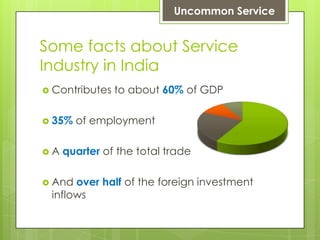
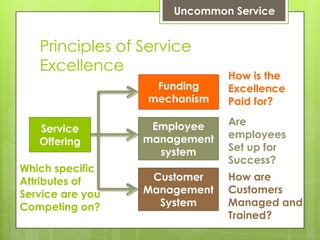
The document discusses the importance of designing effective service models in the service industry, particularly in India, to deliver exceptional customer experiences. It outlines key principles and truths for achieving service excellence, including the need to prioritize customer values, manage employee performance, and effectively engage customers. It emphasizes that service excellence stems from strategic choices rather than mere effort and attitude of employees.