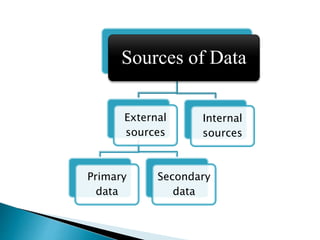
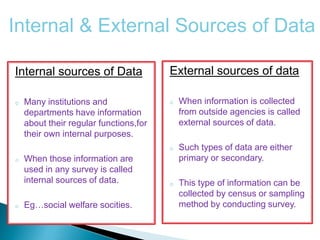
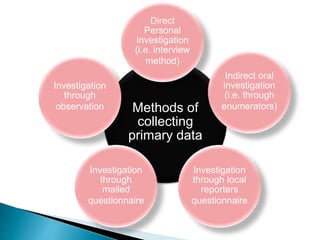
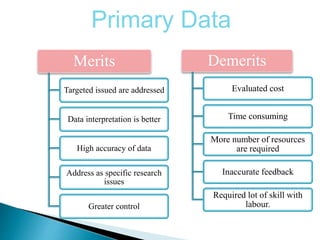
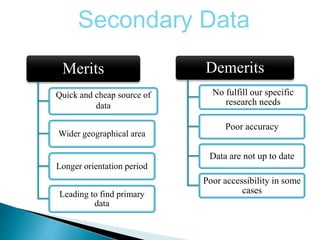
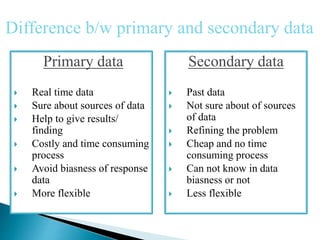
The document explains the importance of data collection in research, distinguishing between primary and secondary data sources. Primary data is firsthand information collected directly by the researcher, while secondary data consists of information previously gathered by others, often through various publications. The document also outlines the merits and demerits of both data types, highlighting their respective roles and challenges in research.