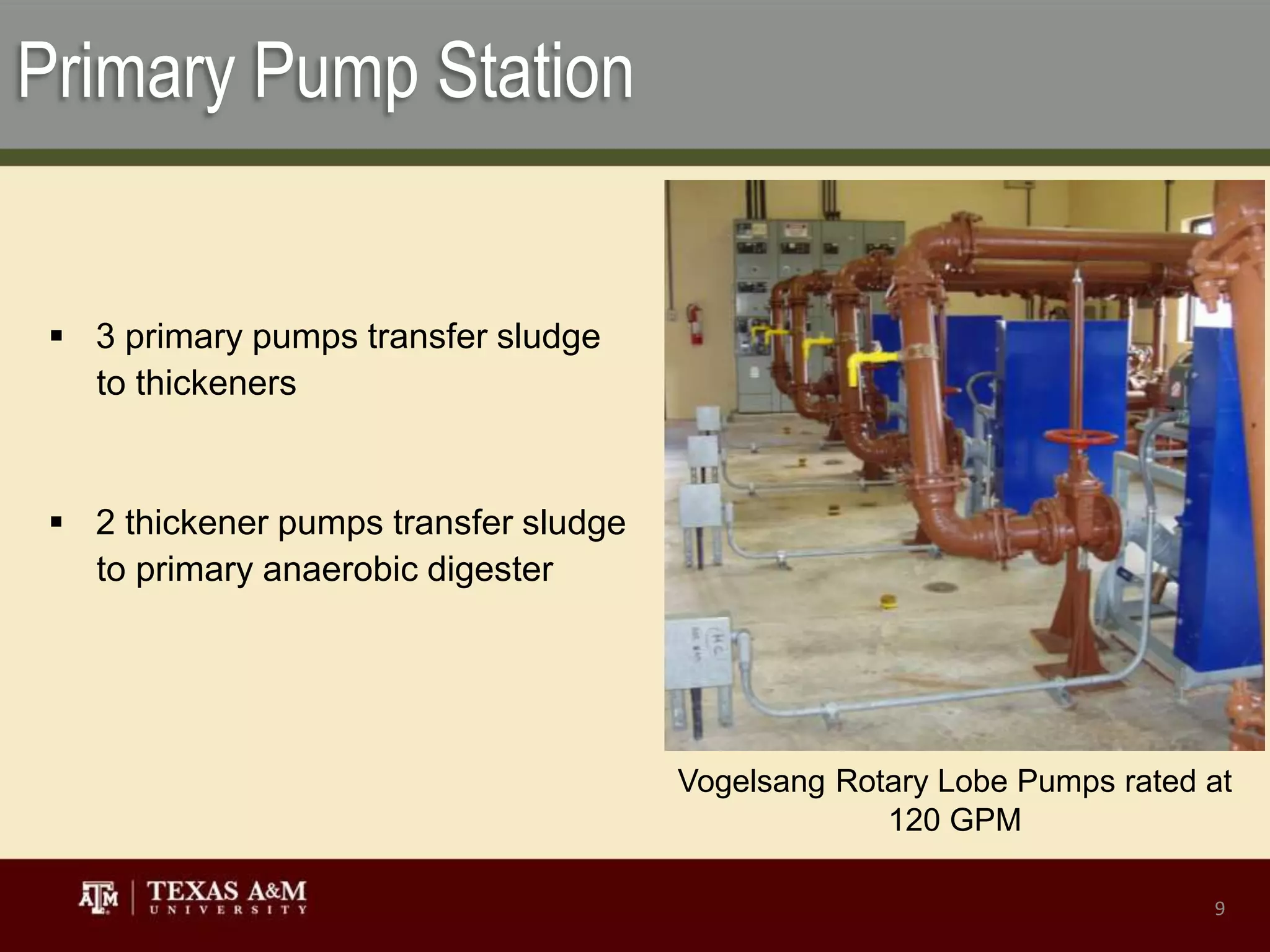
The Texas A&M Wastewater Treatment Plant uses conventional activated sludge treatment processes to treat wastewater from campus buildings. It is designed to treat up to 11,700 pounds of biochemical oxygen demand per day from a population equivalent of 69,900 people. The plant utilizes primary and secondary clarification, aeration, ultraviolet disinfection, and land application of biosolids to treat wastewater and remove contaminants before water is recycled or biosolids are used as fertilizer. Laboratory testing ensures the plant meets regulatory requirements for effluent water quality.