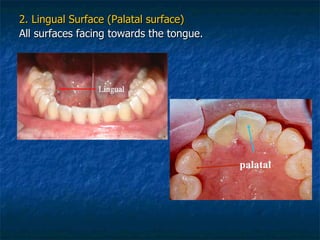
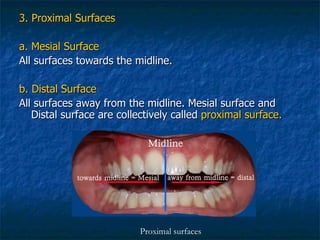
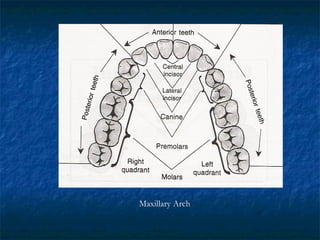
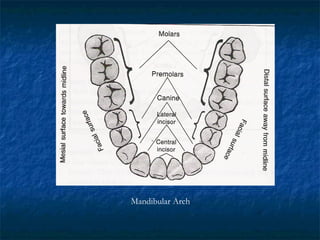
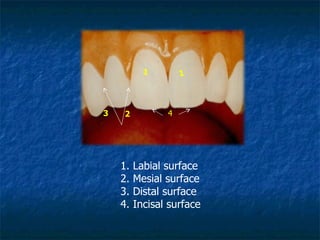
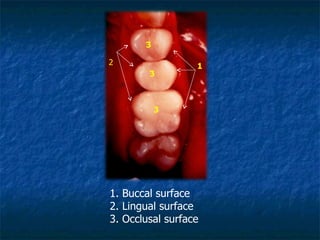
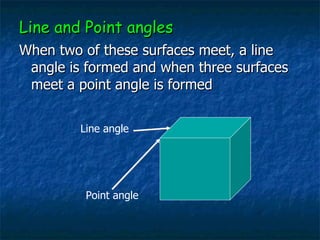
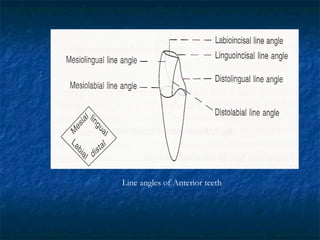
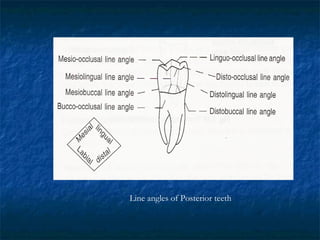
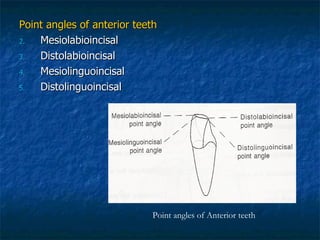
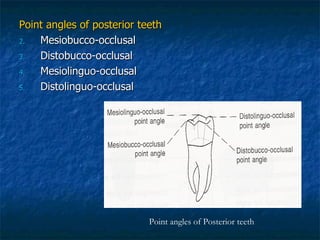
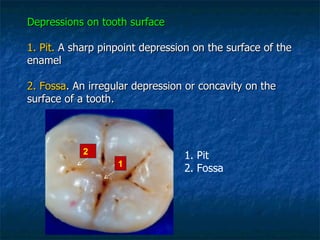
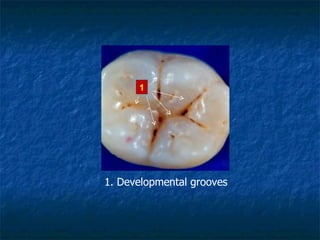
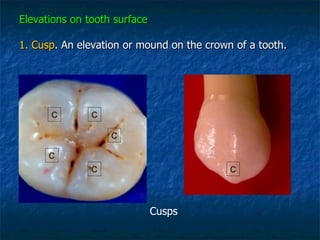
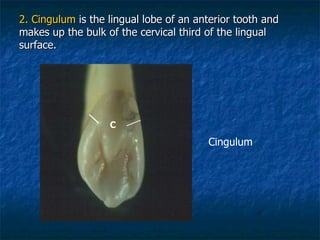
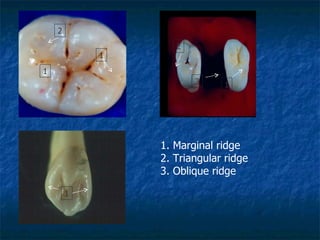
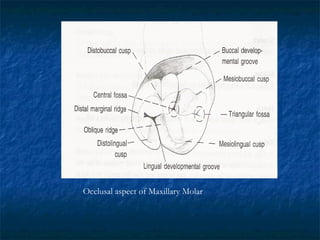
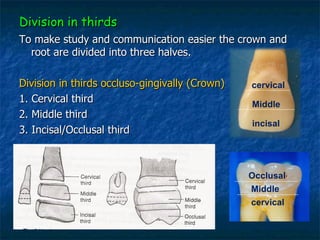
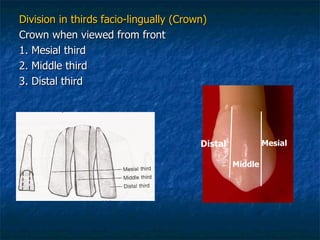
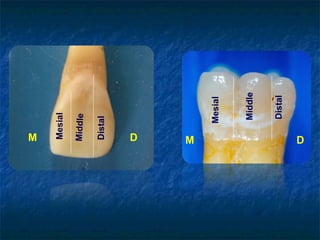
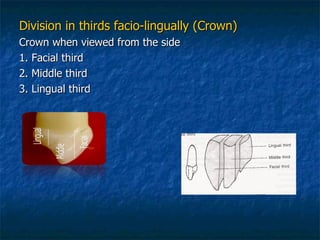
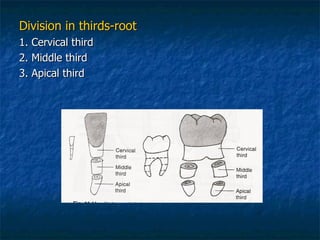
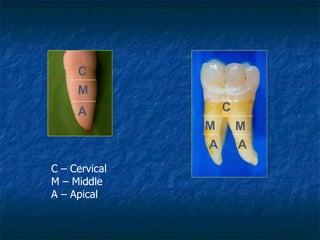
This document provides an overview of dental terminology used to describe the anatomy of teeth. It discusses the surfaces, lines, angles, depressions and elevations found on teeth. Key terms covered include the crown, root, cemento-enamel junction, and facial, lingual, mesial, distal, and incisal/occlusal surfaces. The document also describes how teeth are divided into thirds for study and communication purposes.