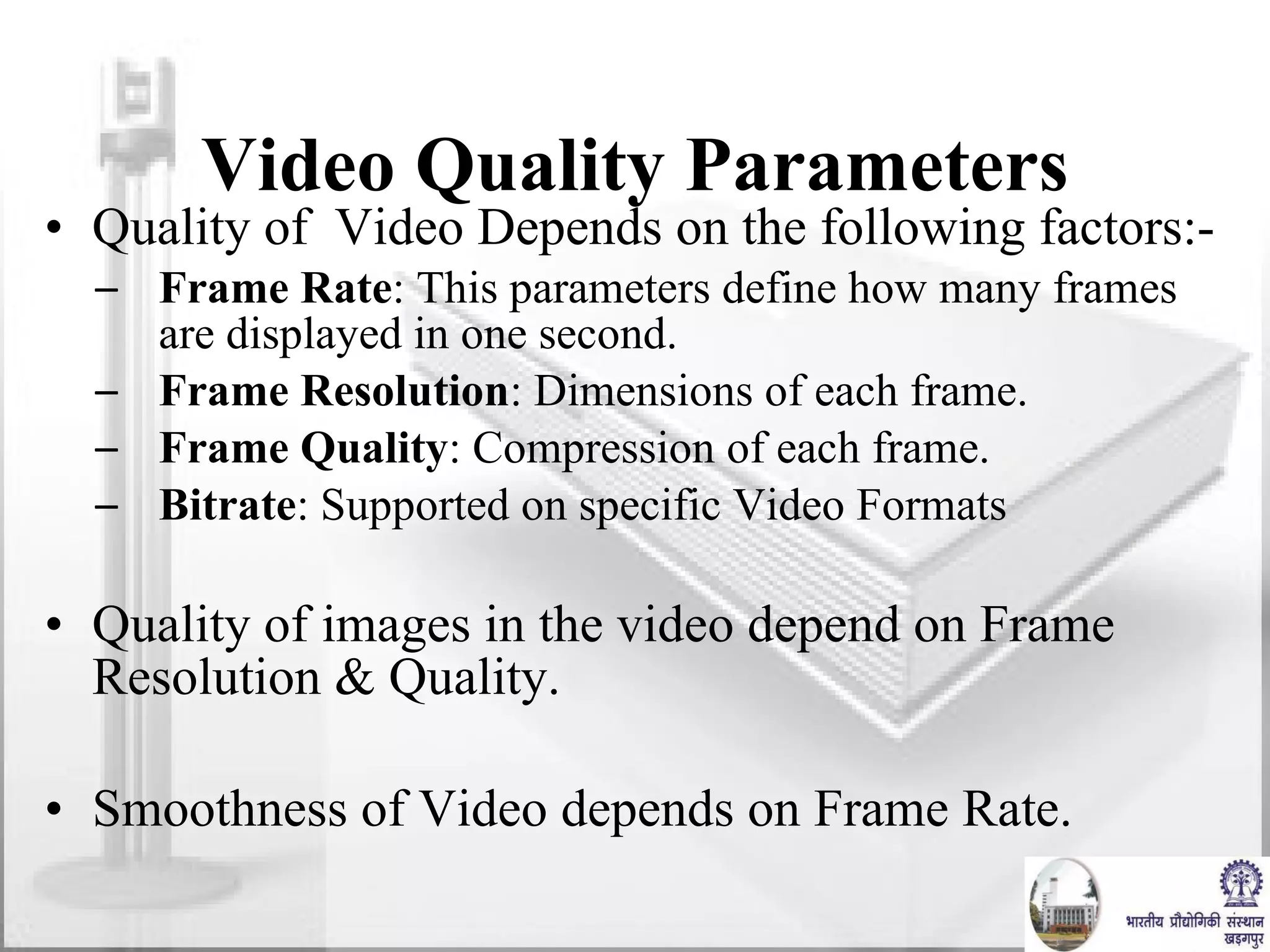
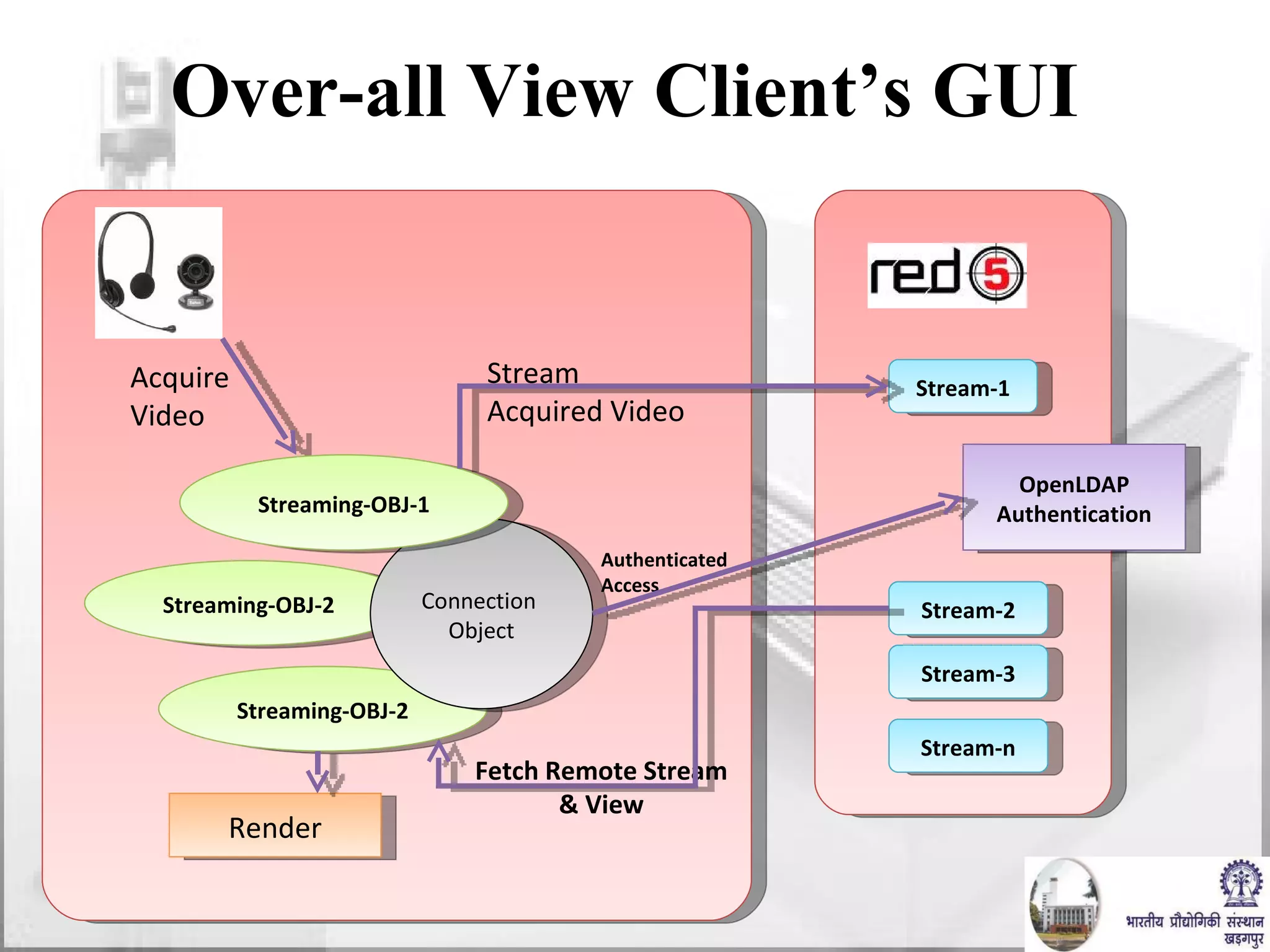
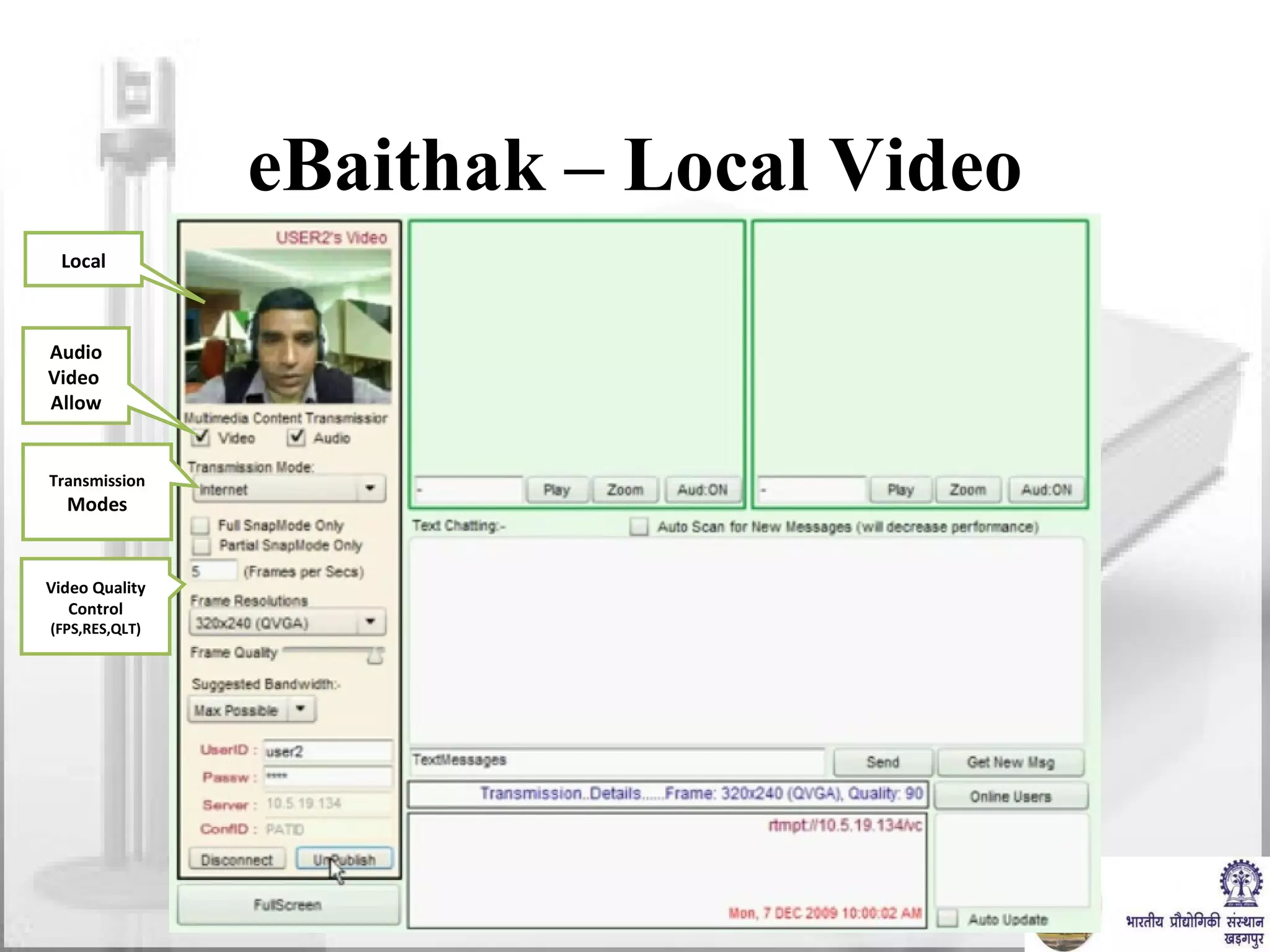
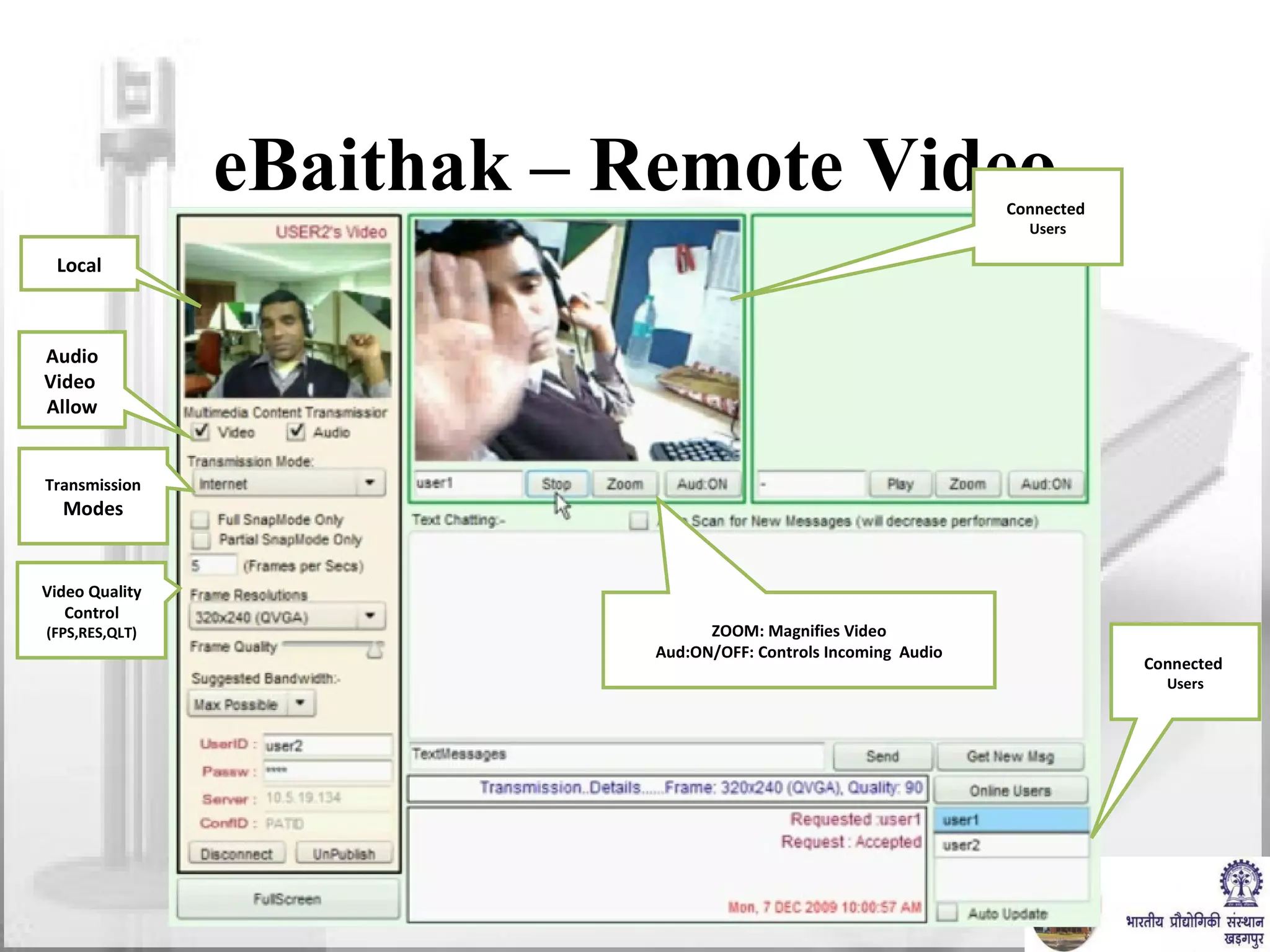
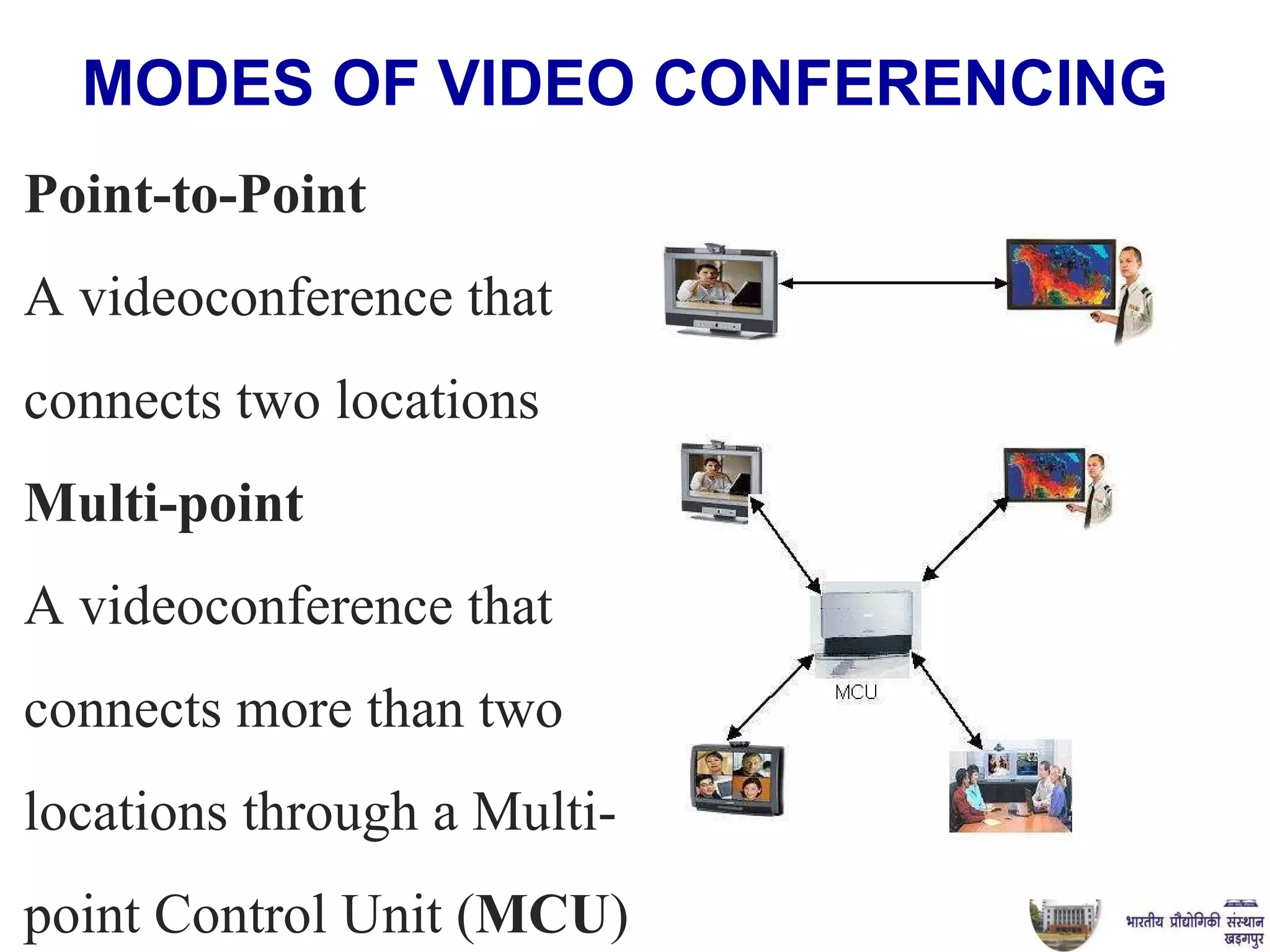
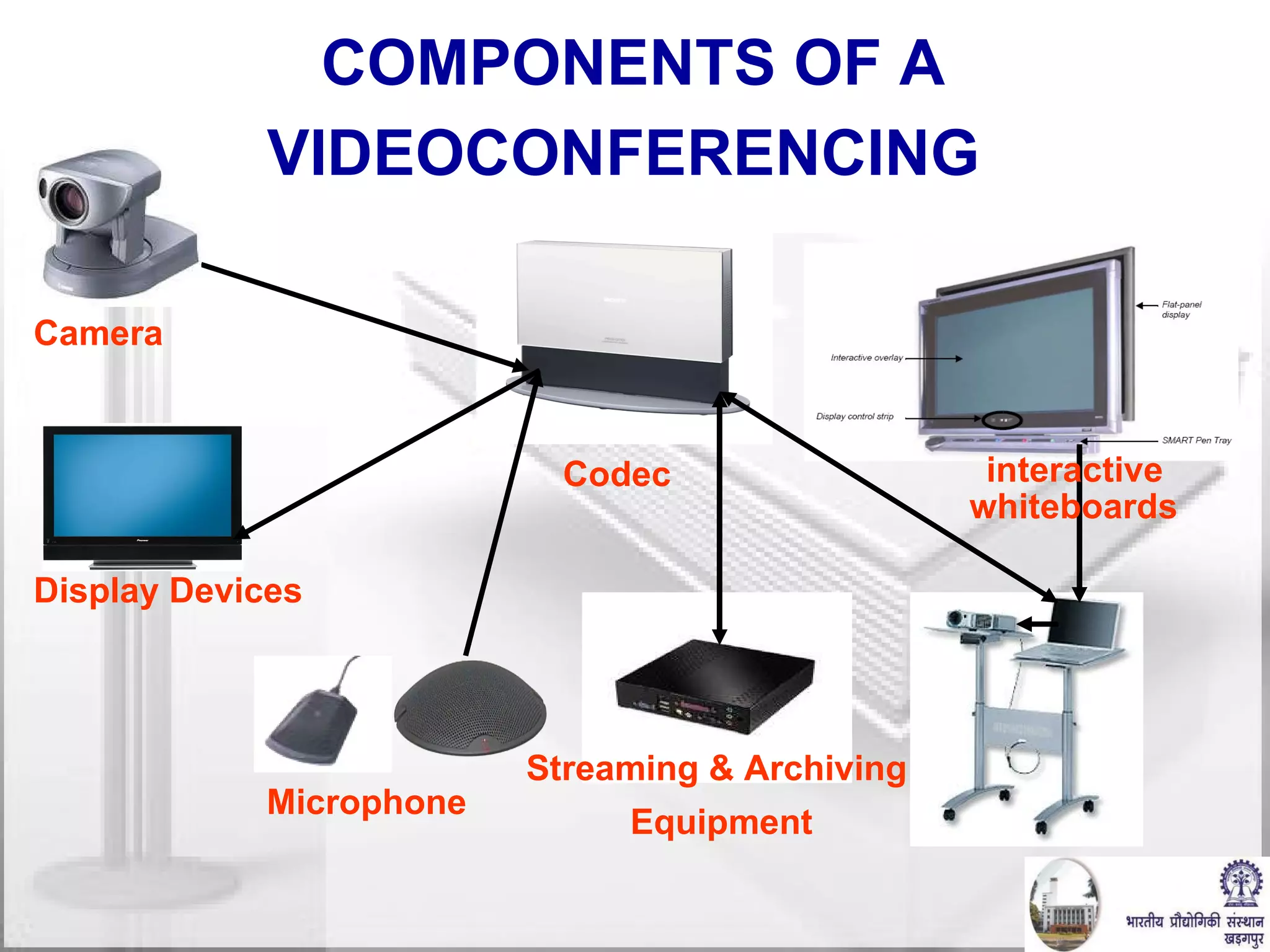
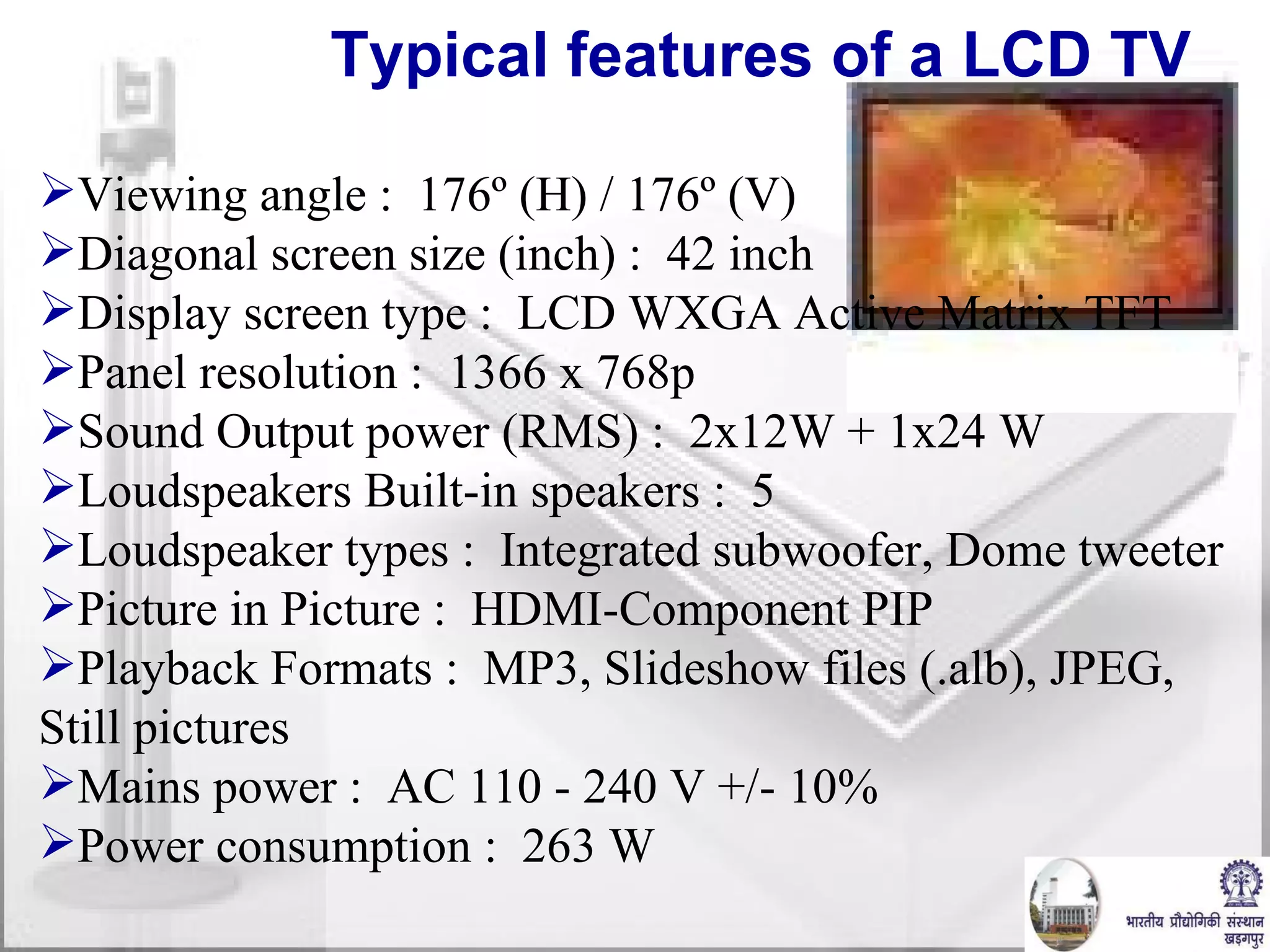
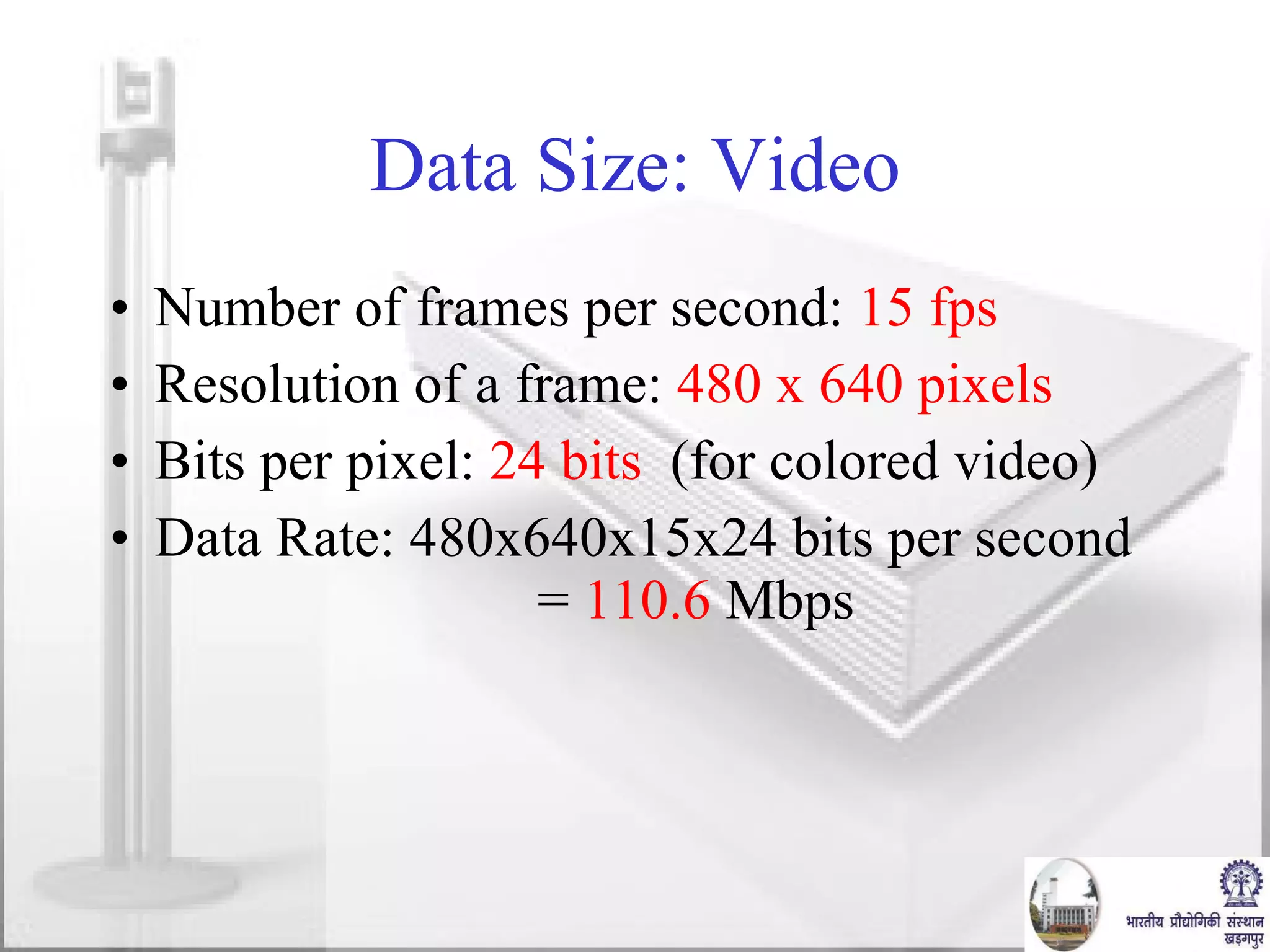
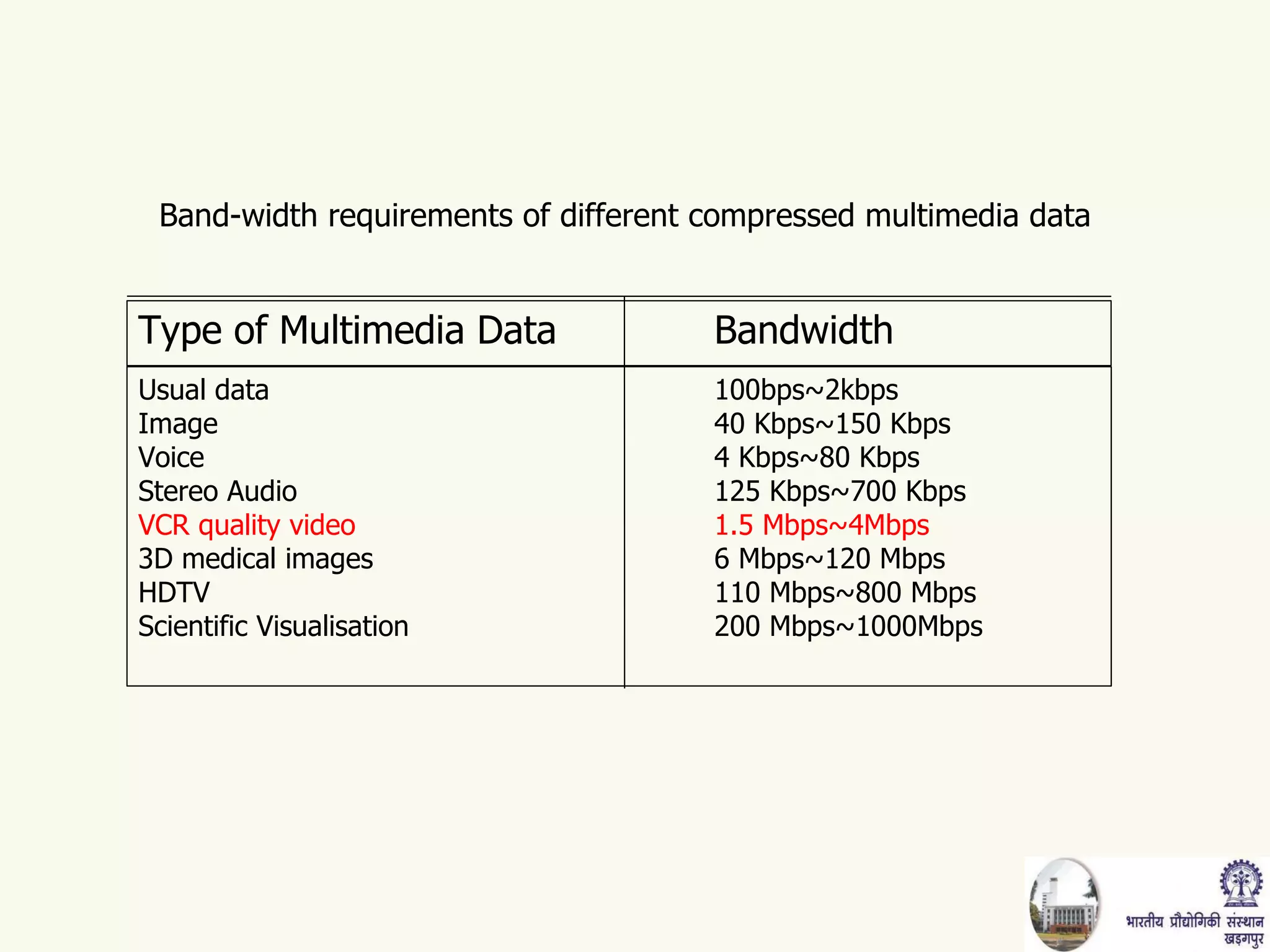
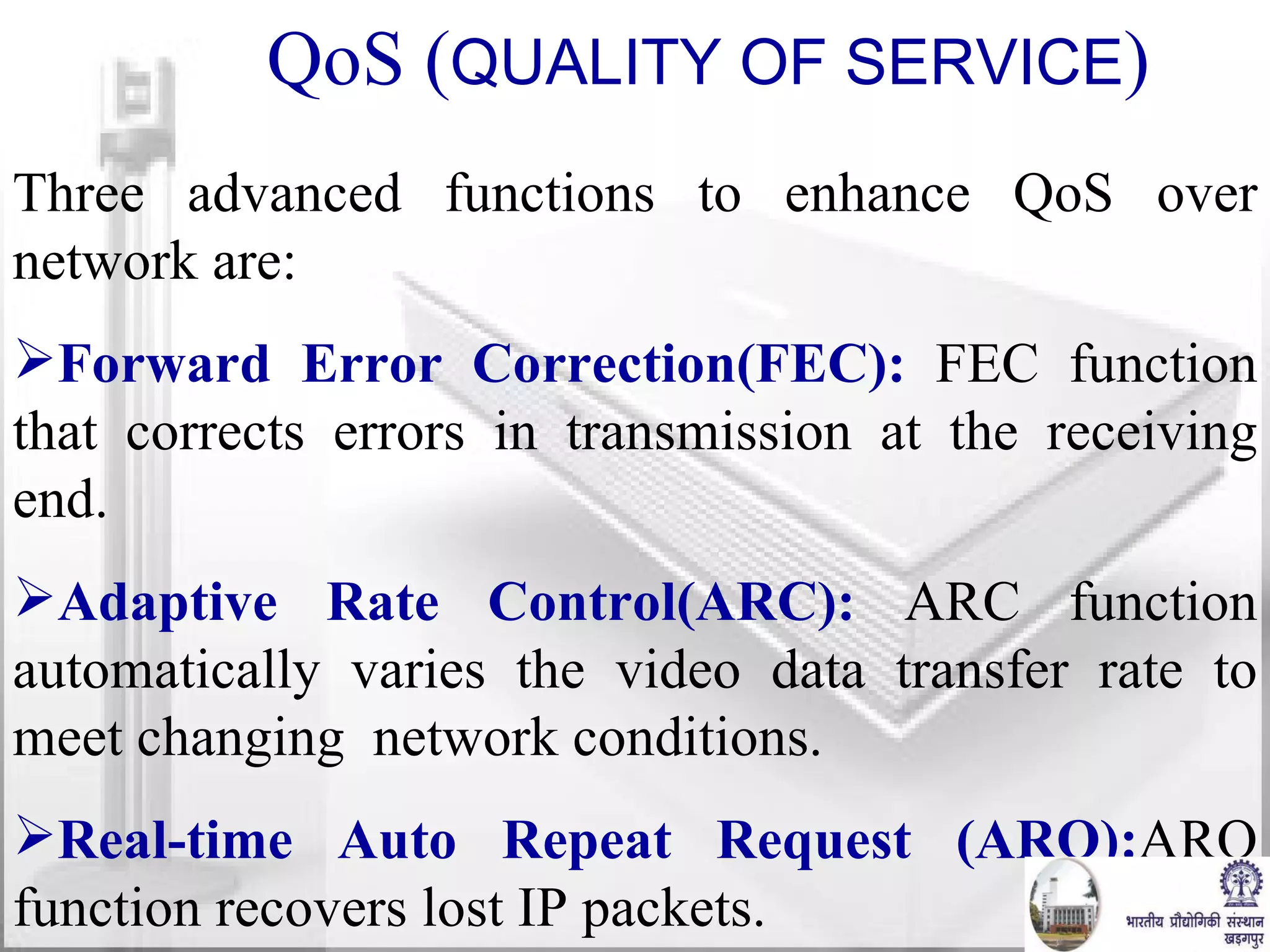
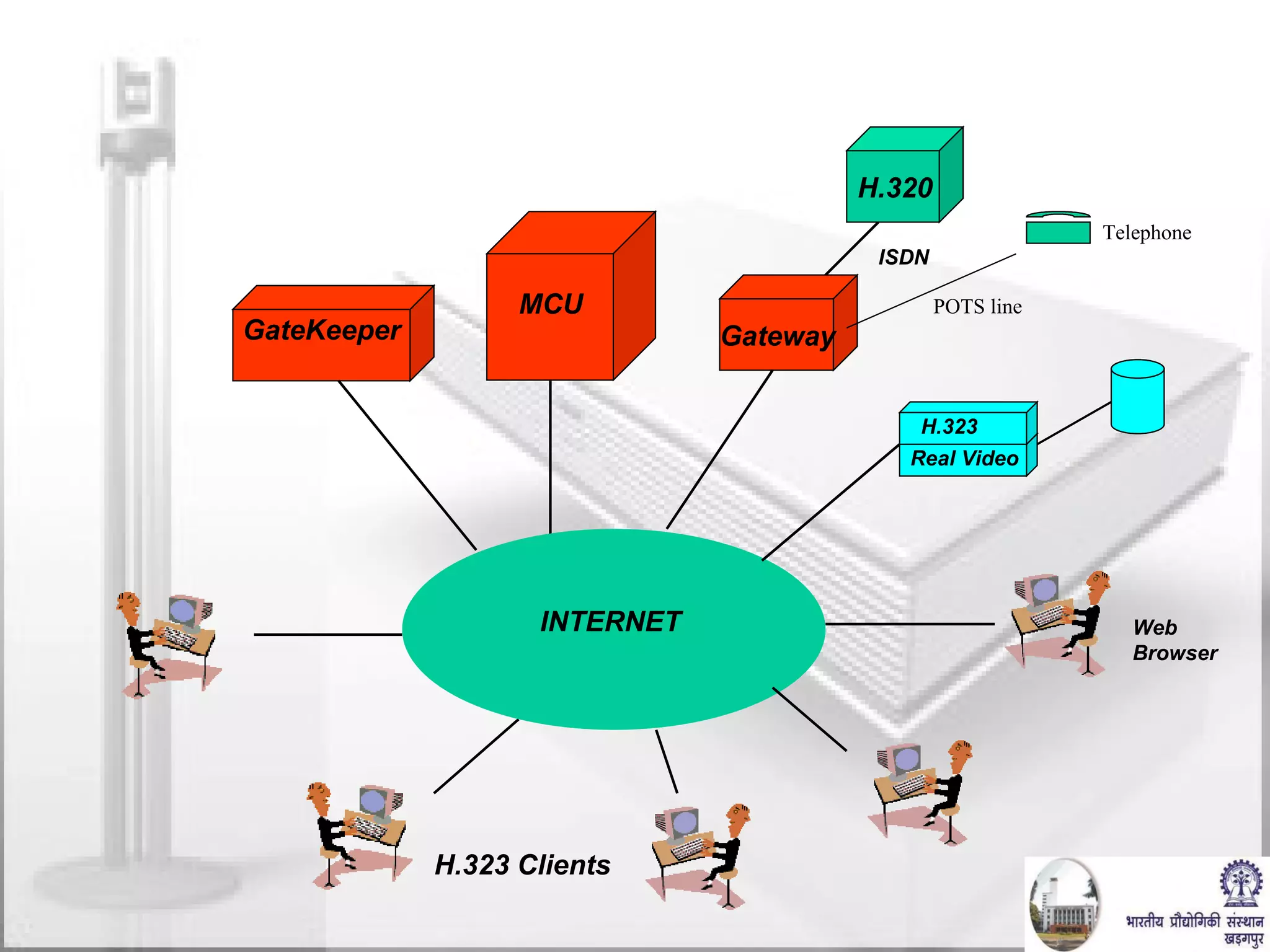
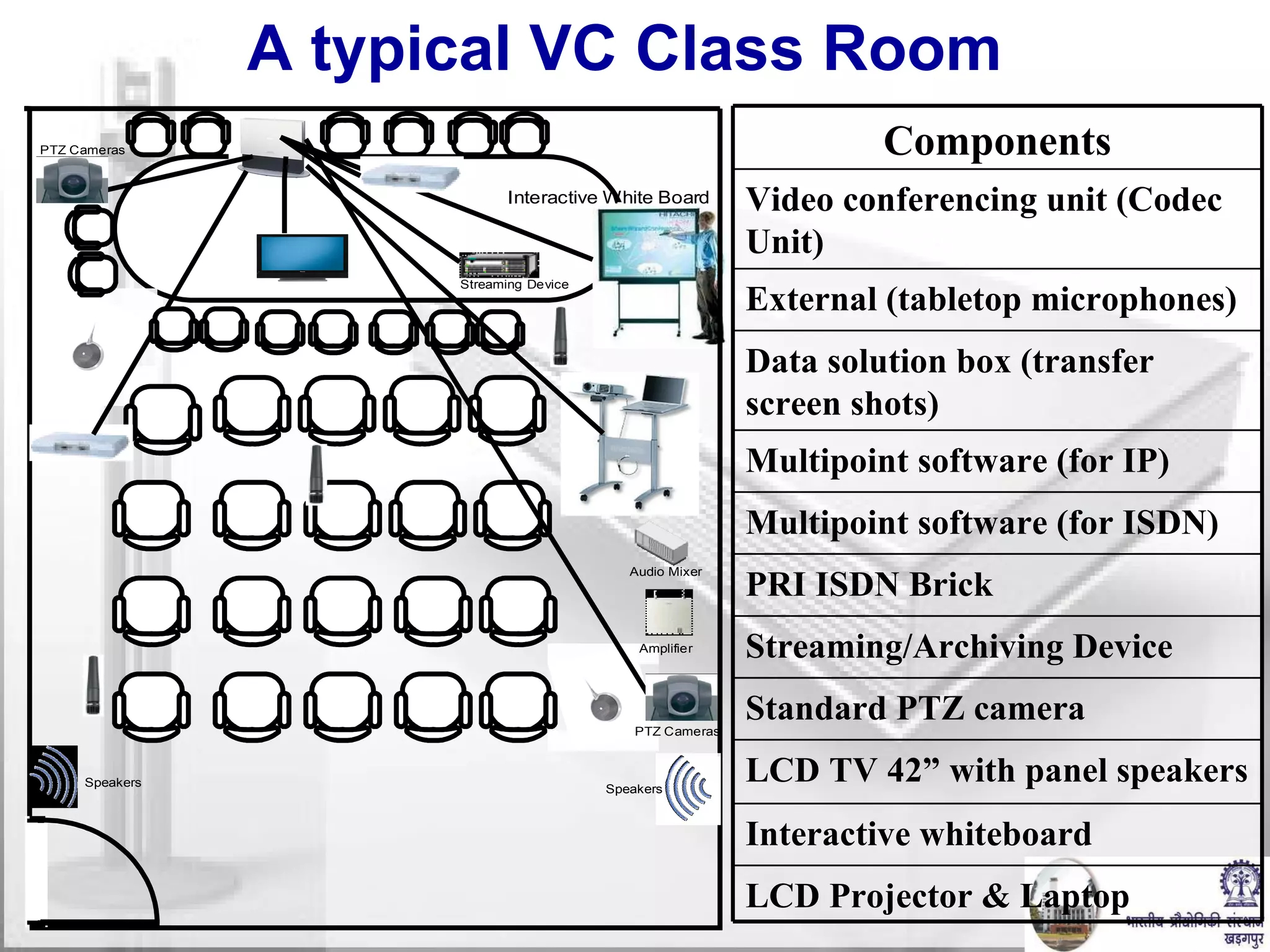
The document discusses video conferencing fundamentals and applications. It covers topics like modes of video conferencing, components, technologies, standards, protocols, bandwidth requirements, quality of service factors, challenges, and the eBaithak desktop video conferencing system developed at IIT Kharagpur.












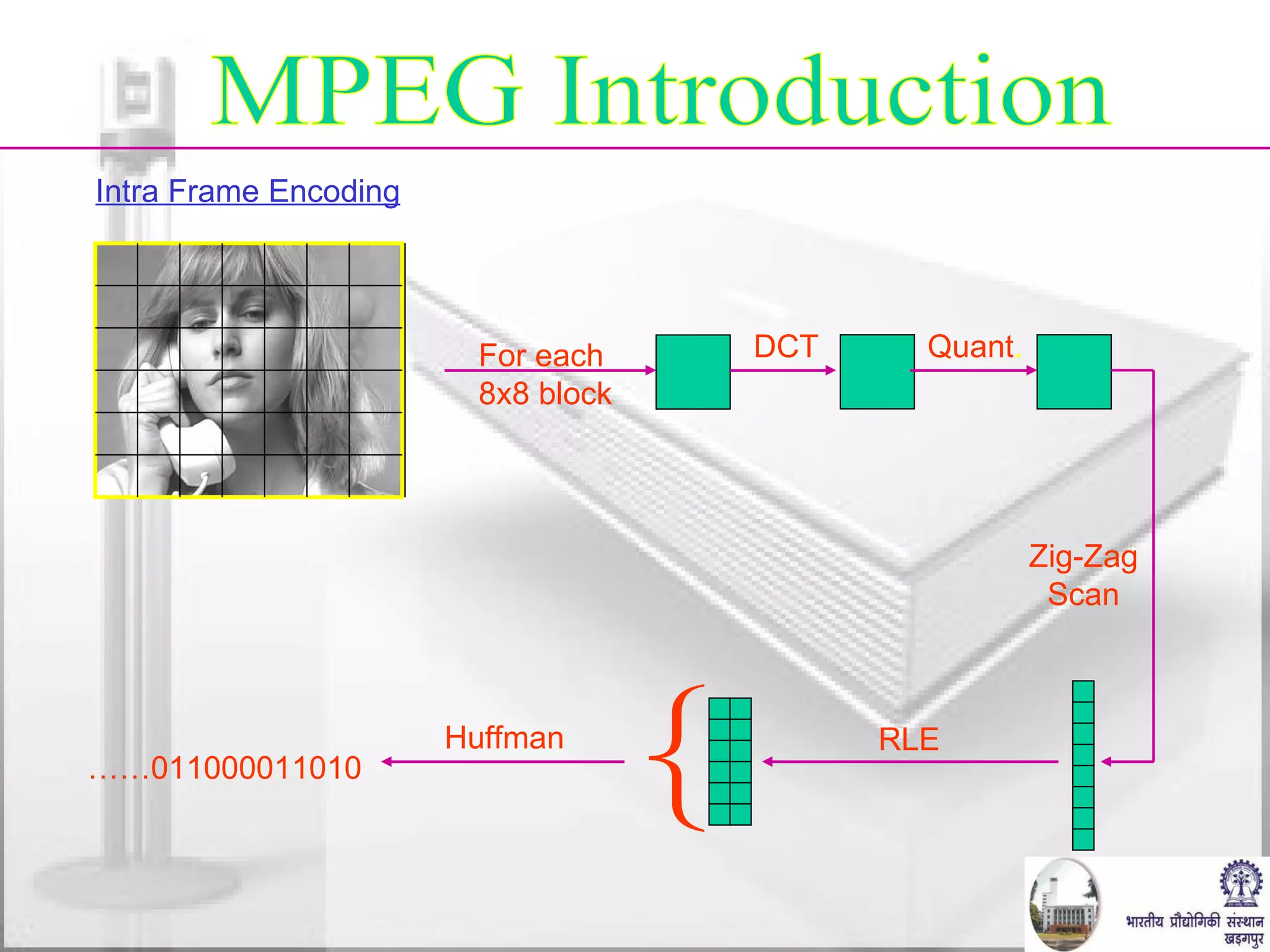
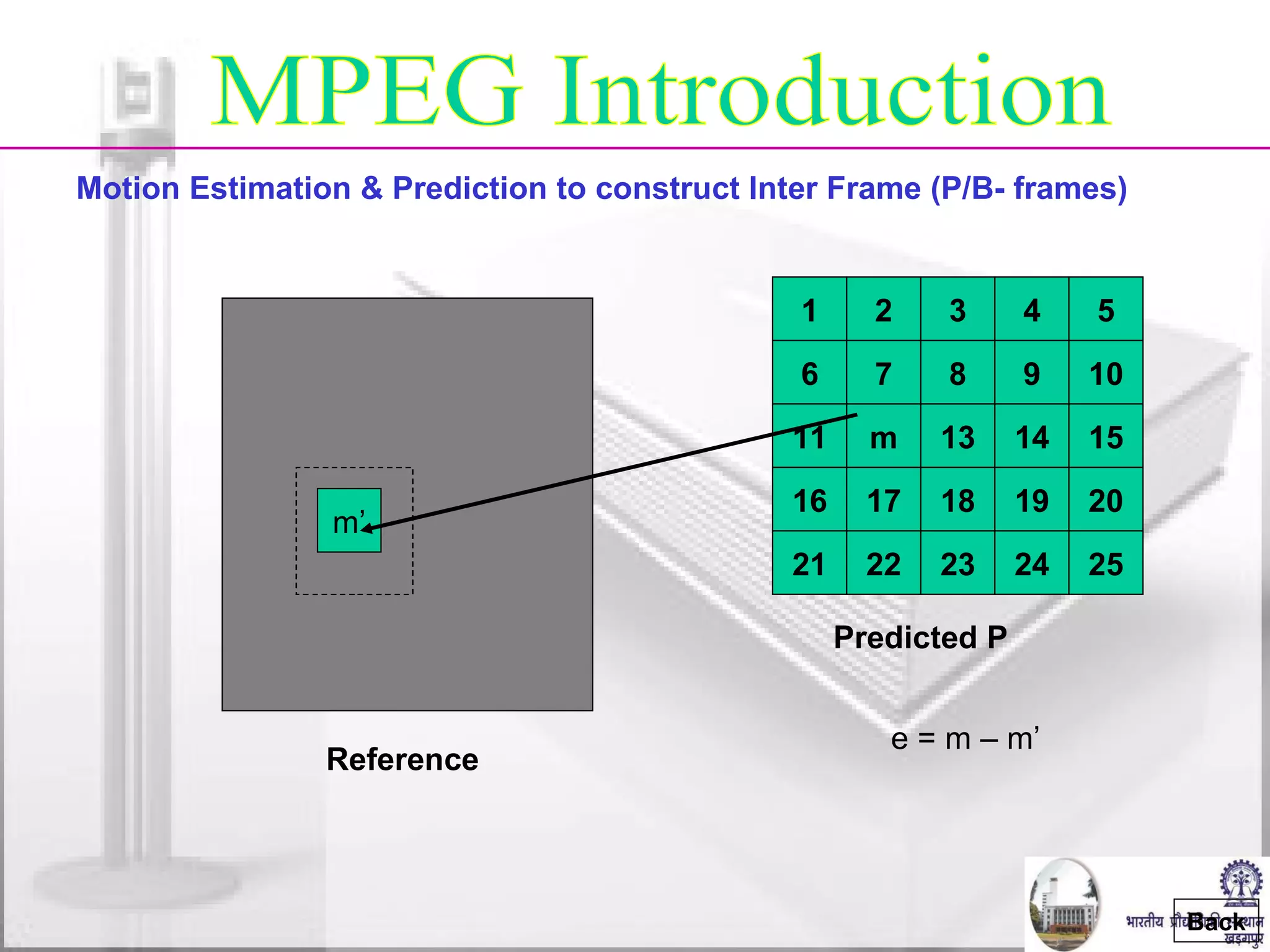
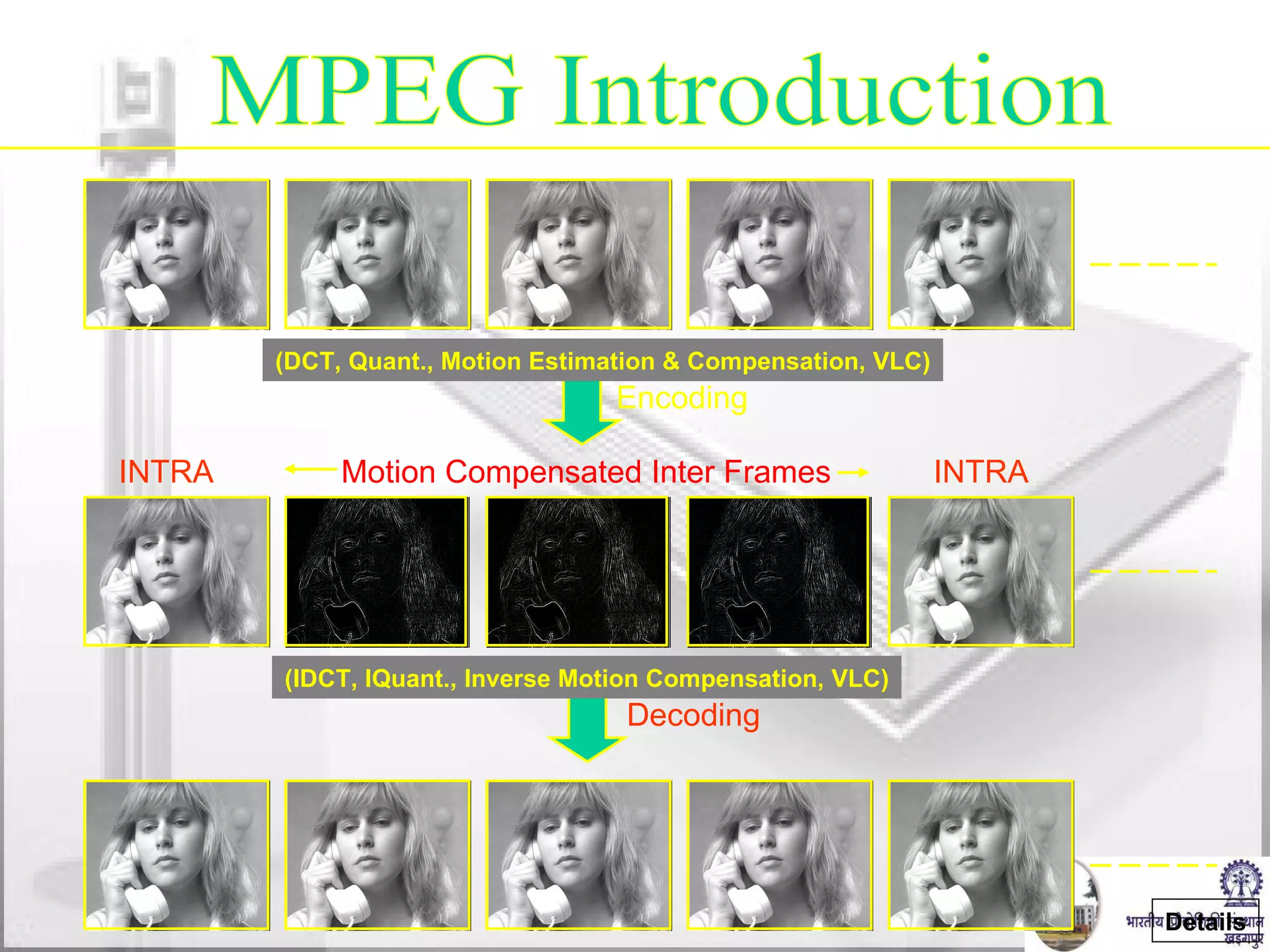
![MPEG Introduction P-Frame Encoding B-Frame Encoding Back Reference Best Match Motion Vector } Difference DCT + Quant. + RLE Huffman 01101100 Past reference Future reference Target [ + ] = - 0.5 x DCT + Quant. + RLE Huffman coder 01101100 Motion vectors](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/video-conferencing-fundamentals-and-application282/75/Video-Conferencing-Fundamentals-and-Application-20-2048.jpg)


















![Example Server Side Program package path.to.my.package; import <all reqd packages> public class Application extends ApplicationAdapter { public boolean appStart(IScope app) { } public boolean appConnect(IConnection conn, Object[] params) {} // and others } Compiled in Java and stored stored in Red5 Server.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/video-conferencing-fundamentals-and-application282/75/Video-Conferencing-Fundamentals-and-Application-50-2048.jpg)