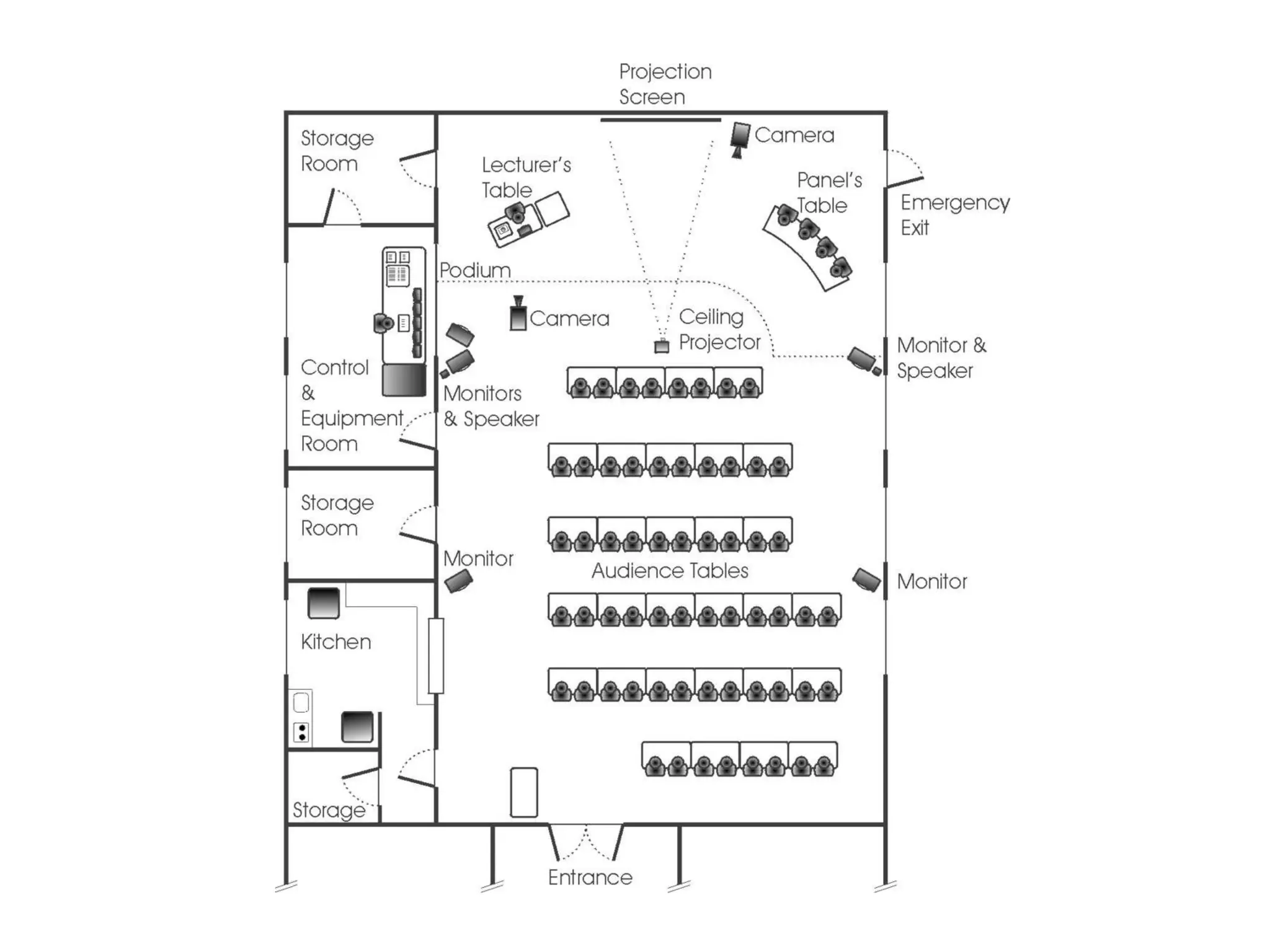
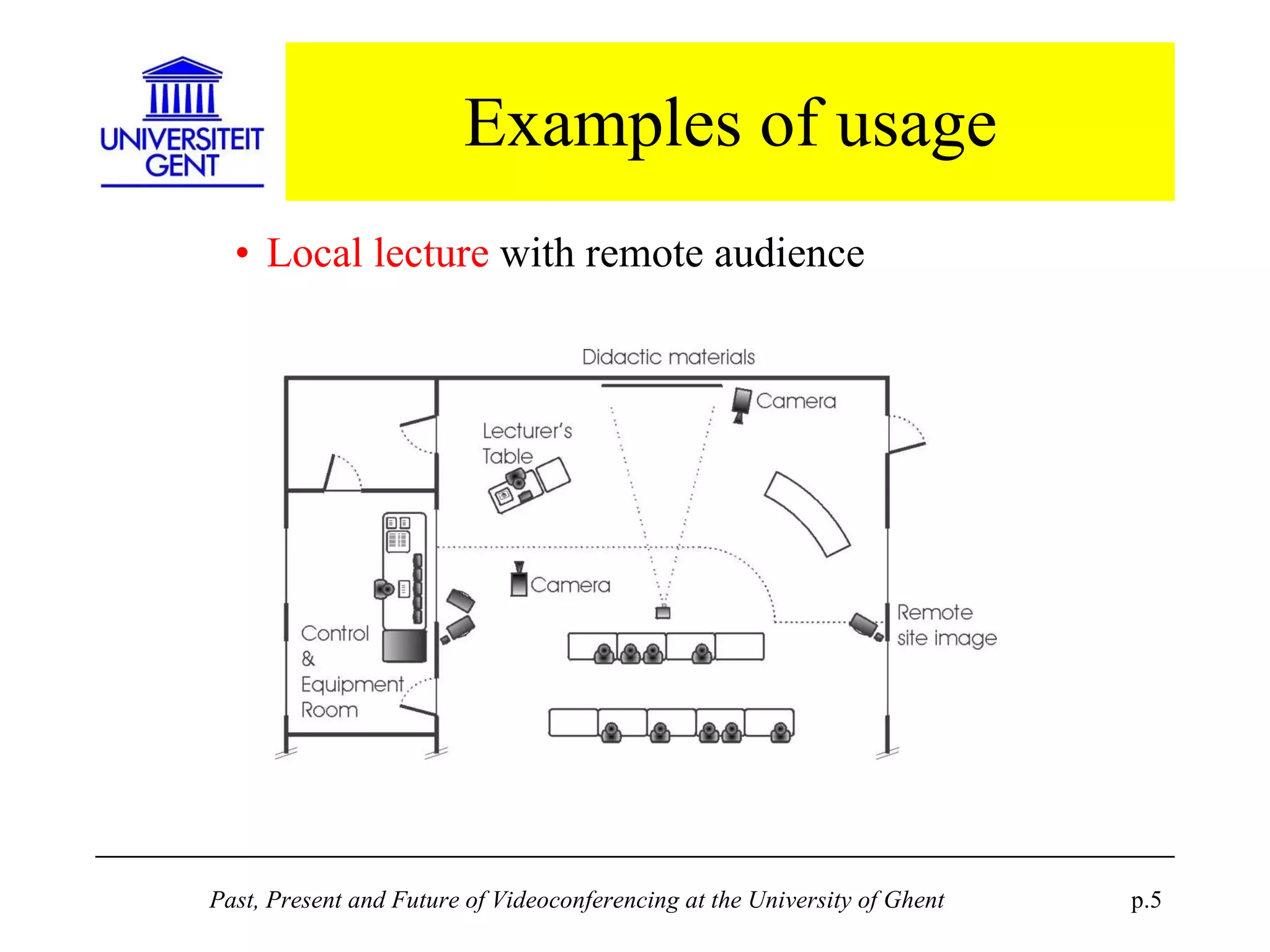
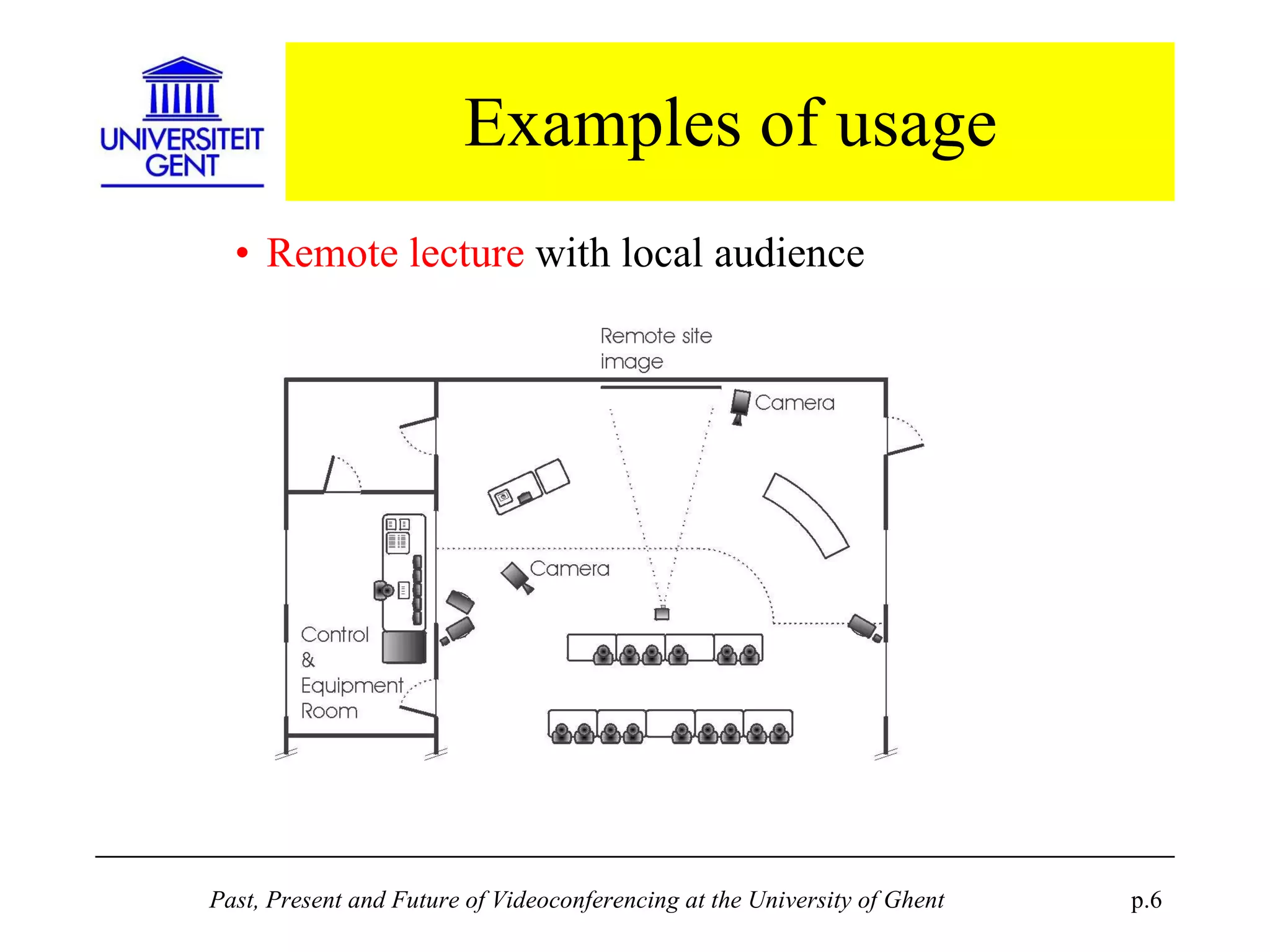
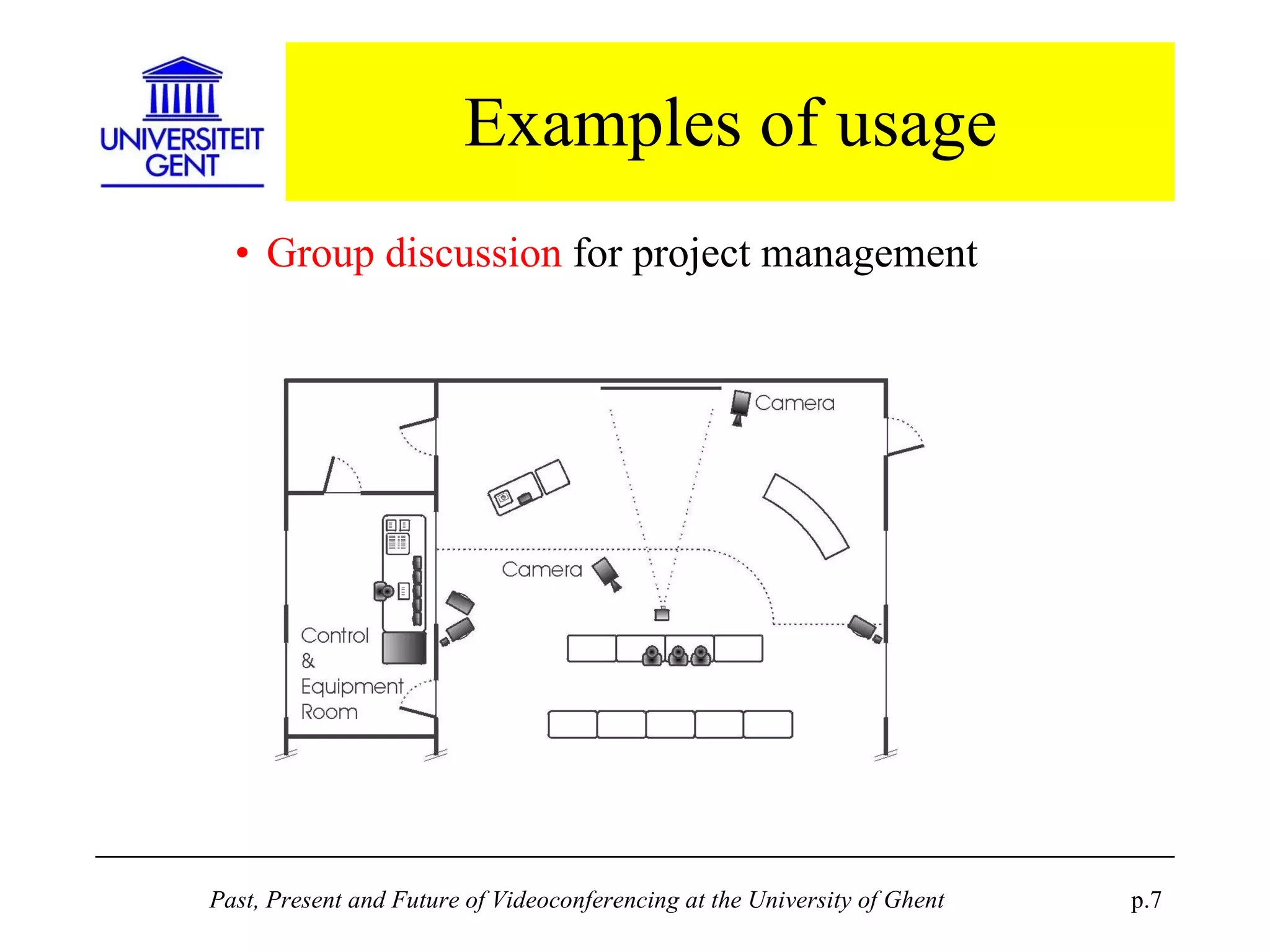
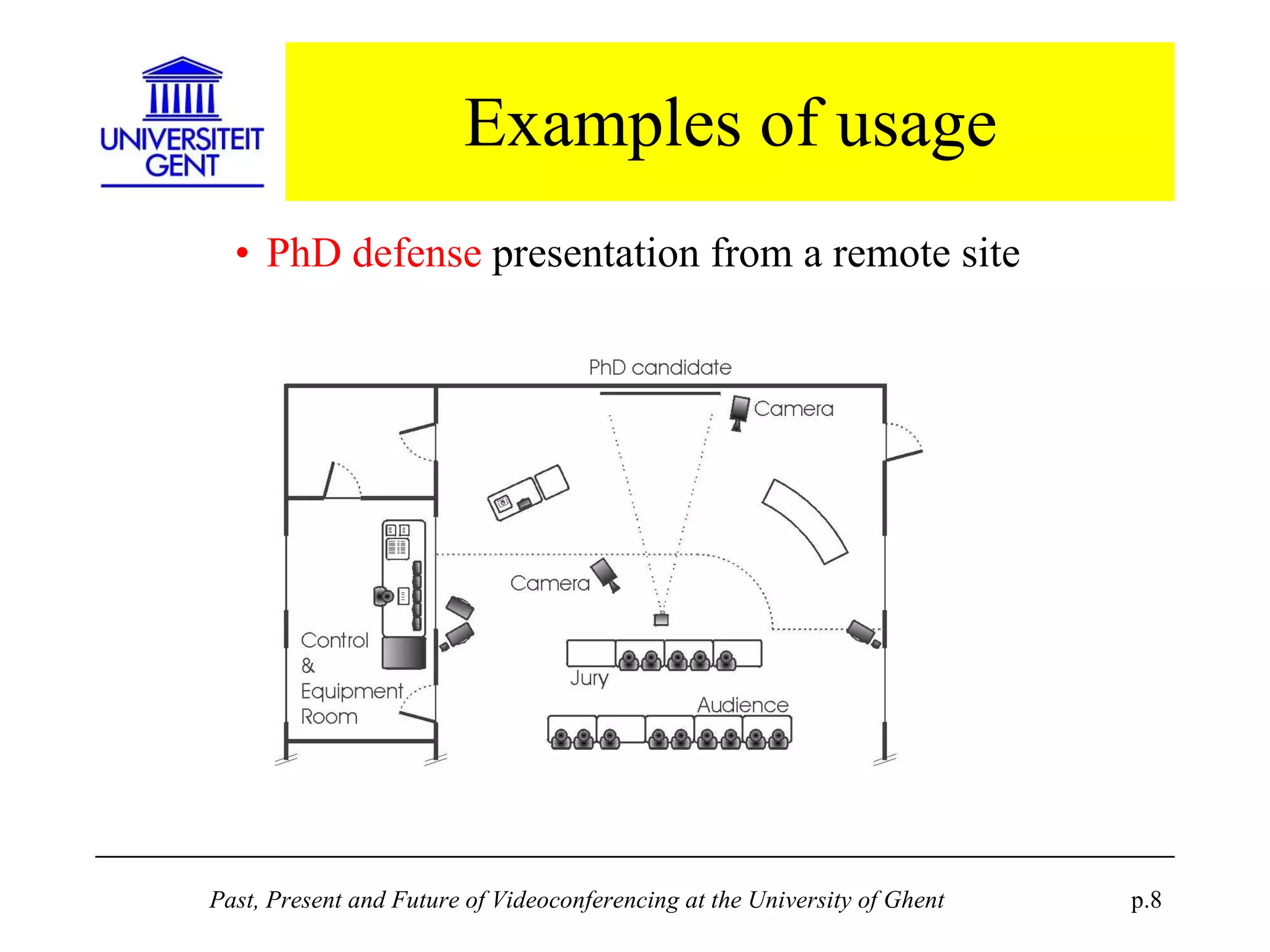
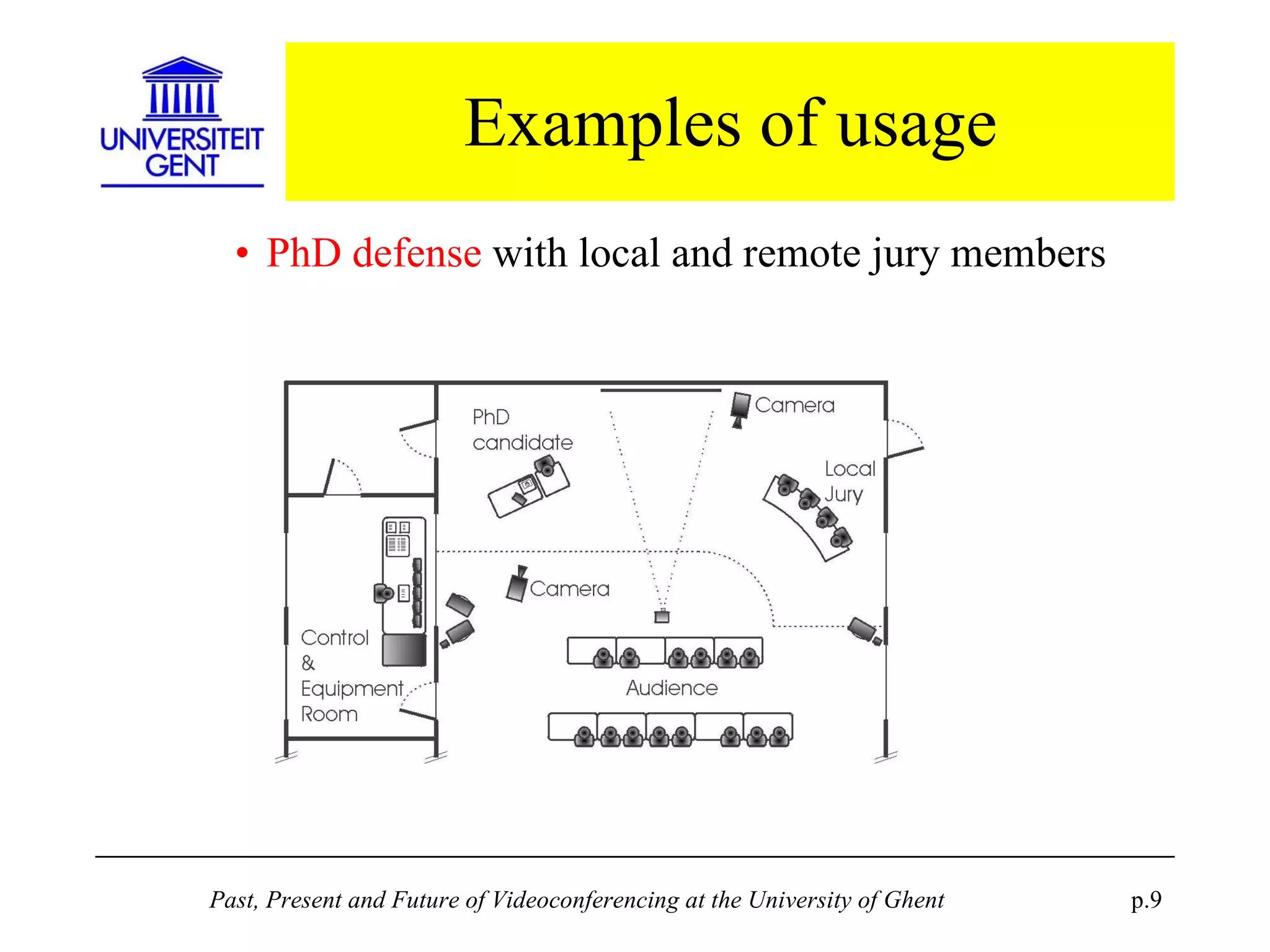
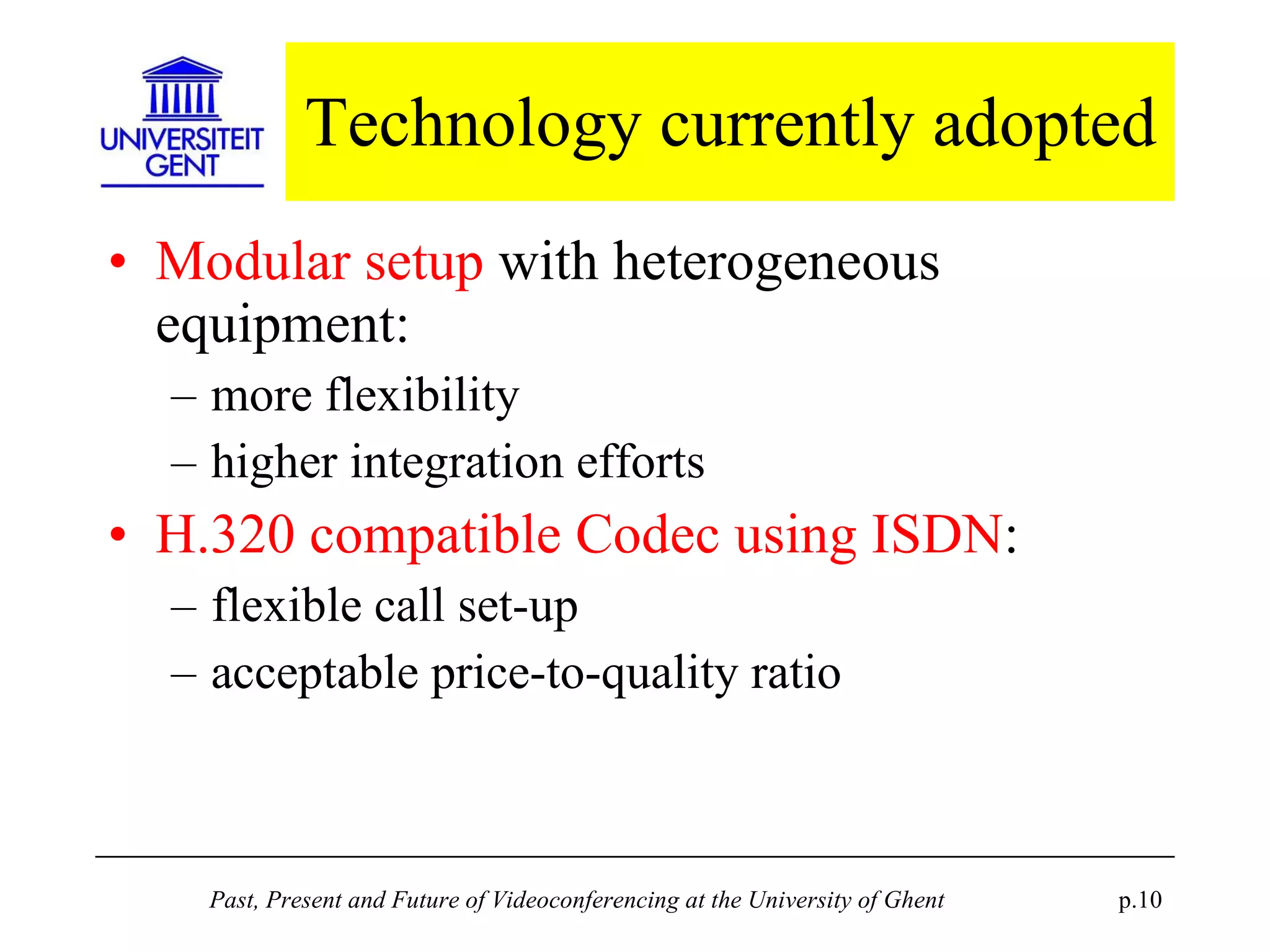
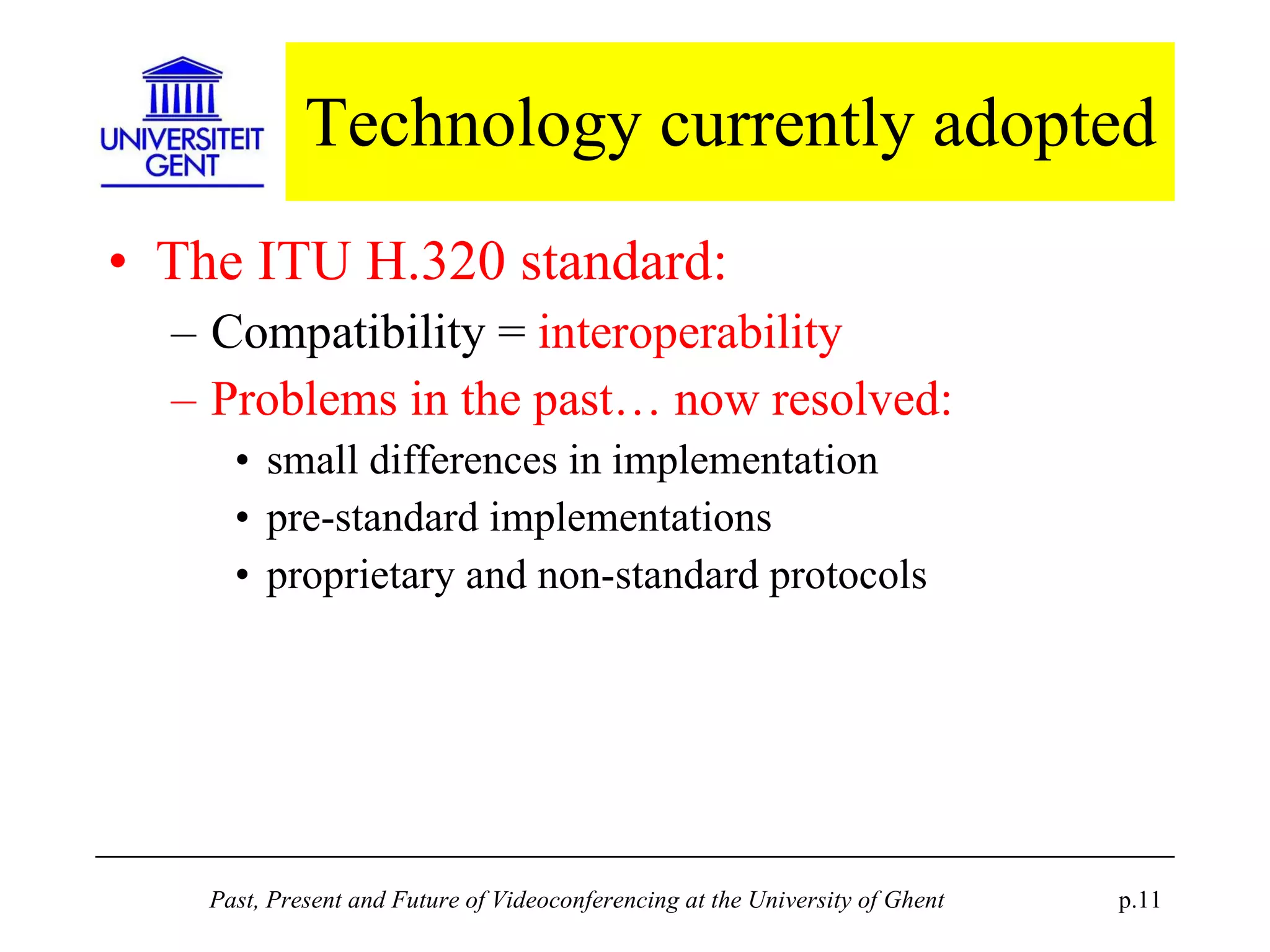
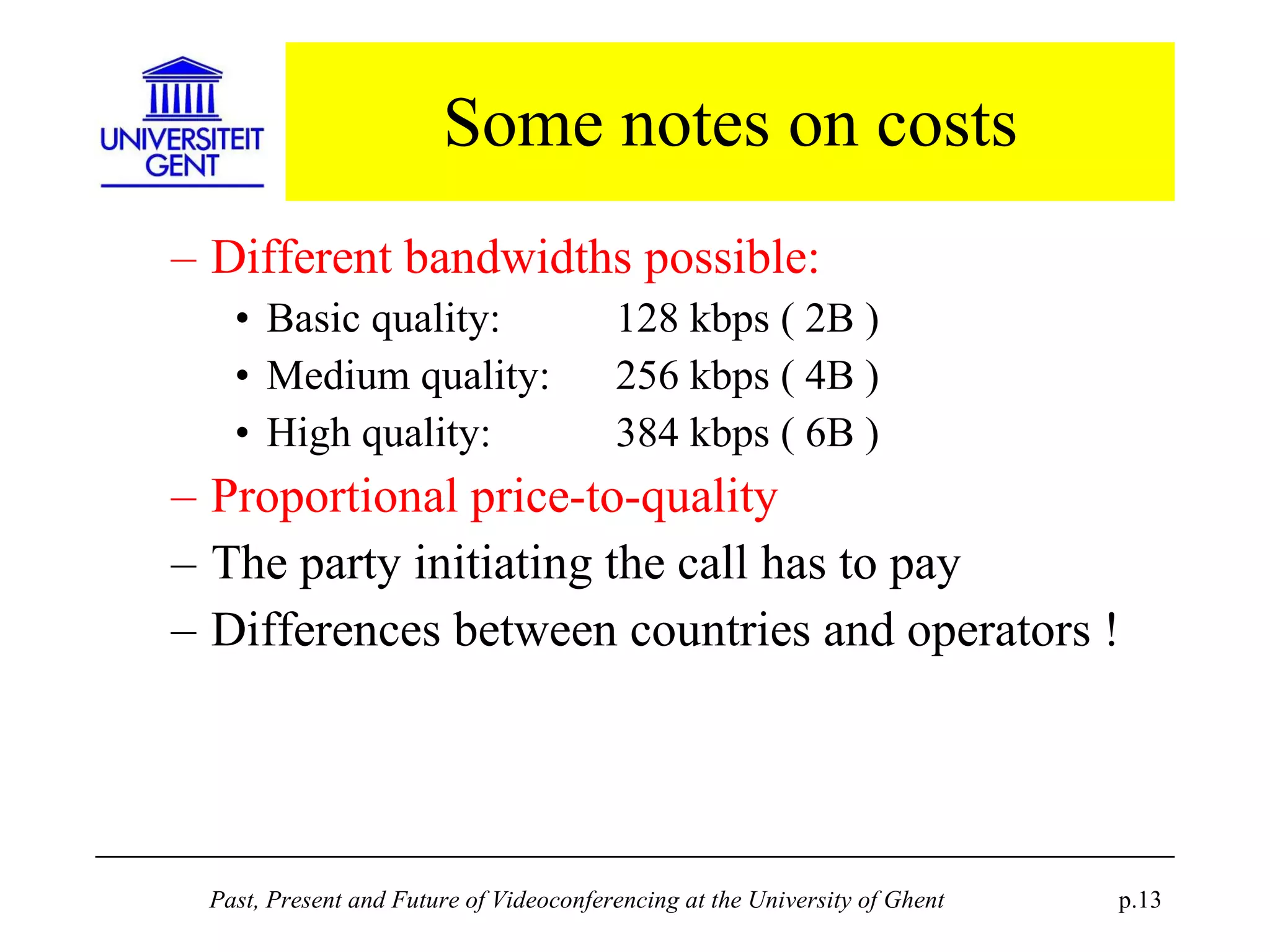
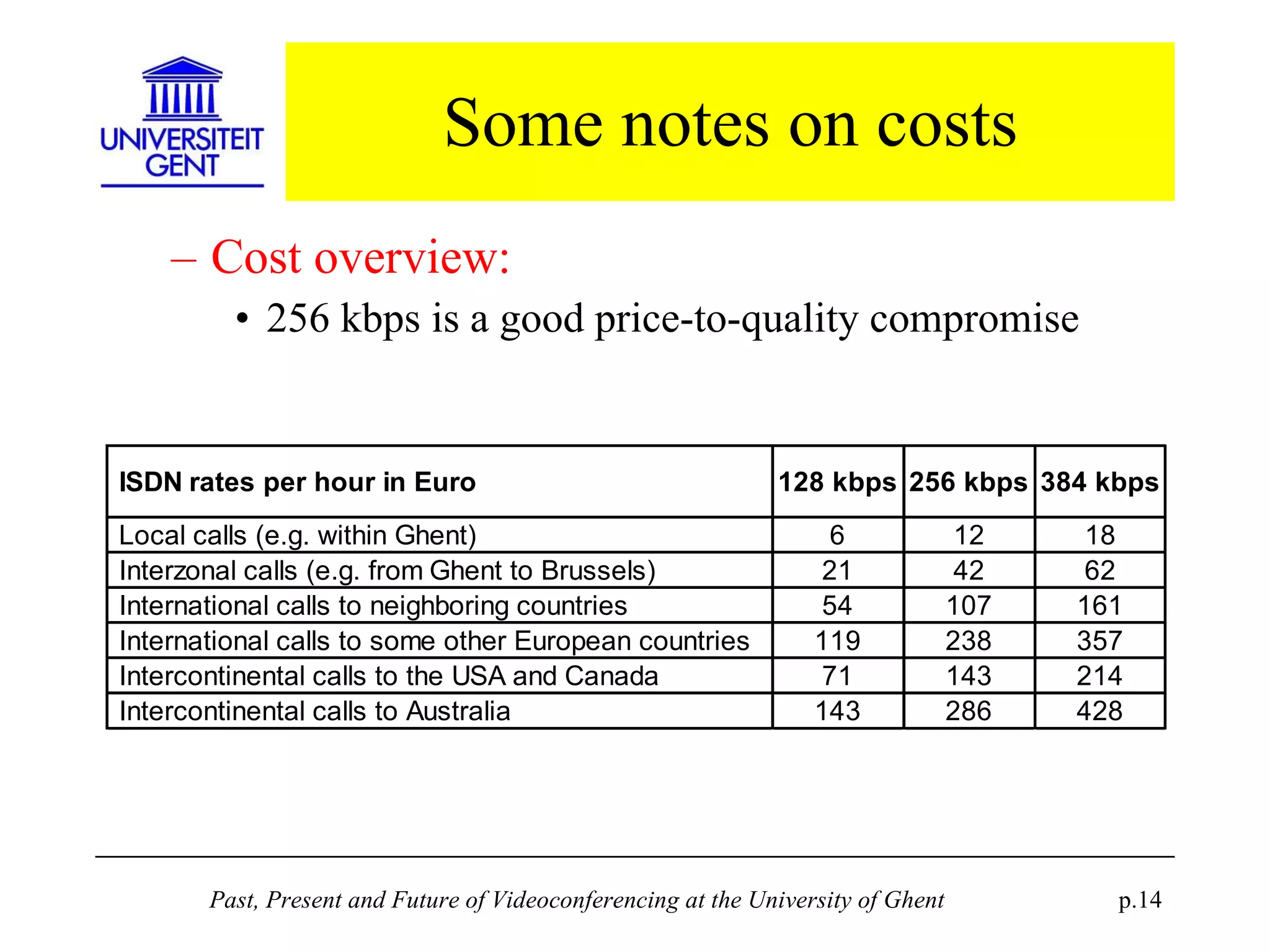
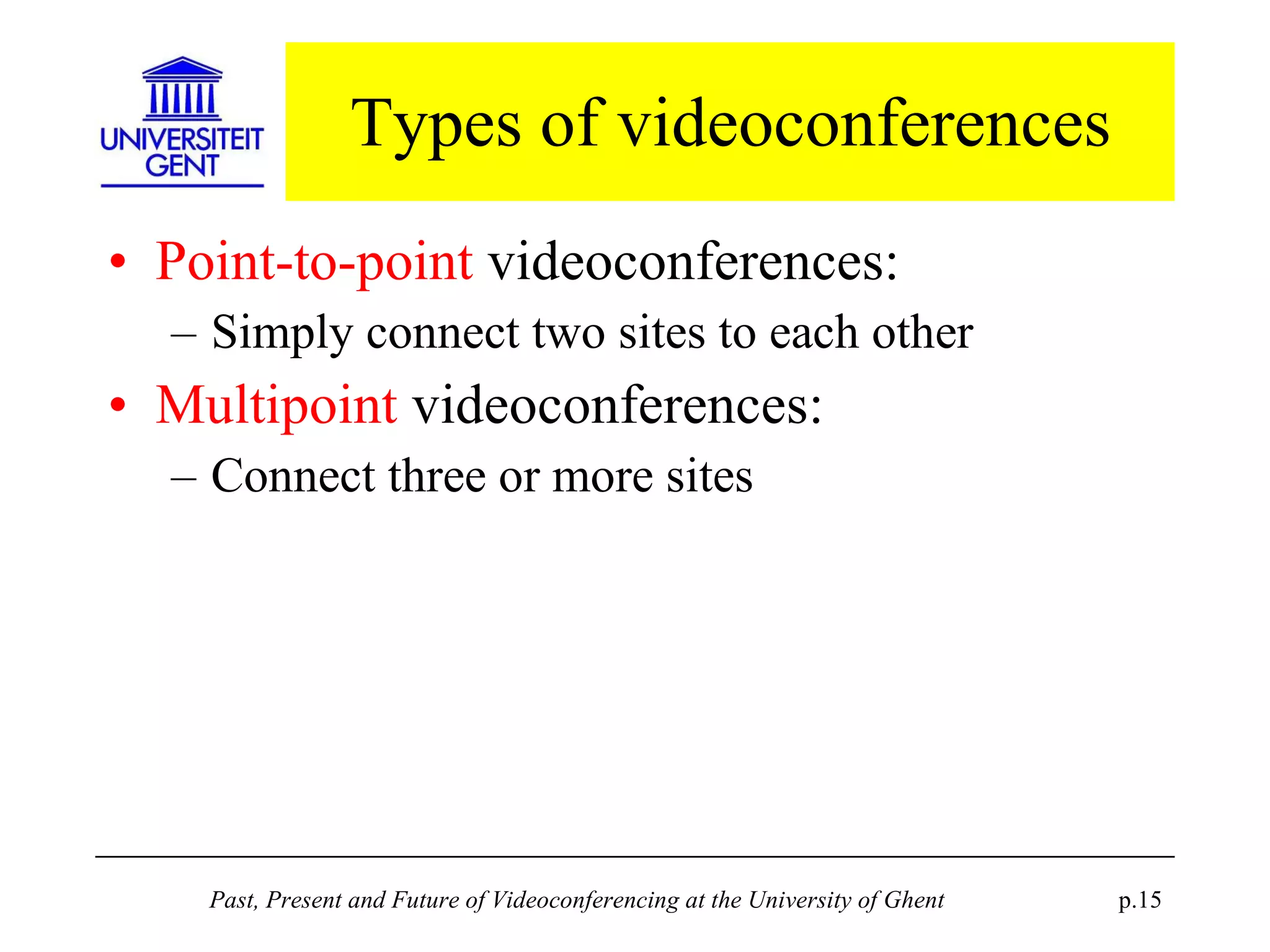
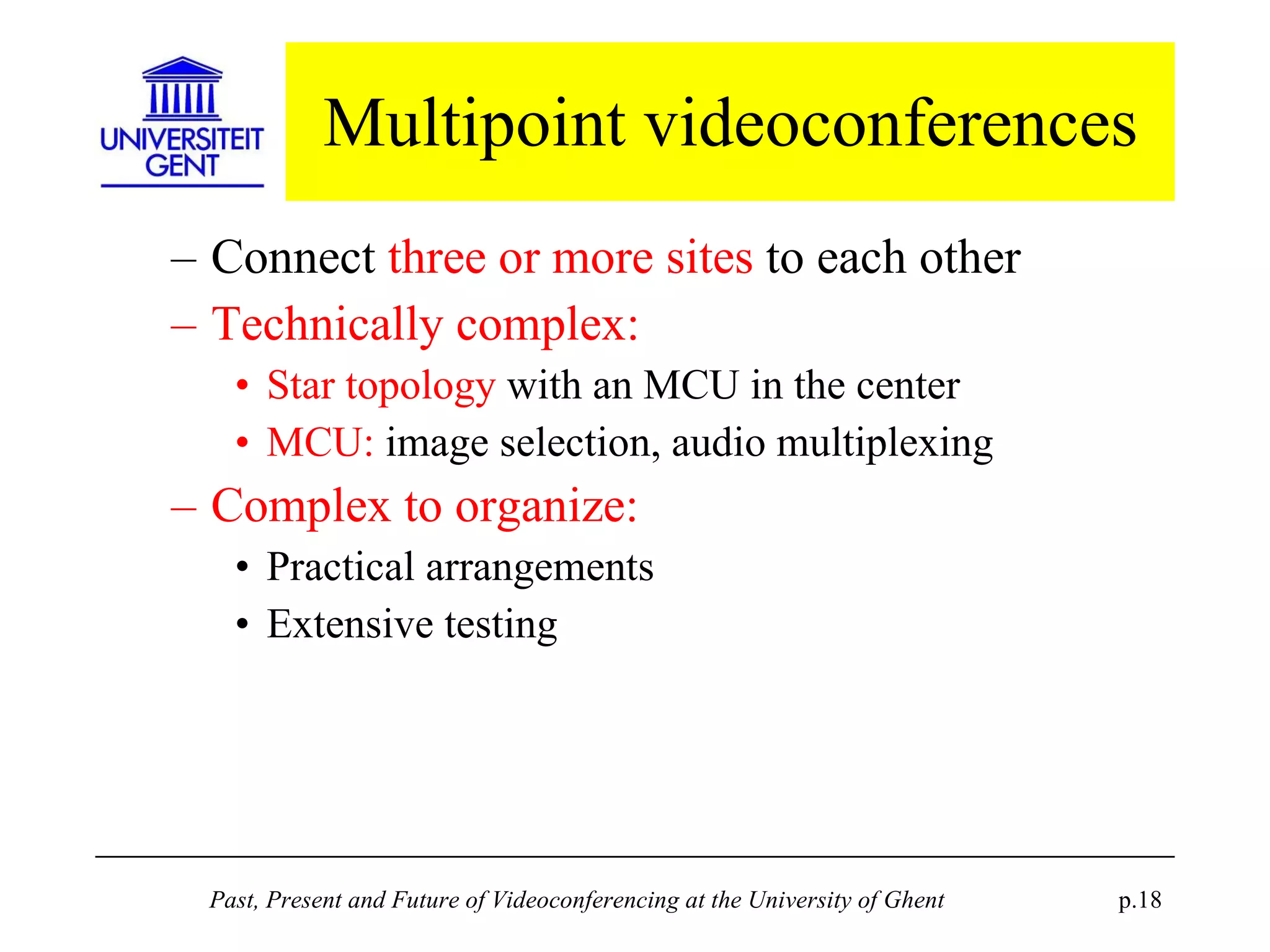
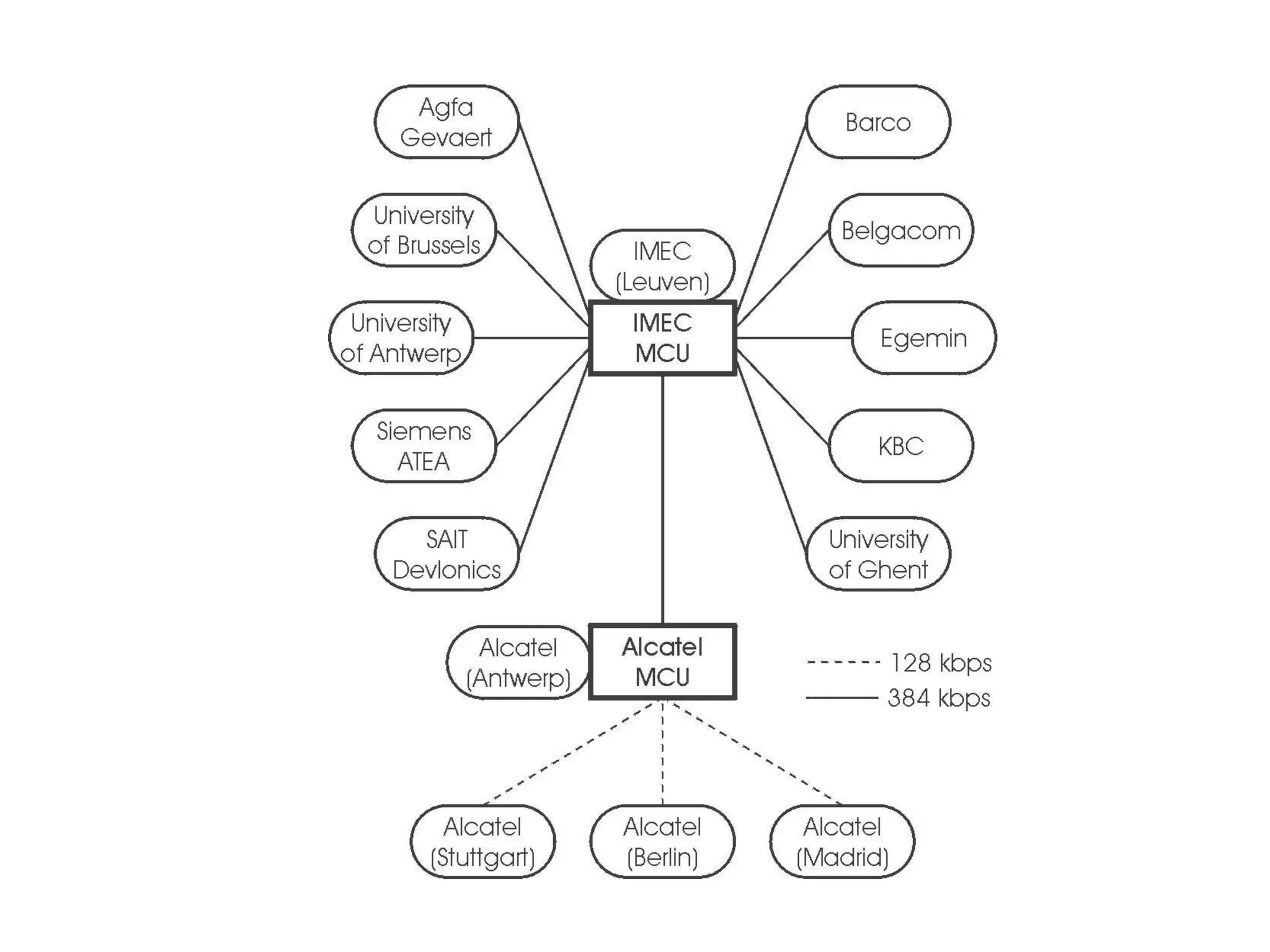
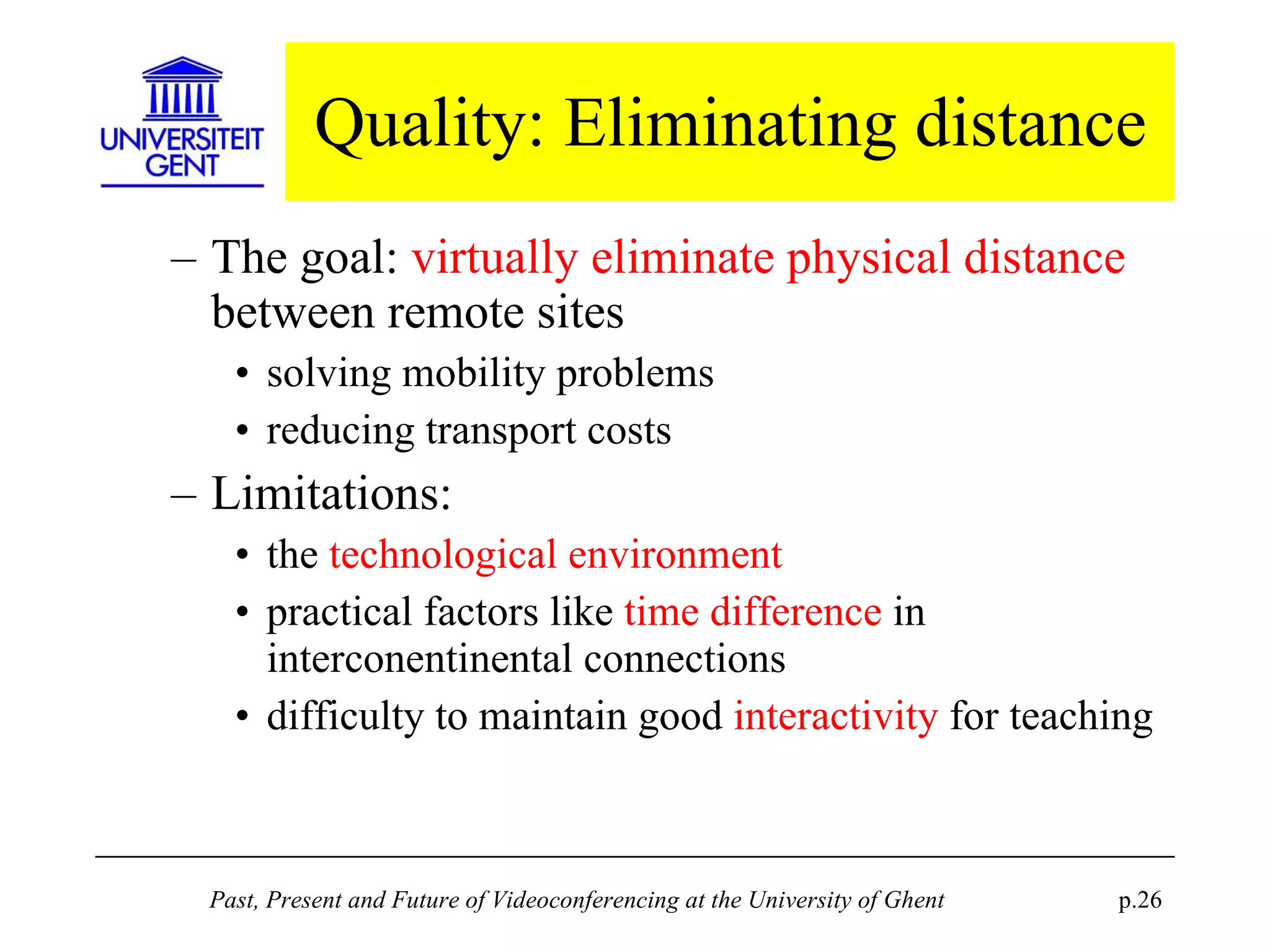
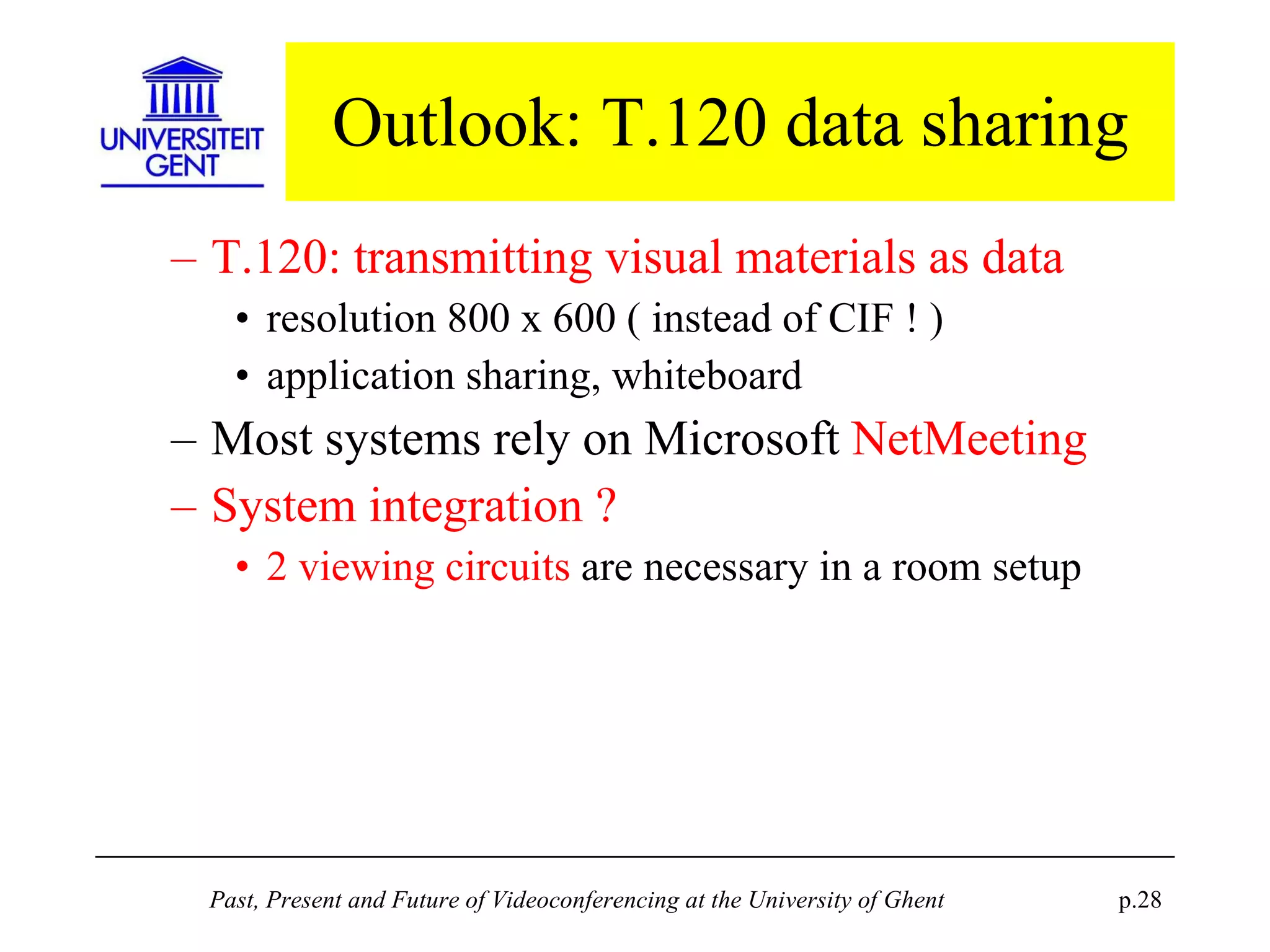
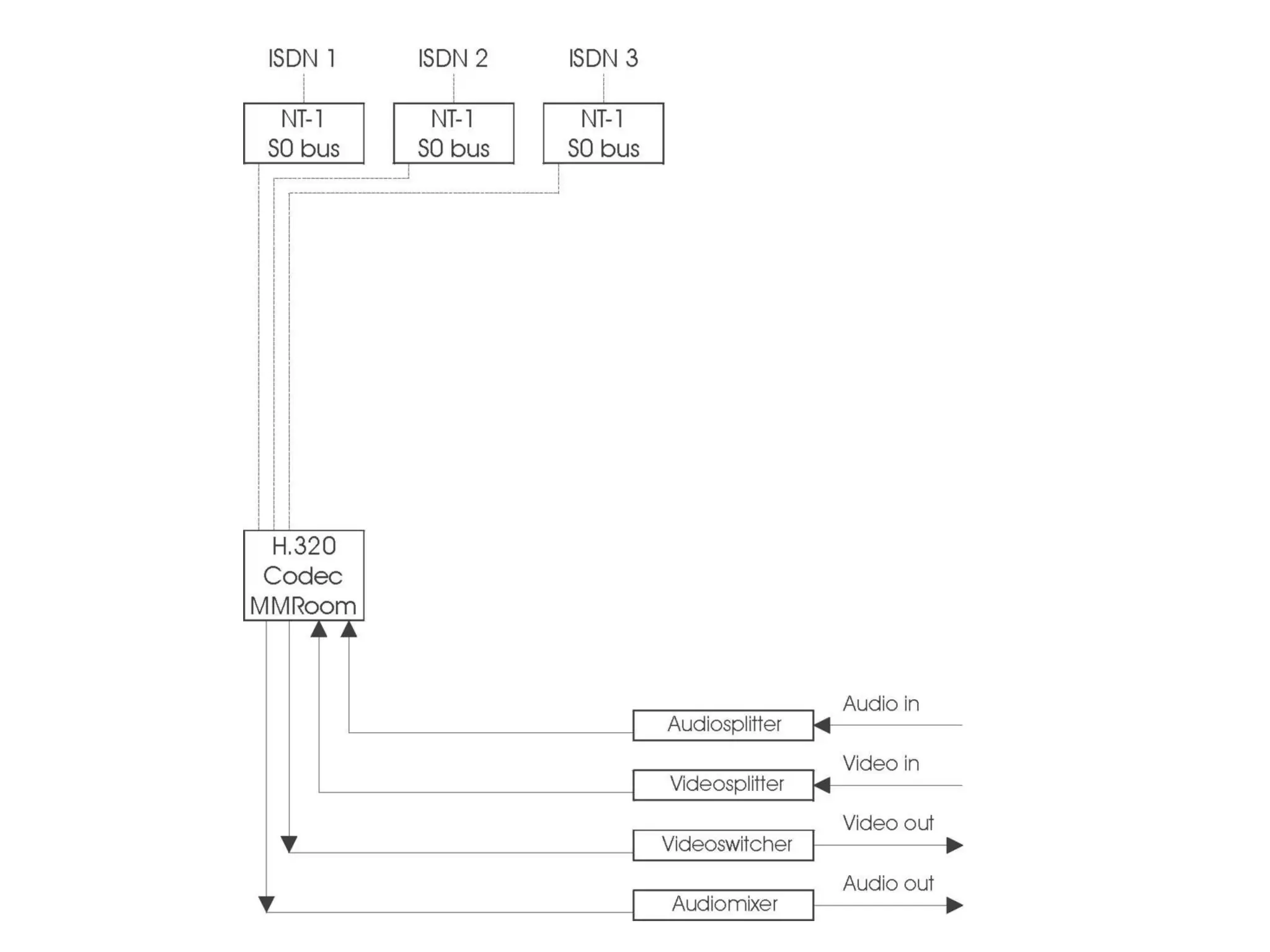
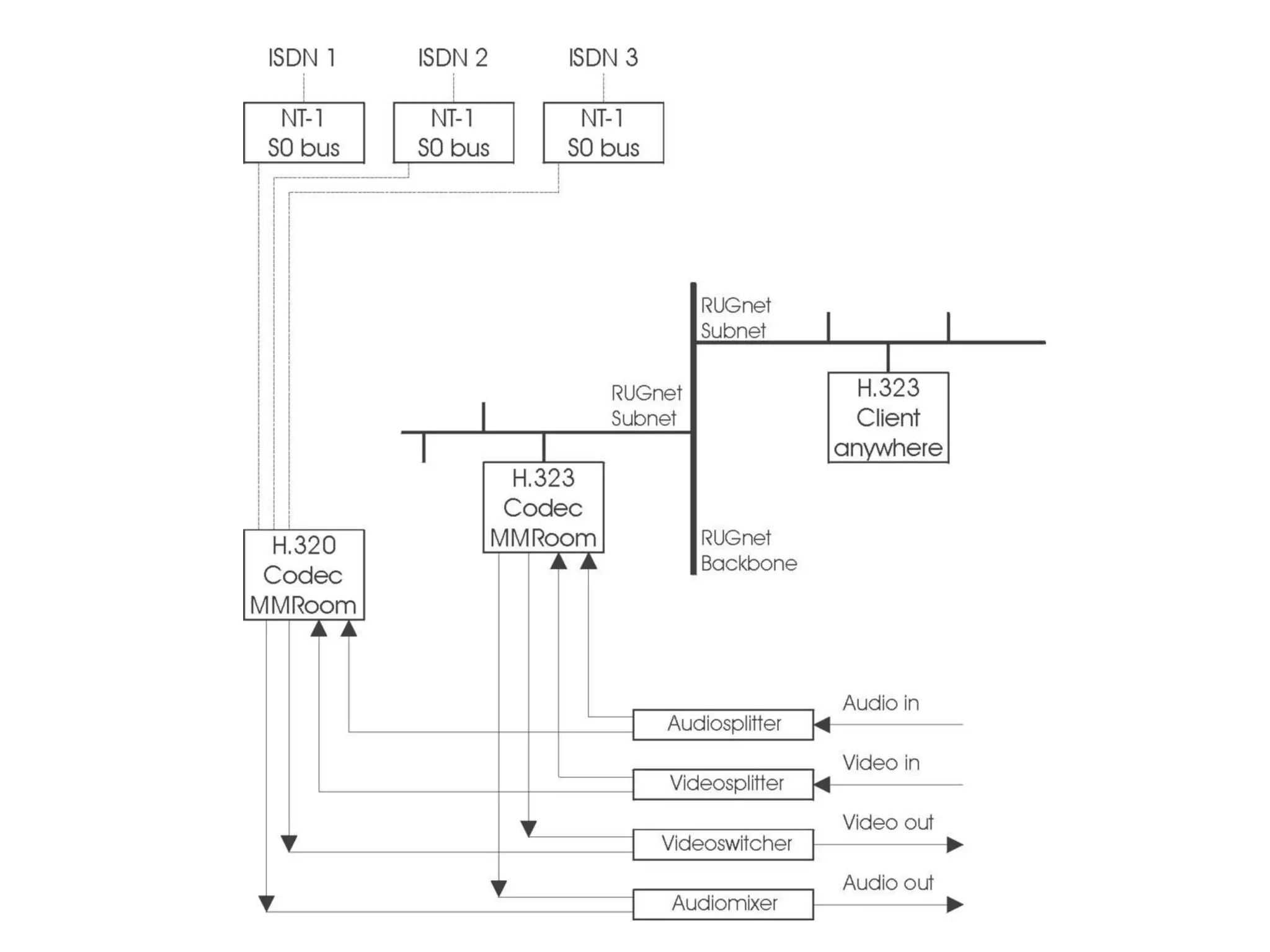
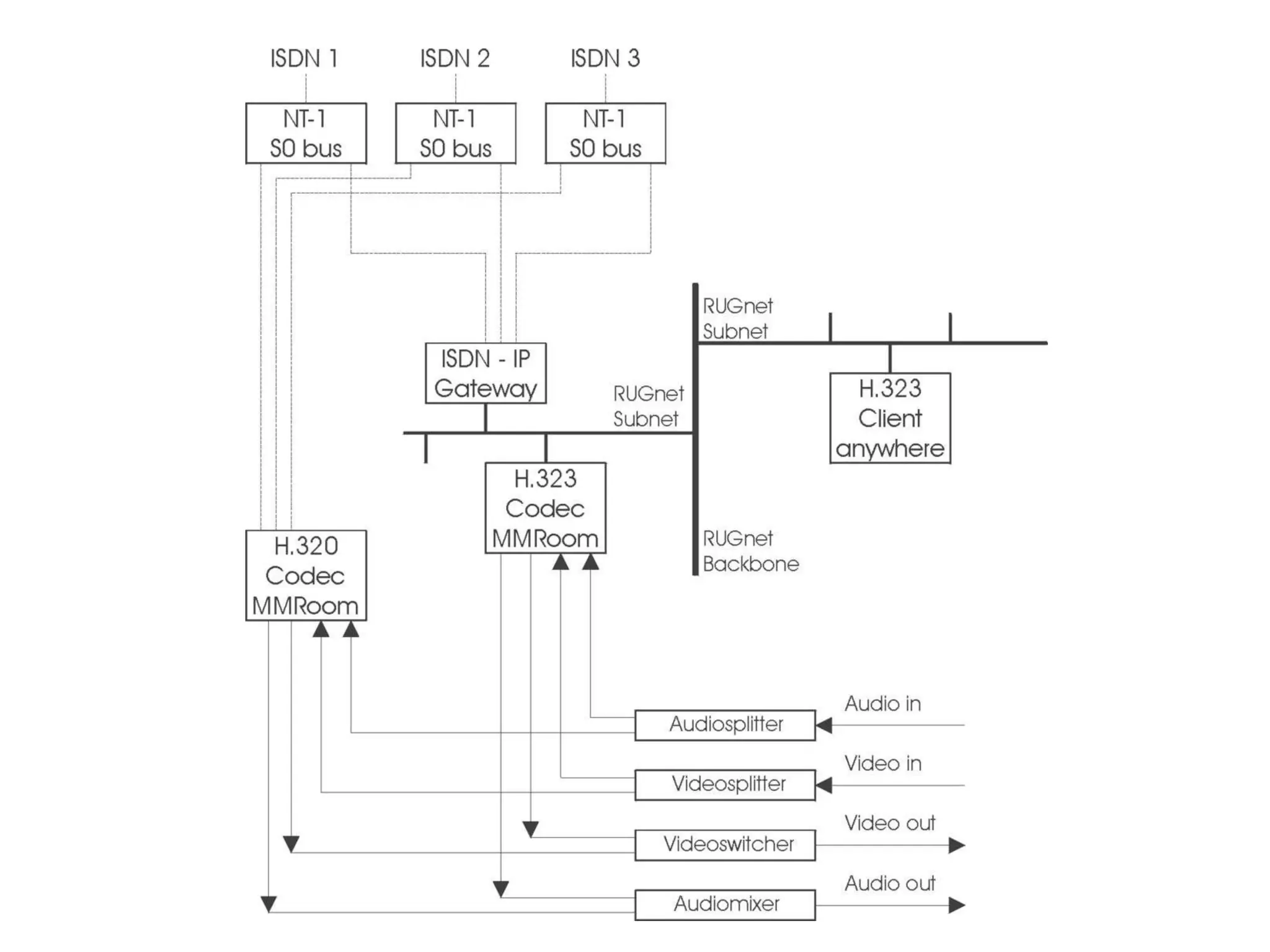
The document discusses the past, present, and future of videoconferencing at the University of Ghent. It describes their central Multimedia Room facility, the technologies used including ISDN and H.320 standards, and types of videoconferences like point-to-point and multipoint. It also outlines costs, quality considerations, and the outlook for future technologies like T.120 data sharing, ATM and IP-based videoconferencing, and gateways to connect heterogeneous systems.