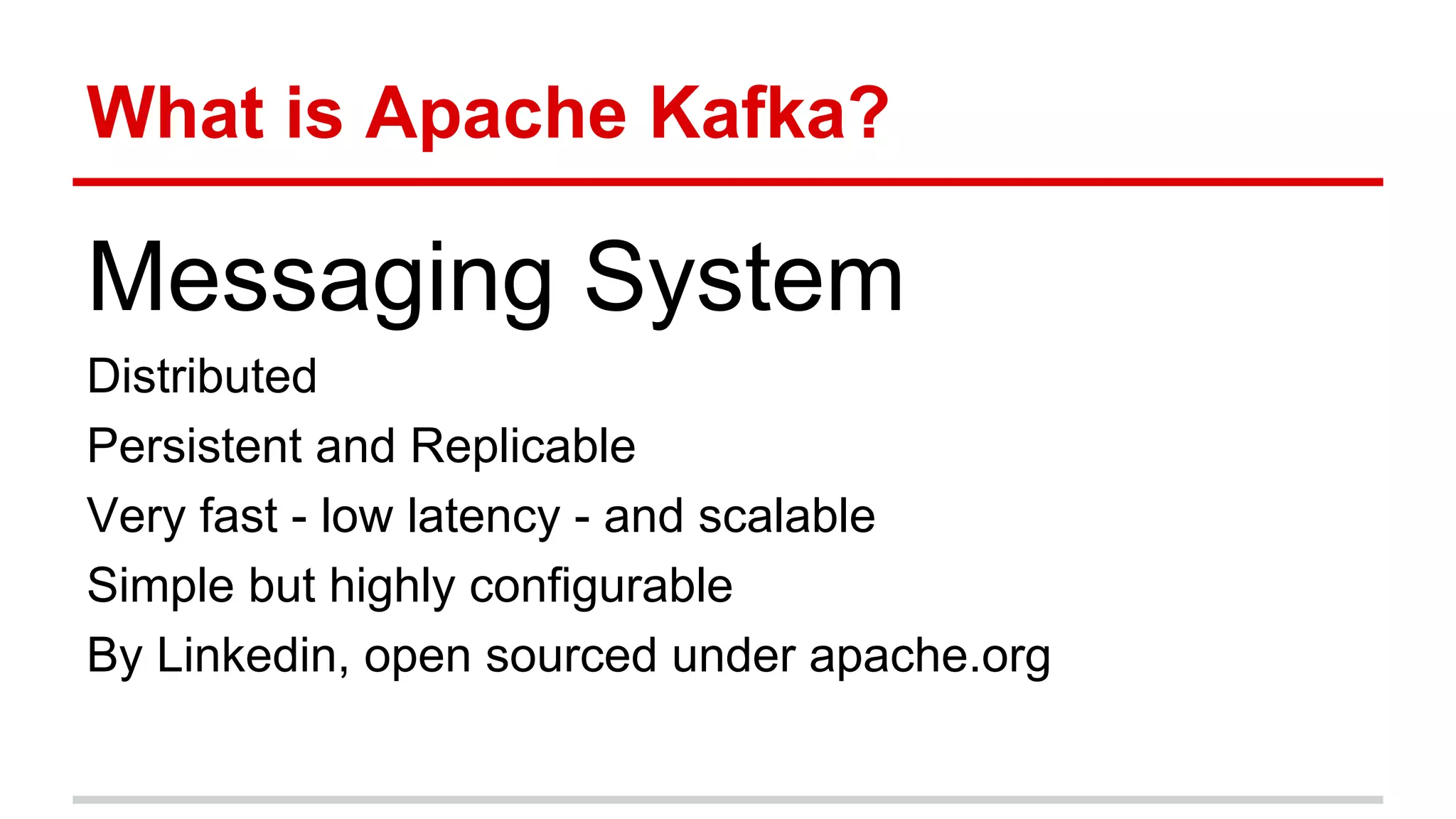
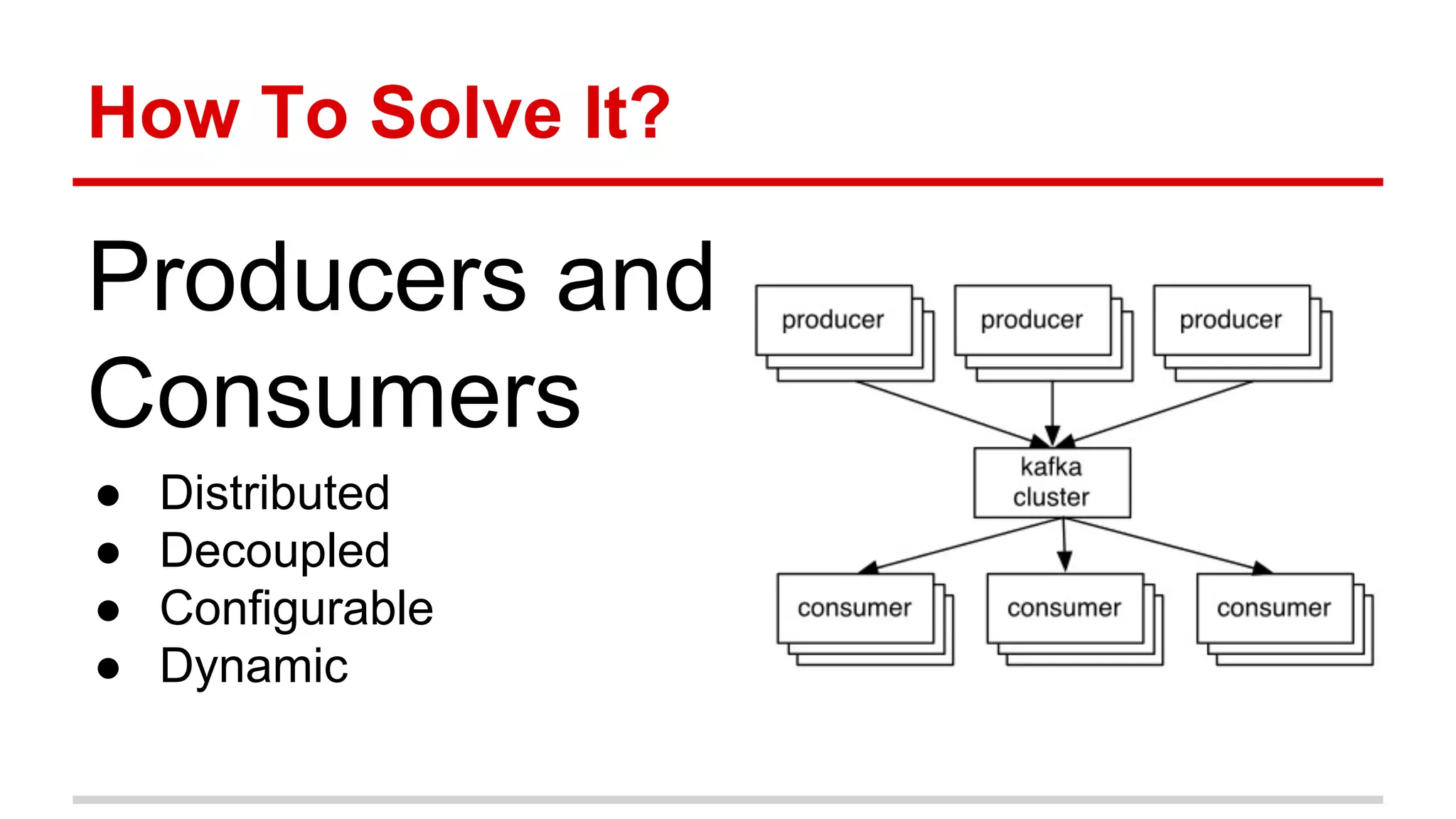
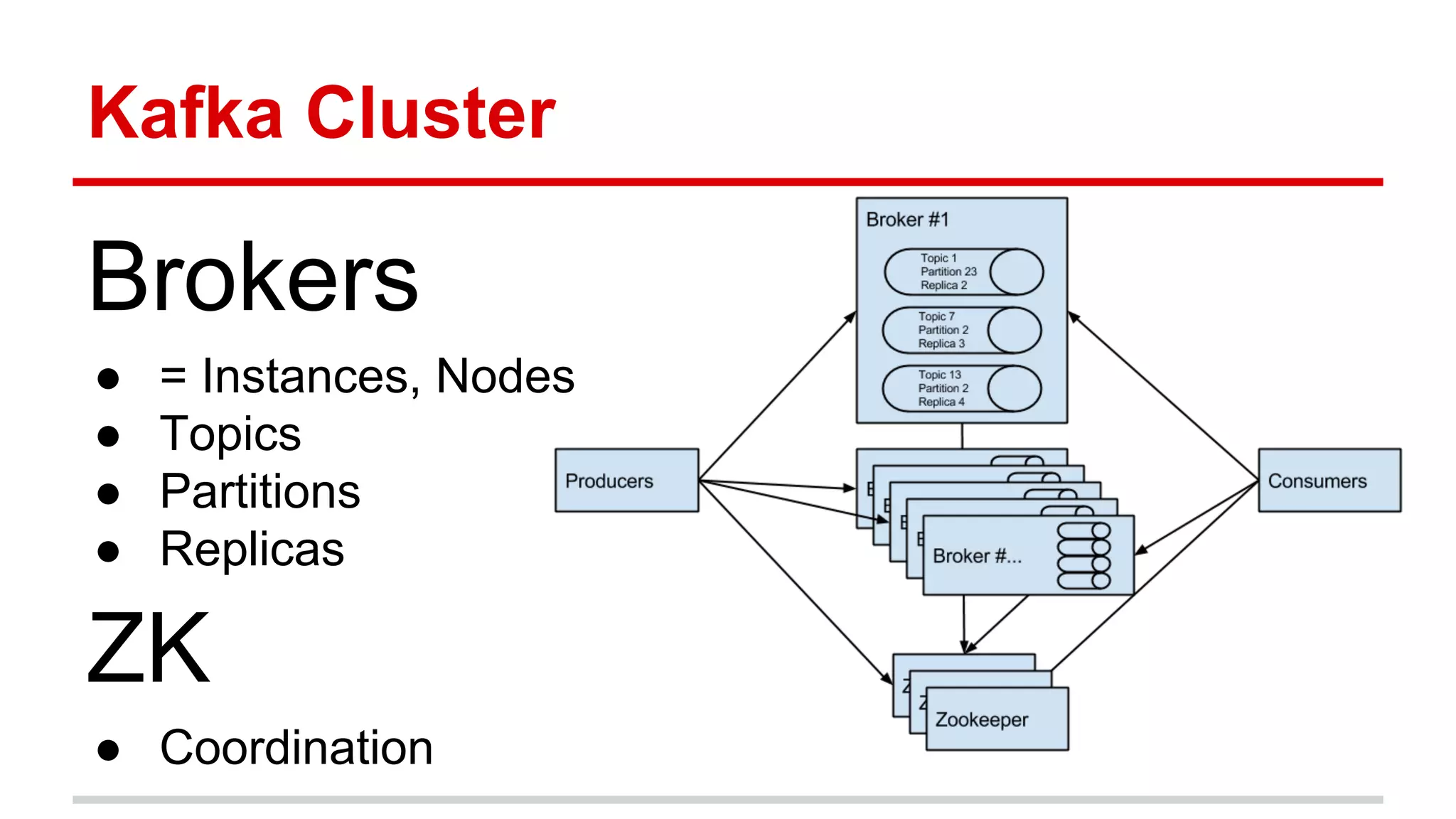
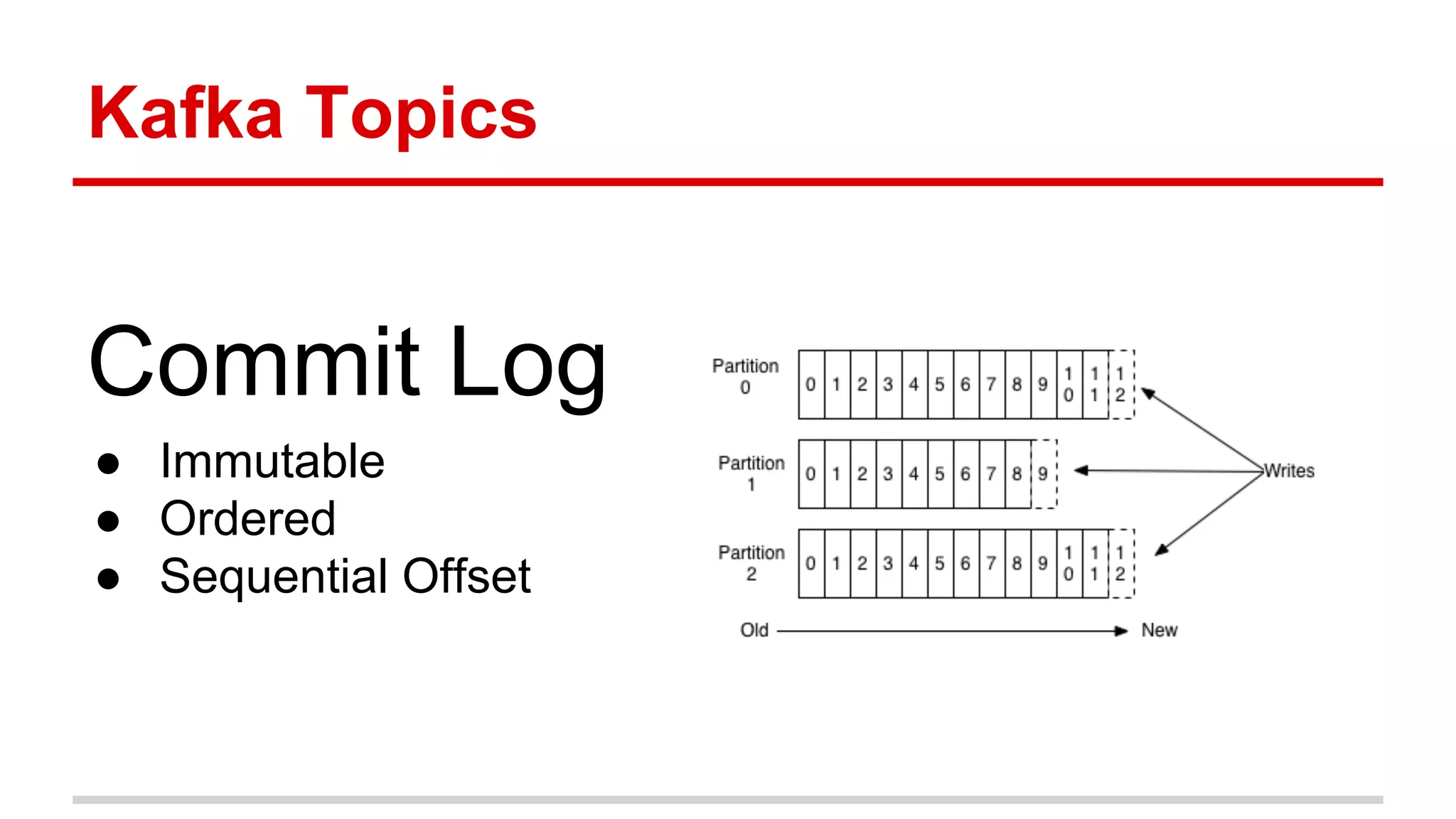
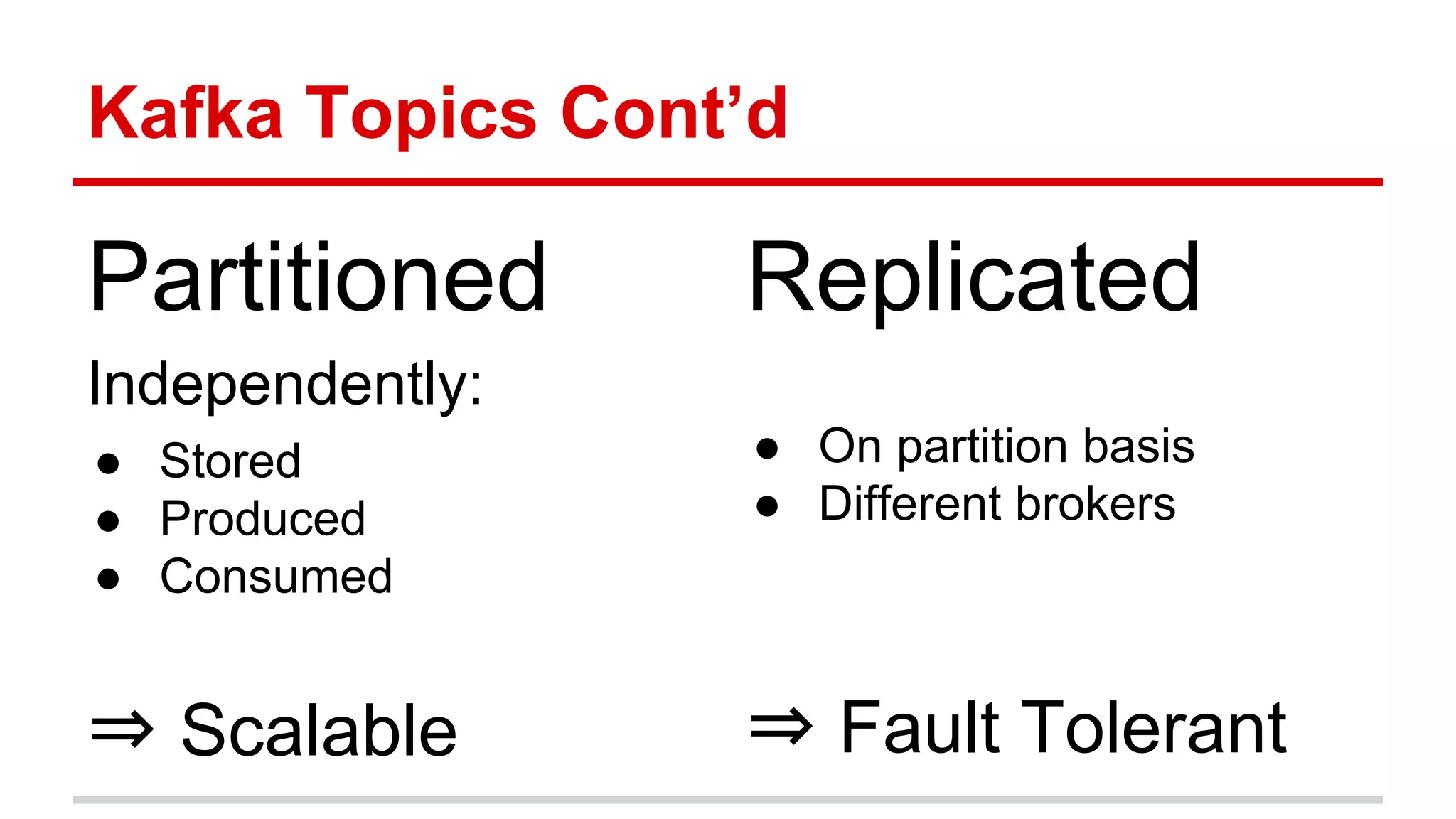
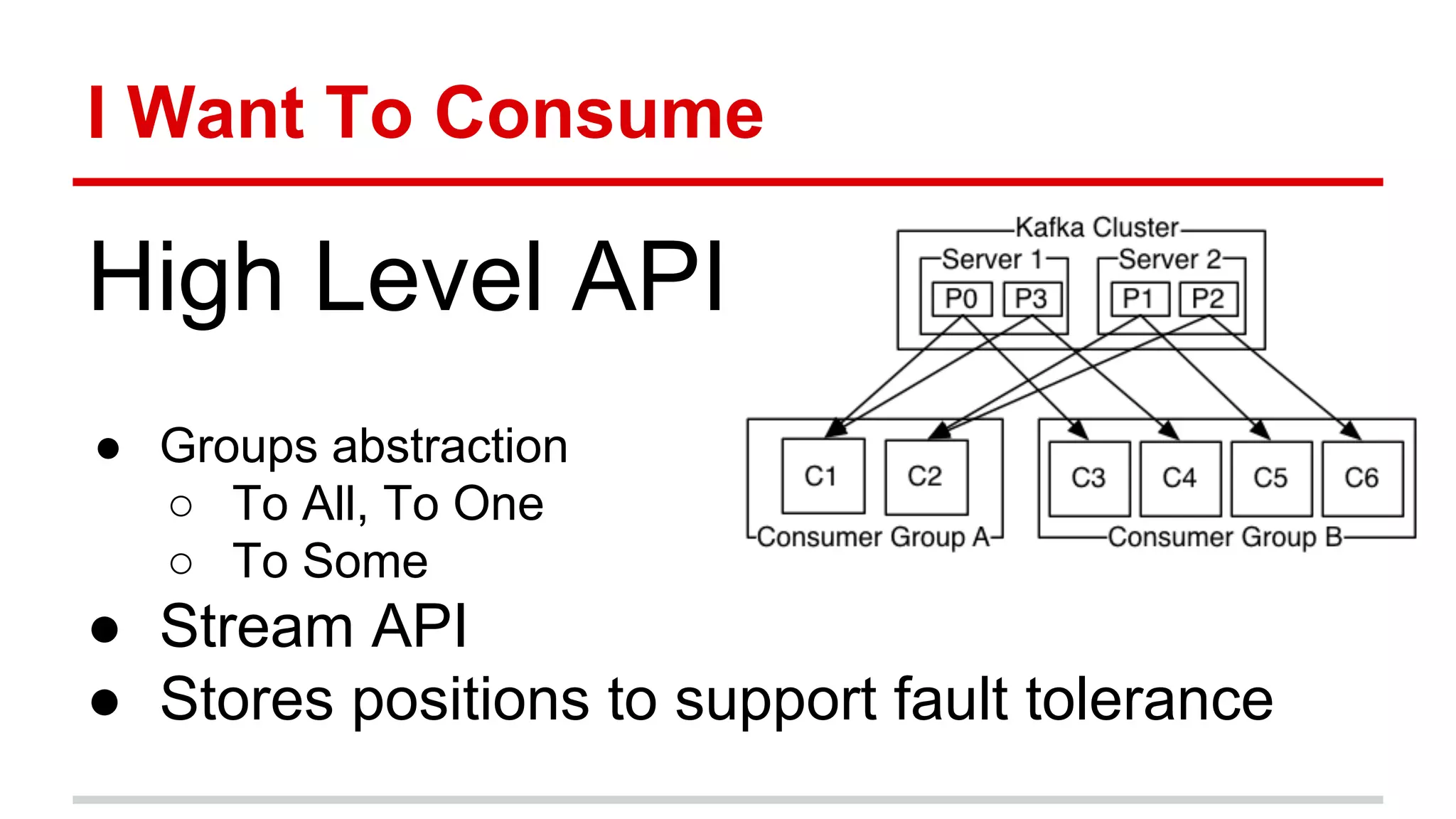
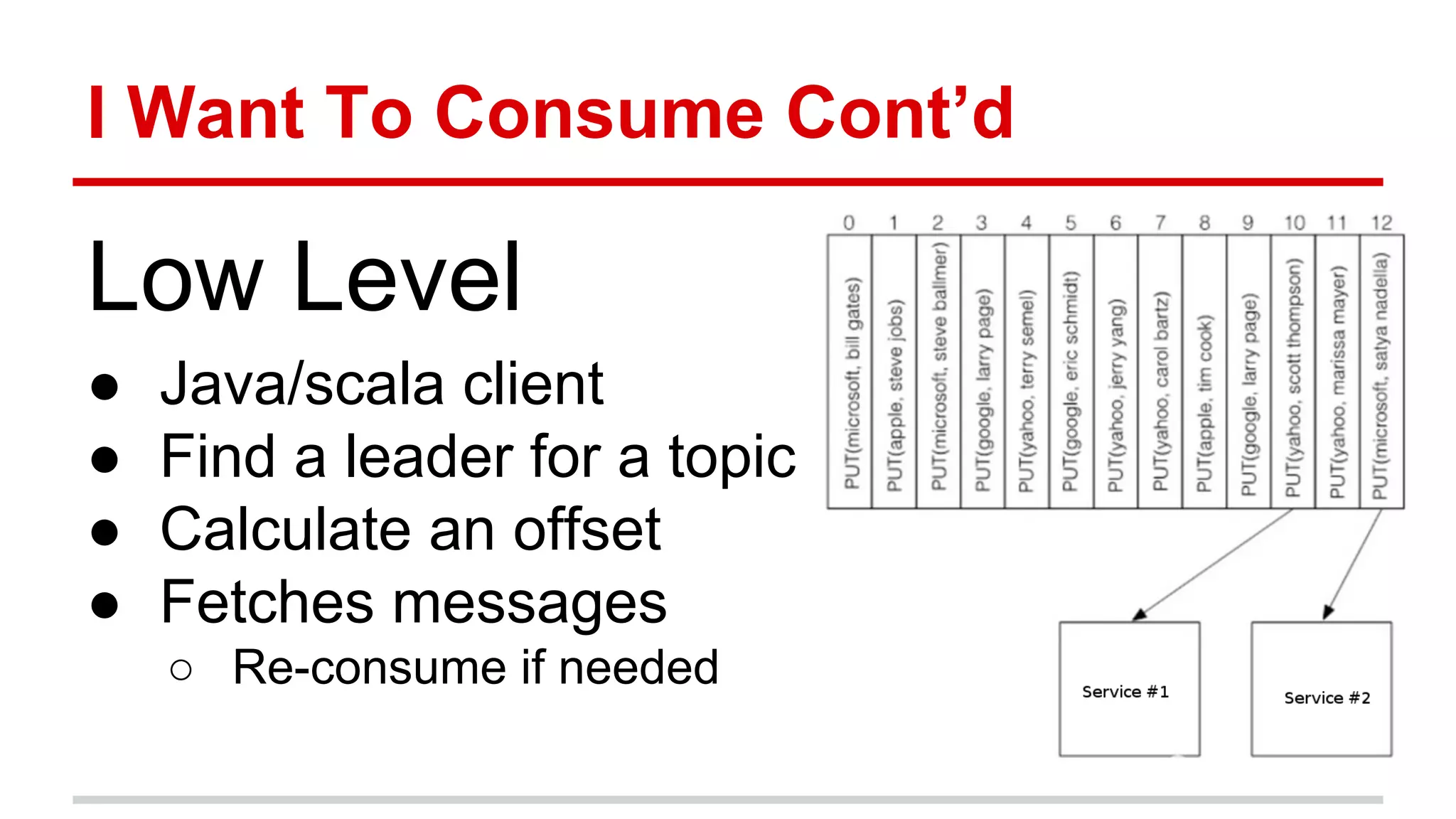
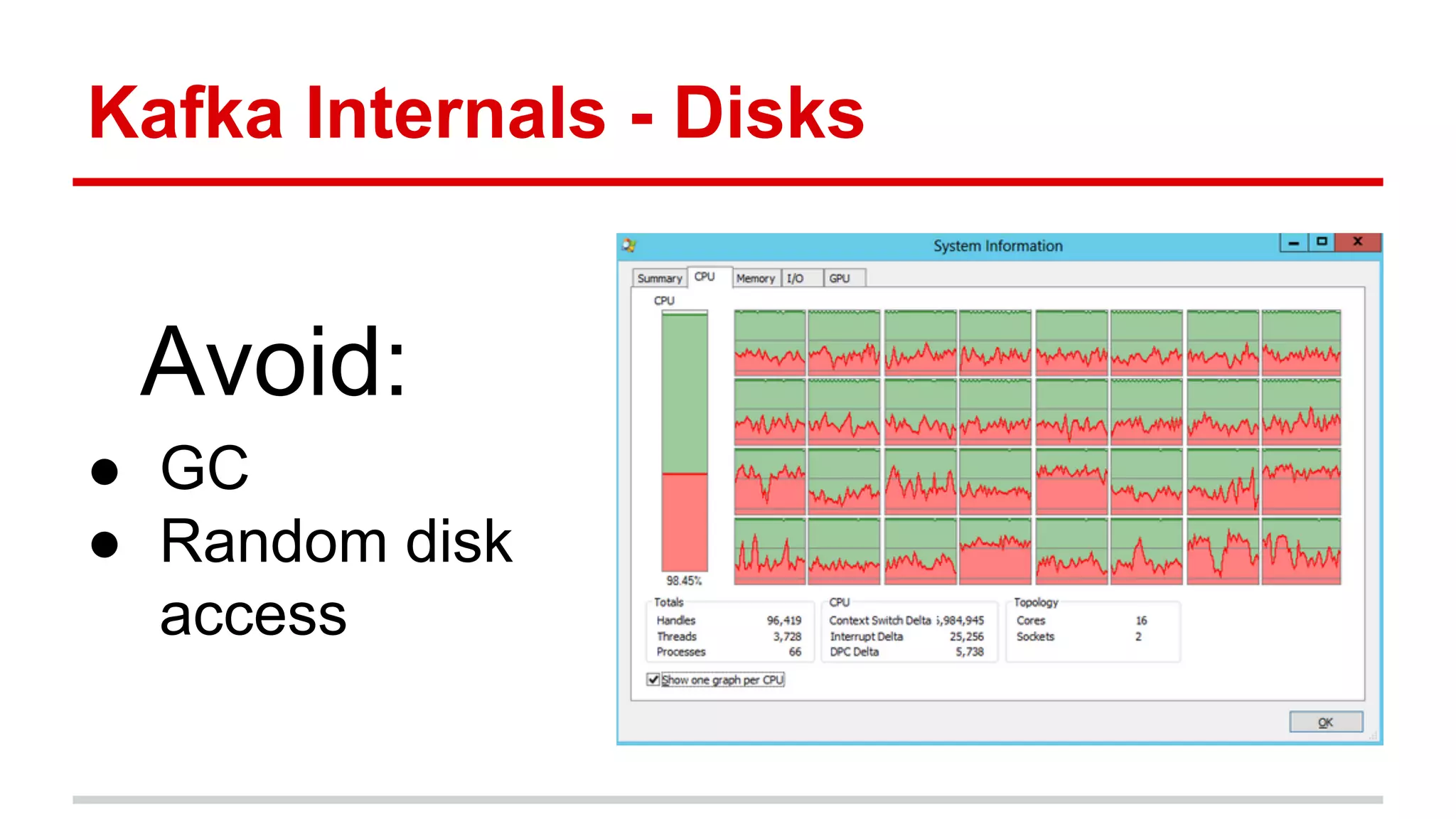
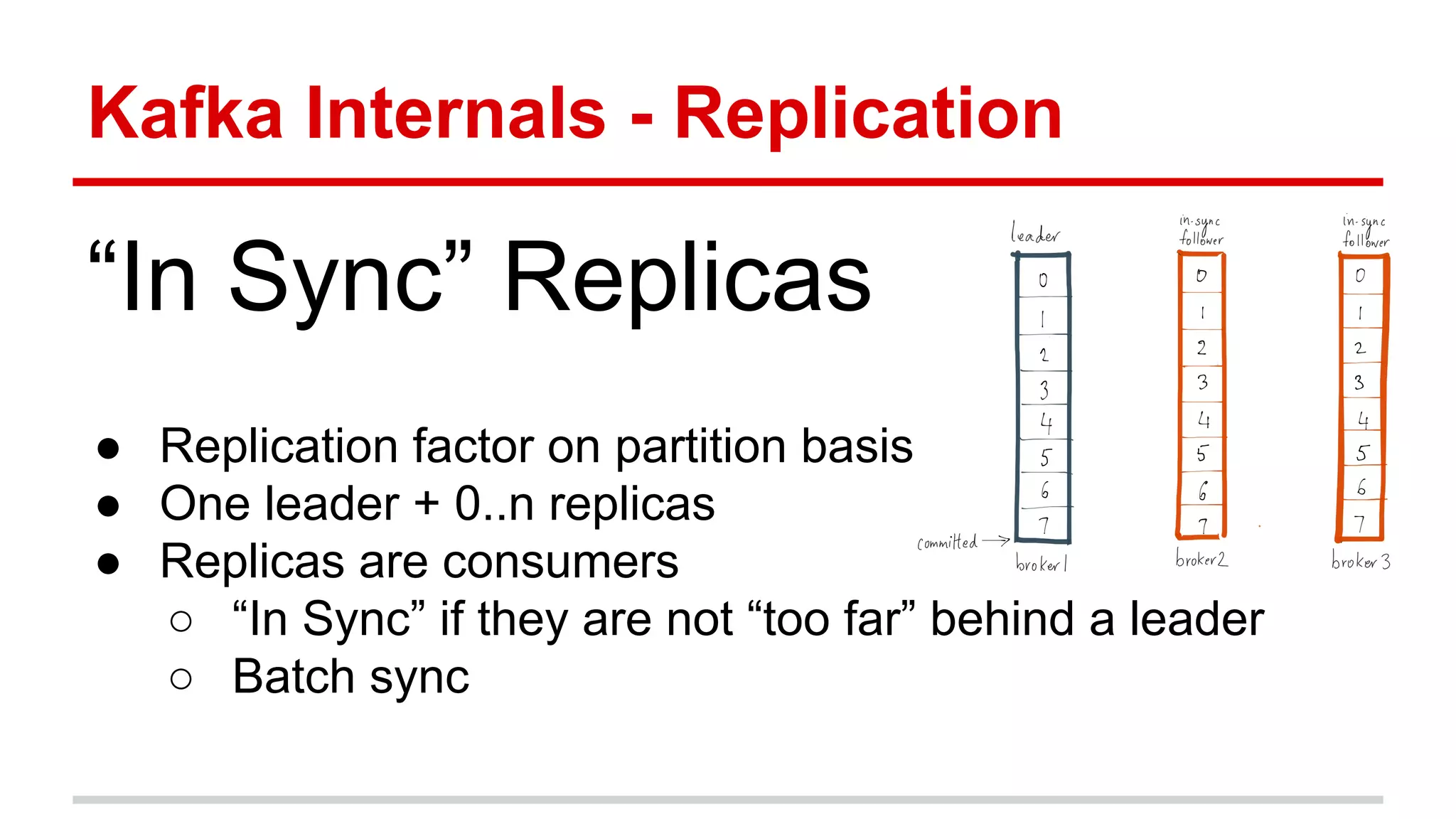
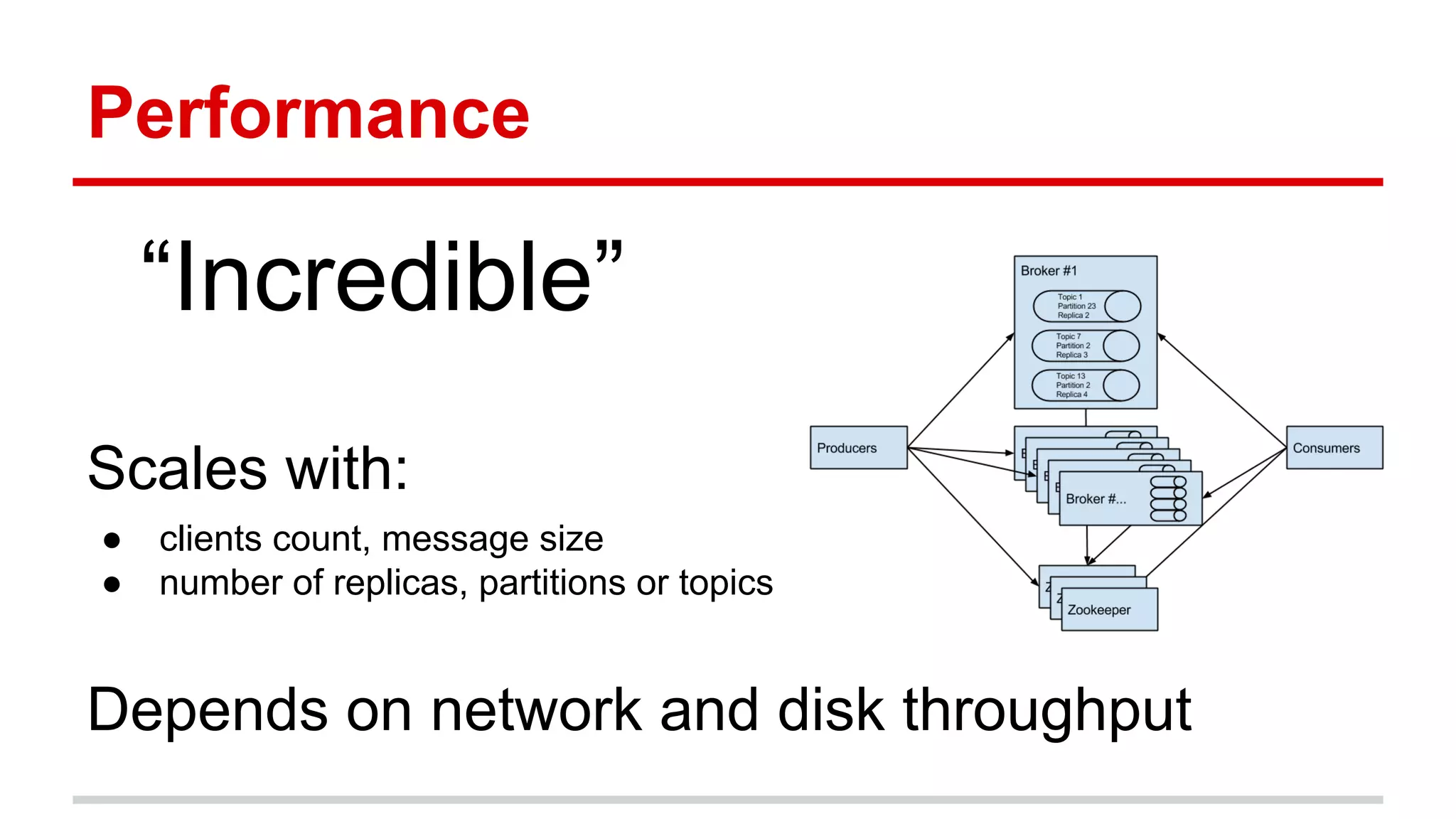
Apache Kafka is a distributed messaging system that allows for publishing and subscribing to streams of records, known as topics, in a fault-tolerant and scalable way. It is used for building real-time data pipelines and streaming apps. Producers write data to topics which are committed to disks across partitions and replicated for fault tolerance. Consumers read data from topics in a decoupled manner based on offsets. Kafka can process streaming data in real-time and at large volumes with low latency and high throughput.








![Performance Cont’d
Our testing
● 3 nodes, master + 2 replicas
● 500 000 msg/s (100 bytes[])
● 400 mbit/s - 1.2 gbit/s network throughput
● end2end latency 2-3 ms
@see http://bit.ly/1FsIR9a](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/apachekafkaczjug-150414011756-conversion-gate01/75/Apache-Kafka-Martin-Podval-20-2048.jpg)


