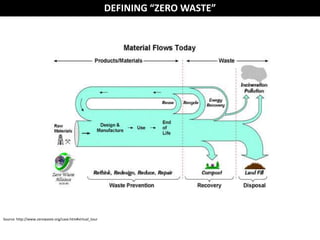
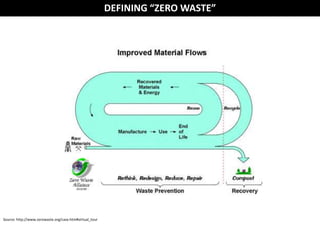
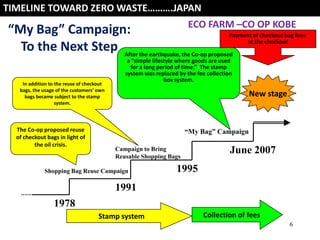
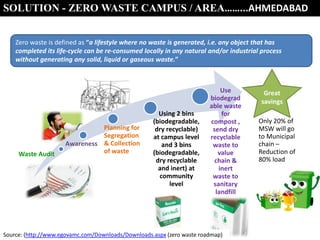
The document discusses the concept of zero waste, which aims to minimize waste generation and maximize resource value. Zero waste is a philosophy that redesigns product life cycles so that all materials are reused. Products are designed for reuse through a "cradle to cradle" model rather than a linear "cradle to grave" model. The 3Rs - reduce, reuse, recycle - are emphasized to achieve zero waste goals.