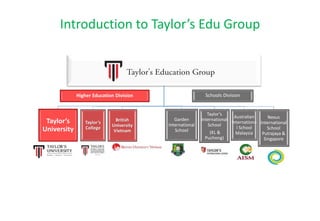
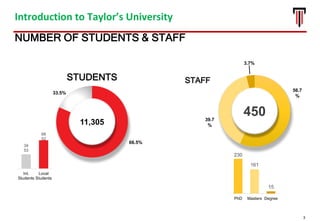
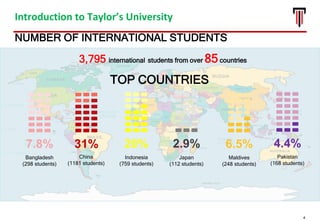
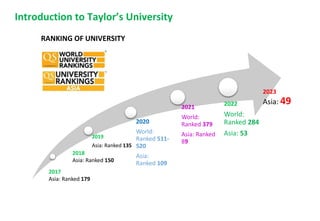
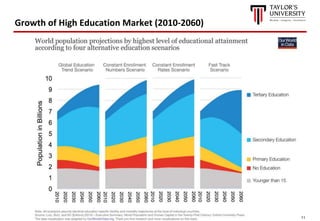
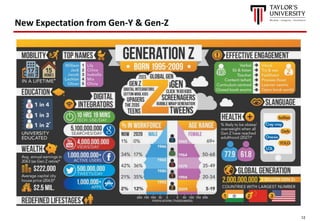
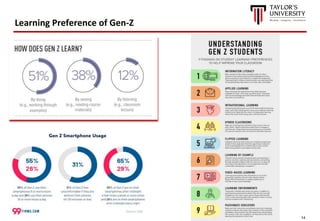
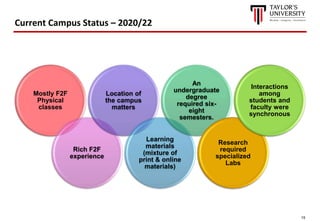
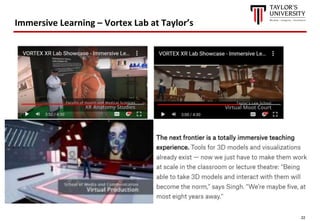
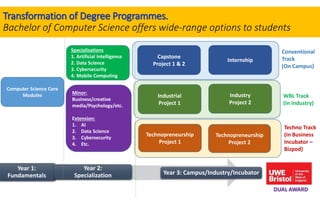
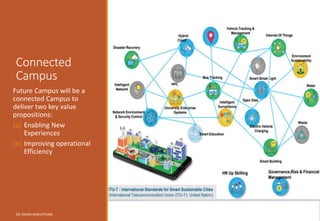
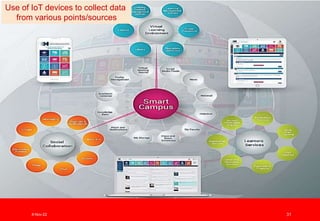
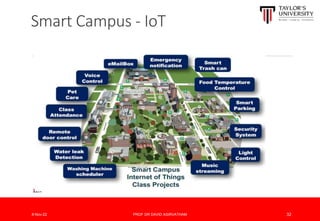
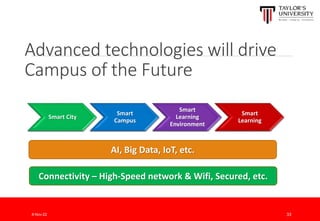
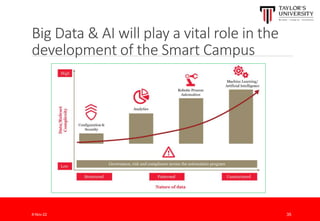
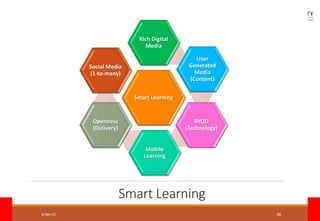
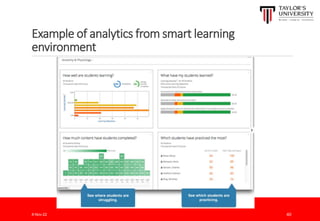
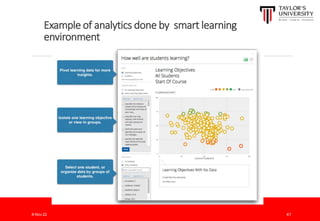
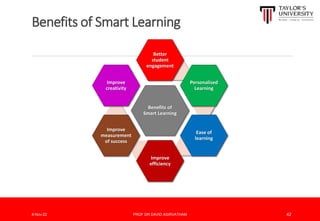
The document outlines the vision for Taylor's University by 2030, emphasizing the integration of technology and hybrid learning approaches to prepare students for evolving job markets. It highlights important trends, such as the increasing demand for flexible learning structures, smart campus development, and the use of innovative educational technologies like AI and big data. The future campus will focus on creating connected, sustainable environments that enhance student engagement and collaboration while addressing the changing needs of Gen-Y and Gen-Z learners.