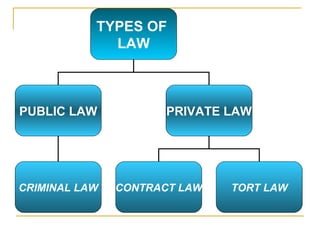
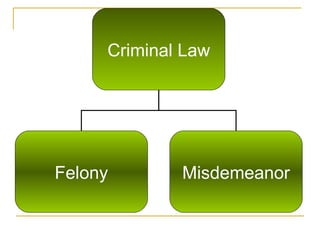
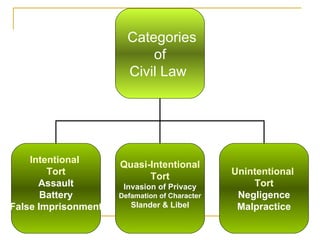
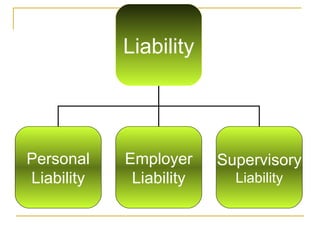
The document discusses several key legal implications in nursing practice, including sources of law, licensure, risk management, and the use of restraints. It notes that law establishes the framework for legal nursing actions and differentiates nurse responsibilities. Licensure is required and can be revoked for incompetence, misconduct or crimes. Risk management focuses on preventing injuries to patients and staff and reducing liability. Restraint use must be ordered, implemented safely and for the least time possible.