telecommunication system
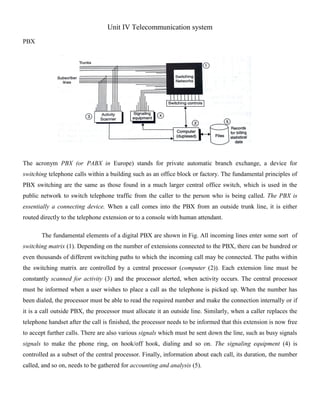
- 1. Unit IV Telecommunication system PBX The acronym PBX (or PABX in Europe) stands for private automatic branch exchange, a device for switching telephone calls within a building such as an office block or factory. The fundamental principles of PBX switching are the same as those found in a much larger central office switch, which is used in the public network to switch telephone traffic from the caller to the person who is being called. The PBX is essentially a connecting device. When a call comes into the PBX from an outside trunk line, it is either routed directly to the telephone extension or to a console with human attendant. The fundamental elements of a digital PBX are shown in Fig. All incoming lines enter some sort of switching matrix (1). Depending on the number of extensions connected to the PBX, there can be hundred or even thousands of different switching paths to which the incoming call may be connected. The paths within the switching matrix are controlled by a central processor (computer (2)). Each extension line must be constantly scanned for activity (3) and the processor alerted, when activity occurs. The central processor must be informed when a user wishes to place a call as the telephone is picked up. When the number has been dialed, the processor must be able to read the required number and make the connection internally or if it is a call outside PBX, the processor must allocate it an outside line. Similarly, when a caller replaces the telephone handset after the call is finished, the processor needs to be informed that this extension is now free to accept further calls. There are also various signals which must be sent down the line, such as busy signals signals to make the phone ring, on hook/off hook, dialing and so on. The signaling equipment (4) is controlled as a subset of the central processor. Finally, information about each call, its duration, the number called, and so on, needs to be gathered for accounting and analysis (5).
- 2. GSM Architecture The figure shows the three main parts that the network architecture can be divided into: Mobile Station (MS). Base Station Subsystem (BSS). Net Subsystem (NS). The Mobile Station consists of the mobile equipment. Typically a mobile phone. The mobile equipment is uniquely identified by the International Mobile Equipment Identity (IMEI), which is there to prevent theft. Furthermore, the MS has to be equipped with a Subscriber Identity Module a so called SIM card. The SIM card identifies the user to the network using a International Mobile Subscriber Identity (IMSI). The SIM card can be used in different mobile equipment. The Base Station Subsystem can be divided into two parts: The Base Transceiver Station (BTS) and the Base Station Controller (BSC). The BTS houses the radio transceivers that defines a cell. The BSC manages the radio resources of one or more BTS. The Network Subsystem consists of the Mobile services Switching Center (MSC) that functions as a normal switching node of a PSTN (Public Switched Telephone Network) or an ISDN node. With the added functionality of handling Mobile stations such as: Registration, authentication, location updating, handovers, and call routing to a roaming subscriber. Furthermore, the Network Subsystem consists of four databases: The Home Location Register (HLR) that contains all the administrative information of the networks subscribers, The Visitor Location Register that contains selected administrative information from the HLR regarding the roaming users in the cells managed by the MSC, The Equipment Identity Register (EIR) and The Authentication Center provides security and authentication.
- 3. GPRS System Architecture The GPRS is an enhancement over the GSM and adds some nodes in the network to provide the packet switched services. These network nodes are called GSNs (GPRS Support Nodes) and are responsible for the routing and delivery of the data packets to and form the MS and external packet data networks (PDN). The figure 2.2 below shows the architecture of the GPRS system. The most important network nodes added to the existing GSM networks are: SGSN (Serving GPRS Support Node). GGSN (Gateway GPRS Support Node). The serving GPRS support node (SGSN) is responsible for routing the packet switched data to and from the mobile stations (MS) within its area of responsibility. The main functions of SGSN are packet routing and transfer, mobile attach and detach procedure (Mobility Management (MM)), location management, assigning channels and time slots (Logical Link Management (LLM)), authentication and charging for calls. It stores the location information of the user (like the current location, current VLR) and user profile (like IMSI addresses used in packet data networks) of registered users in its location register. The gateway GPRS support node (GGSN) acts as interface between the GPRS backbone and the external packet data network (PDN). It converts the GPRS packet coming from the SGSN into proper packet data protocol (PDP) format (i.e. X.25 or IP) before sending to the outside data network. Similarly it converts the external PDP addresses to the GSM address of the destination user. It sends these packets to proper SGSN. For this purpose the GGSN stores the current SGSN address of the user and his profile in its location register. The GGSN also performs the authentication and charging functions. In general there may be a many to many relationship between the SGSN and GGSN. However a service provider may have only one GGSN and few SGSNs due to cost constraints. A GGSN proved the interface to several SGSNs to the external PDN.
- 4. UMTS (Universal mobile telecommunication services) UMTS offers tele-services (like speech or SMS) and bearer services, which provide the ability for information transfer between access points. It is possible to negotiate and renegotiate the characteristics of a bearer service at session or connection establishment and during ongoing session or connection. Both connection oriented and connectionless services are offered for point to-Point and Point-to-Multipoint communication. Bearer services have different QoS parameters for maximum transfer delay, delay variation and bit error rate. Offered data rate targets are: 144 kbits/s satellite and rural outdoor 384 kbits/s urban outdoor 2048 kbits/s indoor and low range outdoor UMTS network services have different QoS classes for four types of traffic: Conversational class (voice, videotelephony, video gaming) Streaming class (multimedia, video on demand, webcast) Interactive class (web browsing, network gaming, database access) Background class (email, SMS, downloading) UMTS will also have a Virtual Home Environment (VHE). It is a concept for personal service environment portability across network boundaries and between terminals. Personal service environment means that users are consistently presented with the same personalized features, User Interface customization and services in whatever network or terminal, wherever the user may be located. UMTS also has improved network security and location based services. 3. UMTS Architecture
- 5. A UMTS network consist of three interacting domains; Core Network (CN), UMTS Terrestrial Radio Access Network (UTRAN) and User Equipment (UE). The main function of the core network is to provide switching, routing and transit for user traffic. Core network also contains the databases and network management functions. The basic Core Network architecture for UMTS is based on GSM network with GPRS. All equipment has to be modified for UMTS operation and services. The UTRAN provides the air interface access method for User Equipment. Base Station is referred as Node-B and control equipment for Node-B's is called Radio Network Controller (RNC). UMTS systems (including satellite) Public Land Mobile Network (PLMN) MSC/VLR or SGSN Location Area Routing Area (PS domain) UTRAN Registration Area (PS domain) Cell Sub cell DECT Functional Concept The DECT subsystem is a microcellular or picocellular cordless telephone system that may be integrated with or connected to a Private Automatic Branch Exchange (PABX) or to the Public Switched Telephone Network (PSTN). A DECT system always consists of the following five functional entities as shown in Figure Portable Handset (PH): This is the mobile handset or the terminal. In addition, cordless terminal adapters (CTAs) may be used to provide fax or video communications. Radio Fixed Part (RFP): This supports the physical layer of the DECT common air interface. Every RFP covers one cell in the microcellular system. The radio transmission between RFP and the portable unit uses multi carrier TDM A. A full duplex operation is achieved using time division duplexing (TDD). Cordless Controller (CC or Cluster Controller): This handles the MAC, DLC, and network layers for one or a cluster of RFPs and thus forms the central control unit for the DECT equipment. Speech coding is done in the CC using 32 kbps ADPCM. Network-specific Interface Unit : This supports the call completion facility in a multihandset environment. The interface recommended by the CCITT is the G.732 based on ISDN protocols.
- 6. Supplementary Services: This provides centralized authentication and billing when DFCT is used to provide telenoint services and mobility management when DECT is used in multilocation PAPX network. Wi-Fi (wireless fidelity) Wi-Fi is a popular wireless networking technology. Wi-Fi stands for “wireless fidelity”. The Wi-Fi was invented by NCR corporation/AT&T in Netherlands in 1991. By using this technology we can exchange the information between two or more devices. Wi-Fi has been developed for mobile computing devices, such has laptops, but it is now extensively using for mobile applications and consumer electronics like televisions, DVD players and digital cameras. There should be two possibilities in communicating with the Wi-Fi connection that may be through access point to the client connection or client to client connection. Wi-Fi is a one type of wireless technology. It is commonly called as wireless LAN (local area network). Wi-Fi allows local area networks to operate without cable and wiring. It is making popular choice for home and business networks. A computer’s wireless adaptor transfers the data into a radio signal and transfers the data into antenna for users. The following list summarizes some of the benefits of a Wi-Fi network. • Wireless Ethernet: Wi-Fi is an Ethernet replacement. Wi-Fi and Ethernet, both IEEE 802 networks, share some core elements. Extended Access: The absence of wires and cables extends access to places where wires and cables cannot go or where it is too expensive for them to go. Cost Reduction: As mentioned above, the absence of wires and cables brings down cost. This is accomplished by a combination of factors, the relatively low cost of wireless routers, no need for trenching, drilling and other methods that may be necessary to make physical connections. Mobility: Wires tie you down to one location. Going wireless means you have the freedom to change your location without losing your connection. Flexibility: Extended access, cost reductions, and mobility create opportunities for new applications as well as the possibility of creative new solutions for legacy applications. Blue tooth Bluetooth works in the Industrial, Scientific and Medical (ISM) band from 2400-2483.5 MHz (including guard bands) from mobile as well as fixed devices by creation of PANs with high security level. Several
- 7. devices can be connected by using this technology, overcoming synchronization problems. Bluetooth uses technology called Frequency-Hopping Spread Spectrum (FHSS) which is a radio technology. The data to be transmitted is first divided into packets and then each packet is made to transmit on one among the designated 79 Bluetooth channels. Bandwidth of each channel is 1 MHz. The very first channel starts at frequency of 2402 MHz and goes up to 2480 MHz in steps of 1 MHz. Usually it performs 1600 hops per second Bluetooth is a packet-based protocol which is having a master-slave structure. In a piconet up to 7 slaves can be communicated by one master. Timing on the network can be controlled by Bluetooth by designating one device as a slave and the other as a master. The unit which initiates communication link is master and the other participants are slaves. After breakdown of link, the designations of master/slave no longer apply. Fact is that, every Bluetooth device is having both master and slave hardware. The network is called as piconet, which means a small network. When number of slaves is only one, then link is called as point-to-point. In a point-to-multipoint configuration up to seven active slaves can be controlled by a master When a device want to connect to another device via Bleutooth it first enters an inquiry substate. This allows it to scan, or inquire, for detectable devices. Every device that is detectable enters inquiry scan substate once per given time. When the inquiry scan substate registers an inquiry from a master device it enters the inquiry response substate and answers with an inquiry response message which includes the device’s address and clock. The master will receive such a message from all detectable devices in range. Therefore the wanted device is usually manually detected. When this is done the device enters paging substate. If the other device is set to connect to other devices it enters page scan substate once per given time.
- 8. When the slave receives a page packet from the master it responds with a page response packet. Upon receiving the master shall send several synchronization packets to adjust synchronize the frequency hopping and clock in both devices. When this is done the devices go into connection state. In transmission state the devices take on any of the four following states: active sniff, hold or park state. Active state means that both devices are connected constantly and are always listening transmitting or receiving on the channel. In sniff state the slave stops scanning for the masters packets on all channels but listens in on specific channels on specific times, saving energy. In hold mode the slave does not listen to channels connecting multiple devices in the piconet. It goes into a low power sleep mode allowing the channel to be used for paging and scanning. When in park mode the slave is not an active part of the network or piconet. Its Bluetooth address switches from active member address to passive member address FAX The essential parts of a fax system are the transmitting devices that translate the graphic material into electrical impulses according to a set pattern, and a synchronized receiving device that retranslates these impulses and prints that. In a typical system, the fax scanner consists of a rotating cylinder, a source projecting a narrow beam of light and a photoelectric cell. The copy to be transmitted is wrapped around the cylinder and is scanned by the light beam, which moves along the cylinder as it revolves. The output of the photoelectric cell is amplified and transmitted to the receiving end, where a similar cylinder, covered with specially impregnated paper, revolves in synchronism with the transmitting cylinder. A light of varying intensity moves along the rotation cylinder and darkens the paper by chemically reproducing the pattern of the original. When the fax is done, it pops out as a blue print of what the other person sent. 1. To send a fax, you feed the page into the input slot and it's pulled in between several pairs of rollers. Larger fax machines have built-in document feeders that automatically feed in multiple pages from a stack, so you don't have to stand at the machine feeding in pages one at a time. 2. As the paper moves down, a bright light shines onto it. White areas of the page reflect a lot of light; black areas reflect little or none. 3. The light reflects off the page into a light-detecting CCD (charged-coupled device)
- 9. 4. The CCD turns the analog pattern of black and white areas on the page into a numeric (digital) pattern of binary zeros and ones and passes the information to an electronic circuit. 5. The circuit sends the digital information down the telephone line to the fax machine at the receiving end. 6. When you receive a fax, the same circuit takes incoming digital information from the phone line and routes it to a built-in printer. 7. In a typical personal fax machine, paper is pulled from a large roll inside the machine. (In a larger office fax machine, it usually comes from a plain-paper hopper, similar to the one in a laser printer.) 8. The thermal (heat-based) printer, operated by the circuit, reproduces the incoming fax on the paper as it moves past. 9. An automatic blade cuts the page and the printed fax emerges from the output slot. IMT 2000 IMT 2000 (International Mobile Telecommunications for the year 2000) is a worldwide set of requirements for a family of standards for the 3rd generation of mobile communications. The IMT-2000 "umbrella specifications" are developed by the International Telecommunicatons Union (ITU). Originally it was the intention to have only one truly global standard but that turned out to be impossible. IMT-2000 should provide worldwide mobile broadband multimedia services via a single global frequency band. The frequency range should be around 2000 MHz.
- 10. In the umbrella specification a number of characteristics are defined which the underying technologies should meet. The main characteristics are: Worldwide usage, integration of satellite and terrestrial systems to provide global coverage; Used for all radio environments, (LAN, cordless, cellular, satellite); Wide range of telecommunications services, (voice, data, multimedia, internet); Support both packet-switched (PS) and circuit-switched (CS) data transmission; Offer high data rates up to 2 Mbps, o 144 kbps for high mobility, o 384 kbps with restricted mobility and, o 2 Mbps in an indoor office environment; Offer high spectrum efficiency; Wireless Local Loop Local loop is a circuit line from a subscriber’s phone to the local central office (LCO). But the implementation of local loop of wires is risky for the operators, especially in rural and remote areas due to less number of users and increased cost of installation. Hence, the solution for it is the usage of wireless local loop (WLL) which uses wireless links rather than copper wires to connect subscribers to the local central office. WLL components: 1. PSTN: It is Public Switched Telephone Network which is a circuit switched network. It is a collection of world’s interconnected circuit switched telephone networks. 2. Switch Function: Switch Function switches the PSTN among various WANUs. 3. WANU: It is short for Wireless Access Network Unit. It is present at the local exchange office. All local WASUs are connected to it. Its functions includes: Authentication, Operation & maintenance, Routing, Transceiving voice and data. It consists of following sub-components: Transceiver: It transmits/receives data.
- 11. WLL Controller: It controls the wireless local loop component with WASU. AM: It is short for Access Manager. It is responsible for authentication. HLR: It is short for Home Location Register. It stores the details of all local WASUs. 2. WASU: It is short for Wireless Access Subscriber Units. It is present at the house of the subscriber. It connects the subscriber to WANU and the power supply for it is provided locally. Advantages of WLL: It eliminates the first mile or last mile construction of the network connection. Low cost due to no use of conventional copper wires. Much more secure due to digital encryption techniques used in wireless communication. Highly scalable as it doesn’t require the installation of more wires for scaling it. Features of WLL: Internet connection via modem Data service Voice service Fax service
