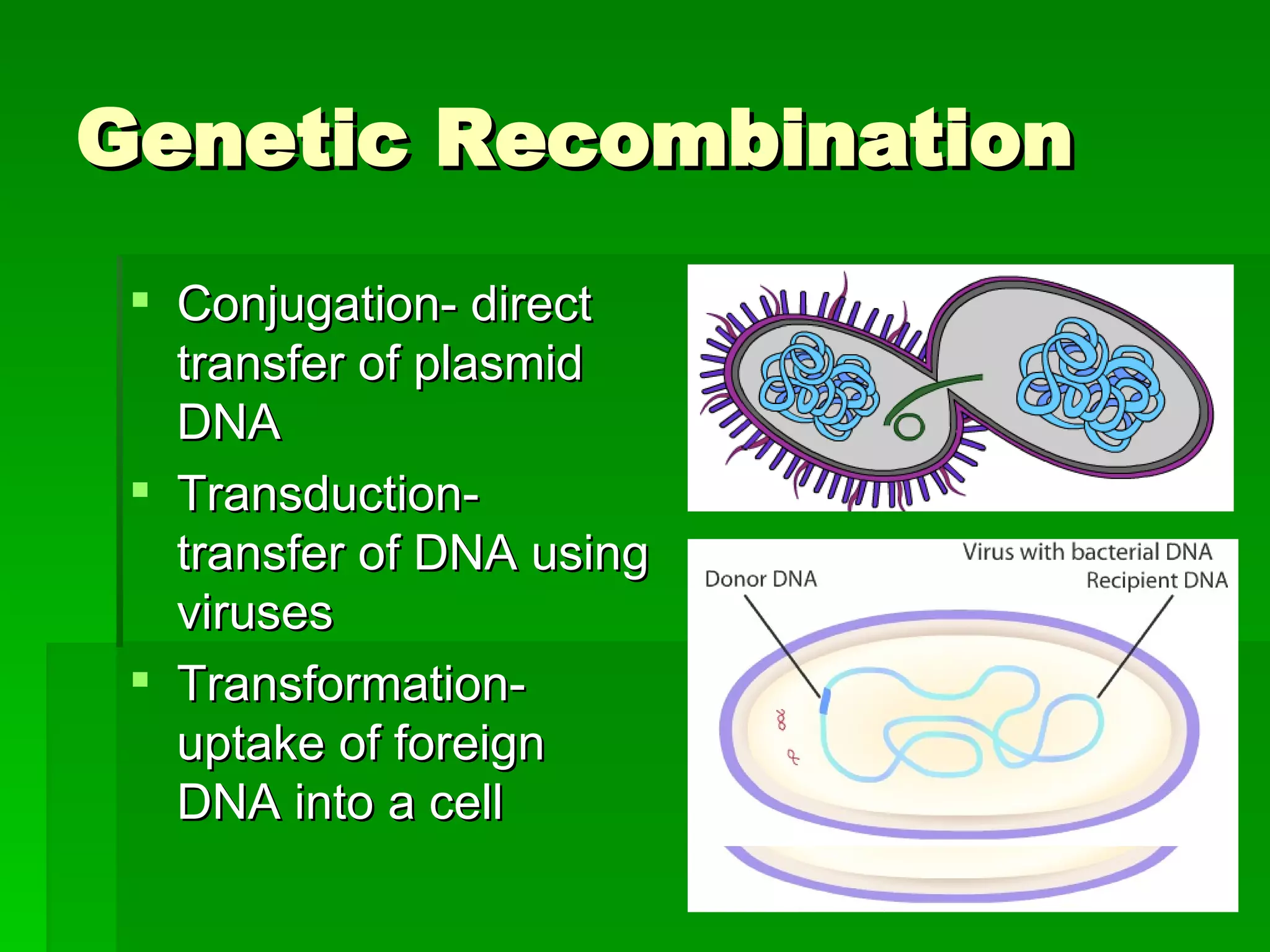
Bacteria are classified into several phyla based on their characteristics. Cyanobacteria are photosynthetic while Spirochetes are spiral shaped, with Treponema pallidum causing syphilis. Proteobacteria is the largest phylum and contains both pathogenic and beneficial bacteria. Bacterial cells have structures like cell walls, cell membranes, cytoplasm, and sometimes capsules or pili that aid in functions and survival. Bacteria can obtain nutrients through autotrophy or heterotrophy like saprophytism. Genetic recombination between bacteria can occur through conjugation, transduction, or transformation. Bacterial diseases harm hosts through exotoxins, endotoxins, or digestive enzymes, and antibiotics are used to