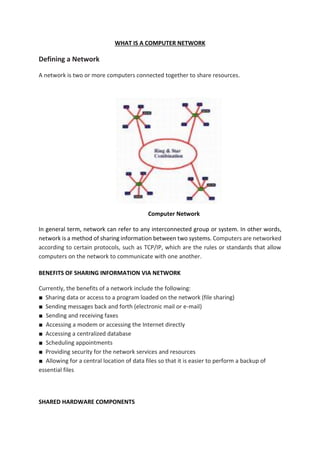
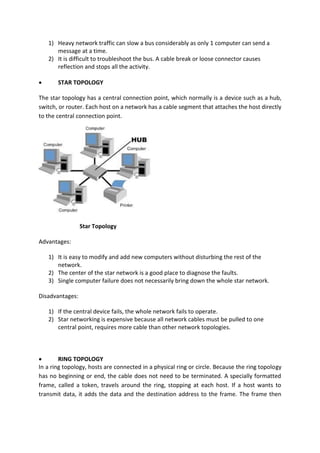
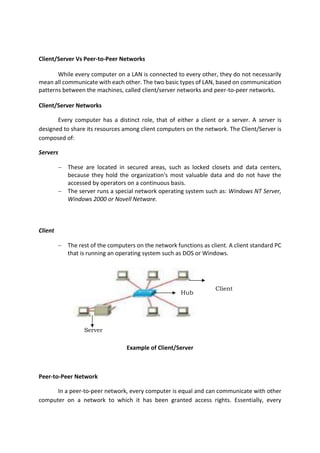
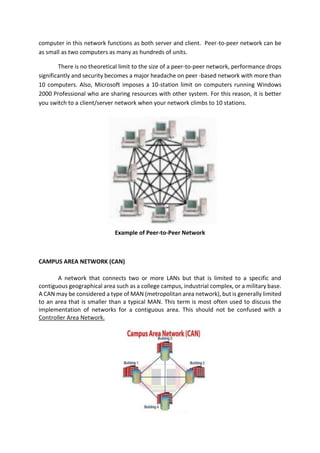
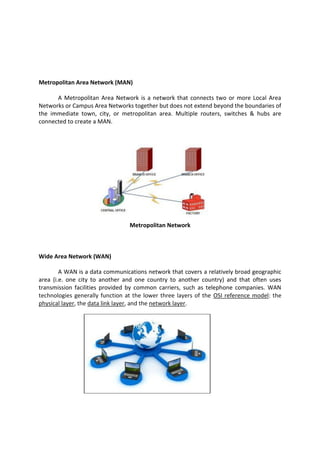
The document outlines a computer system servicing program focusing on the installation of network cables, detailing necessary competencies, tools, and safety procedures. It describes various network topologies (bus, star, and ring) and their advantages and disadvantages, along with types of networks including PAN, LAN, CAN, MAN, WAN, and GAN. The document emphasizes the importance of following established procedures and safety standards to ensure successful network setup and operation.