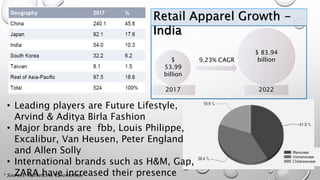
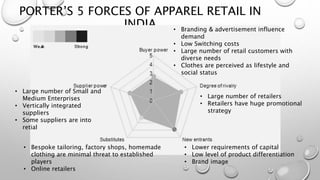
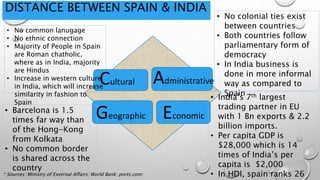
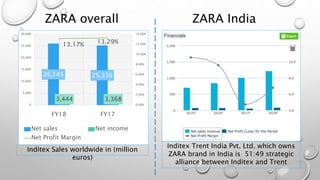
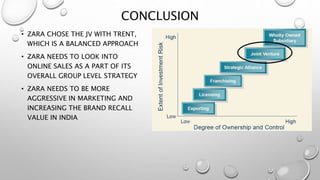
The document outlines Zara's international expansion, discussing its business model, market entry strategies, and adaptation to local markets. It highlights the company's evolution from local to global markets, emphasizing a transnational strategy for efficiency and responsiveness. The analysis includes insights into the Indian market potential and challenges, reflecting on cultural differences and strategic partnerships.