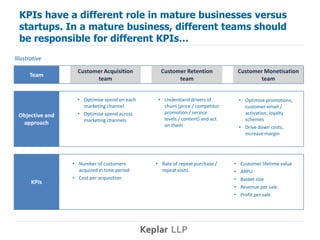
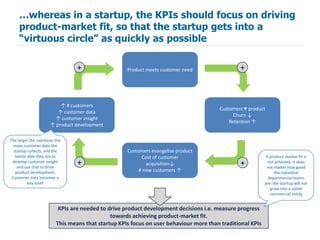
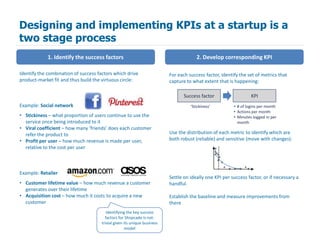
KPIs play a different role in startups than mature businesses. In startups, KPIs should focus on measuring progress towards achieving product-market fit rather than traditional metrics like customer acquisition and retention. To develop startup KPIs, companies first identify key success factors that drive product-market fit, then establish one or a few KPIs to measure each success factor. Good startup KPIs are relevant, responsive, easy to understand, and part of a broader analytics effort to inform ongoing product development.