7 Upper respiratory tract infections
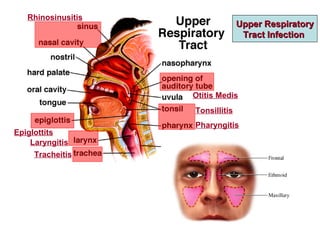
- 1. Upper RespiratoryUpper Respiratory Tract InfectionTract Infection Rhinosinusitis Otitis Medis Epiglottits Laryngitis Tracheitis Tonsillitis Pharyngitis
- 2. Importance of URTIImportance of URTI • Very commonly encountered condition in all age groups and all geographic regions. • Common cause for loss of school or work days. • Though a viral etiology is the most common, inappropriate antibiotic use has been a major contributor to the development of antibiotic resistance. Up to 70% of patients with sore throat seen in 1ry care settings receive prescriptions for antibiotics, while only 20 – 30 % are likely to have streptococcal pharyngitis. • Though most infections are mild and self limited, they may have important complications, particularly in pediatric age (infectious and non- infectious complications).
- 3. Respiratory Infections are the Most Common Reason for Office Visits America NDTI (National Disease Therapeutics Index) 2001. Mehrotra A. Health Affairs 2008 Sep-Oct;27(5):1272-82. NumberofOfficeVisits(millions) Respiratory Hypertension Gastrointestinal Diabetes Depression Infections Disorders 180 100 80 60 40 20 0 161 73 55 35 26
- 4. Over half of Antibiotic Use in Adults is for Respiratory Tract Infections 2004-2005 Physician Drug & Diagnosis Audit (PDDA)
- 5. RhinosinusitisRhinosinusitis IDSA Guidelines, 2012 – Update 2014IDSA Guidelines, 2012 – Update 2014 • Rhinitis (allergic and non-allergic) is closely associated with sinusitis (acute, chronic). • Viral etiology is more common, but antibiotic prescriptions outnumber those for any other condition. • Many other common conditions are closely associated as: - Otitis media: should be looked for when evaluating a case of rhinosinusitis. The reverse is true. - Bronchial asthma: ARS may initiate or worsen asthma. Management of CRS often results in improvement of asthma. - GERD
- 6. Types • ABRS (acute bacterial rhinosinusitis): symptoms for < 12 weeks RARS: recurrent acute rhinosinusitis: > 3 episodes of ABRS/year. • CRS (chronic rhinosinusitis): symptoms for > 12 weeks. It is a chronic inflammatory, rather than an infectious process. It is subdivided into CRSwNP and CRSsNP (with and without nasal polyps). Etiology • Non- Infectious: - Allergens - Irritants • Infectious: - Viral (90 – 98 %) - Bacterial (2 – 10 %) - Fungal The commonest cause of ARS is viral infection (acute catarrhal rhinitis – coryza – common cold) Commonest Bacteria in ABRS • Strept. Pnumoniae • Haemophilus influenzae. • Moraxella Catarrhalis. Other possible isolates in CRS • Staph. aureus. • P. aeruginosa. • Anerobes
- 7. Clinical Picture • Symptoms: - Purulent rhinorrhoea. - Nasal obstruction. - Post- nasal drainage. - Hyposmia/anosmia. - Facial/dental pain. - Headache. Acute Bacterial Rhinosinusitis (ABRSAcute Bacterial Rhinosinusitis (ABRS)) • Signs: - Discolored nasal, oropharyngeal secretion. - Mucosal erythema. - Sinus tenderness. - Fever (+/-).
- 8. How to Distinguish Bacterial from Viral Infection:How to Distinguish Bacterial from Viral Infection: • Persistent Symptoms: Symptoms last > 10days without improvement. • Severe Symptoms: High fever (> 39 O C), purulent nasal discharge > 3 - 4 days. • Worsening Symptoms: Apparent improvement followed by sudden worsening after > 3 – 4 days (double sickening). Awareness to certain features is important to avoid overuse of antibiotics:
- 9. InvestigationsInvestigations Plain X-Ray, CT: non- specific, do not distinguish bacterial from viral ARS. Culture of Paranasal Sinus Aspirate: The gold standard for diagnosis of ABRS is recovery of bacteria (> 104 CFU/mL) from cavity of paranasal sinus. It is particularly indicated in: - Cases refractory to medical treatment. - Immunocompromised patients in whom early identification of organism is required.
- 10. Main bacterial causes of ABRS are generally covered with β-lactam antibiotics. Because oral Amoxicillin has better PK/PD properties than oral penicillin, it is the preferred oral β-lactam agent. The addition of Calvulinic Acid improves coverage of ampicillin resistant H. influenzae and M. catarrhalis. Antibiotics are given orally, except in presence of severe infection, suppurative complications (as orbital cellulitis) or intolerance to oral route, when they are given IV. Duration: 5 – 7 days in adults, 10 – 14 days in children. TreatmentTreatment
- 11. 1st Line Anti-Microbial Therapy Amoxicillin/ Clavulinic Acid (Amoxaclave) 500/125 mg PO TID Or 875/125 mg PO BID Investigate for treatment failure
- 12. 22ndnd Line Anti-Microbial TherapyLine Anti-Microbial Therapy Risk of Antibiotic Resistance or Failed Initial Therapy: • Amoxaclave 2000/125 mg PO BID. • Levofloxacin 500 mg PO QD • Moxifloxacin 400 mg PO QD β-Lactam Allergy: • Doxycycline 100 mg PO BID (Vibramycin) • Levofloxacin 500 mg PO QD (Tavanic) • Moxifloxacin 400 mg PO QD (Avalox) Anti-Microbial Therapy of Severe InfectionAnti-Microbial Therapy of Severe Infection • Ampicillin/Sulbactam 1.5 – 3 gm IV / 6h (Unasyn) • Levofloxacin 500 mg IV QD • Moxifloxacin 400 mg IV QD • Ceftriaxone 1 – 2 gm IV / 12 – 24 h (Rocephin)
- 13. Adjunctive MeasuresAdjunctive Measures Intra- Nasal Corticosteroids • Primarily in patients with history of allergic rhinitis. • ↓ mucosal inflammation → improve sinus drainage. • Adverse reactions: epistaxis, ↑ susceptibility to oral candidiasis. Intra- Nasal Saline Irrigation • Relieve nasal burning, irritation. • If home made, use sterile or boiled water ( to avoid risk of amoebic encephalitis). Mucolytics Improve sinus drainage. Decongestants produce transient symptomatic relief of nasal obstruction that may be followed by rebound congestion. Antihistaminics Decrease rhinorrhoea and sneezing but may produce drowsiness, xerostomia.
- 14. Causes of Treatment FailureCauses of Treatment Failure • Inadequate dosing or non- compliance. • Non- Infectious etiology. • Resistant organism. • Structural abnormalities as nasal polyps, deviated septum. • Suppurative complications Orbital Cellulitis Cavernous Sinus Thrombosis
- 15. Chronic Rhinosinusitis (CRSChronic Rhinosinusitis (CRS)) Symptoms • Similar to ABRS but more subtle. • Pain is much less whereas hyposmia/amosmia are more common, esp. in CRSwNP. Investigations • Aeroallergen testing. • Sinus culture: in patients with persistent sinus discharge despite antibiotic treatment. • CT Scan: in unilateral cases to exclude tumours, anatomic defects, foreign bodies. • Tests for underlying disorders as cystic fibrosis and ciliary dyskinesia.
- 16. Treatment of CRSTreatment of CRSSystemic Antibiotics • Their role is controversial, but they should be used in acute exacerbations. • Usually continued for > 14 days. • Anaerobic pathogens may need to be considered. • Long- term systemic macrolide antibiotics may have anti- inflammatory effects, but clinical studies indicating their benefit are limited. Topical Antibiotics esp. if culture directed, eg, for S. aureus: Mupirocin or gentamycin irrigation. Topical aminoglycosides should be used cautiously and for a defined period only. Some patients may develop sensorineural hearing loss. Adjunctive Measures as in ABRS.
- 17. CRSwNP Some medical measures may help reduce polyp size “medical polypectomy” They improve smell and reduce nasal obstruction. However, benefit is variable and may ↓ with repeated courses. • Doxycyclin: 200 mg on 1st day followed by 100 mg once daily for 20 days. • Oral Steroids: Prednisone 30 mg/day for 4 days 25 mg for 2 days 20 mg for 2 days 15 mg for 2 days 10 mg for 2 days 5 mg for 2 days (Total 14 days) • Nasal Steroids.
- 18. Vasomotor RhinitisVasomotor Rhinitis Differential diagnosis of rhinitis includes: infectious, allergic, vasomotor, drug- induced (rhinitis medicamentosa) and occupational rhinitis • It is a diagnosis of exclusion. • No prospective studies had explicitly differentiated allergic from non- allergic rhinitis. Since there is significant overlap in treatment, differentiation is primarily significant only when considering environmental control, oral antihistaminics and immunotherapy, which have proven benefit only in allergic rhinitis. Etiology unknown.. Theories: • Runners: increased cholinergic glandular secretory activity. • Dry Patients: increased sensitivity to usually innocent stimuli Triggering factors include odours, fumes, emotions, changes in temperature and pressure.
- 19. Clinical Picture a highly diverse group of rhinitis syndromes. Symptoms may be seasonal or perennial. There are 2 subgroups: • Runners: rhinorrhoea mainly. • Dry Patients: nasal obstruction mainly. Treatment - Avoid triggering factors. - Runners: nasal anticholinergics as Ipratropium bromide (Atrovent). - Dry Patients: nasal steroids - Both: nasal antihistamincs as Azelastine (Azelast drops, Zalastin spray) - Pregnant women: Symptoms of rhinitis ↑ during pregnancy, possibly due to VD induced by pregnancy hormones and hypervolaemia (gestational rhinitis). Intranasal saline instillatin is safest. Other topical agents are pregnancy category B or C. - No evidence for: oral antihistaminics, oral decongestants.
- 20. Rhinitis MedicamentosaRhinitis Medicamentosa ((Rebound, Chemical, Drug- Induced RhinitisRebound, Chemical, Drug- Induced Rhinitis)) • It is a condition induced by overuse of nasal decongestants. • Also used to describe the adverse nasal congestion that develops when using other medications as: o Antihypertensives: α, β, ACEI, central sympathetic blockers. o PDE5Is. o Oestrogens (including hormonal contraceptives). o NSAIDs. o Major tranquilizers. • It is a relatively common condition, more in young, middle- aged adults. Diagnostic Criteria (not validated) • History of prolonged use of nasal decongestants (or use of other drugs). The condition develops after 3 to 30 days of decongestant use. (10 days is a rational compromise). • Constant nasal obstruction with little or no other nasal symptoms.
- 21. 2ry Effects of Chronic Nasal Obstruction - Mouth breathing → dry mouth, sore throat. - Insomnia, snoring. - Loss of nasal physiologic functions such as filtration of particles and regulation of temperature and humidity → predisposition to: • Atrophic rhinitis. • Nasal polyposis. • Chronic sinusitis. • Otitis media. - Psychological dependence → Cessation produces an abstinence syndrome characterized by headache, restlessness, anxiety. Some authors used the word : “addiction” when describing this syndrome.
- 22. Pathogenesis unknown.. Theories: • Downregulation of nasal mucosal α adrenoceptors (tachyphylaxis). • Feedback inhibition of endogenous noradrenaline secretion, which may persist even after discontinuation of the exogenous sympathomimetic. • Benzalkonium chloride, a preservative used to prevent bacterial contamination in many nasal sprays may ↑ the risk of RM by inducing mucosal swelling. In all cases, ↓ vasoconstrictor response to the nasal decongestant encourages the patient to ↑ the dose which further augments the problem (vicious circle). Pathology Nasal mucosa shows: • Nasociliary loss. • Squamous metaplasia. • Epithelial oedema. • Epithelial cell denudation. • Inflammatory cell infiltration.
- 23. Treatment • Stop nasal decongestant (or other offending drug): It is difficult and not recommended to stop the nasal decongestant abruptly. Gradual cessation may be done by: - Instilling into one nostril only at a time. - Decreasing the nasal decongestant dose and frequency. - Replacing the decongestant with a lower concentration or saline. - Nasal steroids ↓ nasal inflammation, oedema, obstruction. They should be continued for several weeks to obtain maximal benefit. • Other options as antihistaminics (oral/nasal), mast cell stabilizers: no significant evidence to support their use. Prevention RM is a preventable condition. This highlights the importance of increasing awareness of both patients and health care providers.
- 24. Group A Streptococcal (GAS) PharyngitisGroup A Streptococcal (GAS) Pharyngitis IDSA Guidelines, 2012IDSA Guidelines, 2012
- 25. Pharyngeal Congestion Palatal Petechae Strawberry Tongue Follicular Tonsillitis
- 26. Acute Pharyngitis MicrobiologyAcute Pharyngitis Microbiology Commonest bacterial etiology: GAS: 5 – 15 % of sore throat visits in adults (20 – 30 % in children).
- 27. How to Distinguish Bacterial from Viral Infection:How to Distinguish Bacterial from Viral Infection:
- 28. Laboratory DiagnosisLaboratory Diagnosis Rapid Antigen Detection Test (RADT) • Proved useful to aid early treatment → ↓ morbidity and complications (infectious, non- infectious). • Test fluid is extracted from throat swab specimen. • Accuracy depends on the quality of the swab sample. • Specificity is comparable to throat culture, but sensitivity is less.
- 29. Throat Culture • Gold standard for diagnosis, but time consuming (read at 24, 48 h). • Swab obtained from surface of tonsils, posterior pharyngeal wall. Other areas of mouth, oropharynx are not acceptable. • False negative if pt received antibiotics shortly before taking the swab. • Back Up Culture (after – ve RADT): Recommended in children due to relatively higher incidence of GAS pharyngitis and relatively greater risk of acute rheumatic fever. The reverse is true in adults. Anti-Streptolysisn O Titre * Not useful in diagnosis of acute pharyngitis bec. Ab titre may not peak until 3 - 8 weeks after infection, and may remain elevated for months or years without active GAS infection. * Useful in diagnosis of non- infectious sequelae.
- 30. Infectious (Suppurative) ComplictionsInfectious (Suppurative) Complictions • GAS pharyngitis is the only commonly occurring form of acute pharyngitis for which antibiotic therapy is definitely indicated. This need is mainly due to the risk of complications. • Otitis media (more in children) • Peritonsillar abscess • Sinusitis • Toxic shock syndrome
- 31. Non- Infectious (Non- Suppurative) ComplictionsNon- Infectious (Non- Suppurative) Complictions • Rheumatic fever • Post- streoptococcal glomerulonephritis
- 33. Treatment of GAS PharyngitisTreatment of GAS Pharyngitis •The aim of treatment is to eradicate the organism from the pharynx to prevent development of supppurative and non- suppurative complications (PSGN occurrence is not affected by treatment). • A clinical response is usually achieved within 24 – 48 h. • Persistence of symptoms beyond that suggests either; o Development of suppurative complications. o The condition was actually viral pharyngitis. Even if GAS were detected by RADT or culture, this may reflect pharyngeal carrier state rather than infection. •Penicillin remains the treatment of choice for GAS pharyngitis because of its proven efficacy, safety, narrow spectrum and low cost. Penicillin resistant GAS were never documented. • Penicillin V may be used in place of penicillin injection. • Amoxicillin may be used in place of penicillin V in children (suspension more palatable). • Antimicrobial chemoprophylaxis is not needed except in patients who had a previous attack of rheumatic fever.
- 35. Penicillin AllergyPenicillin Allergy • Allergy to penicillin and related antibiotics is the most commonly reported drug allergy. • 10% of patients report a history of “penicillin allergy”, but true allergy may be present in 1% only. • Hypersensitivity reactions are among the most serious reactions caused by cephalosporins. • The risk of cephalosporin allergy is increased in patients with penicillin allergy. However, the risk of cross reactivity between penicillins and cephalosporins is lower than what was historically reported. • Cross reactivity between penicillins and cephalosporins was attributed to the β lactam ring which is common to penicillins, cephalosporins, carbapenems and monobactams. • It was later realized that cross reactivity is more closely linked to the side chain structure. Therefore, only 1st generation cephalosporins cause noteworthy cross reactivity. Changes in the chemical structure of most cephalosporins that are 2nd generation and higher make cross reactivity less a problem.
- 36. • Penicillin skin test has poor positive predictive value but excellent negative predictive value. • Patients who were tolerant to penicillin may at some time develop penicillin allergy. Conversely, patients allergic to penicillin may lose this reaction with time. This may be further aided by desensitization therapy. • Dispensing a cephalosporin to a penicillin allergic patient should be evaluated based on the type of allergic reaction and the drug prescribed: 1) Avoid Cephalosporins if the patient had a history of penicillin allergy which is: A. Type I (immediate or anaphylactic, which is the most life threatening) B. Non Type I but potentially serious, eg, * Stevens Johnson syndrome (SJS) * toxic epidermal necrolysis (TEN) * interstitial nephritis, vasculitis, cytopenias. 1) Penicillin allergy exclusive of what listed above can permit dispensing of some cephalosporins of 2nd generation or higher.
- 37. SJSTEN
- 38. GAS Throat CarriersGAS Throat Carriers • Throat carriers have GAS in pharynx, but no disease and no immunologic response (normal ASOT). • RADT, throat culture do not distinguish active infection from throat carrier state. • So, these tests should only be used in presence of suggestive clinical features. • GAS carriers are unlikely to spread GAS pharyngitis to their close contacts, and unlikely to develop infectious or non- infectious complications. • GAS carriers do not generally justify efforts for their identification, nor do they generally require antibiotic treatment.
- 39. GAS Throat CarriersGAS Throat Carriers(cont(cont.).) • Eradication of GAS carrier state is desirable in some situations: • During a community outbreak of acute rheumatic fever, acute post- streptococcal glomerulonephritis, or invasive GAS infection. • During an outbreak of GAS pharyngitis in a closed community. • Personal or family history of acute rheumatic fever. • If tonsillectomy is being considered only for carriage.
- 40. It is much more difficult to eradicate GAS pharyngitis from throat carriers than from patients. So, compared with their use in treatment of patients, antibiotics are used in higher doses or used with added agents (Calvulanate or Rifampin)
Editor's Notes
- Prevalence of Respiratory Infections Respiratory tract infections make up more than twice the number of office visits made for hypertension, gastrointestinal disorders, diabetes, and depression combined.
- The Physician Drug and Diagnosis Audit (PDDA) is a proprietary monthly survey that monitors disease states and the physician-intended associated drug and nondrug therapy. Approximately 3,400 office-based physicians representing 29 different specialties across the United States report all patient activity during 1 typical workday per month.
- Another photo of follicular tonsillitis