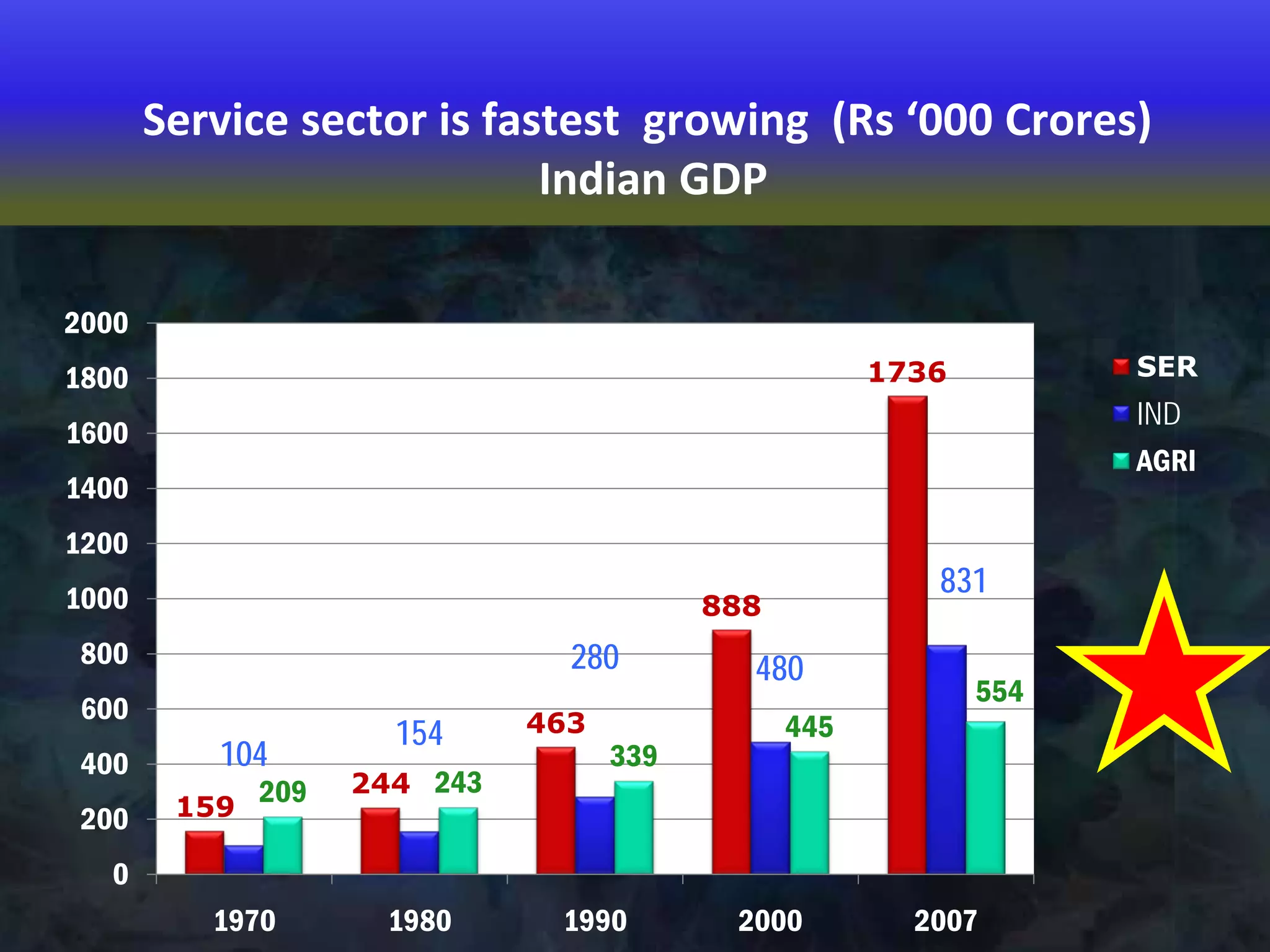
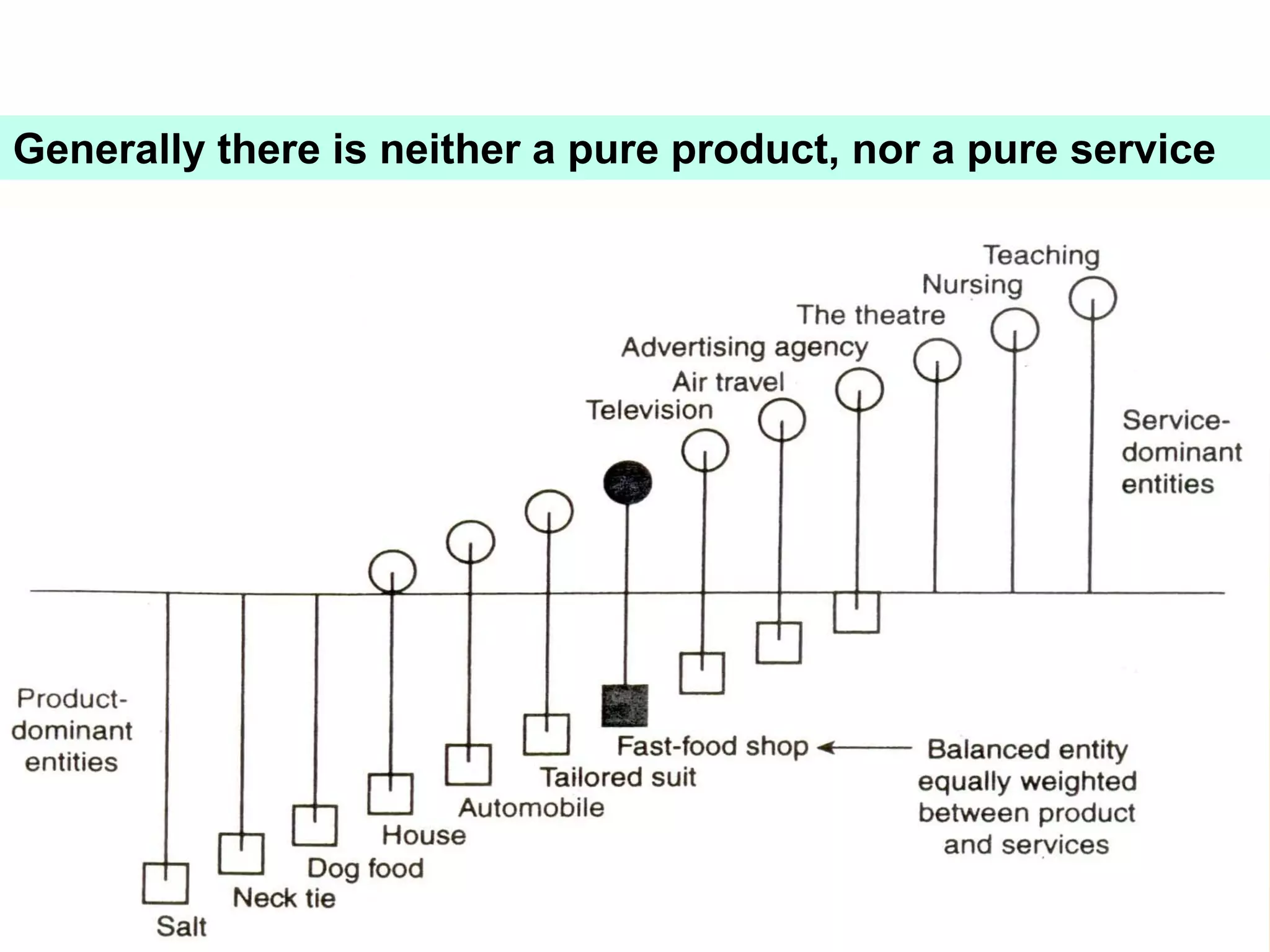
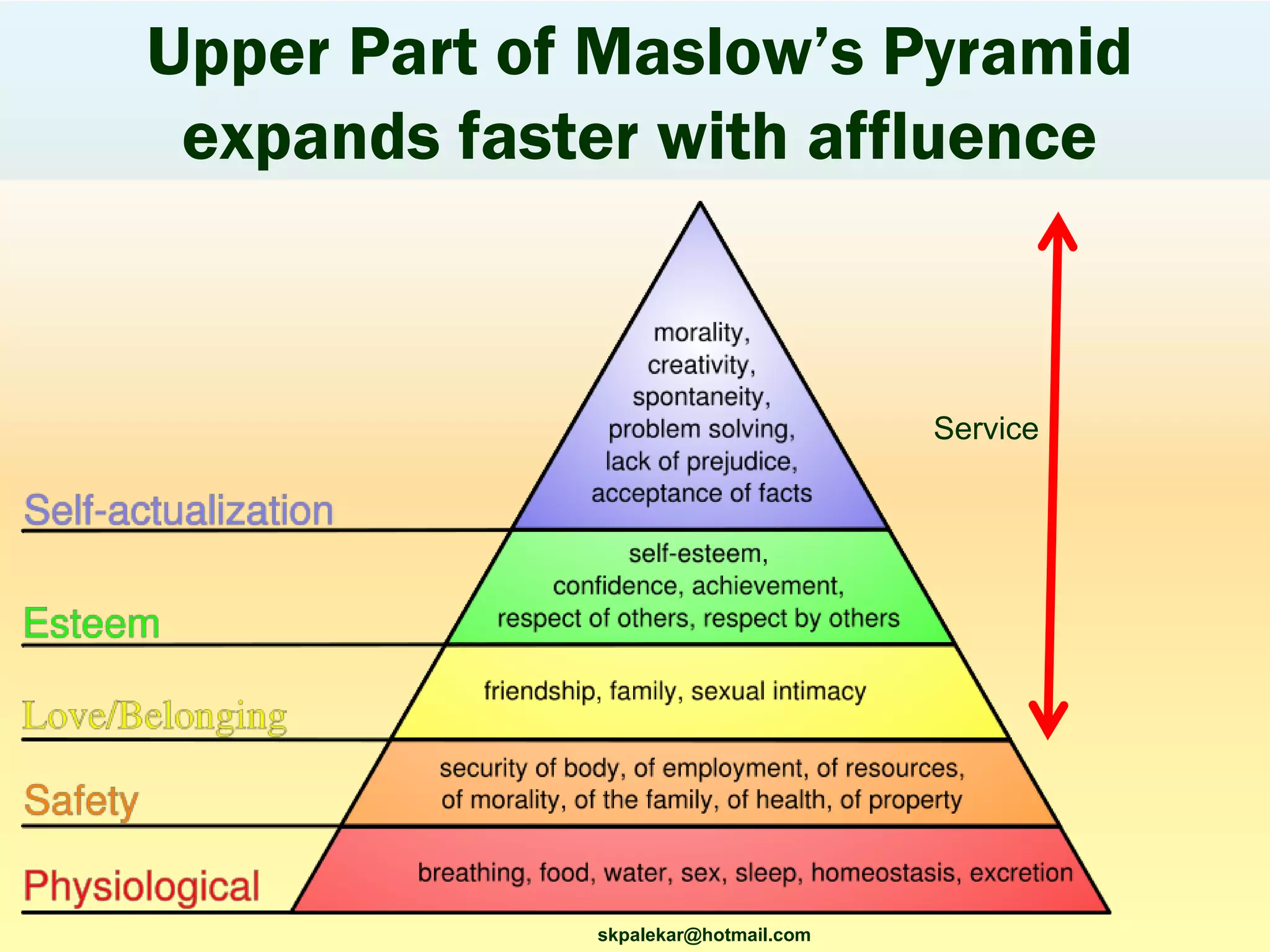
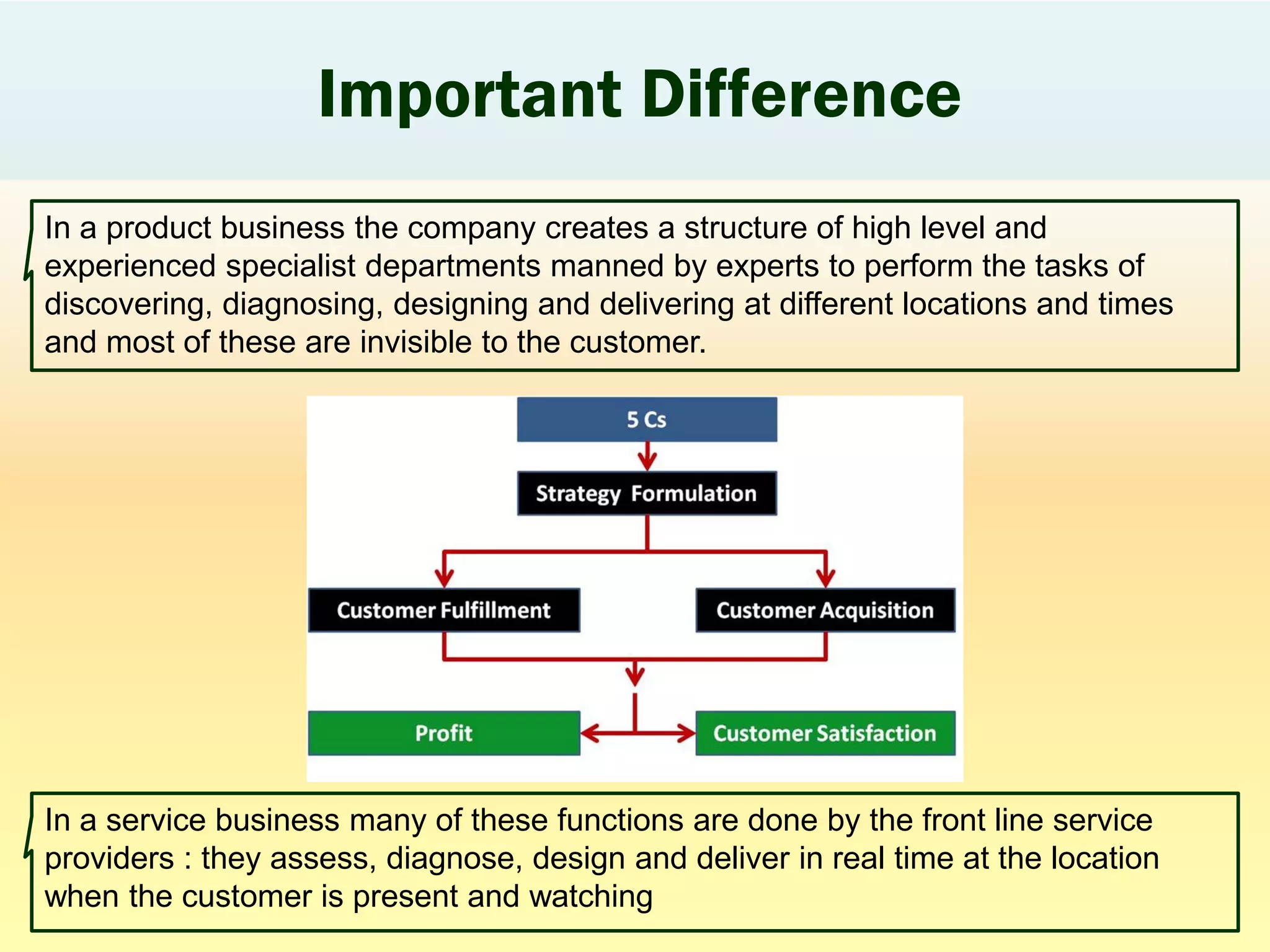
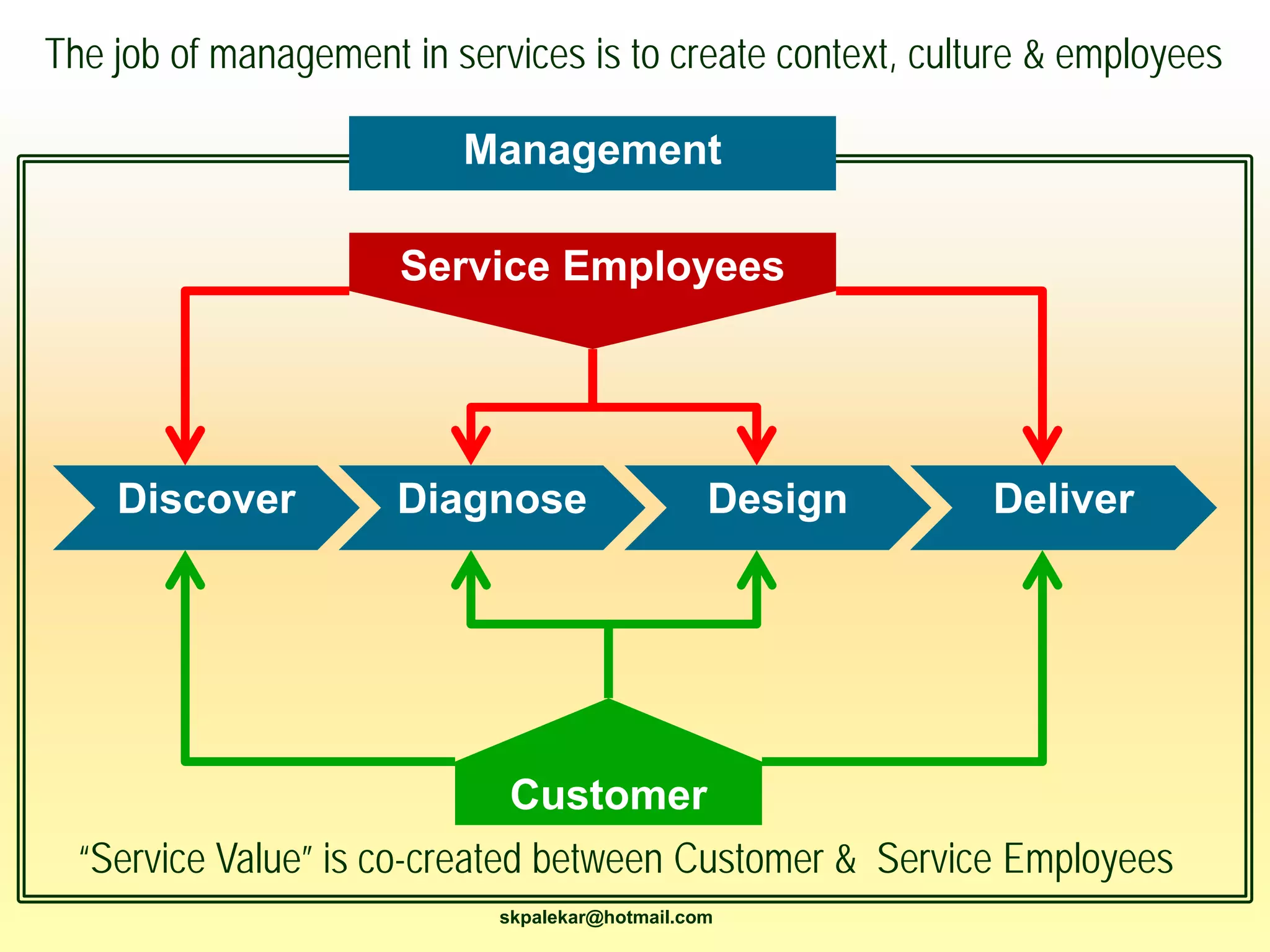
This document provides an overview of a 3-session course on services marketing taught by Prof. S.K. Palekar. The course aims to prepare students for consulting, business development, and operations roles in IT and ITES industries. Key topics covered include an introduction to services, how services differ from products, how services create value for customers, and how to compete in the services sector. The document also discusses different types of services, factors that distinguish high-contact from low-contact services, and how to organize operations and manage quality for each type.