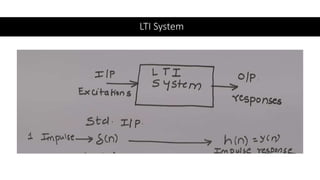
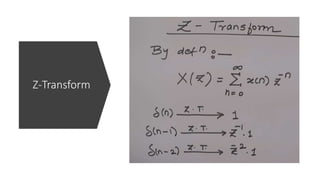
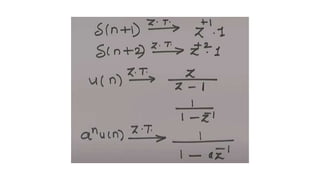
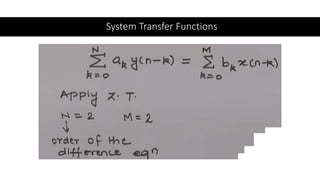
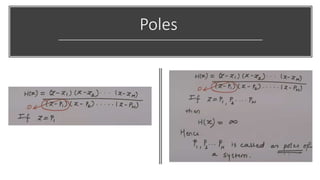
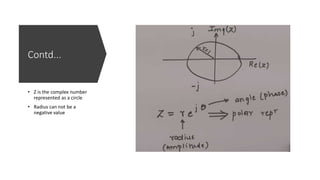
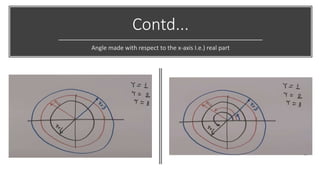
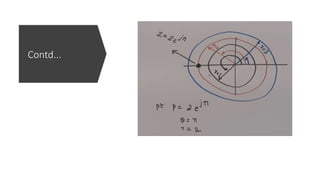
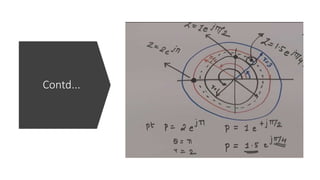
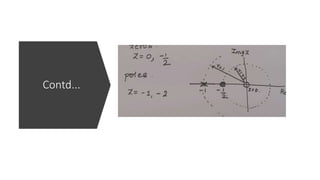
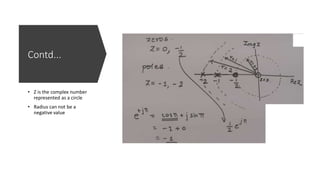
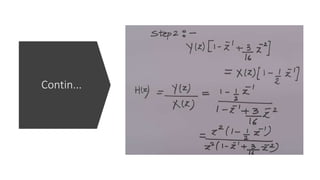
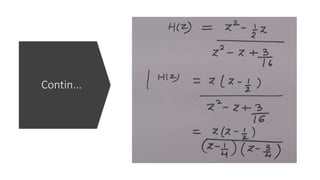
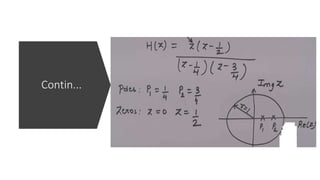
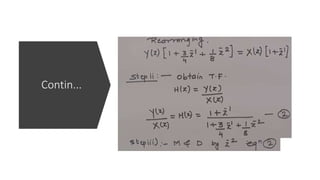
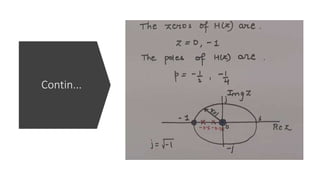
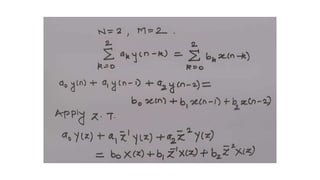The document discusses the z-transform and its application to linear time-invariant (LTI) systems. It covers difference equations, system transfer functions, pole-zero representations, and the significance of poles and zeros. Poles and zeros are represented as points in the z-plane. Poles cause the transfer function to approach infinity while zeros cause it to approach zero. The locations of poles and zeros determine how a system responds to different input frequencies.