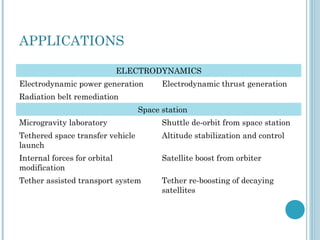
This document discusses electrodynamic tethers, which use the Lorentz force generated by the interaction between a current in the tether and the Earth's magnetic field to propel or deorbit spacecraft. Electrodynamic tethers can be used to accelerate a spacecraft into a higher orbit or decelerate it into a lower orbit without using propellant. They work by either collecting electrons at one end of the tether and expelling them at the other end, or driving current in the opposite direction. Challenges include stabilizing the tether's motion, but feedback algorithms can help maintain stability. Potential applications include propulsion of spacecraft in low Earth orbit, deorbiting of satellites, and reboosting of decaying orbits.