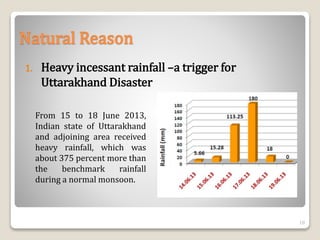
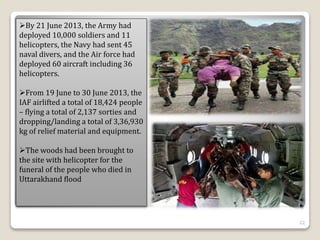
The document summarizes the 2013 Kedarnath tragedy in Uttarakhand, India. Heavy rainfall between June 15-18, 2013 triggered devastating floods and landslides that killed thousands. The rains were about 375% heavier than normal. The collapse of the moraine-dammed Chorabari Glacier lake also contributed to the floods. While natural factors played a role, environmental degradation from deforestation, construction, and tourism development exacerbated the impacts. The disaster destroyed homes and infrastructure, with thousands dead or missing. Rescue efforts involved military, police, and disaster response teams. The long-term recovery required rehabilitation of livelihoods and infrastructure, along with disaster preparedness reforms.