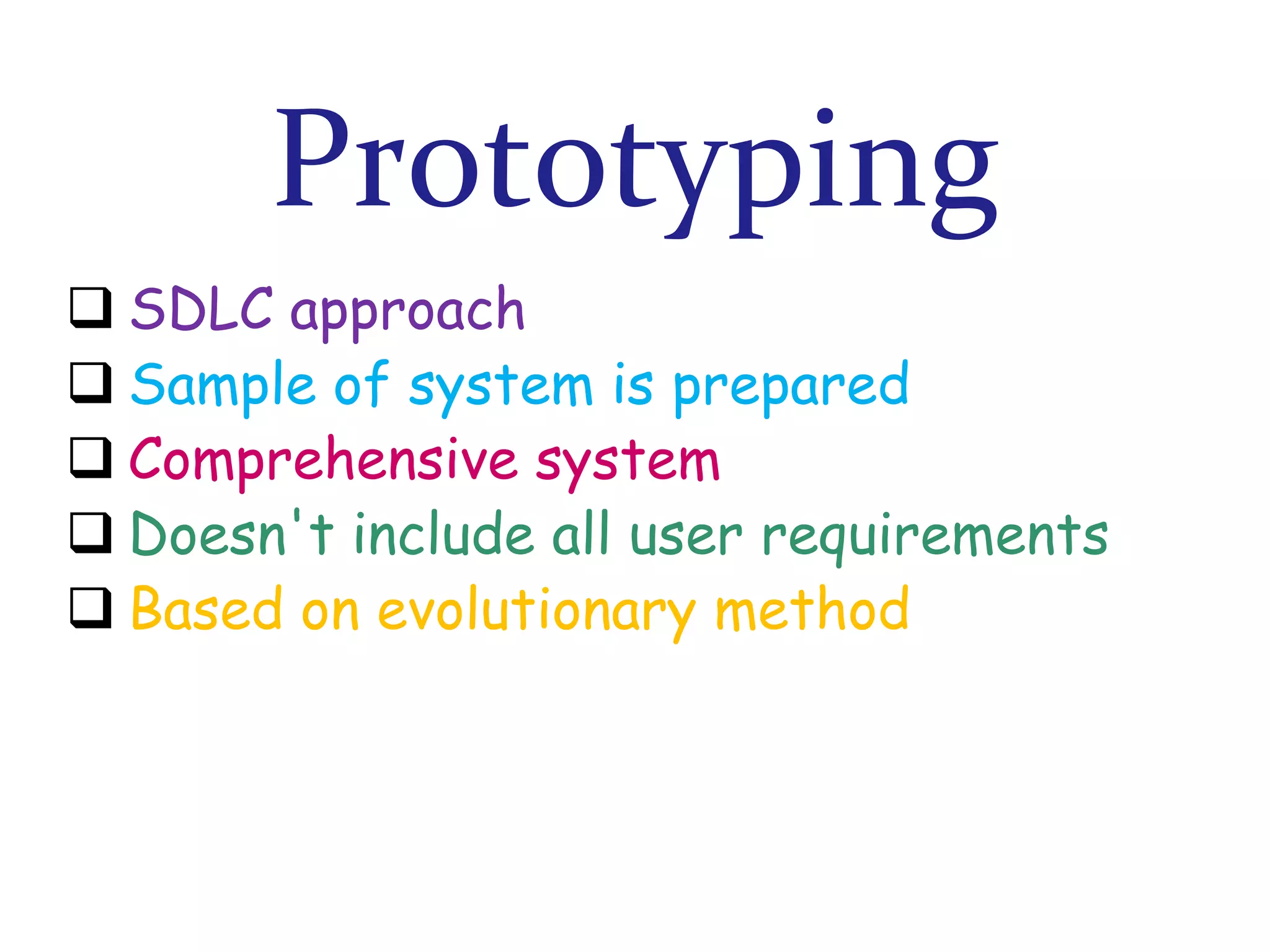
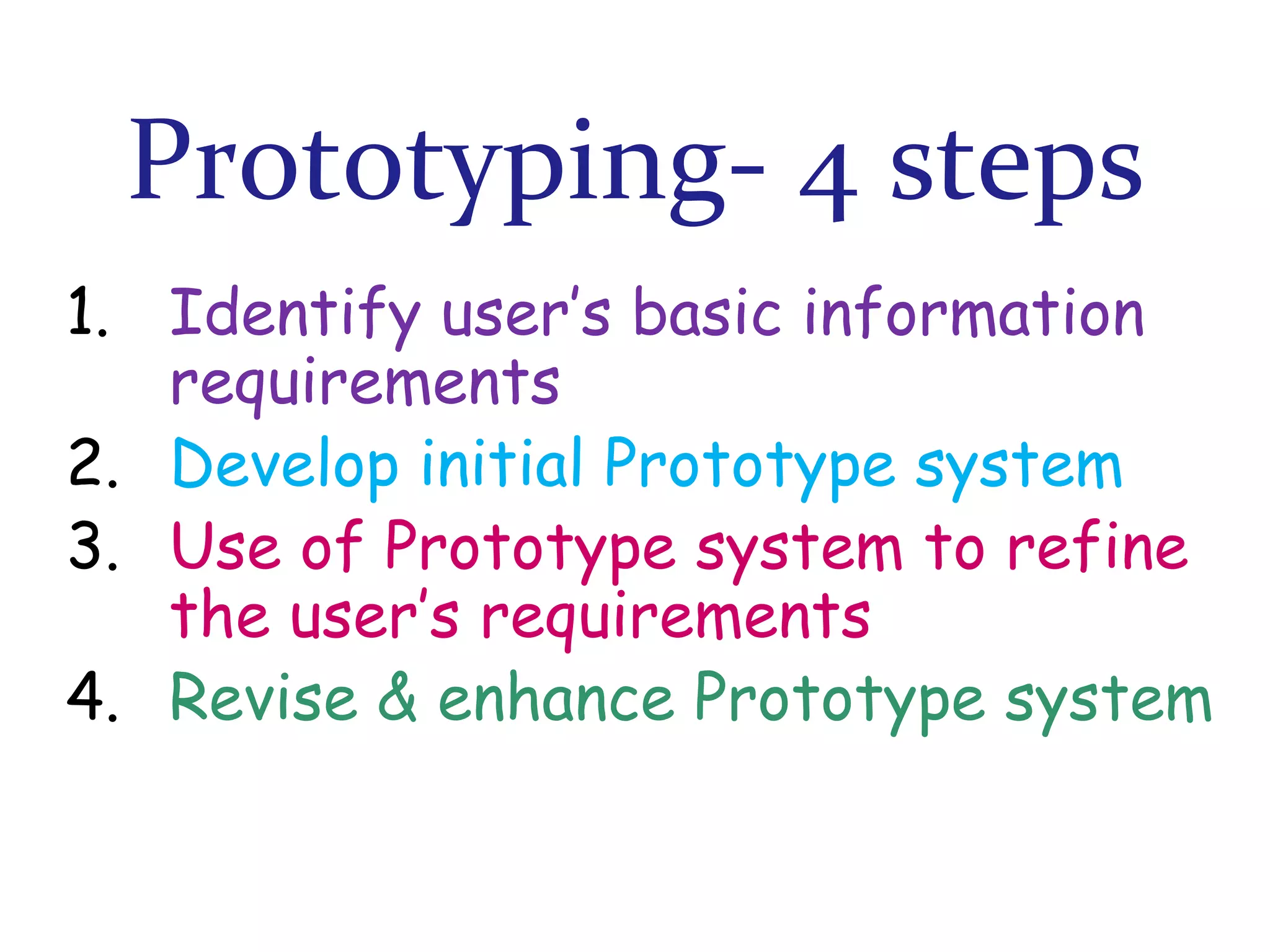
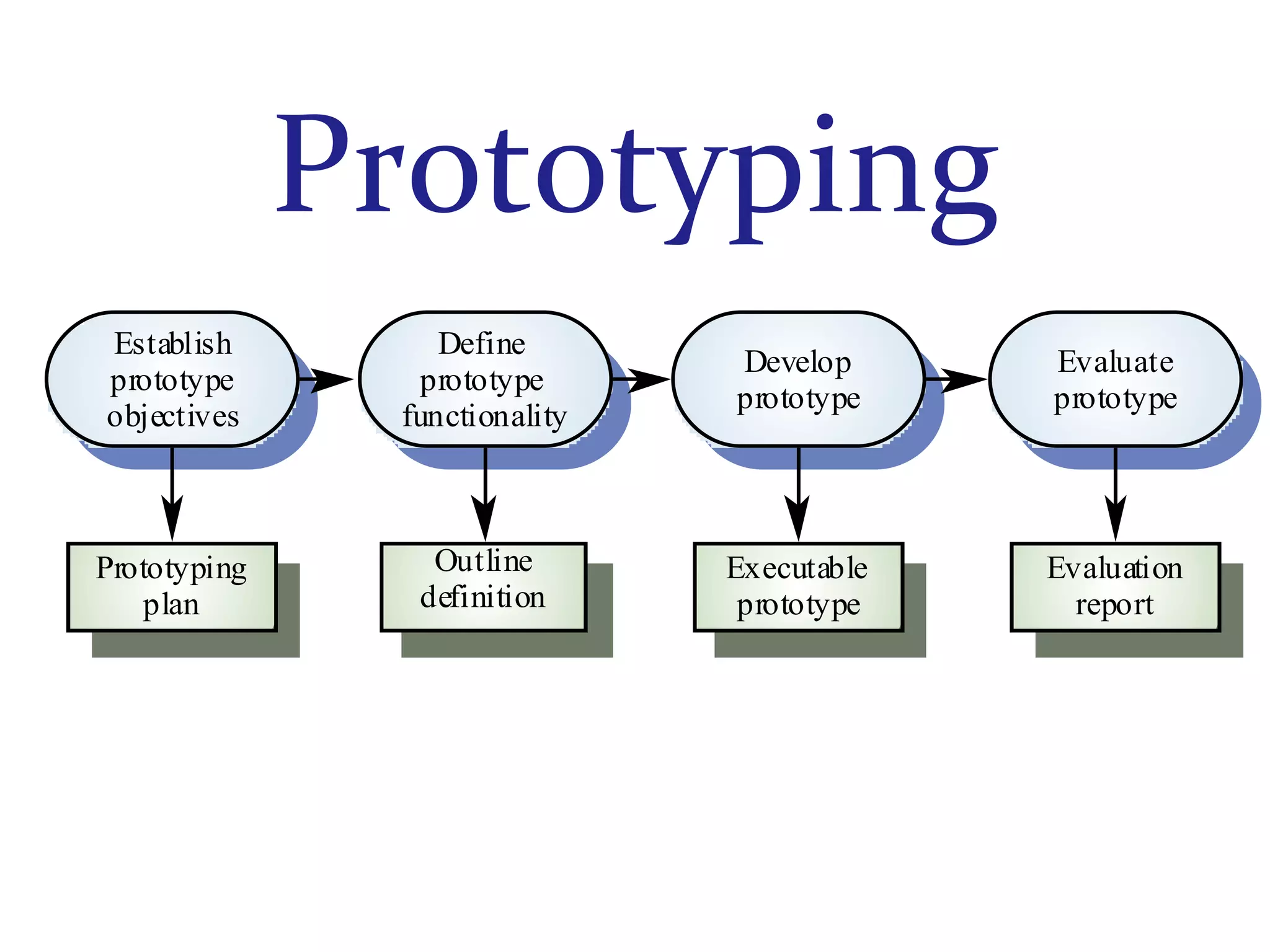
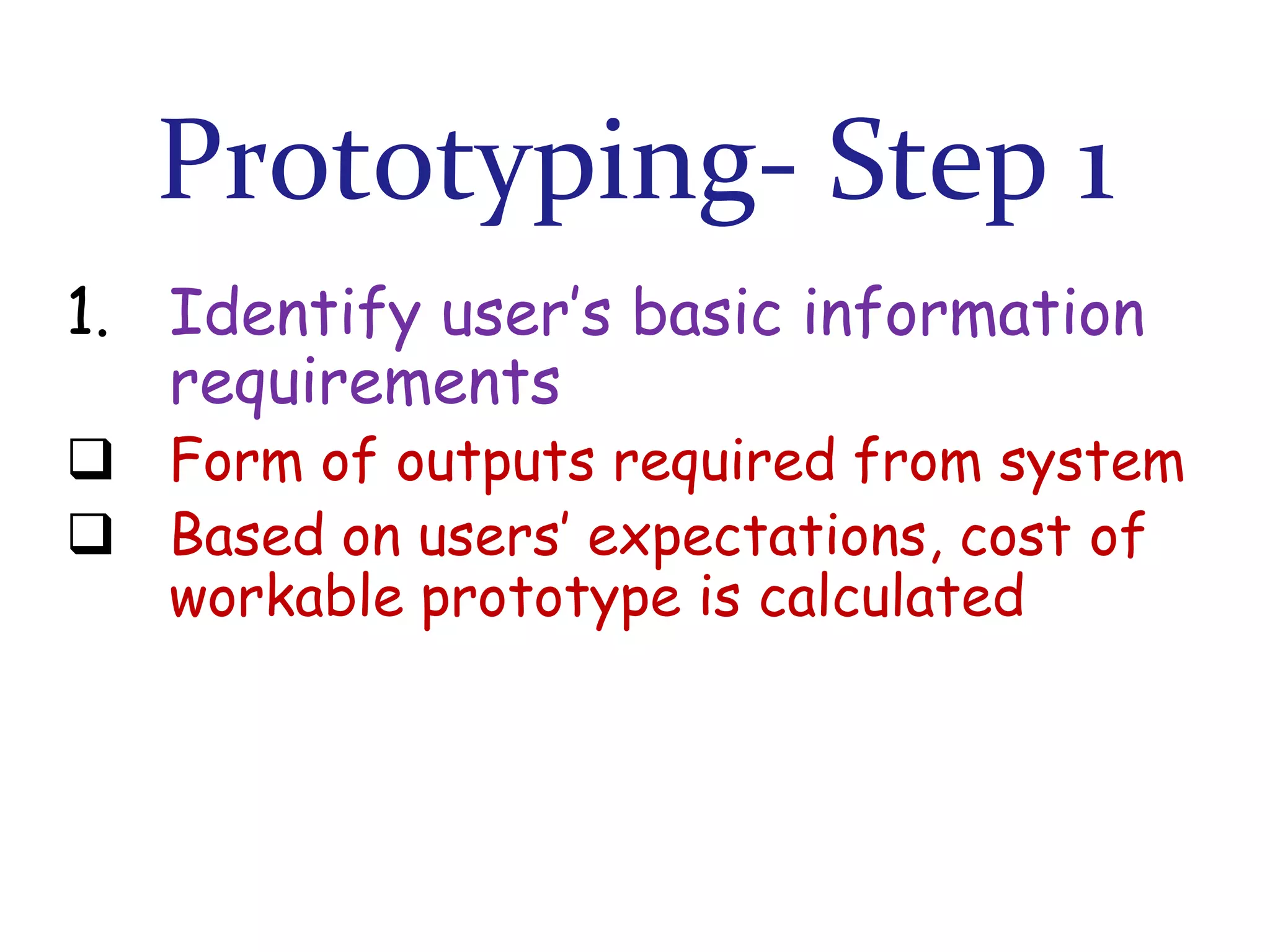
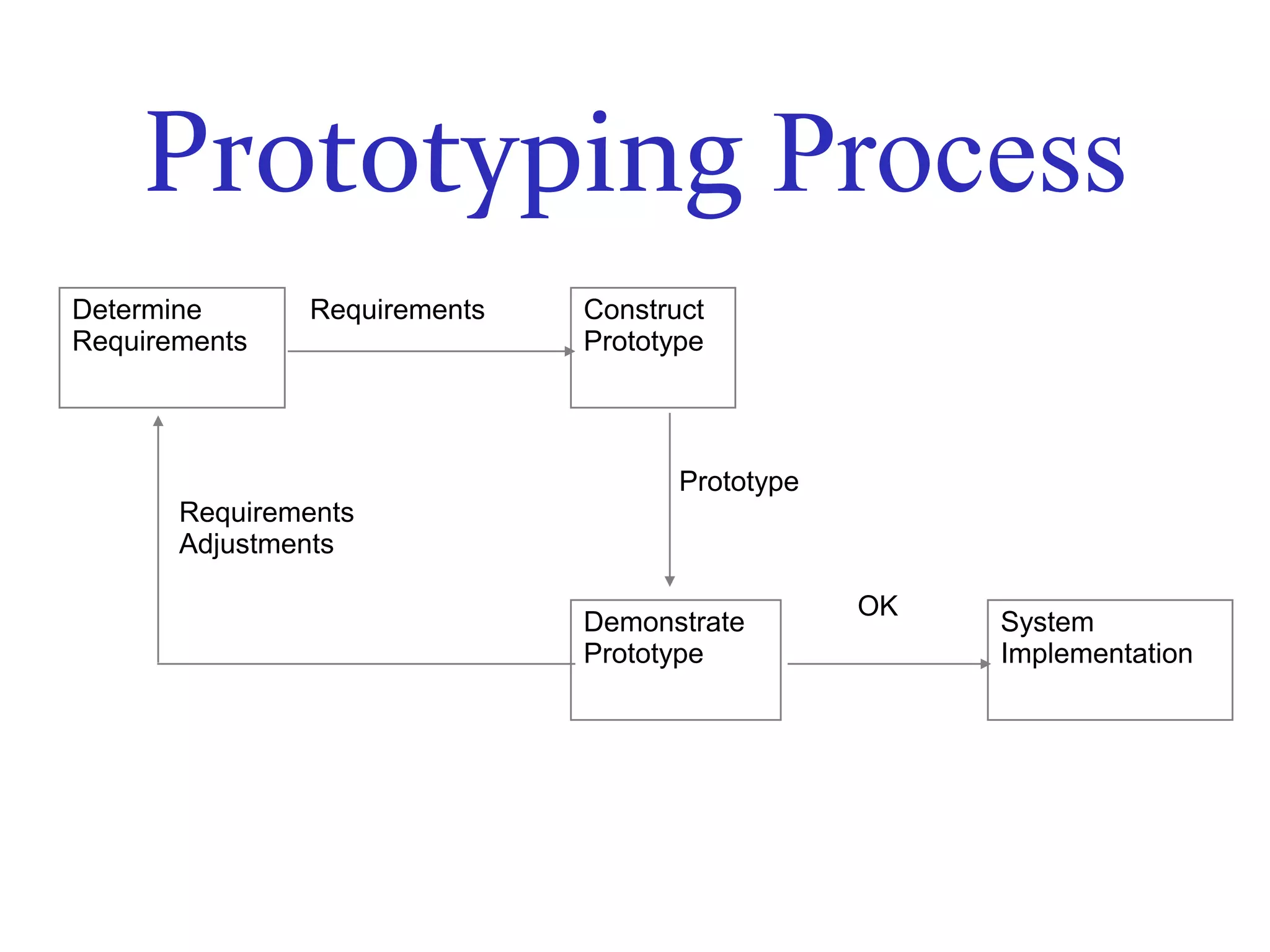
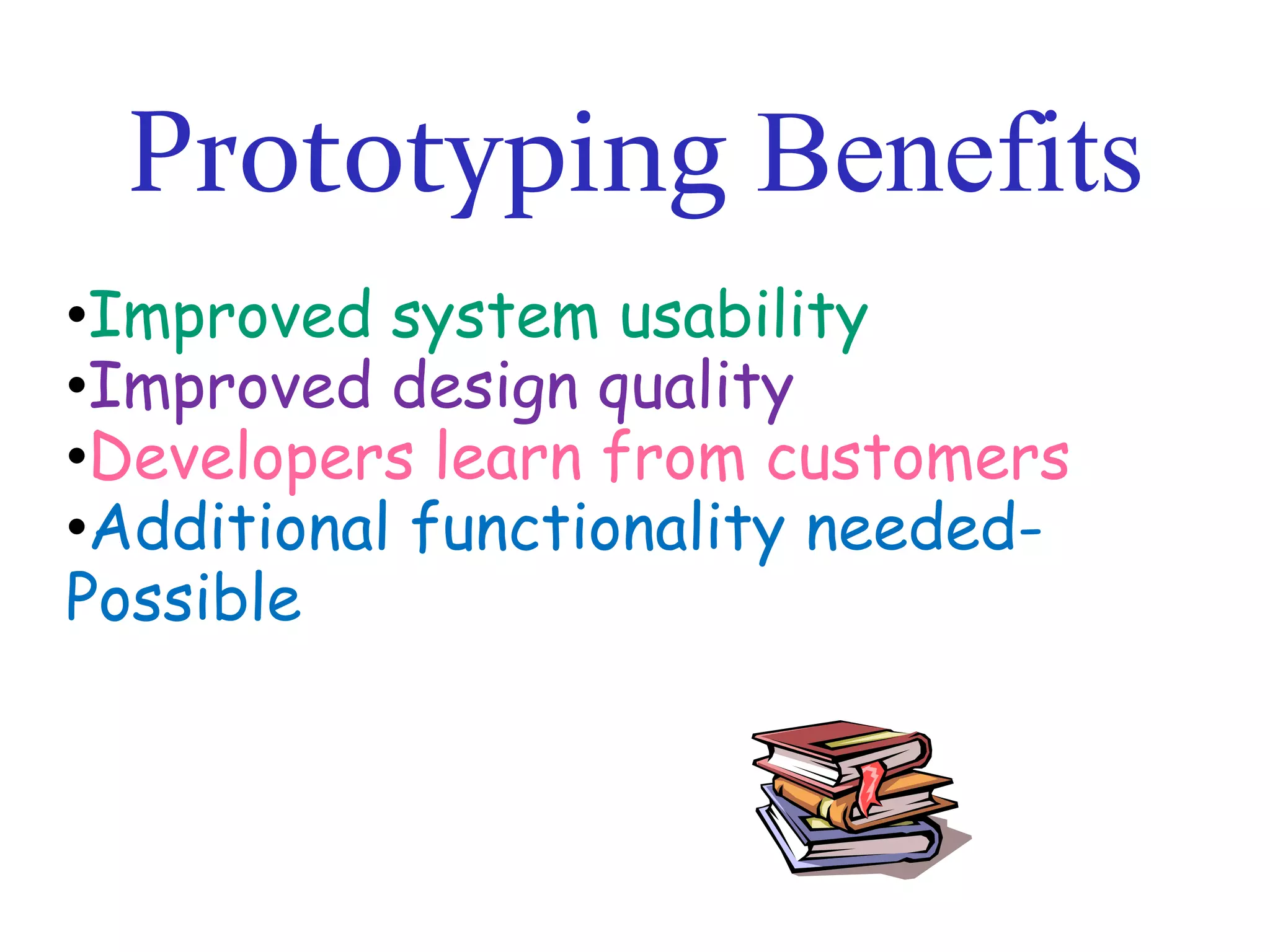
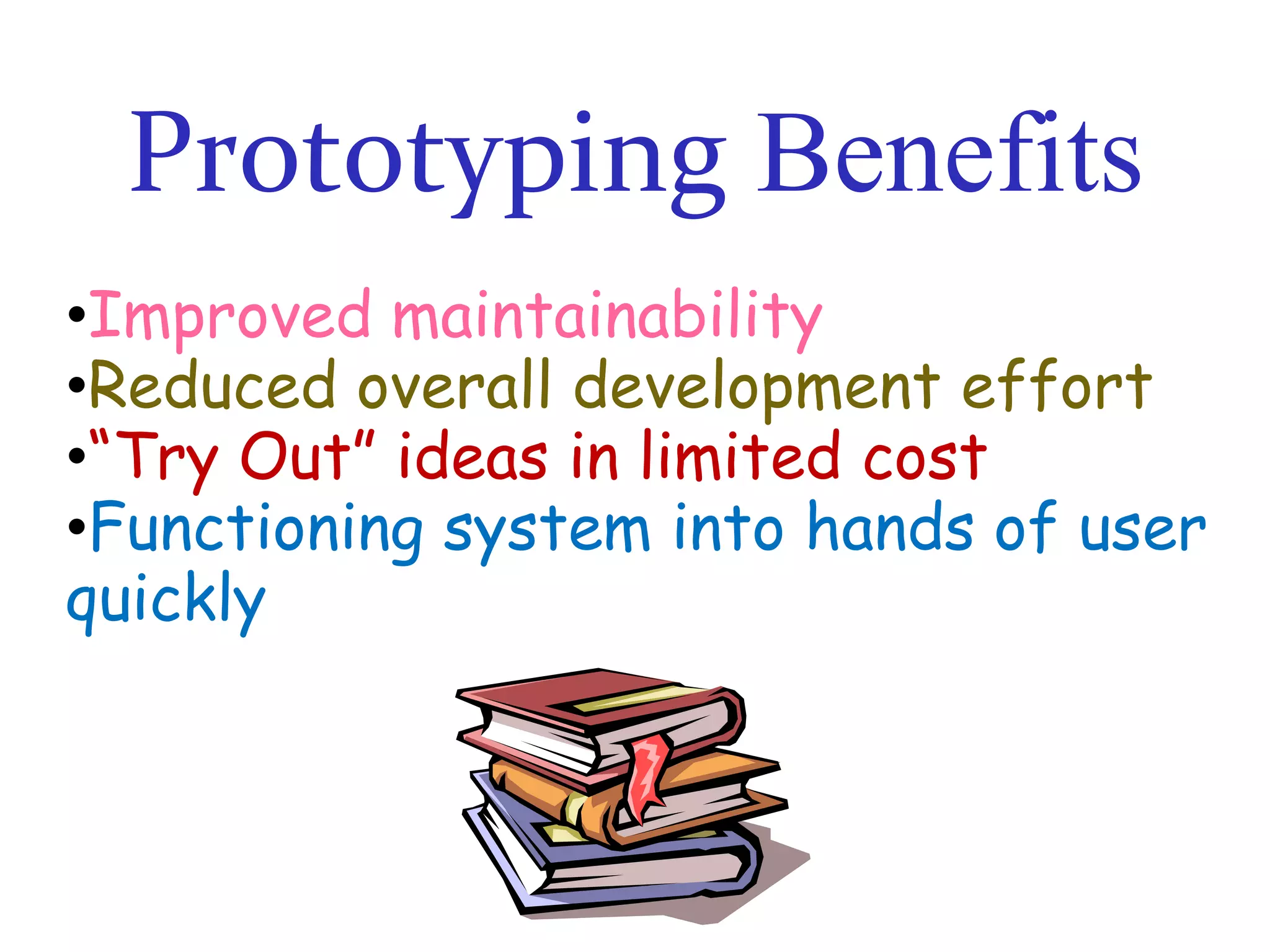
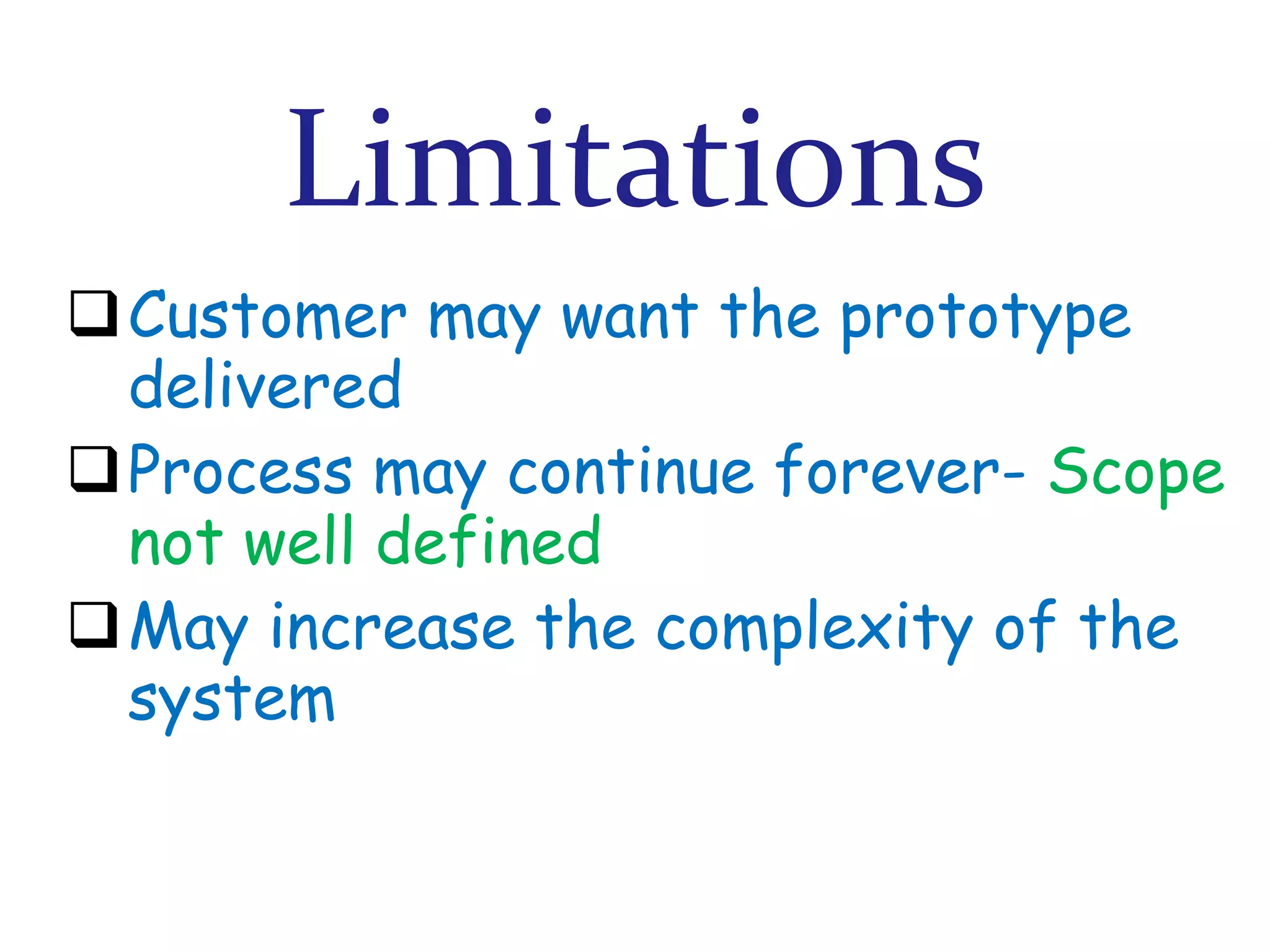
The document discusses prototyping as a software development approach. It involves rapidly creating an initial version of the system (a prototype) to validate requirements with customers and refine them. The prototype may not include all functionality but allows users to experiment and provide feedback to improve the requirements. The process then iterates, revising the prototype based on this feedback until the final system is developed.