This document provides an overview of financial aid, including:
- What financial aid is and how to apply by completing the FAFSA and other forms.
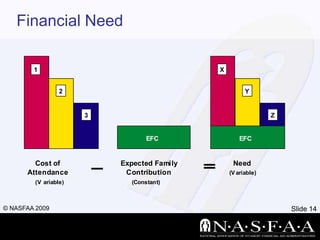
- Key terms like the Expected Family Contribution (EFC), Cost of Attendance (COA), and financial need.
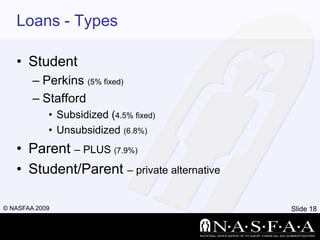
- The different categories, types, and sources of financial aid like grants, loans, scholarships, and work-study.
- Tips for applying for aid, understanding award letters, dealing with special circumstances, avoiding scams, and renewing aid annually.