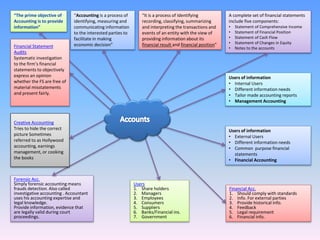
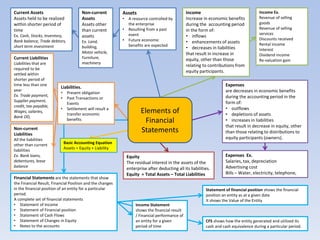
Accounting involves identifying, measuring, recording, and communicating financial information about an entity's transactions and events. This information is presented in financial statements, including the statement of financial position, statement of comprehensive income, statement of cash flows, and statement of changes in equity. Financial accounting provides historical financial information to external users, while management accounting provides customized reports for internal decision-making. Financial statements must comply with accounting standards and undergo auditing to ensure fair presentation and absence of material misstatements.