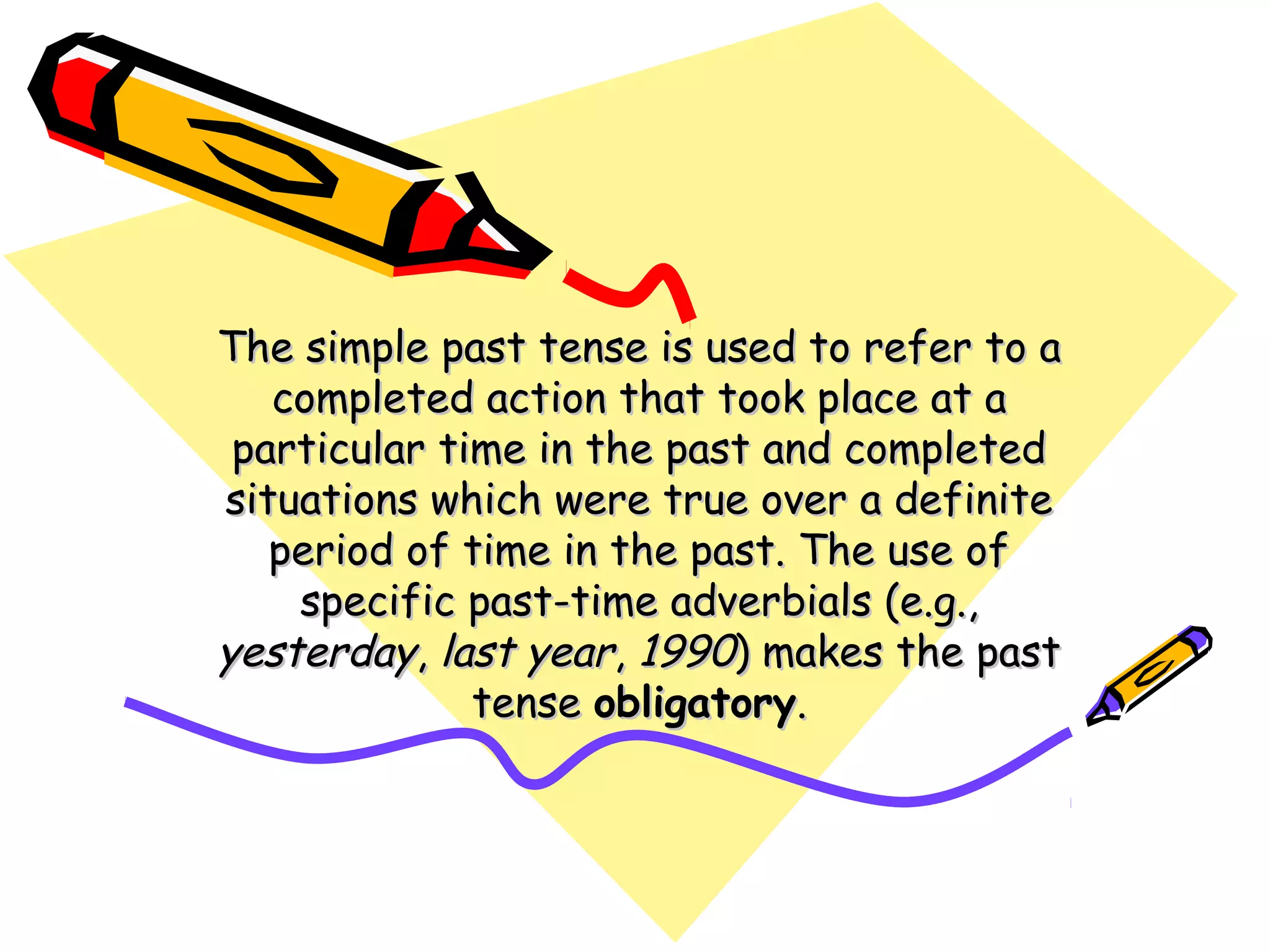
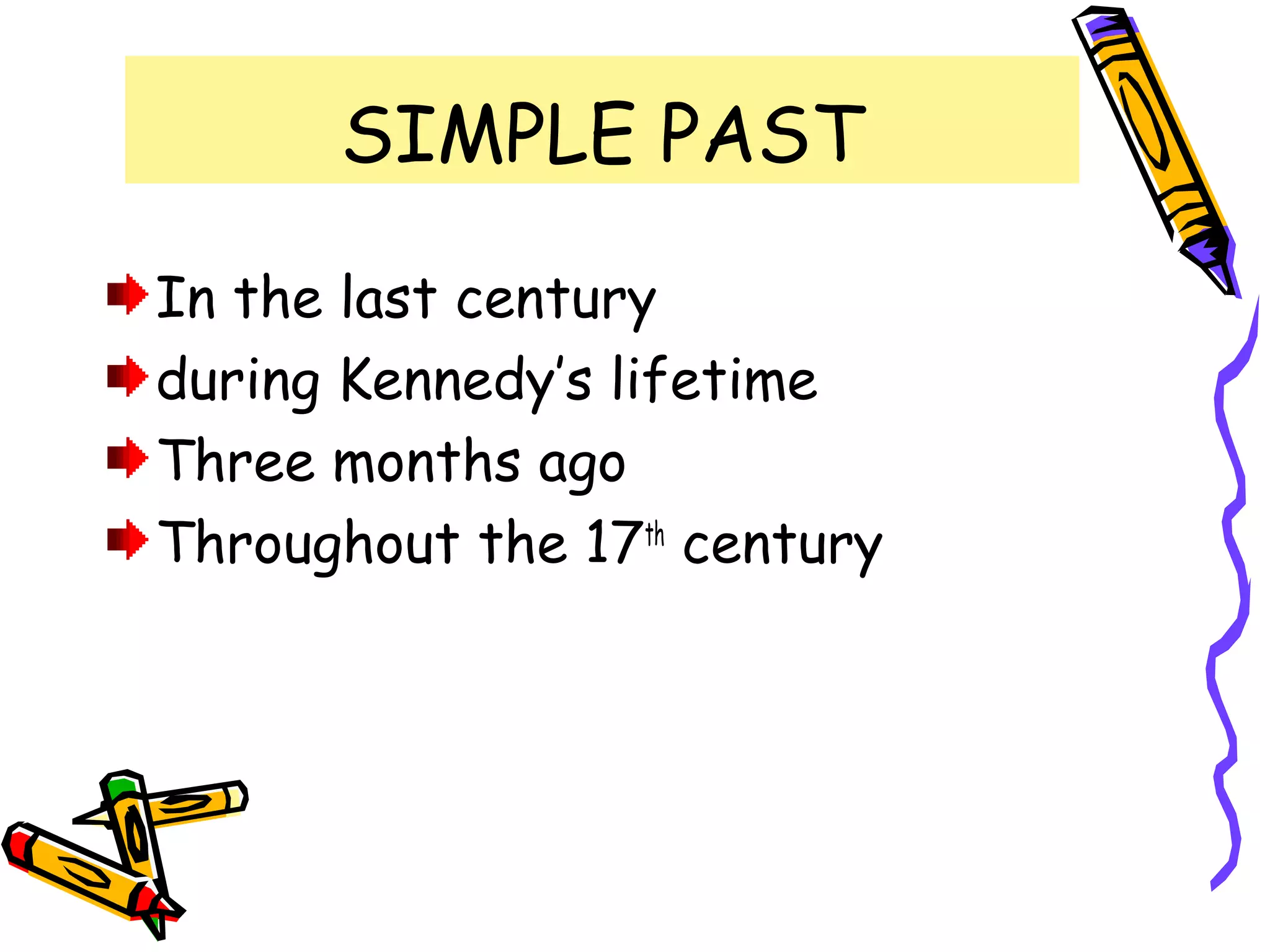
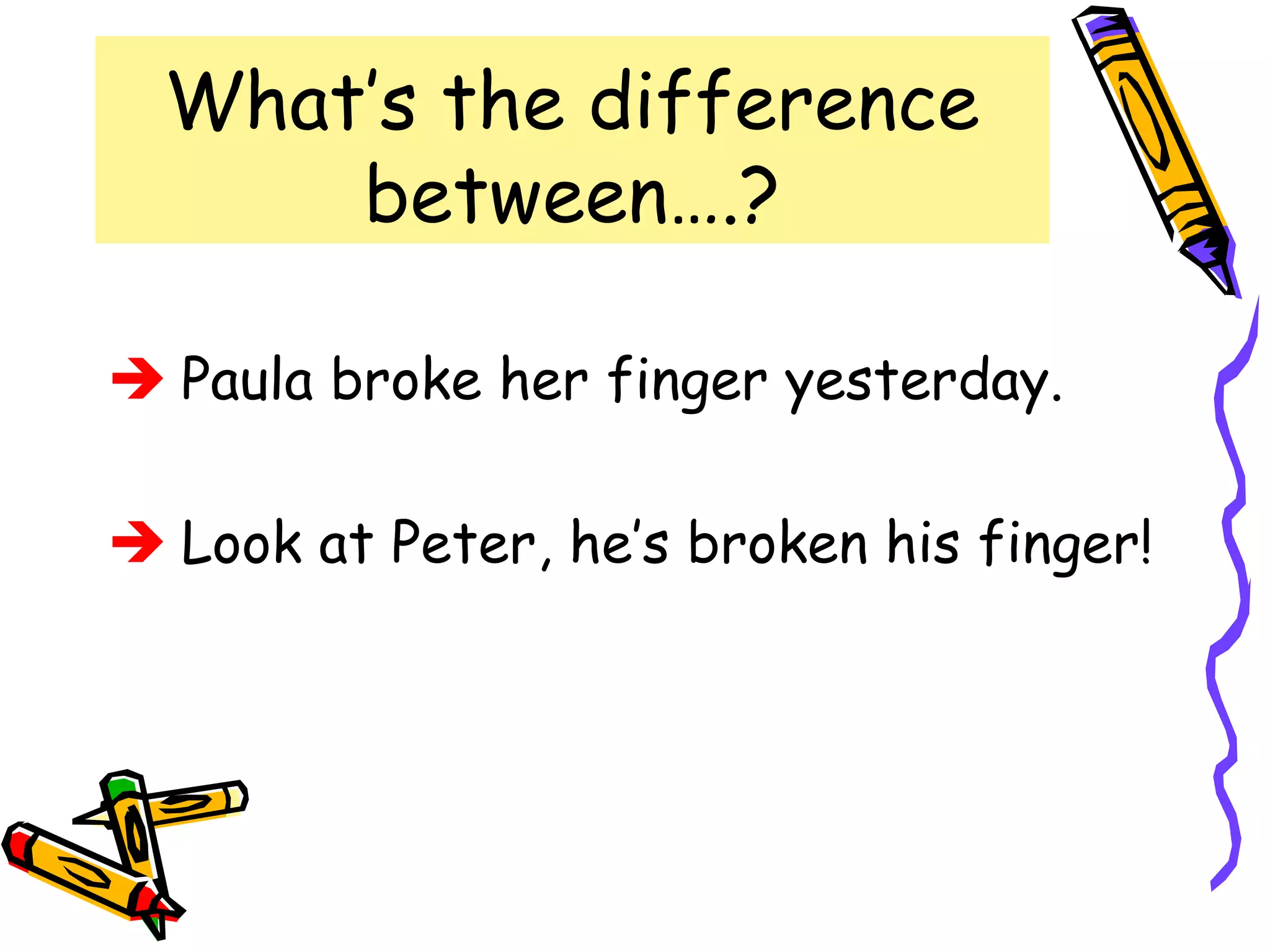
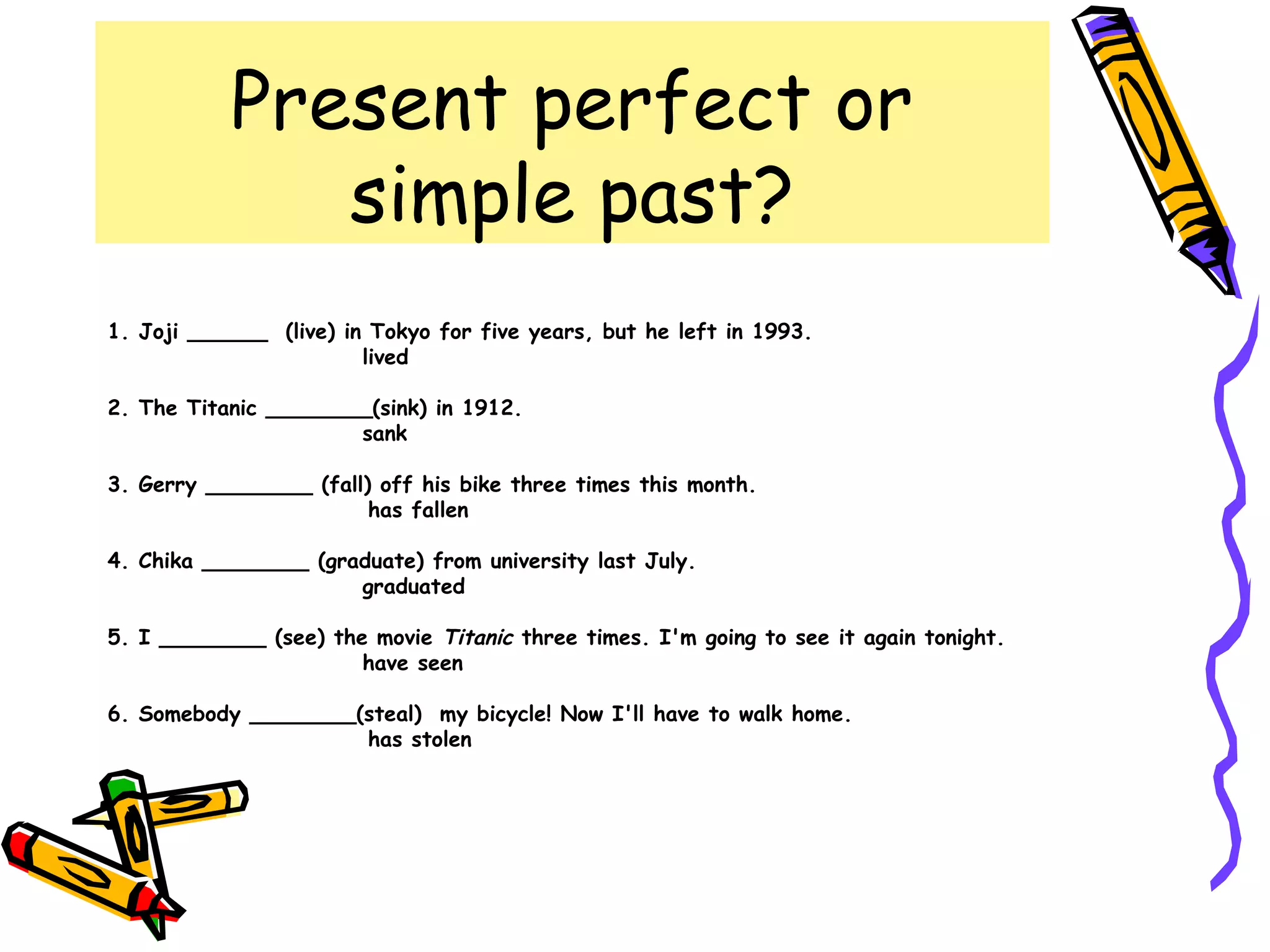
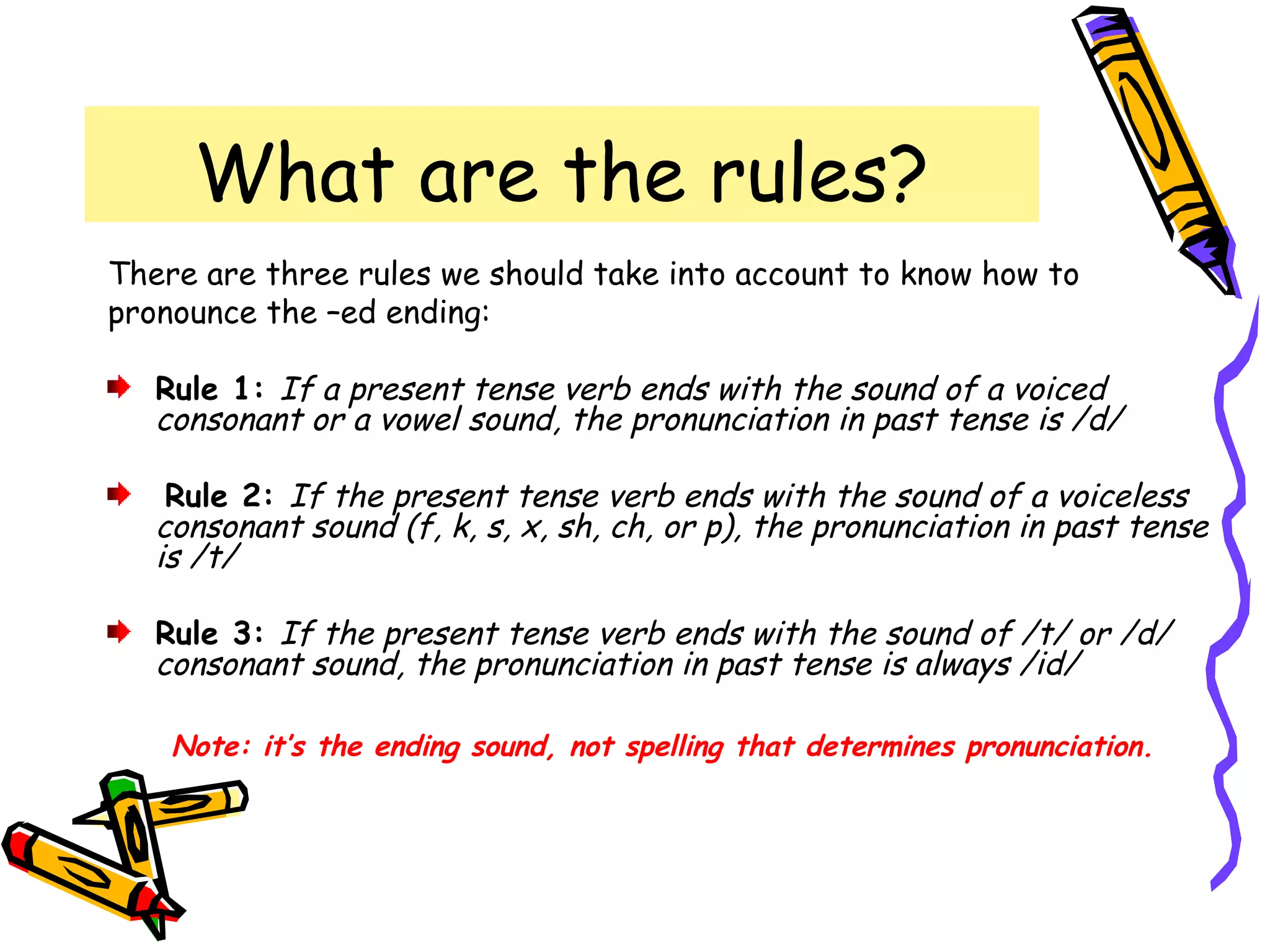
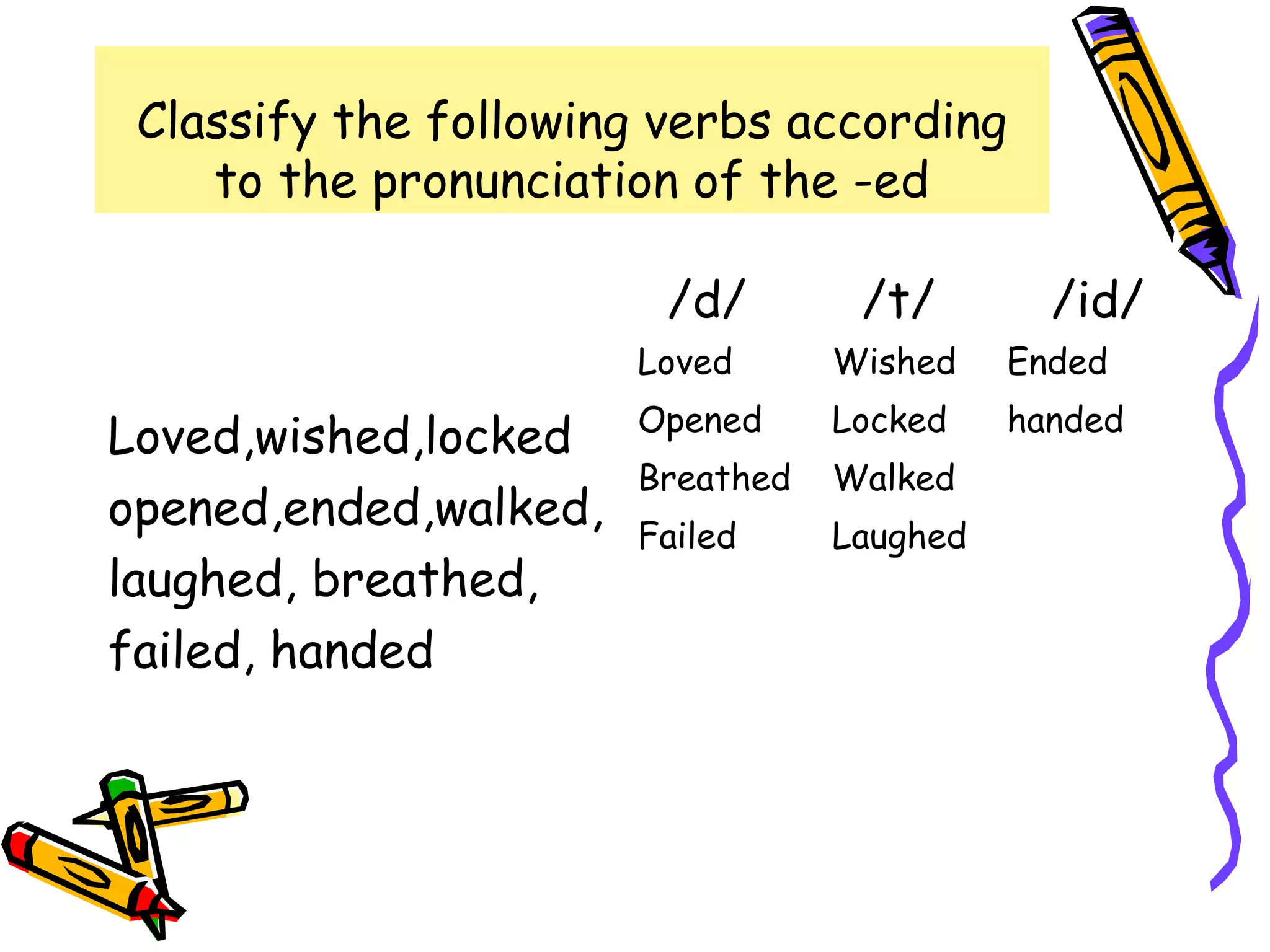
The document discusses the differences between the present perfect and past simple tenses. The past simple is used to refer to completed actions or situations that were true over a definite period in the past. The present perfect is used to refer to situations that began in the past but continue in the present, or when the exact time of an event is unknown. Examples are provided to illustrate using each tense with time phrases like "yesterday" or "up to now." Common verbs are classified by their pronunciation when using the past tense "-ed" ending.