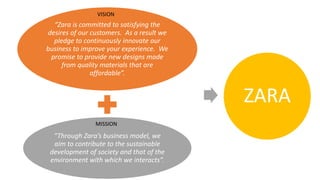
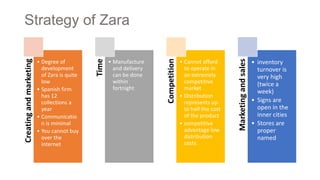
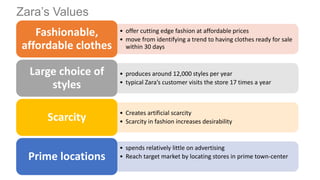
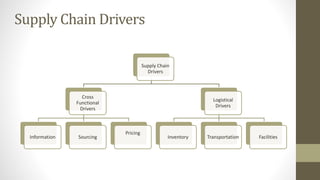
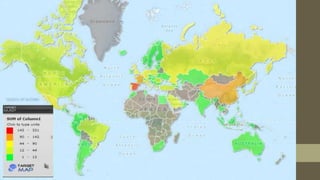
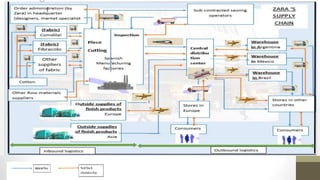
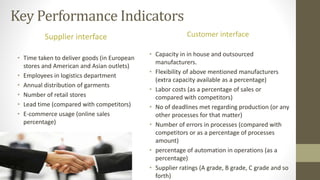
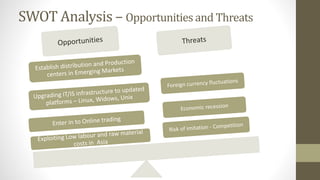
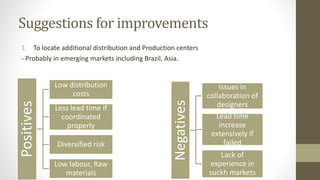
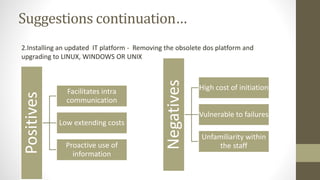
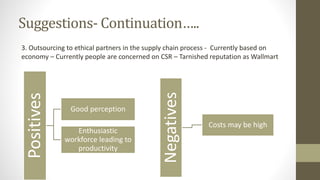
The document details Zara's supply chain practices, emphasizing its commitment to customer satisfaction through innovative, sustainable fashion. Key aspects include rapid inventory turnover, a centralized distribution system, and responsive information flow that enhance efficiency. It also outlines strengths like vertical integration and weaknesses related to high production costs and potential supply chain ethical concerns, along with suggestions for improvements in distribution and IT systems.