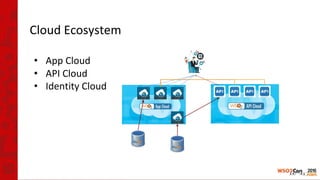
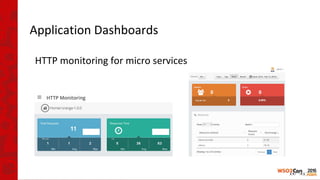
The document provides an introduction to virtualization, containers, Docker, and Kubernetes, highlighting the benefits of using these technologies for deploying applications. It explains key concepts such as container lifecycle management, orchestration, and the architecture of Kubernetes, including pods, replication controllers, and services. Additionally, it discusses deploying WSO2 products on Kubernetes and provides links to further resources.


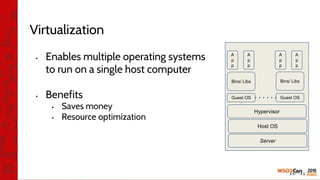




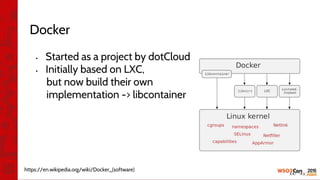
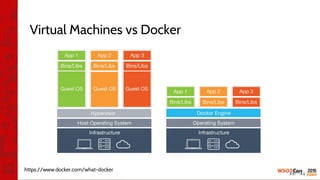
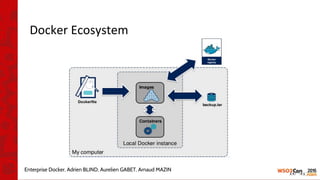

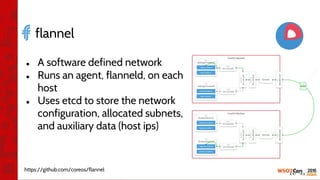
![•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
[1] https://docs.docker.com/engine/installation/
[2] https://github.com/sajhak/wso2as-docker](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/wso2con-asia-2016-app-cloud-with-k8s-160217070101/85/WSO2Con-ASIA-2016-Revolutionizing-WSO2-App-Cloud-with-Kubernetes-Docker-14-320.jpg)

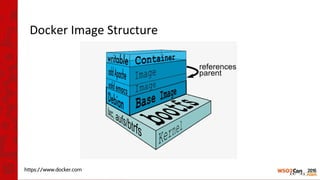
![Why Container Clusters?
• Avoid single point of failure
• Make horizontally scalable
• Have more granular
management for distributed
applications (microservices)
• Self healing systems
http://googlecloudplatform.blogspot.com/2015/01/what-makes-a-container-cluster.html
[image ref] https://www.docker.com/what-docker](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/wso2con-asia-2016-app-cloud-with-k8s-160217070101/85/WSO2Con-ASIA-2016-Revolutionizing-WSO2-App-Cloud-with-Kubernetes-Docker-17-320.jpg)
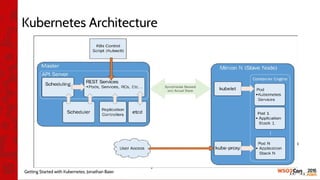

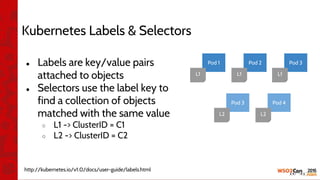
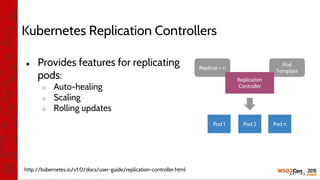
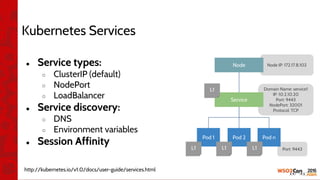
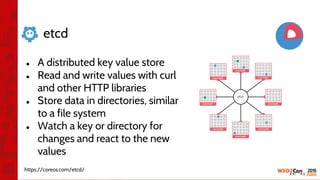

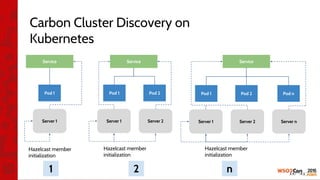
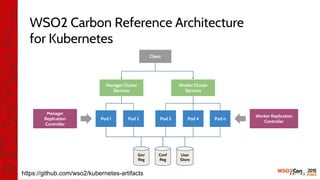
![•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
[1] https://github.com/imesh/kubernetes-vagrant-setup](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/wso2con-asia-2016-app-cloud-with-k8s-160217070101/85/WSO2Con-ASIA-2016-Revolutionizing-WSO2-App-Cloud-with-Kubernetes-Docker-28-320.jpg)