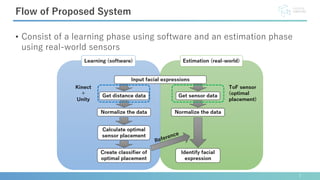
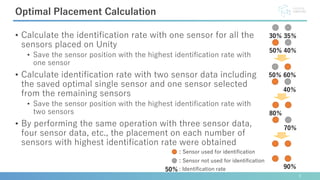
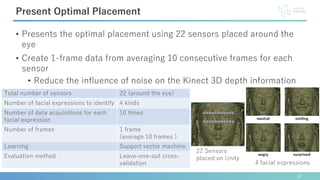
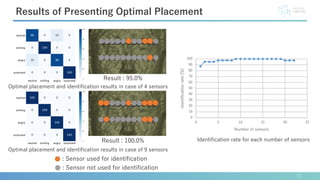
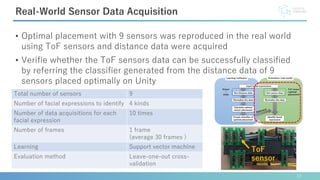
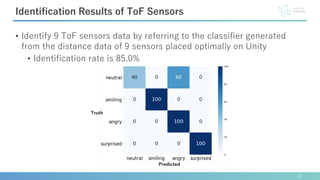
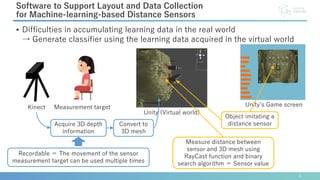
This document describes software developed to optimize the placement of real-world sensors for machine learning applications. The software allows virtually placing different numbers of sensors and calculating identification rates to determine the optimal sensor configuration. It was tested on a facial expression identification task using distance sensors on eyeglasses. The optimal 9-sensor placement identified in software achieved an 85% identification rate when tested with real-world time-of-flight sensors, demonstrating its ability to support sensor layout optimization for machine learning systems.

![• Gesture recognition and posture estimation can be performed by
combining real-world sensors and machine learning.
• The number and position of sensors that can acquire unique sensor
data are often determined by trial and error.
2
Combining Real-World Sensors and Machine Learning
The flow of system design
Examination
of sensor
placement
Create device
Acquire
identification
result
Accumulate
learning data
Combining real-world sensors
and machine learning [1]
[1] Munehiko Sato, Ivan Poupyrev, and Chris Harrison. Touche: Enhancing touch interaction on humans, screens, liquids, and everyday objects. In Proceedings of the SIGCHI Conference on Human Factors in Computing Systems, CHI
'12, pp. 483{492, New York, NY, USA, 2012. ACM.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/asianchiv2simsensor-200924072508/85/Development-of-Real-World-Sensor-Optimal-Placement-Support-Software-AsianCHI2020-2-320.jpg)
![• Learn virtual egocentric video and the posture of a humanoid model
walking in a virtual world
• Estimate the walking postures of people in the real world by combining
data in images shot by a camera attached a pedestrian and learning
data in the virtual world
• Use learning data in the virtual world to estimate the real-world system
3
Simulation of Real-World System on Computer
[2] Yuan Y., Kitani K. (2018) 3D Ego-Pose Estimation via Imitation Learning. In: Ferrari V., Hebert M., Sminchisescu C., Weiss Y. (eds) Computer Vision – ECCV 2018. ECCV 2018. Lecture Notes in Computer Science, vol 11220.
Springer, Cham](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/asianchiv2simsensor-200924072508/85/Development-of-Real-World-Sensor-Optimal-Placement-Support-Software-AsianCHI2020-3-320.jpg)
![• Facial expression identification based on changes in the distance
between distance sensors placed on an eyeglass frame and the skin
surface on a face
6
Facial Expression Identification by Distance Sensor
AffectiveWear [5]
[5] Masai, K., Sugiura, Y., Ogata, M., Kunze, K., Inami, M., Sugimoto, M.: Facial Expression Recognition in Daily Life by Embedded Photo Reflective Sensors on Smart Eyewear. In: Proceedings of the 21st International Conference on
Intelligent User Interfaces (IUI '16), pp. 317-326. ACM, New York, NY, USA (2016).](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/asianchiv2simsensor-200924072508/85/Development-of-Real-World-Sensor-Optimal-Placement-Support-Software-AsianCHI2020-6-320.jpg)