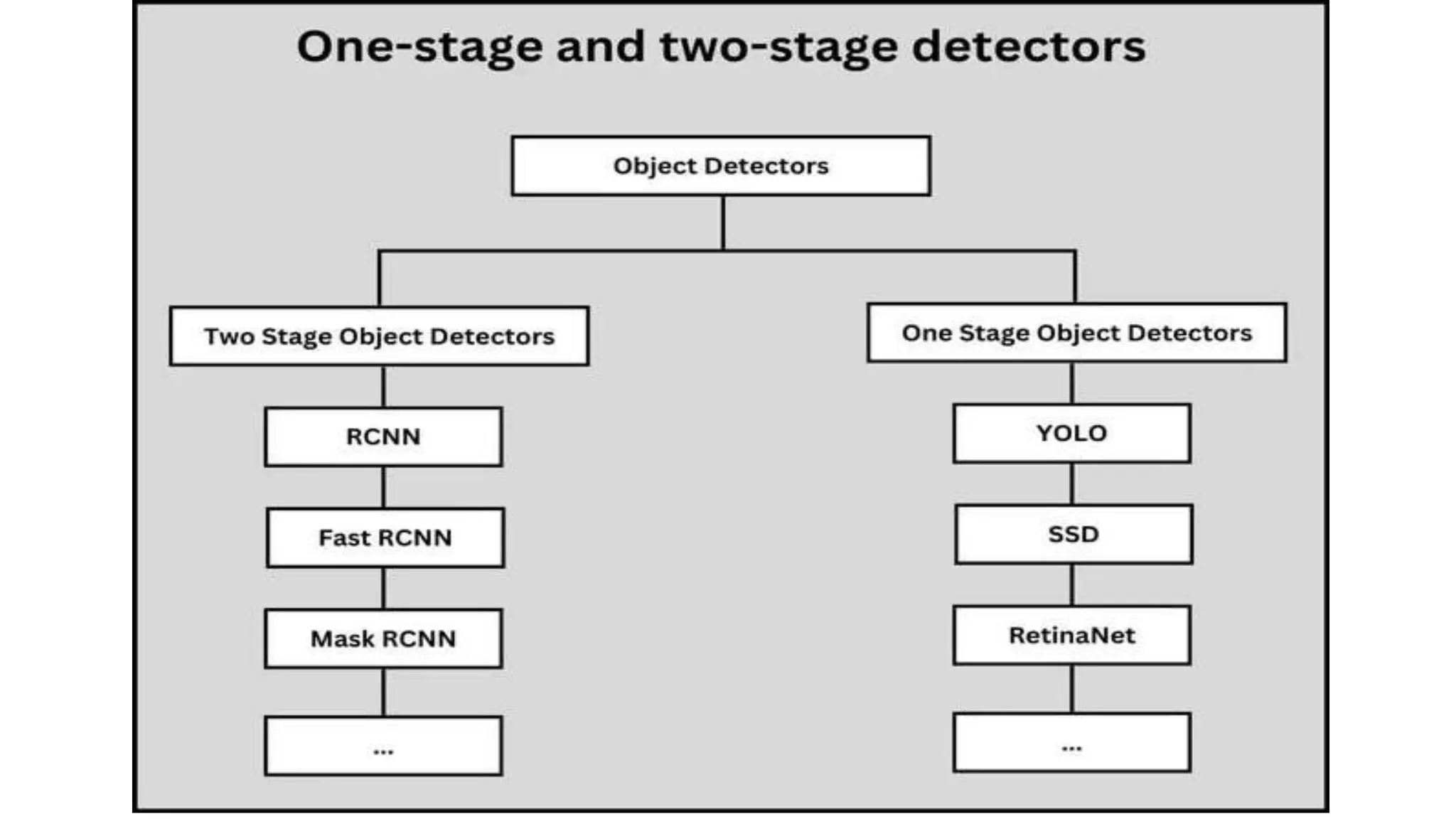
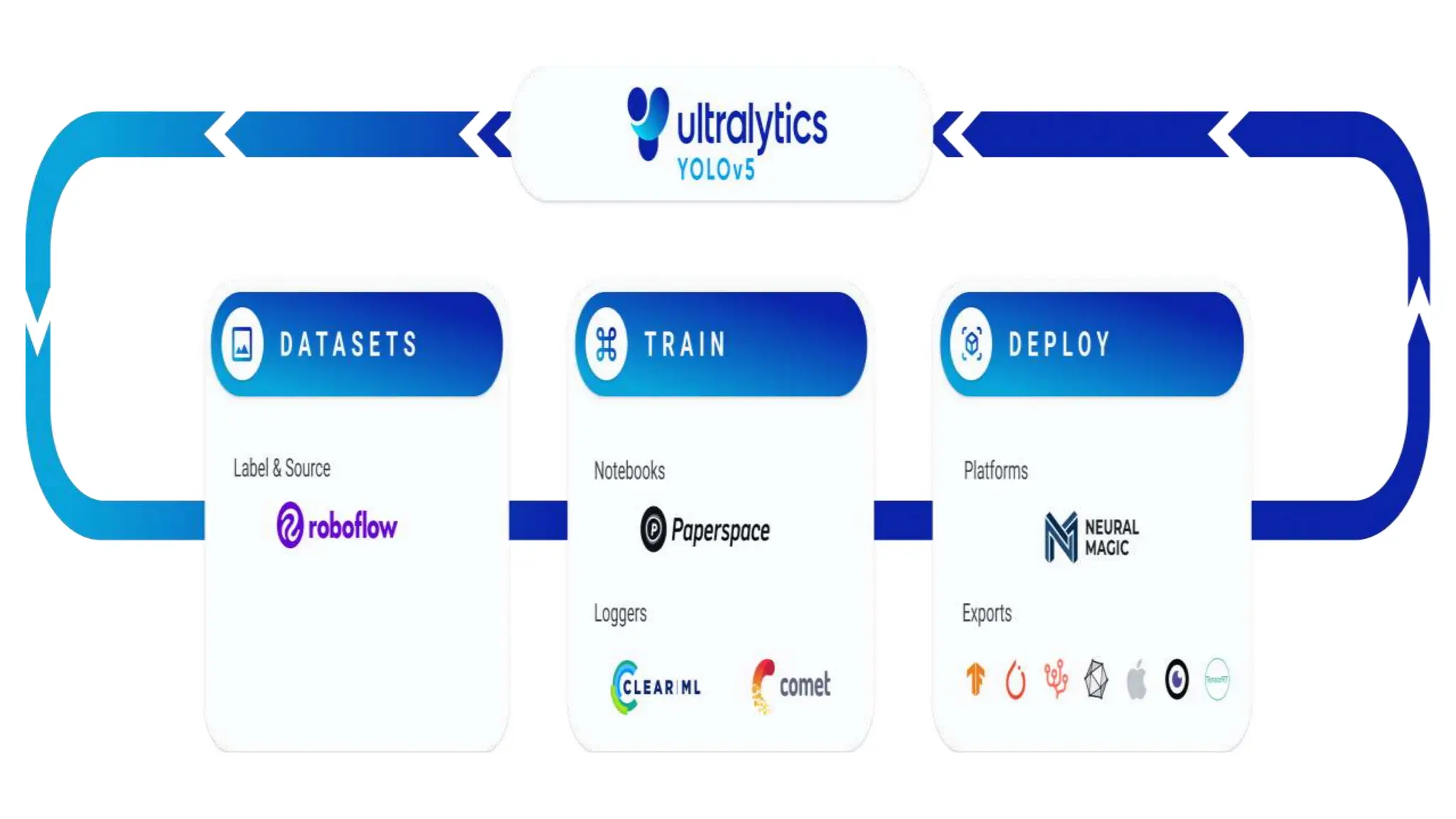
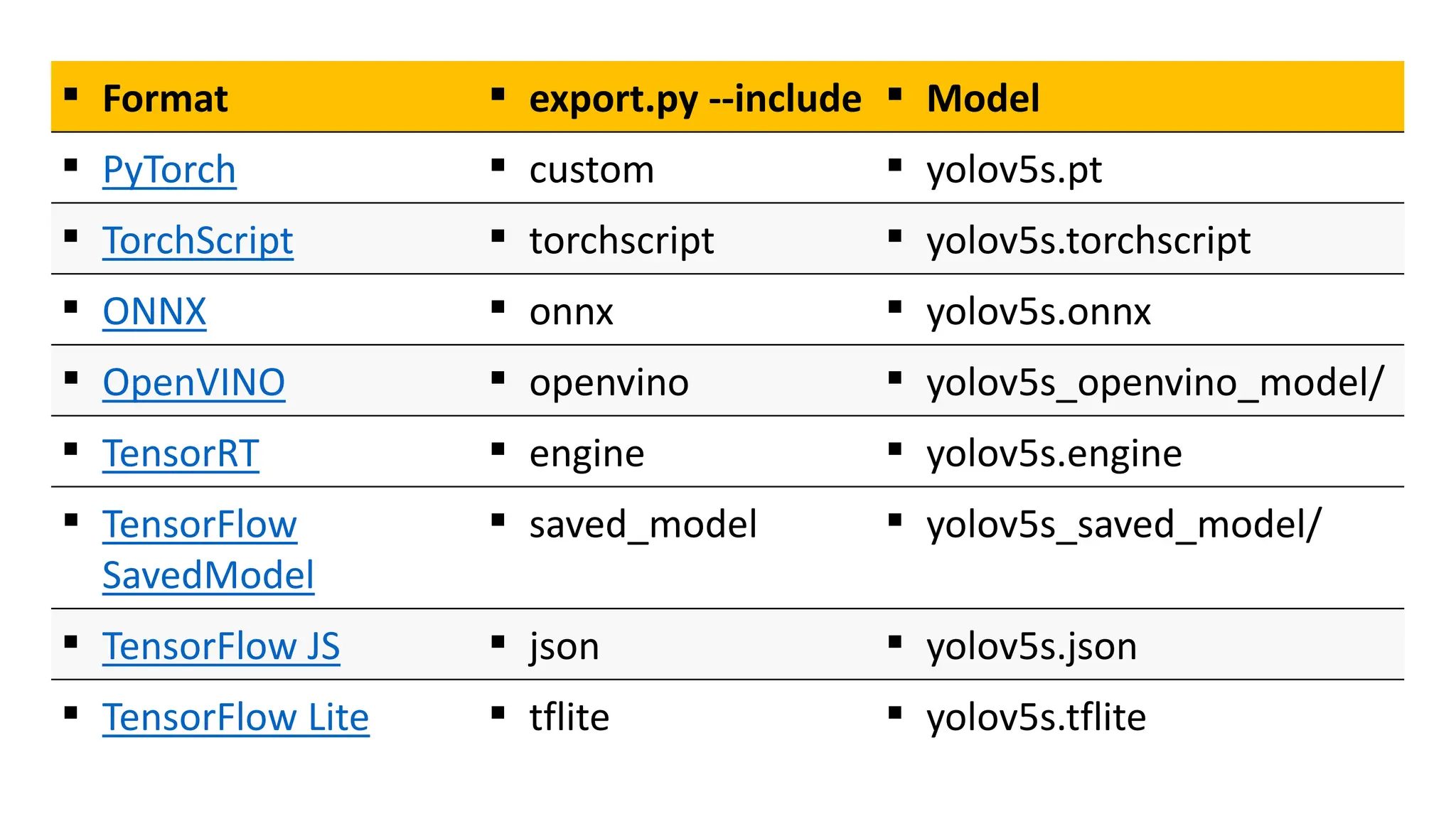
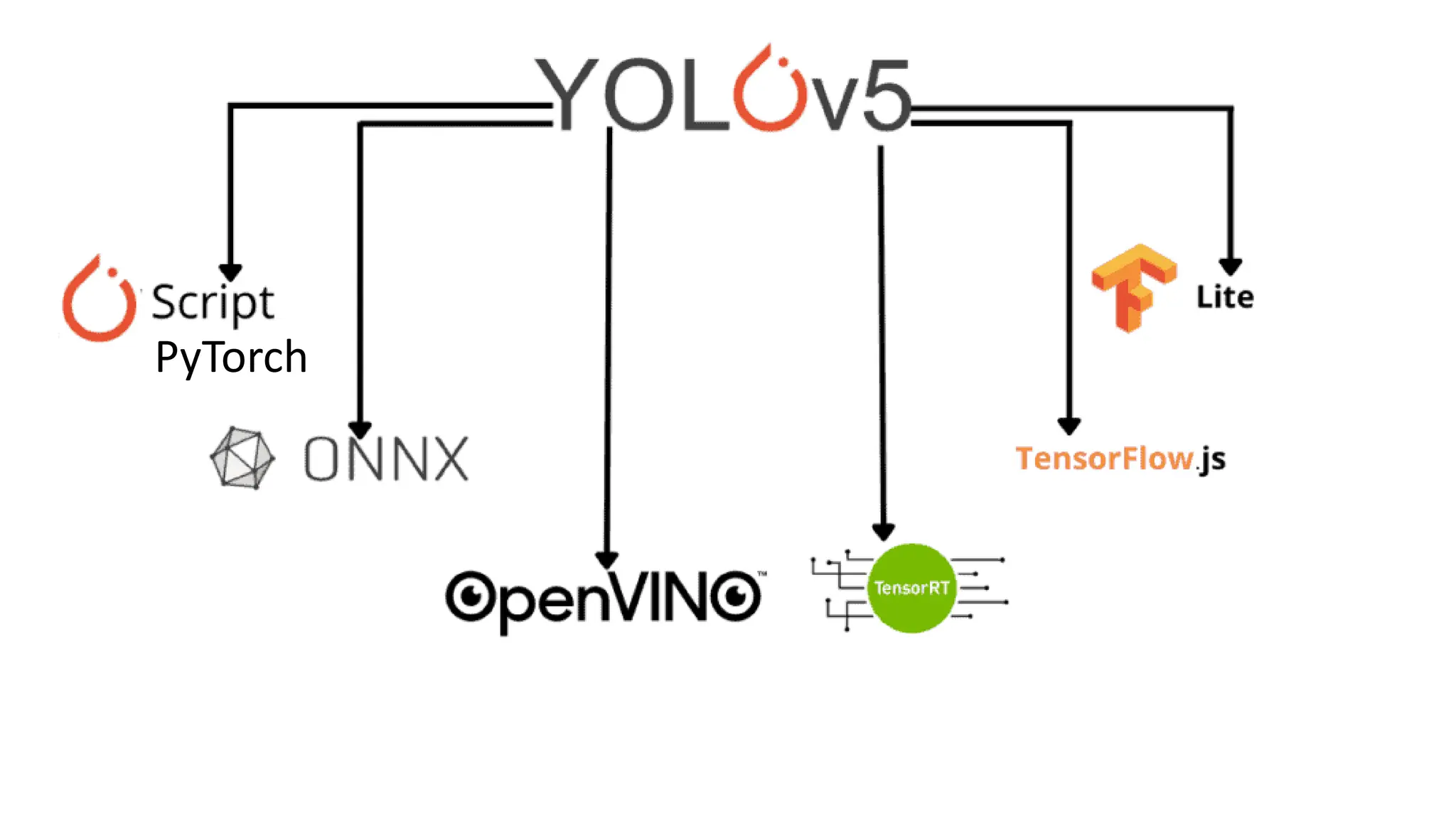
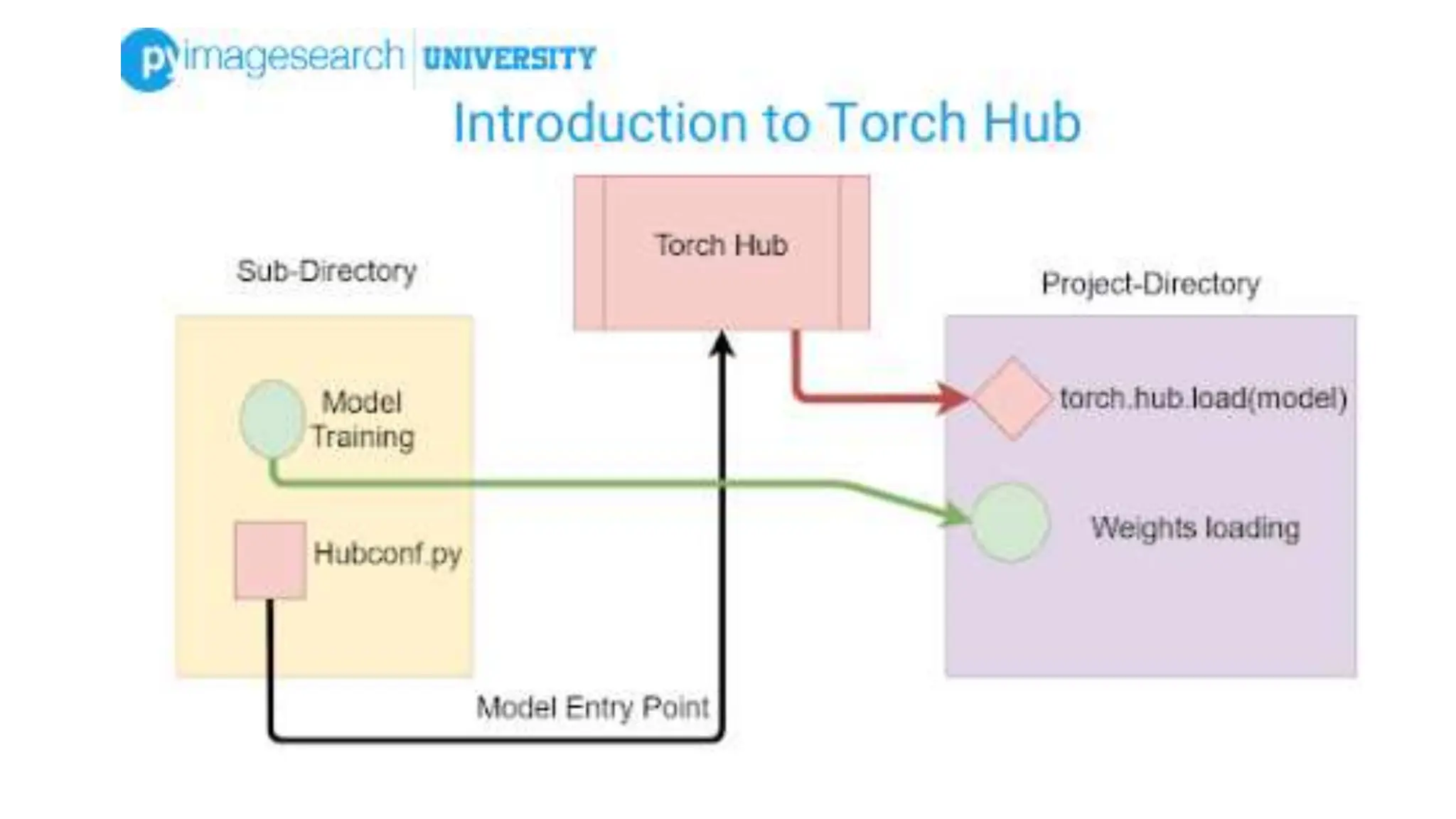
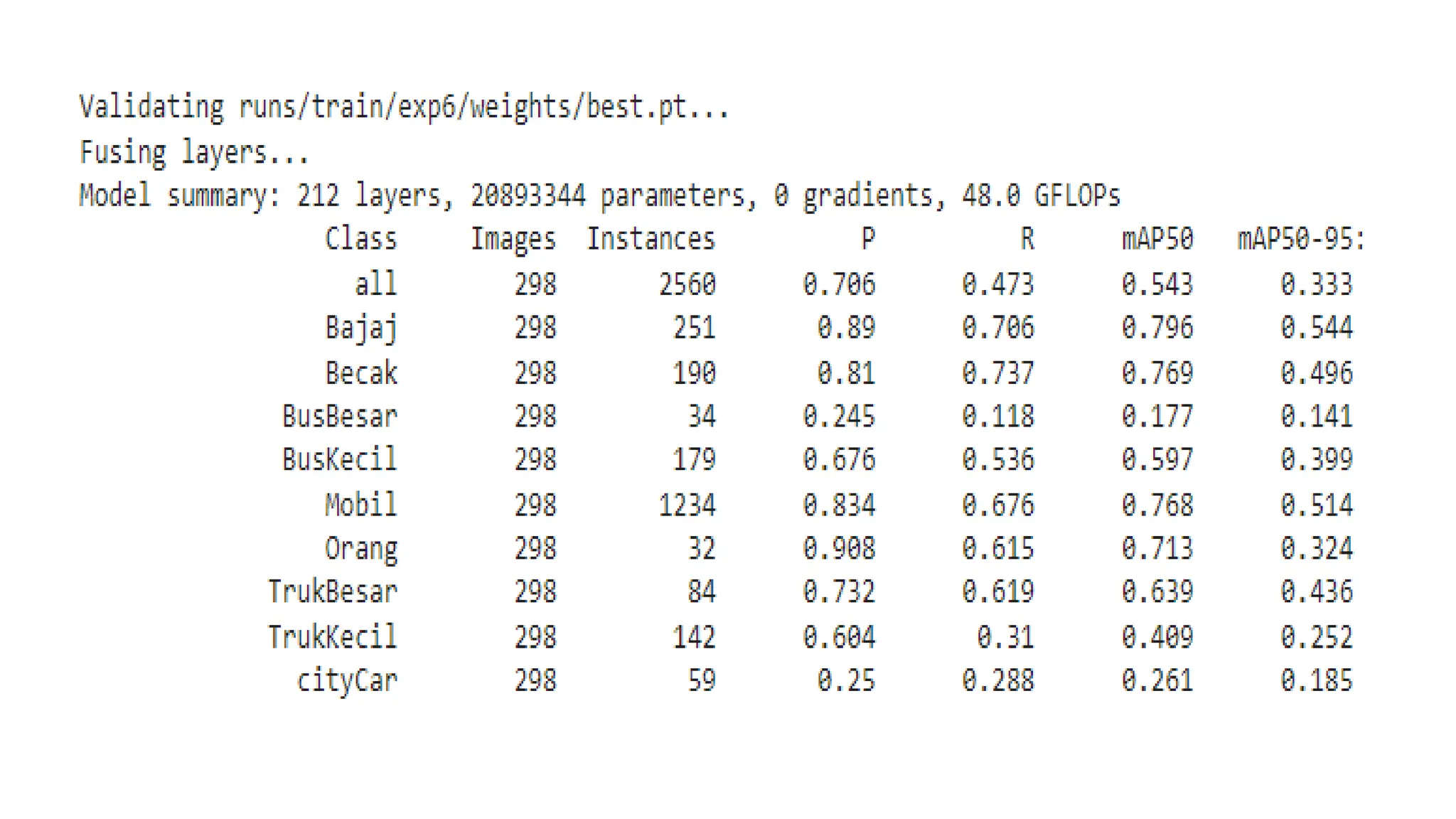
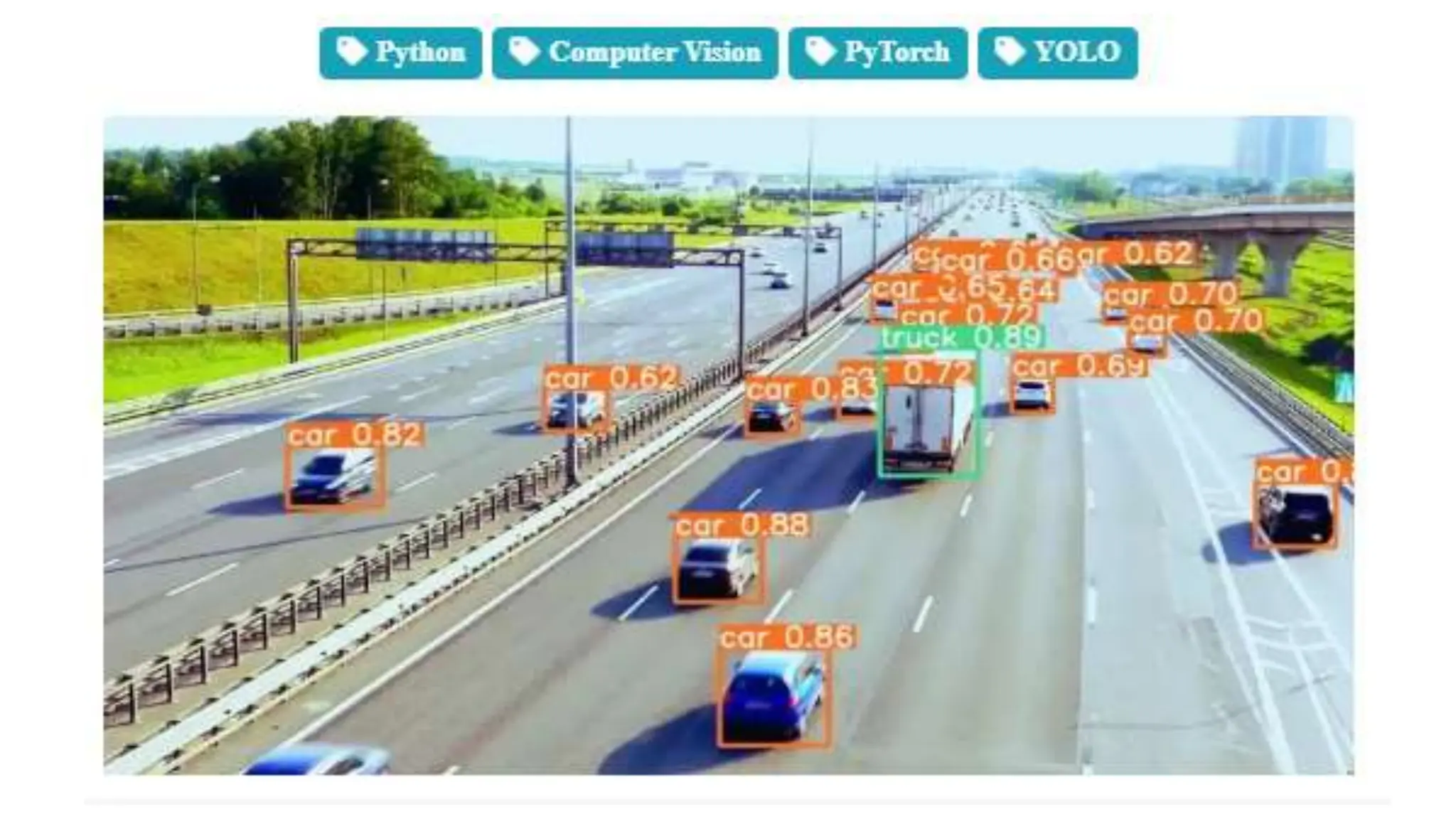
The document lists several formats for exporting a YOLOv5s object detection model, including PyTorch (.pt), TorchScript (.torchscript), ONNX (.onnx), OpenVINO (directory), TensorRT (.engine), TensorFlow SavedModel (directory), TensorFlow JS (.json), and TensorFlow Lite (.tflite). It also provides a short Python code example for loading the PyTorch model and performing inference on images.
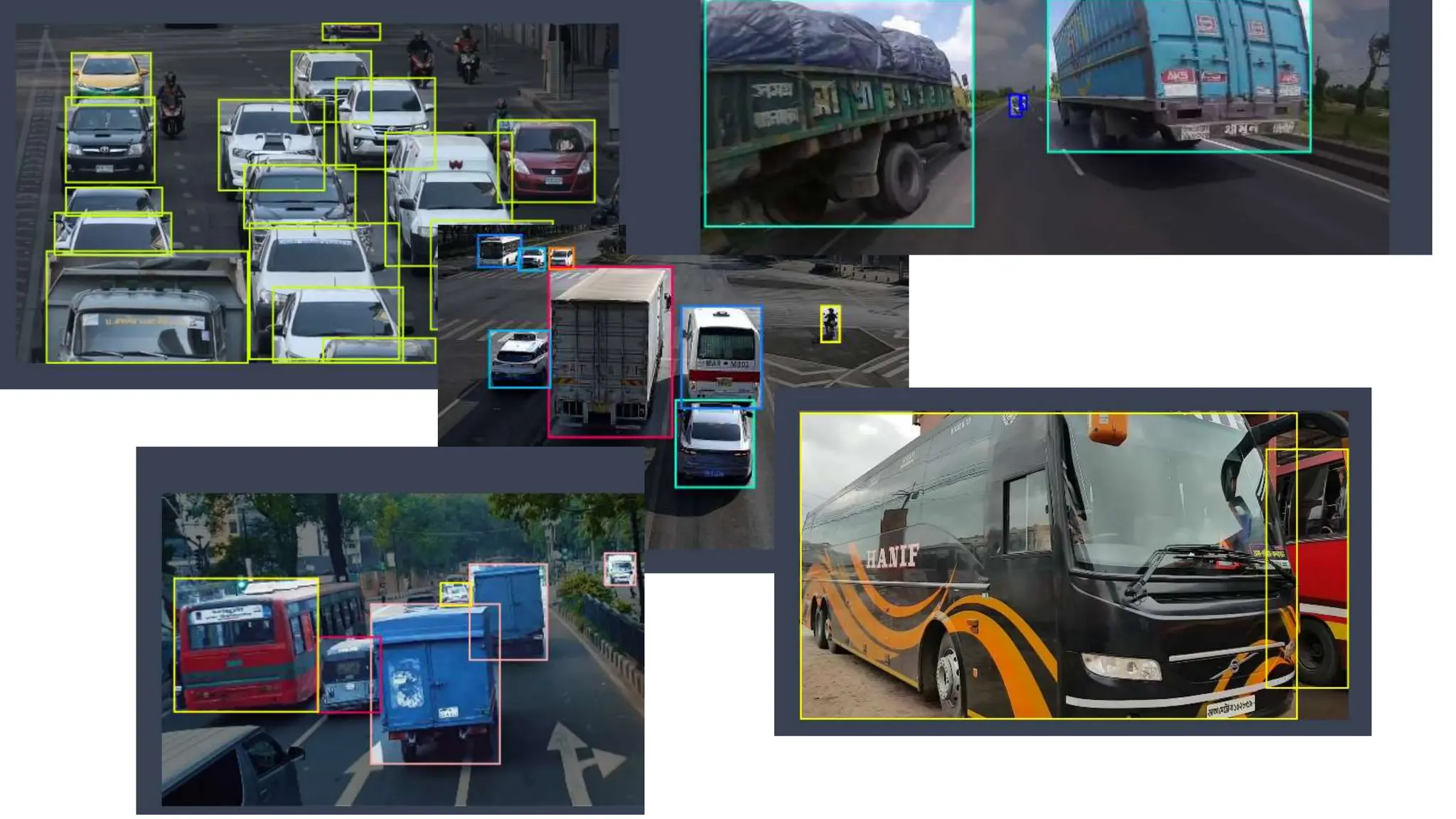




![Import cv2
import torch
Import numpy as np
# Model
model = torch.hub.load('ultralytics/yolov5', 'yolov5s', pretrained=True)
model = torch.hub.load('ultralytics/yolov5’, ‘custom’, path=’best.pt')
# Images
imgs = ['https://ultralytics.com/images/zidane.jpg'] # batch of images
# Inference
results = model(imgs)
# Results
results.print()
results.save()
results.show()
results.xyxy[0] # img1 predictions (tensor)
results.pandas().xyxy[0] # img1 predictions (pandas)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/yolodatasetspytorch-231112131821-7a2d76ca/75/YOLO-datasets-pytorch-pptx-15-2048.jpg)