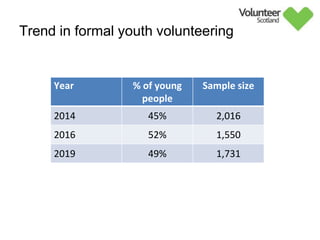
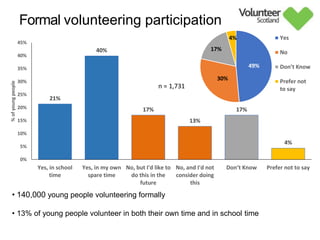
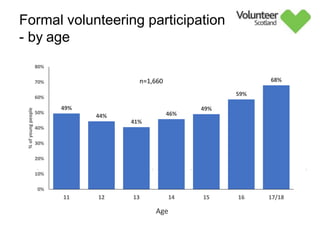
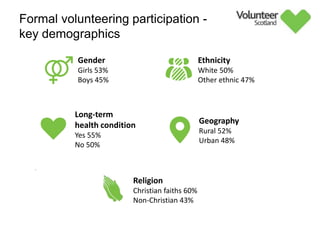
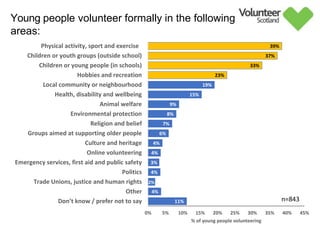
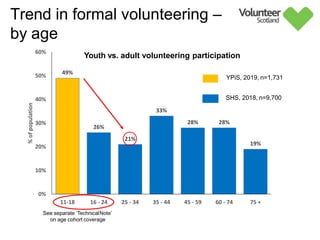
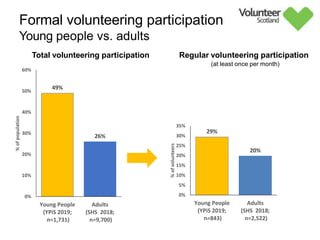
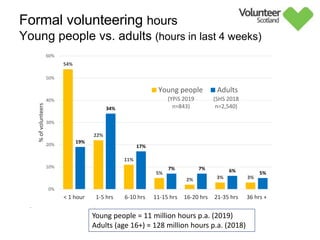
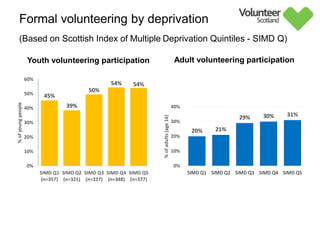
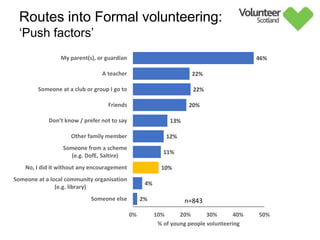
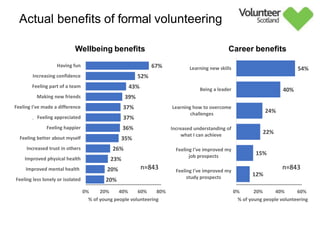
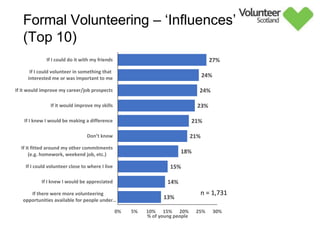
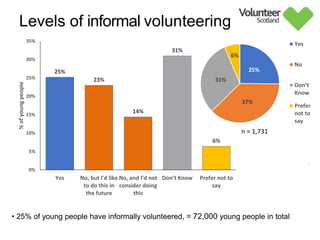
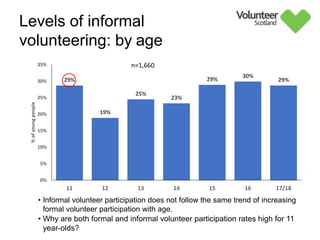
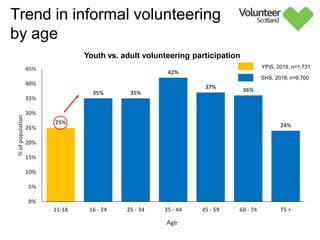
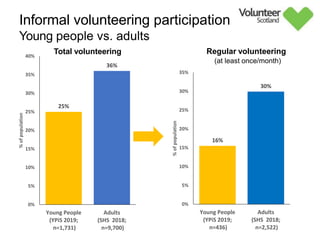
The document summarizes survey results on youth volunteering in Scotland from 2019. It finds that 49% of youth participated in formal volunteering, providing 11 million hours annually, compared to 26% of adults. However, youth volunteered less frequently and intensely than adults. Informal volunteering rates were lower at 25% for youth versus 36% for adults. Parental encouragement was an important influence on youth volunteering participation. The benefits of volunteering for youth well-being were emphasized, in addition to career benefits.