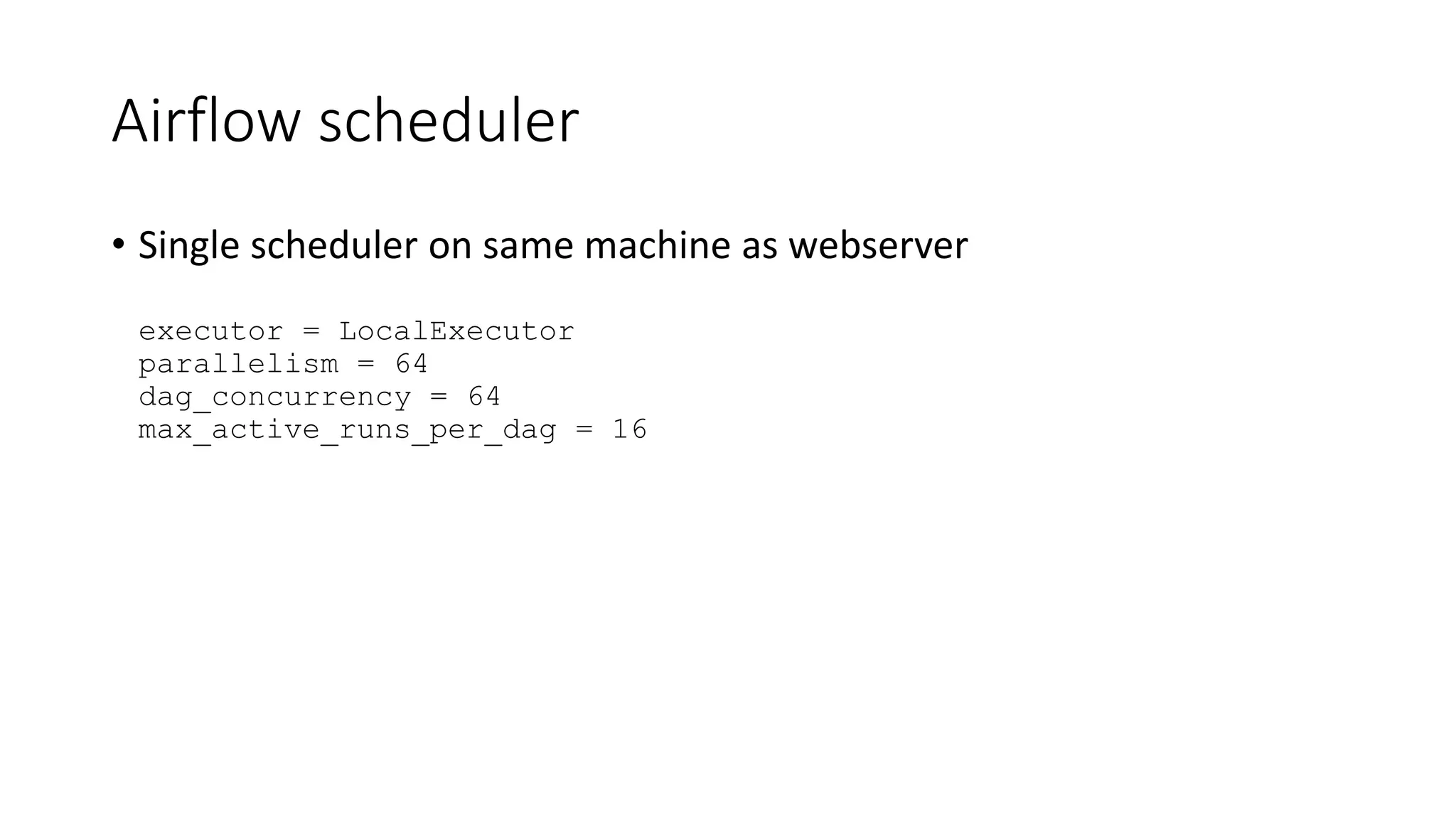
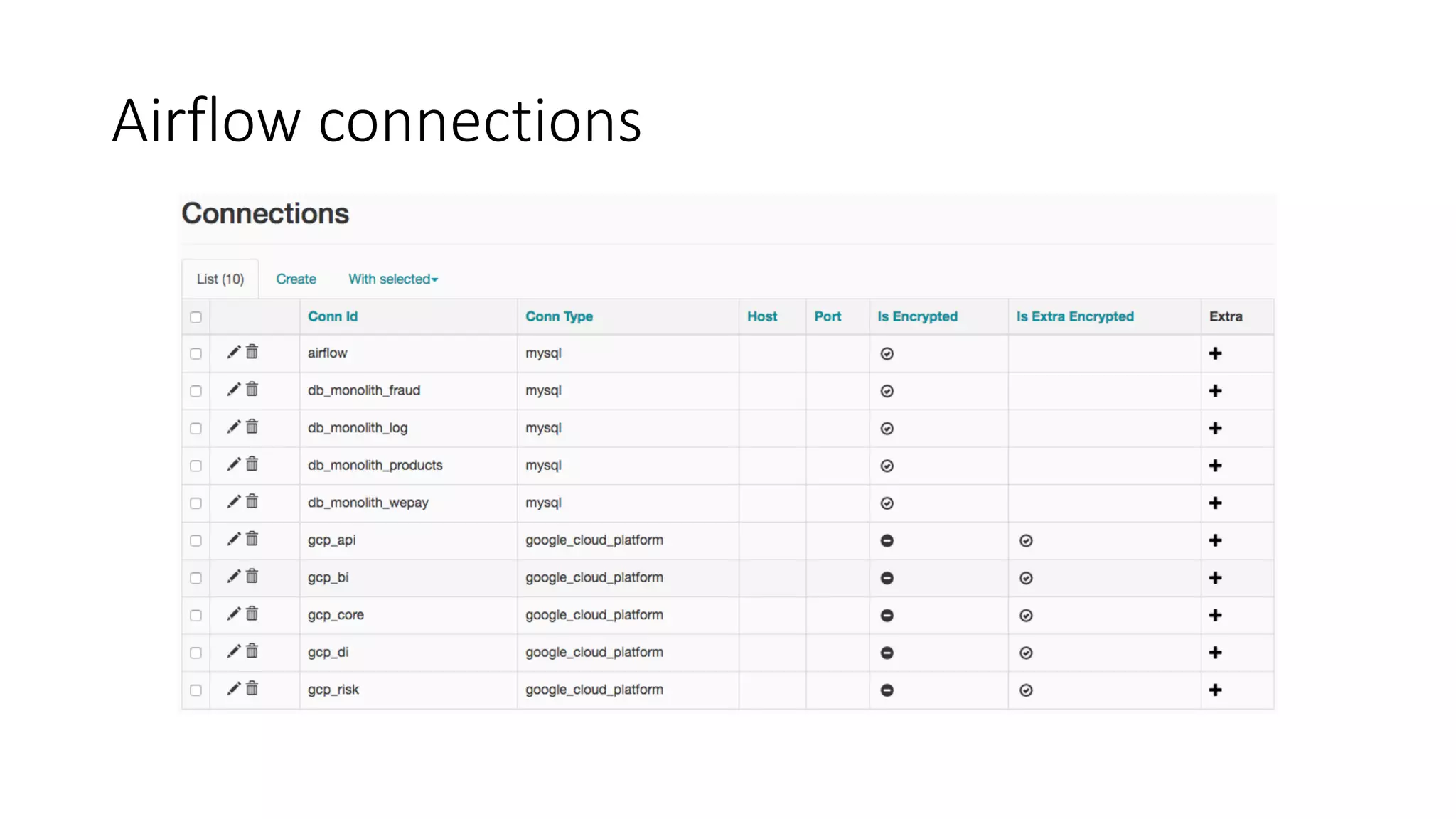
The document discusses the use of Airflow at WePay, detailing its application for ETL, reporting, monitoring, and machine learning, with a deployment on Google Cloud Platform. It outlines the infrastructure setup, including machine specifications, database configuration, and Airflow's operational characteristics such as scheduling and logging. Development practices for DAGs, security measures, and deployment strategies are also highlighted.










![Airflow deployment
pip install git+https://git@our-wepay-repo.com/DataInfra/airflow.git@1.7.1.2-wepay#egg=airflow[gcp_api,mysql,crypto]==1.7.1.2+wepay4](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/2016-06-14-airflow-at-wepay-160616152306/75/Airflow-at-WePay-11-2048.jpg)