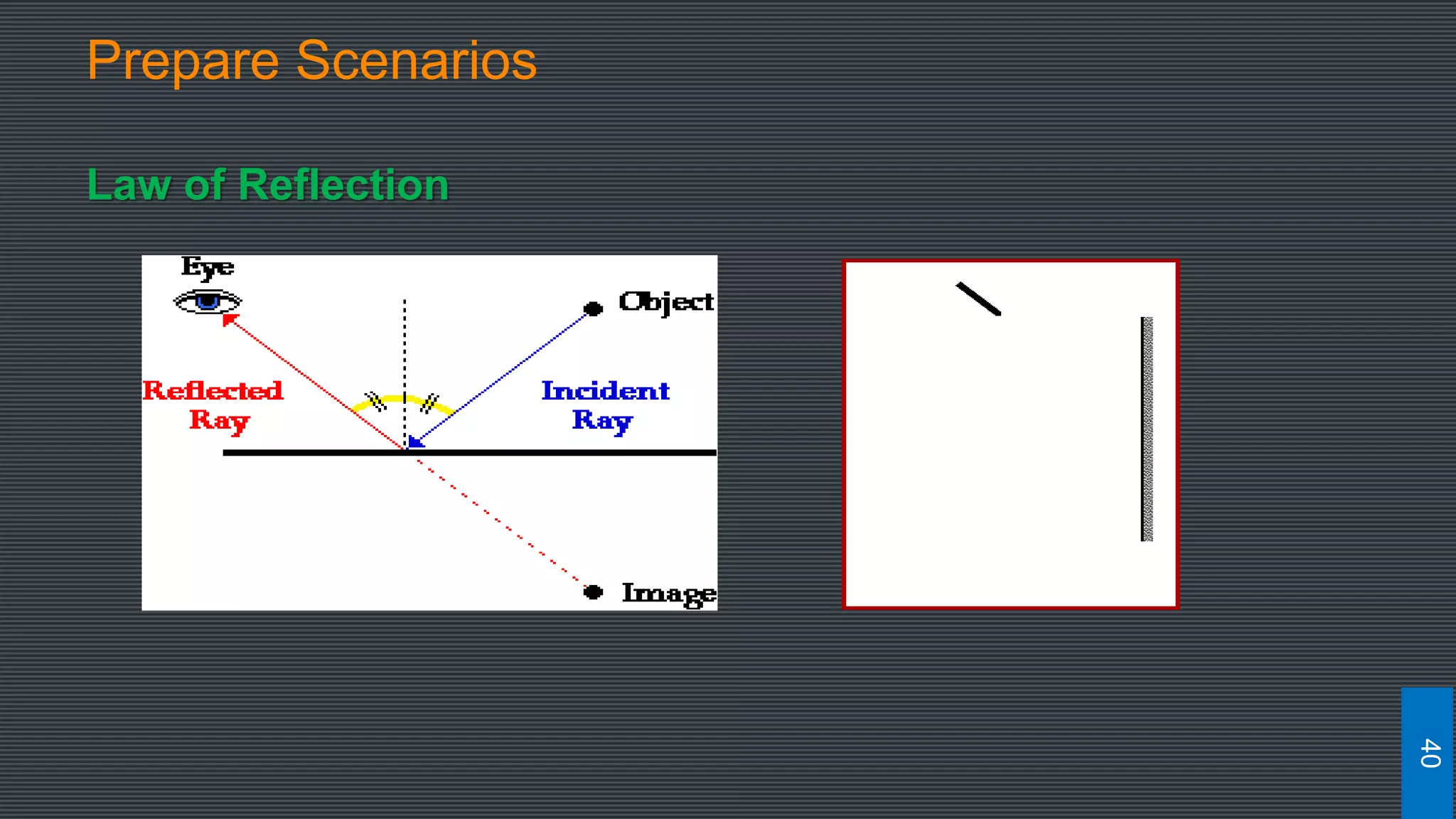
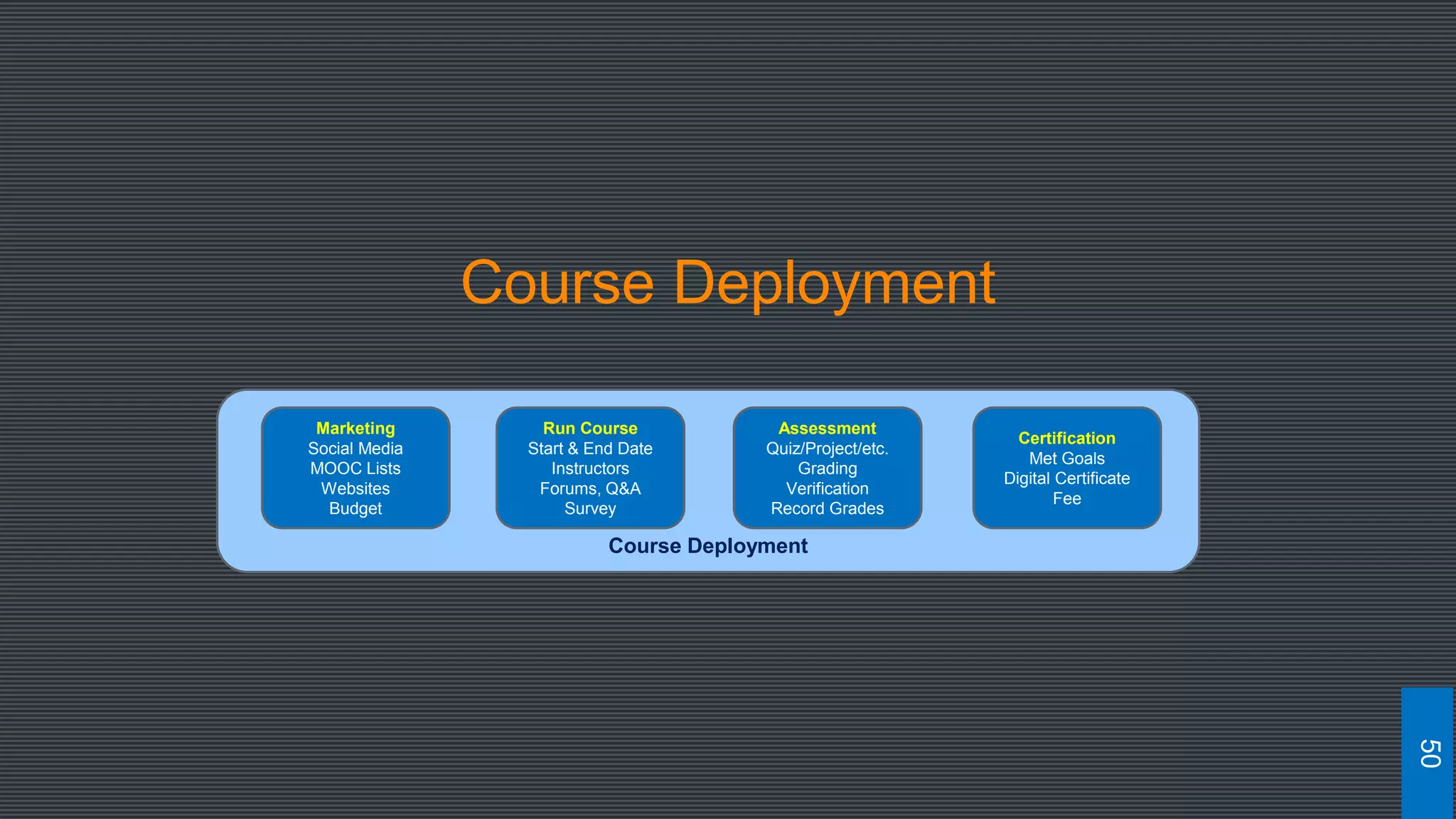
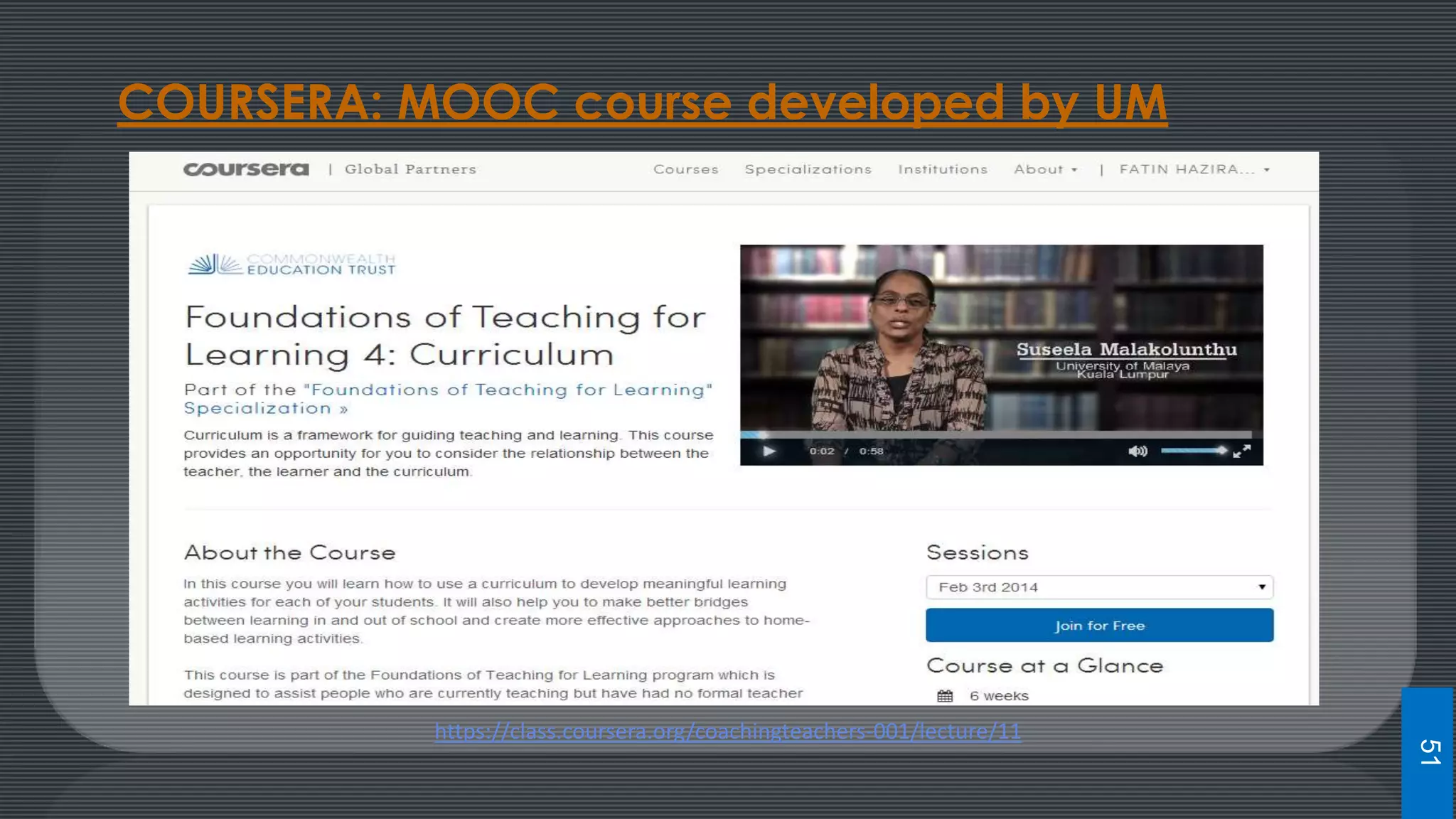
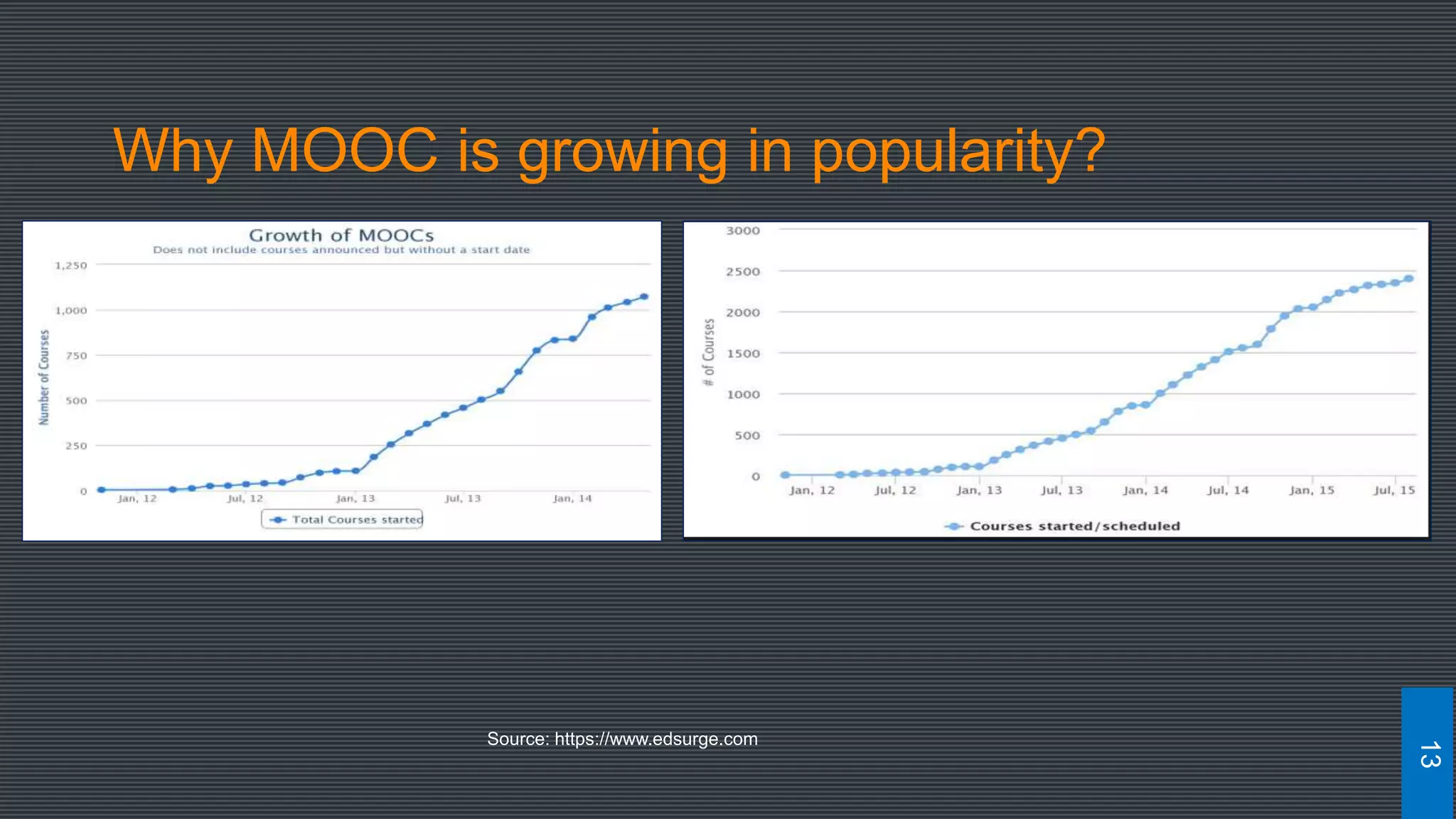
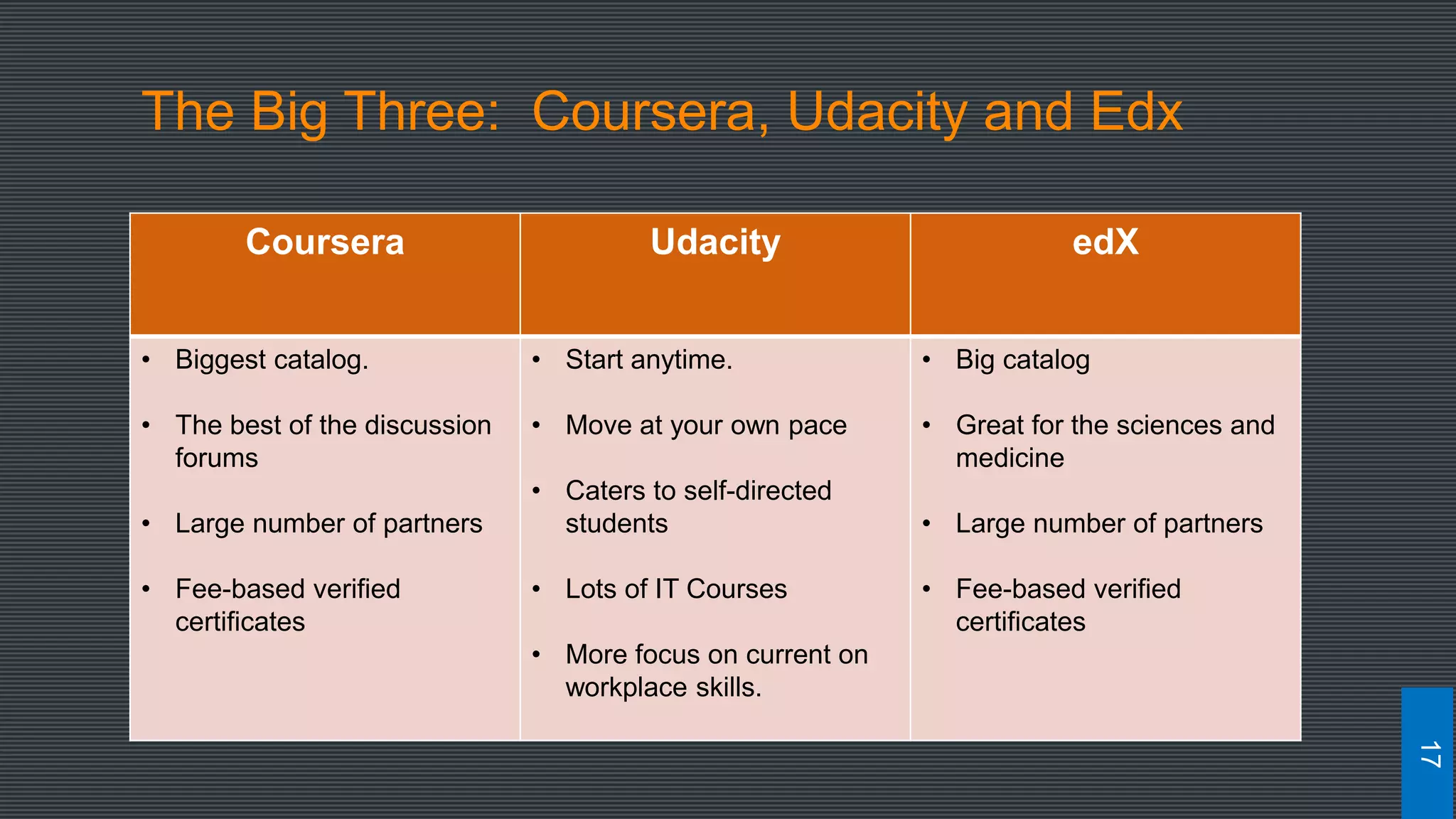
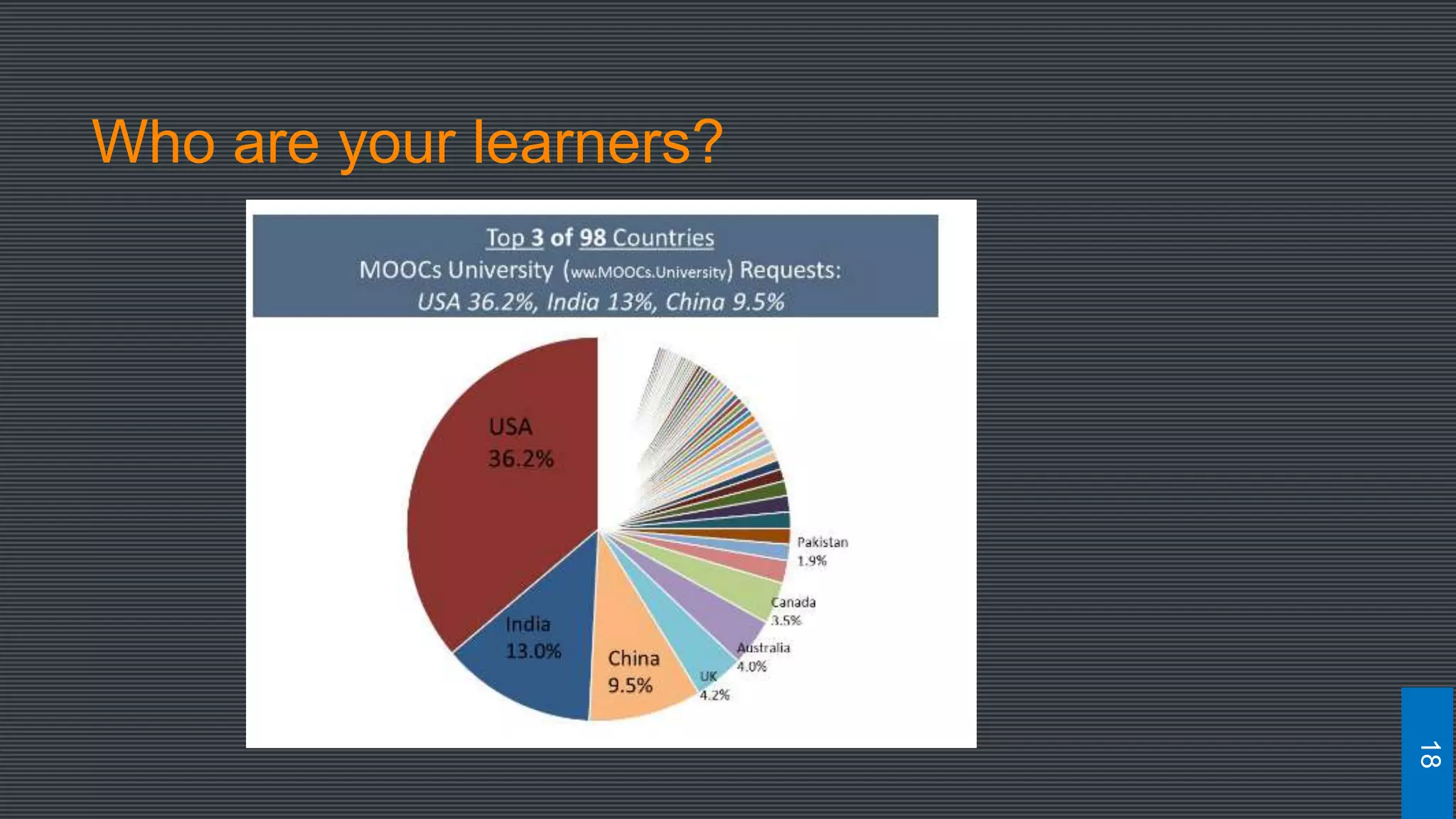
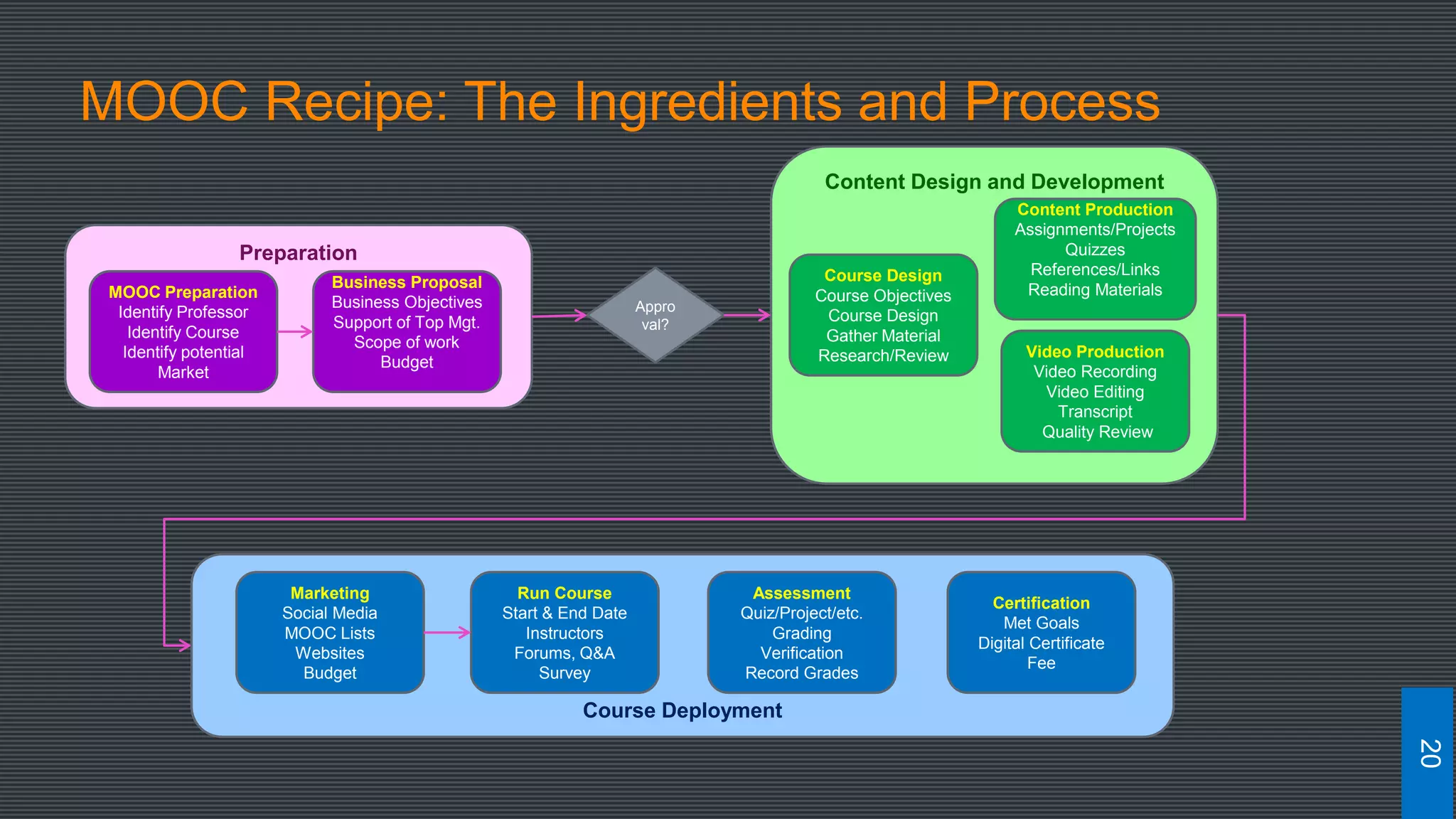
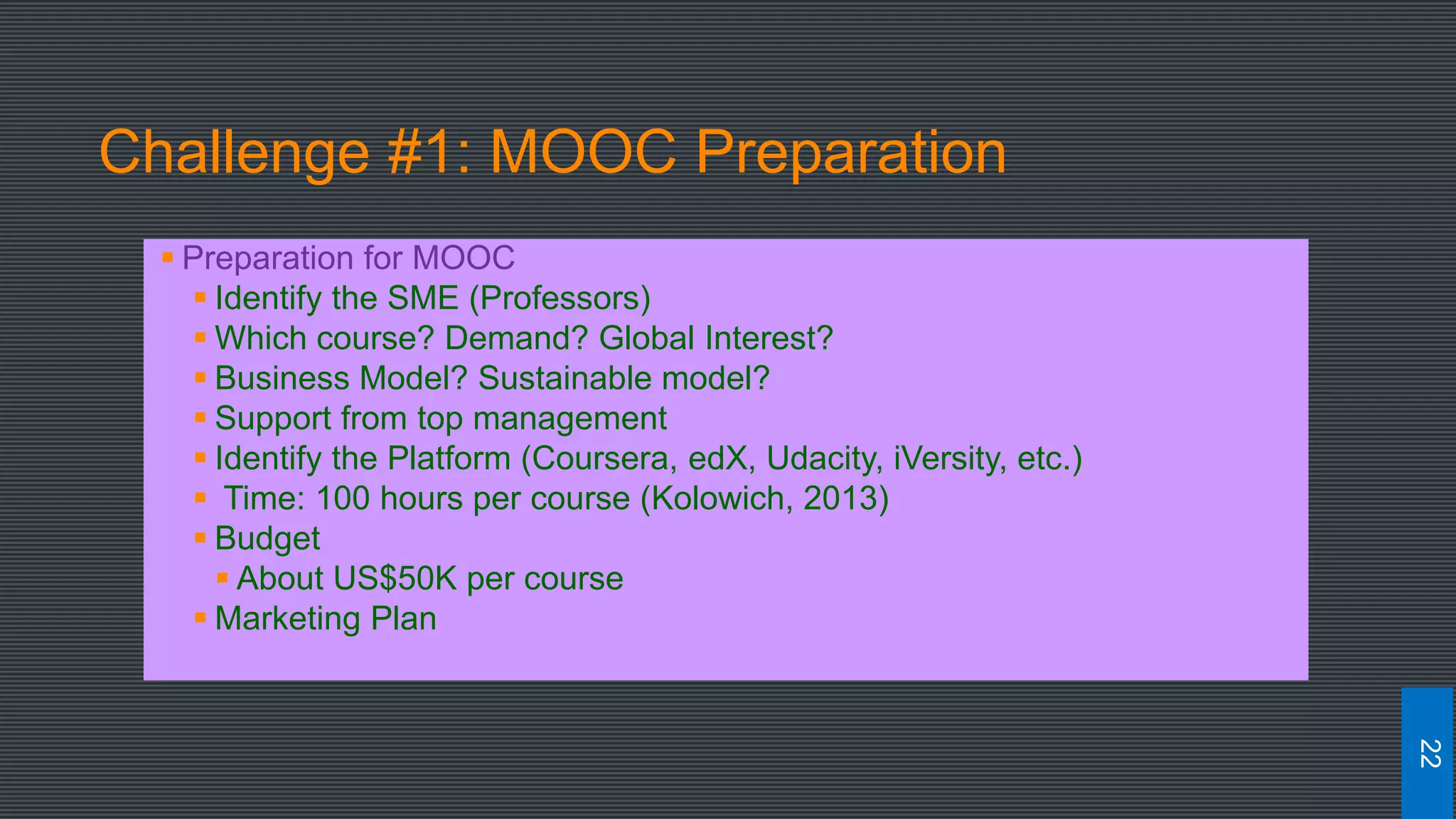
The document discusses best practices for designing MOOCs, focusing on preparation, content development, resources, drop-out rates, and learning outcomes. It emphasizes the shift from traditional education to digital learning spaces, highlighting the importance of technology as an enabler of learning. Key considerations include management support, team development, and effective course design to enhance learner engagement and success.














![MOOC Fundamental Concepts
Many researchers agree that more research and experimentation
about the design of MOOCs is required [McAuley et al., 2010], [Ostashewski
and Reid, 2012]
Two existing perspective: xMOOC and cMOOC [Siemens, 2012a]
xMOOC: adopt a cognitive-behaviorist lecture and knowledge
dissemination pedagogical approach similar to that of traditional
face-to-face
cMOOCs: follow a more connectivist learning approach, where
knowledge is found in the connections between people, and learning
is the development and traversal of those connections
23](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/moocbestpractices-singaporev3-151029080152-lva1-app6891/75/Best-Practices-in-Designing-MOOC-23-2048.jpg)

![MOOC Framework
The MOOC Canvas is a simple and visual framework for
educators that need to design a MOOC from scratch.
The MOOC Canvas is inspired by the ideas and structure
of the Business Model Canvas [Osterwalder and Pigneur, 2010], but
gathering the main issues of logistical, technological,
pedagogical and financial nature that educators need to
think of during the design of a MOOC
25](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/moocbestpractices-singaporev3-151029080152-lva1-app6891/75/Best-Practices-in-Designing-MOOC-25-2048.jpg)
![MOOCBusinessModel
[OsterwalderandPigneur,2010]
26](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/moocbestpractices-singaporev3-151029080152-lva1-app6891/75/Best-Practices-in-Designing-MOOC-26-2048.jpg)
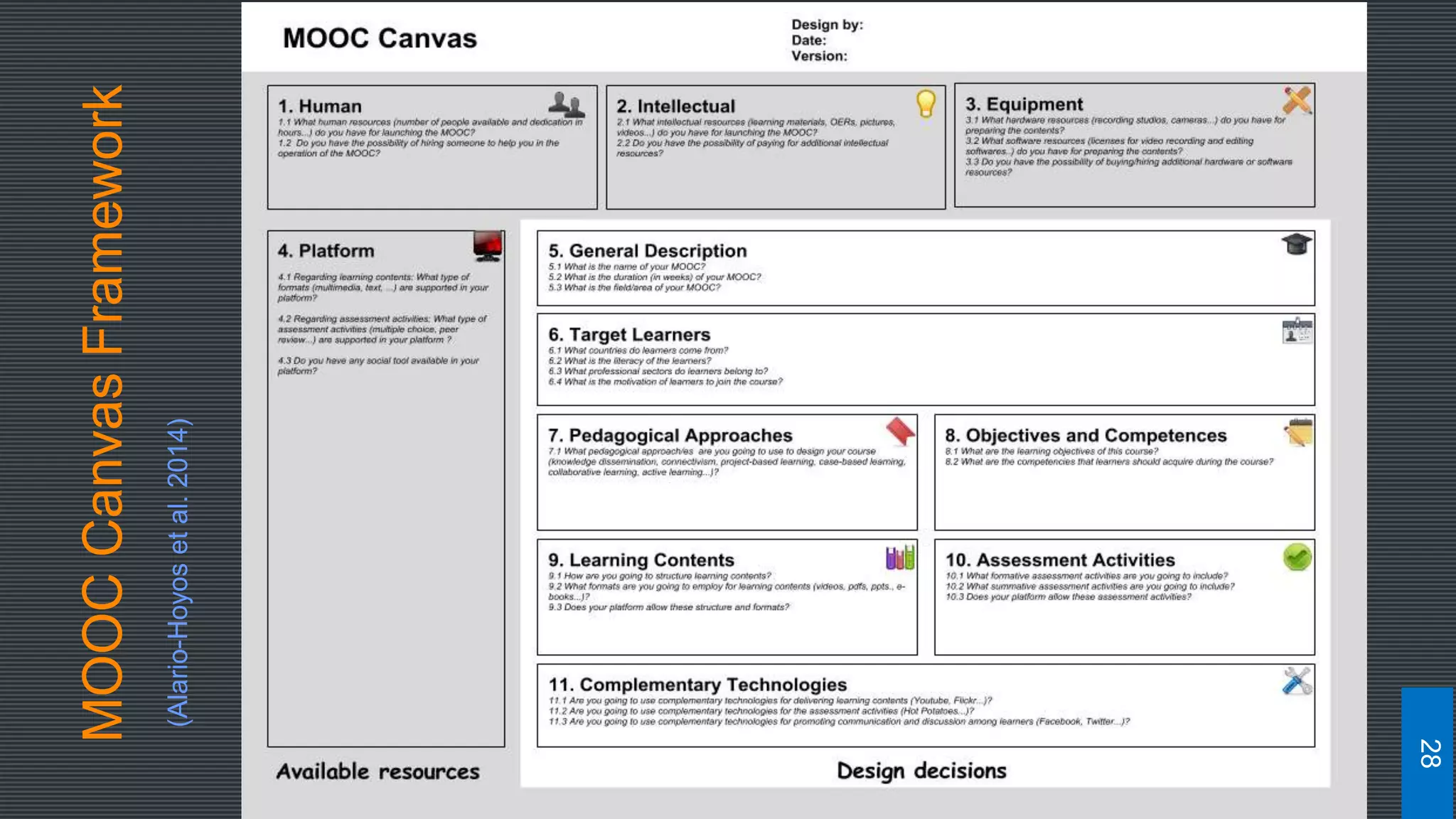
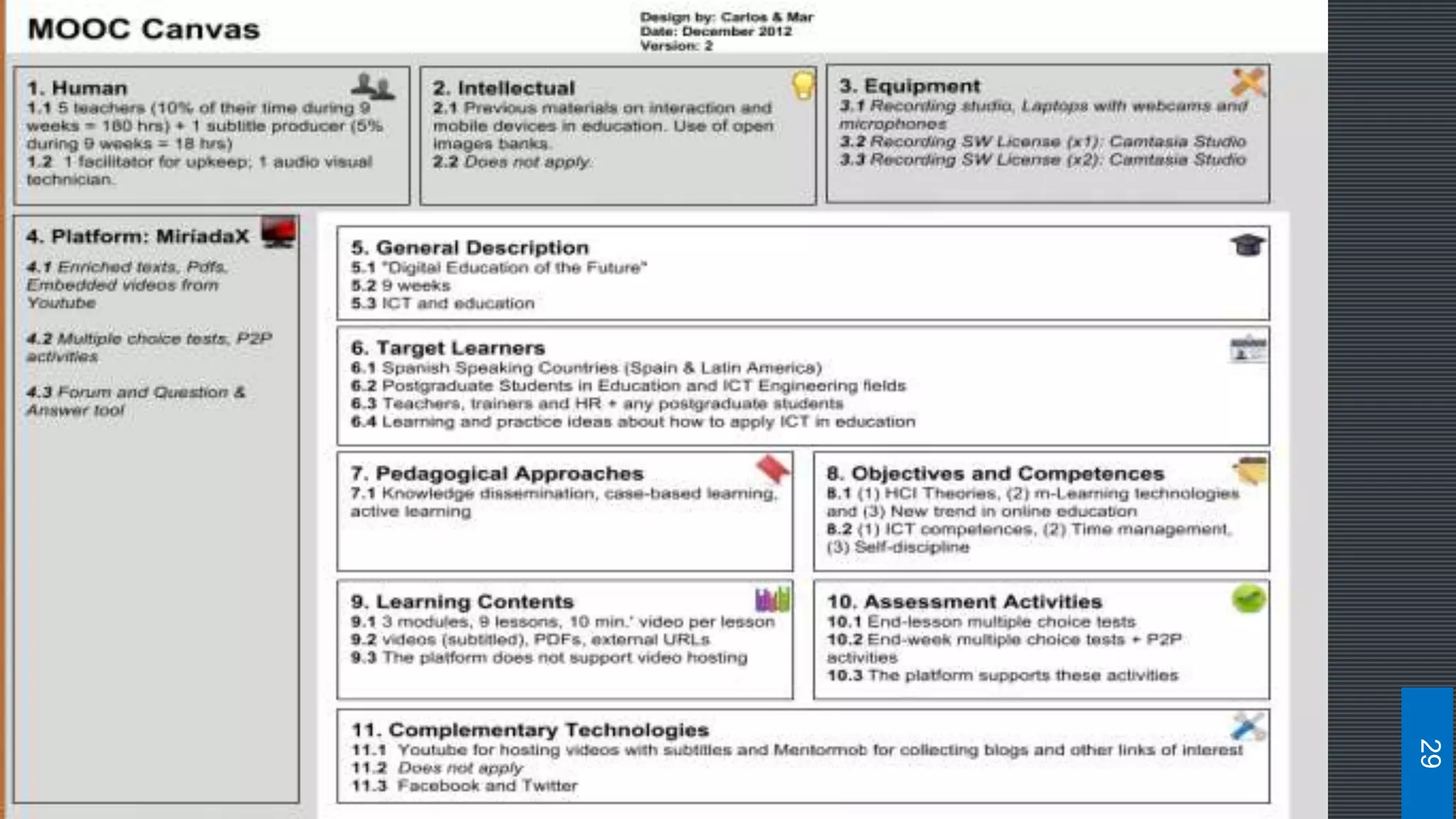
![MOOC Canvas Framework
[Osterwalder and Pigneur, 2010]
A total of 11 issues are addressed:
Available Resources Category:
Human Resources
Intellectual resources
Equipment (hardware and software resources
Platform
Design Decisions Category:
General Description: Course name, duration and field/area
Target learners
Pedagogical approaches ((knowledge dissemination, connectivism, project-based
learning, case-based learning, collaborative learning, active learning, etc.)
Objectives and competencies pursued with the course
Learning contents that will be delivered
Assessment activities employed
Complementary technologies that will support the MOOC
27](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/moocbestpractices-singaporev3-151029080152-lva1-app6891/75/Best-Practices-in-Designing-MOOC-27-2048.jpg)