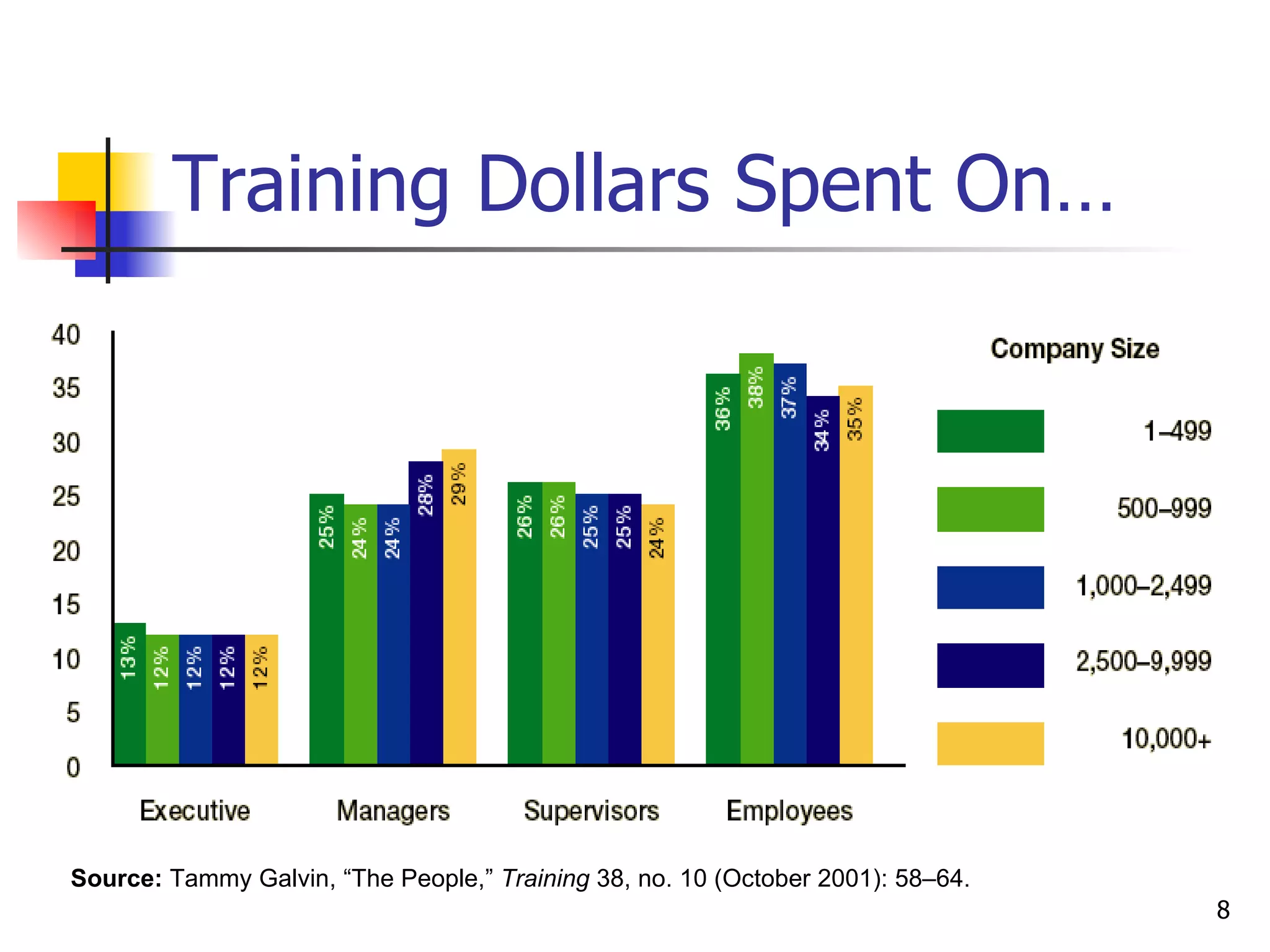
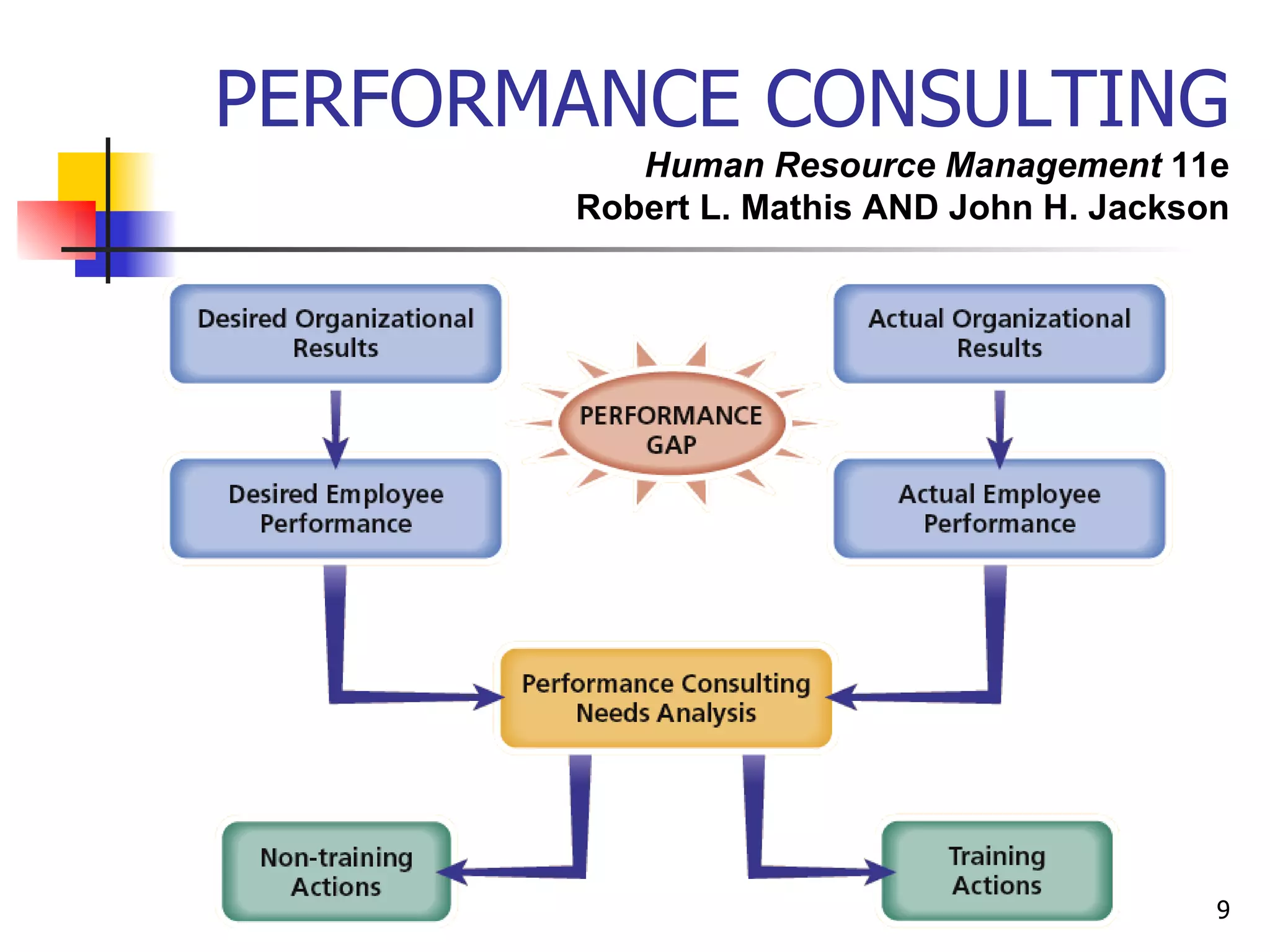
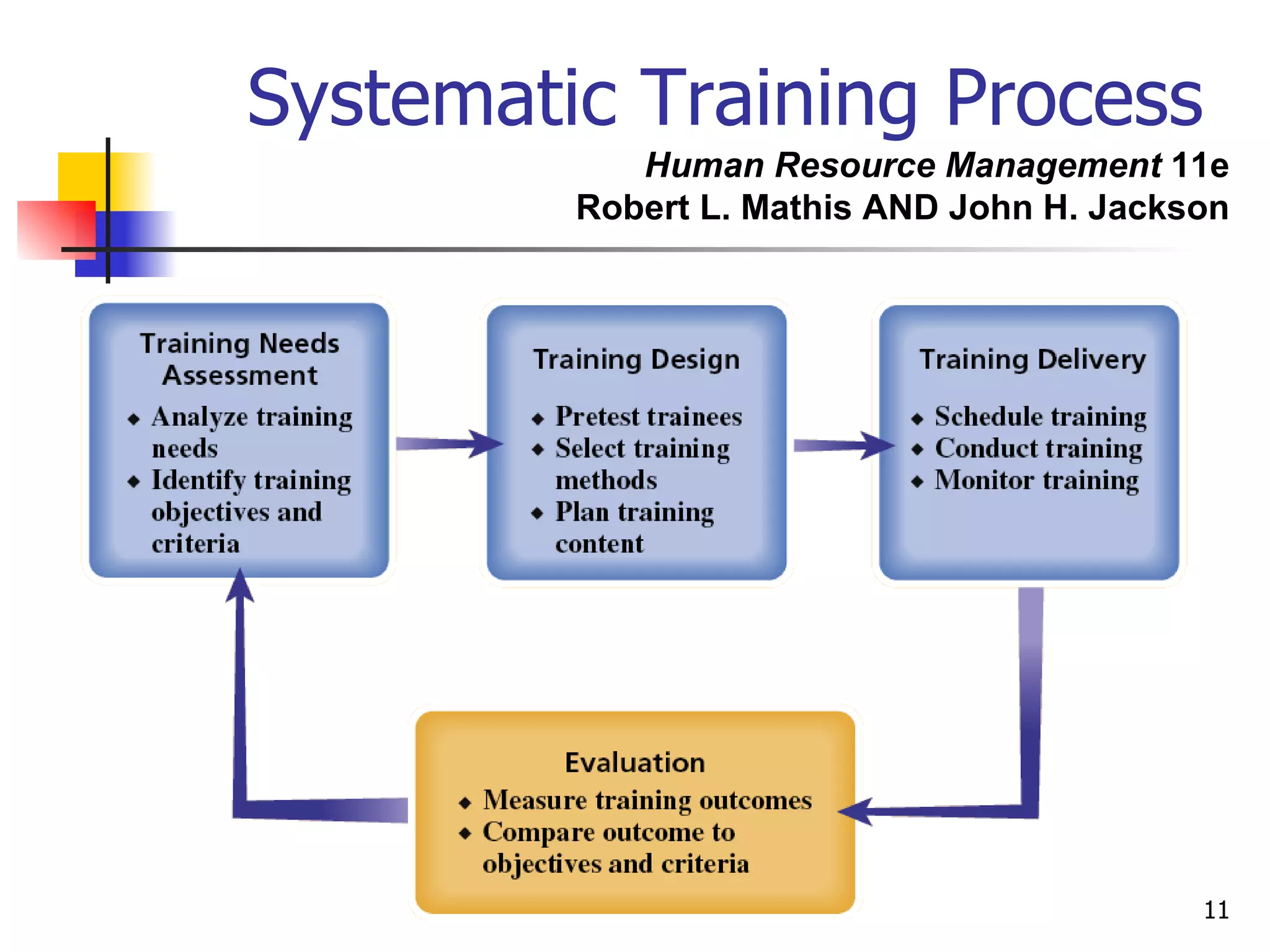
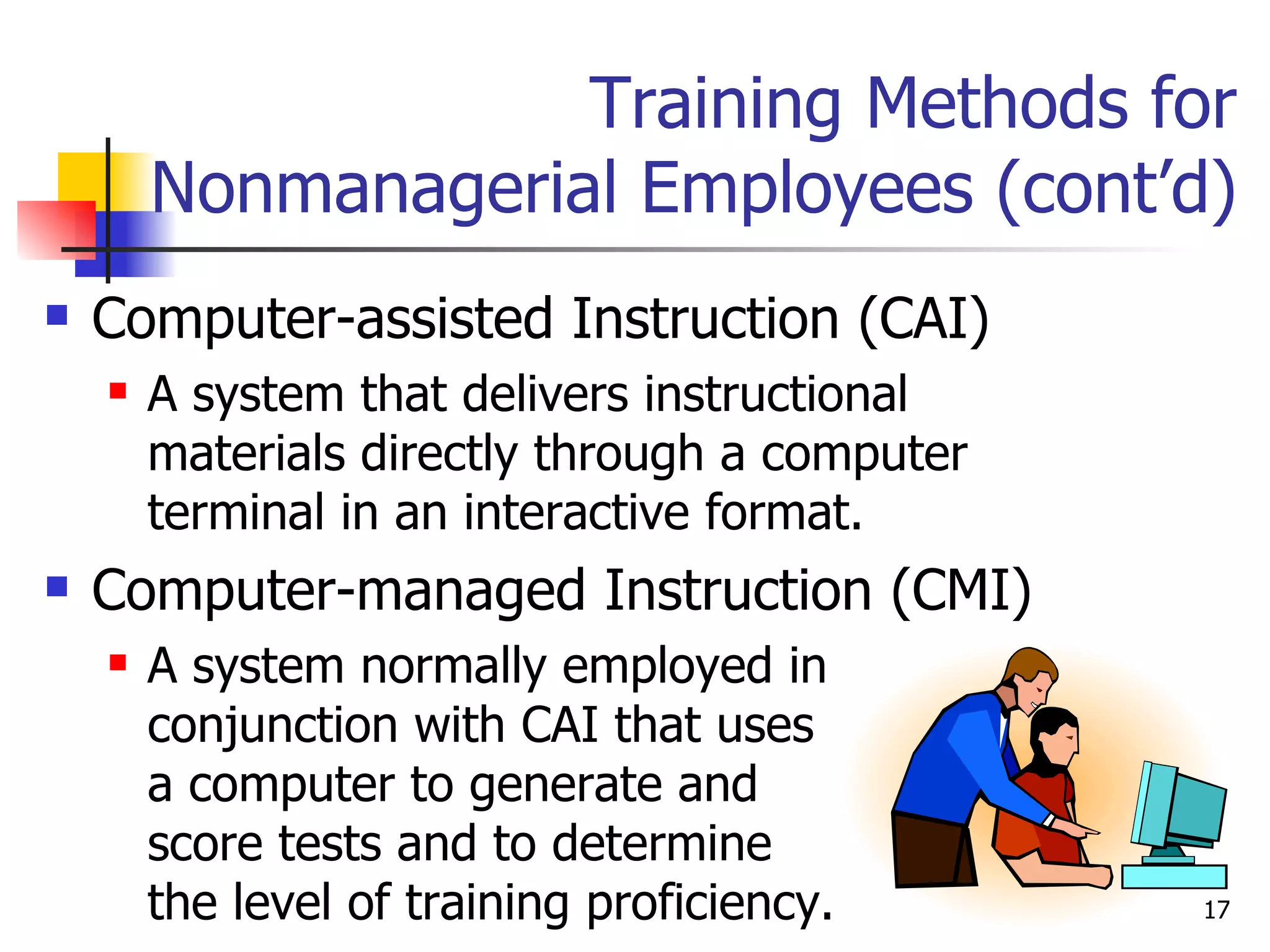
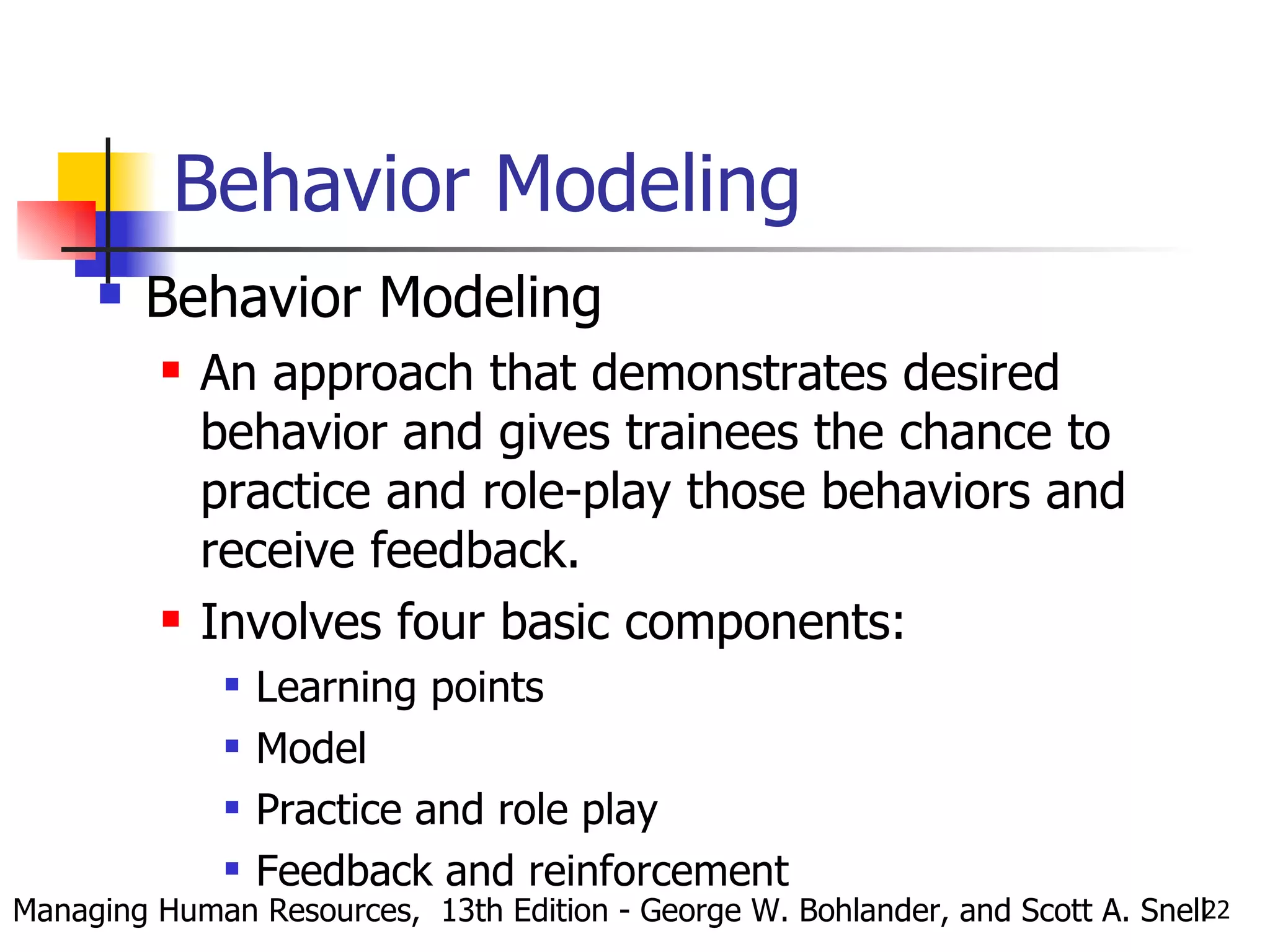
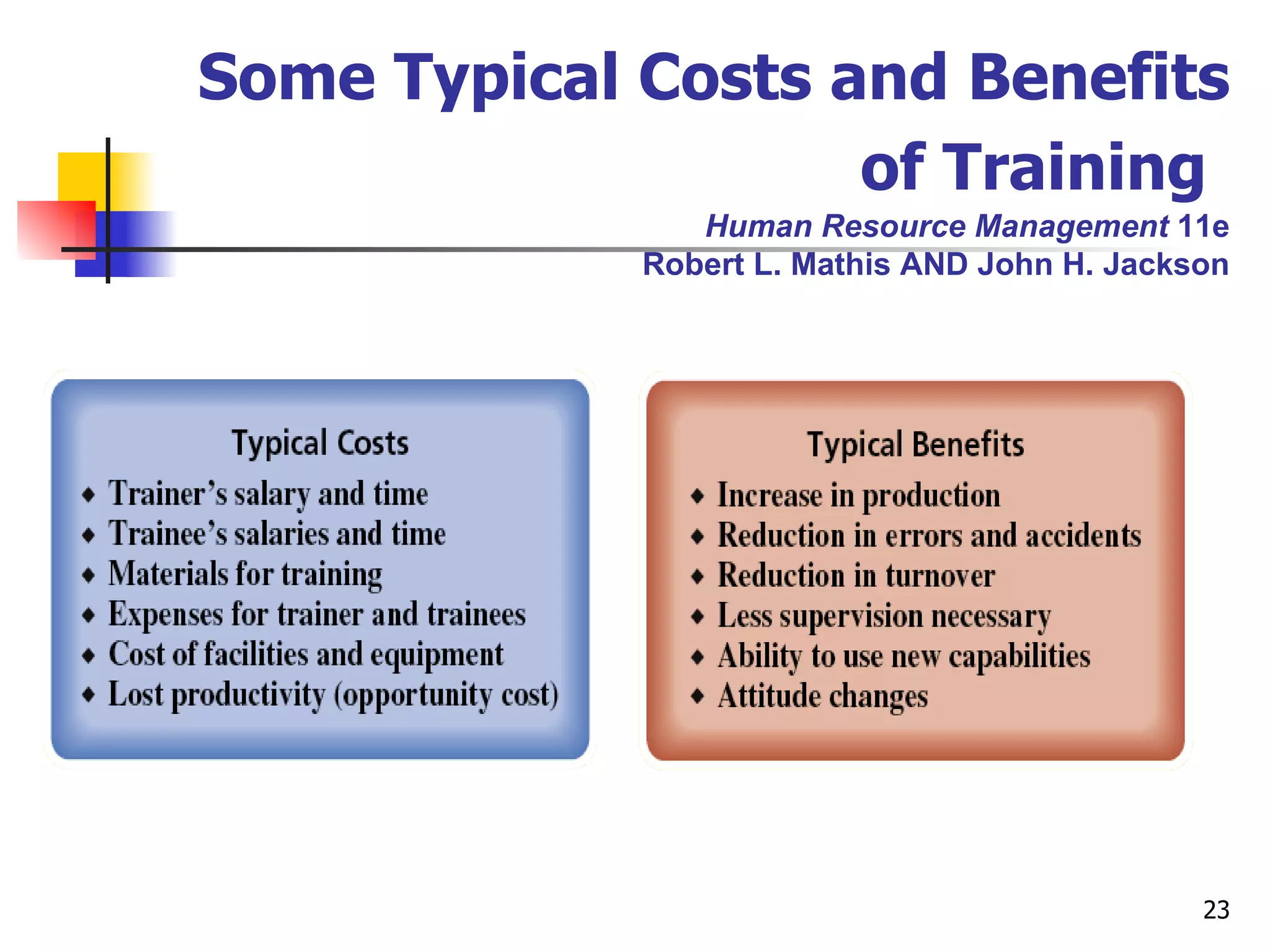
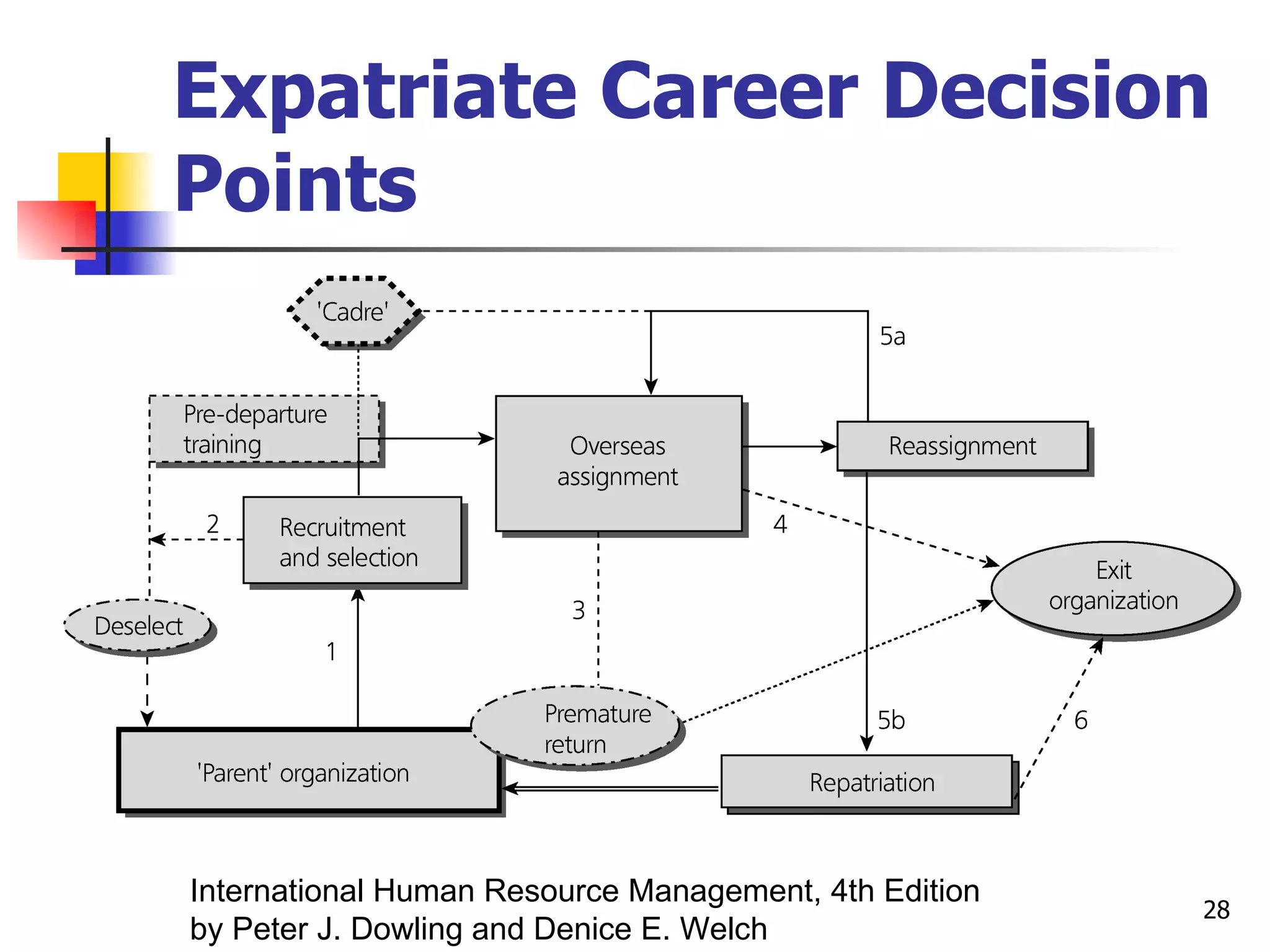
The document discusses training and development in organizations. It defines training as efforts to improve current job skills and development as efforts to increase abilities for future roles. It discusses different training methods for both non-managerial and managerial employees, such as on-the-job training, apprenticeships, seminars, and role playing. It also covers considerations for designing training programs and evaluating their effectiveness.