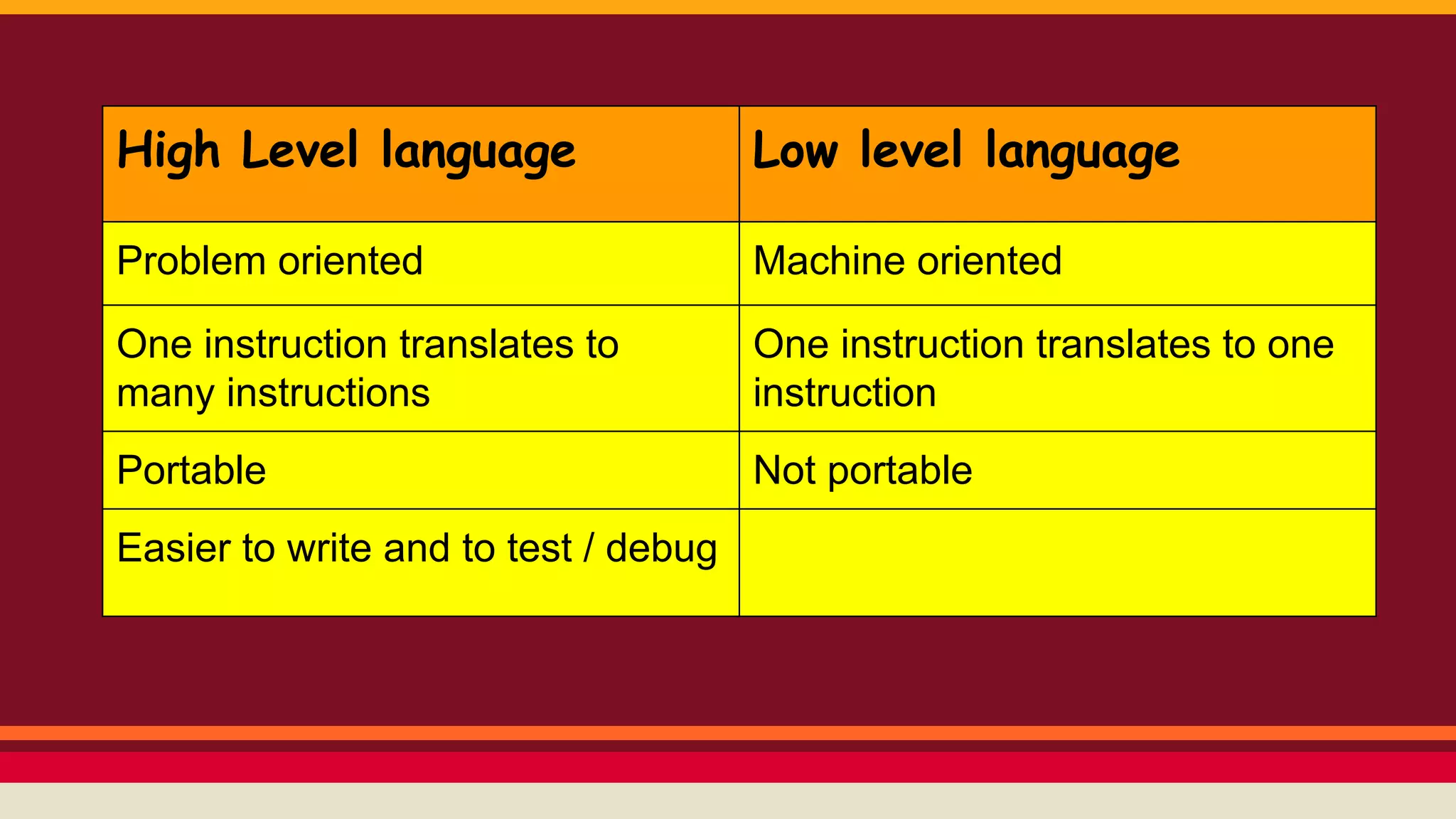
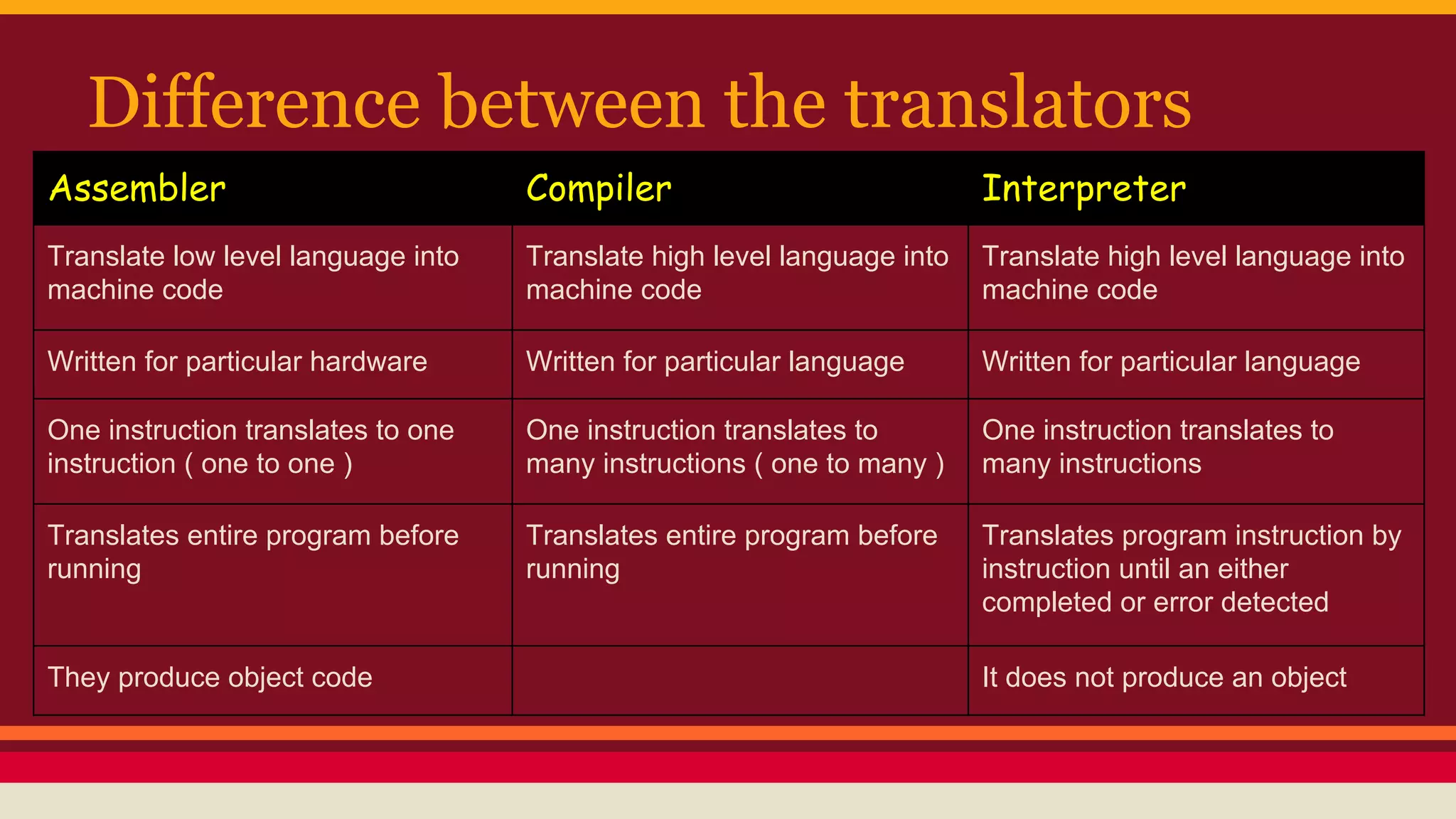
This document discusses programming languages and the translation process between high-level and low-level languages. It explains that all computer programs must ultimately be translated to binary machine code for the computer to understand. There are high-level languages that are easier for programmers but require translation, low-level assembly languages that are closer to machine code, and machine code itself which requires no translation. It describes the roles of compilers, interpreters, and assemblers in translating between these levels, and the differences between them such as how compilers translate entire programs at once while interpreters translate incrementally.