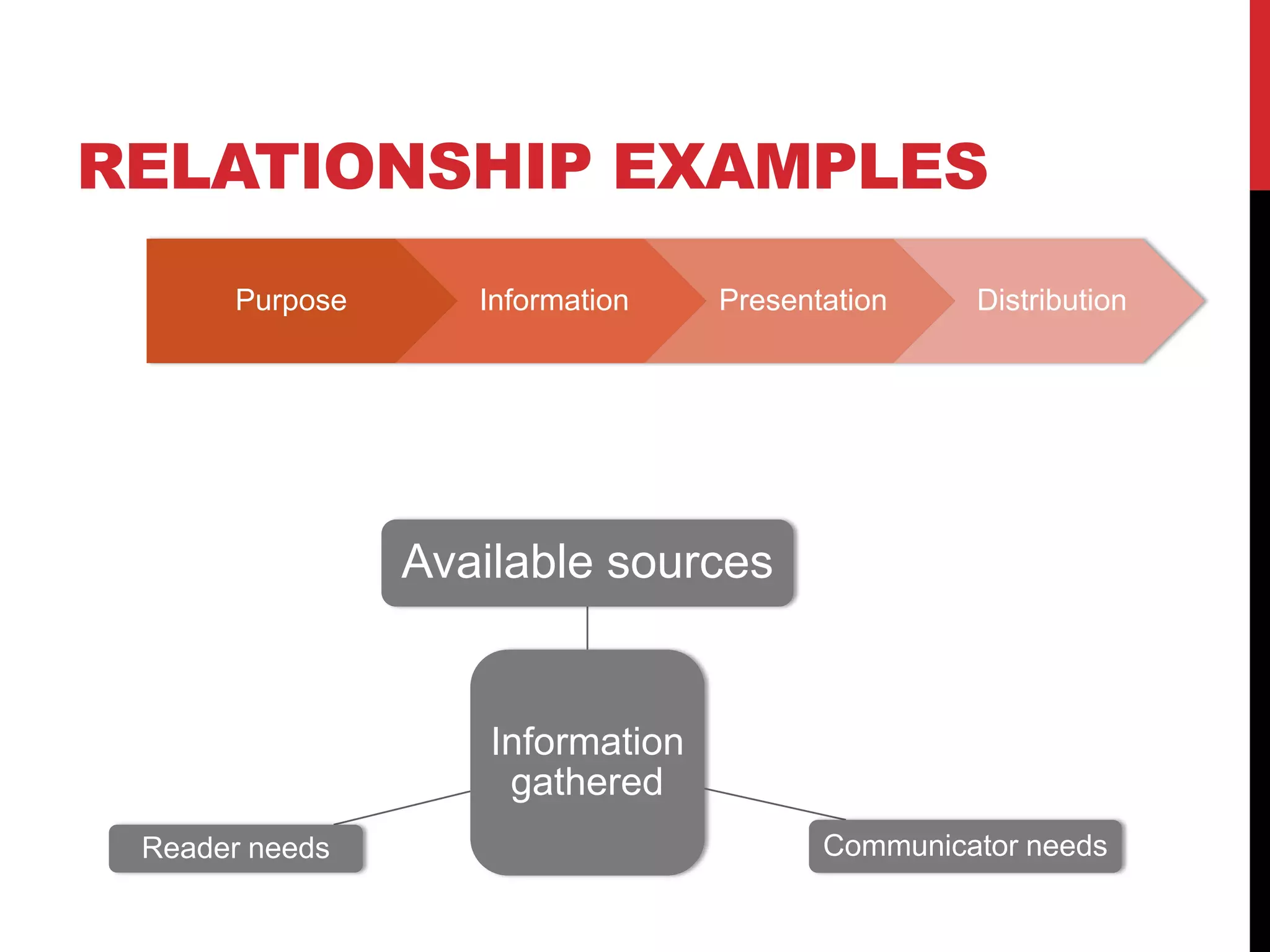
The document outlines the essential components and best practices for creating effective white papers, highlighting their purpose as informative technical documents that address specific audience problems. It emphasizes the importance of understanding the audience, conducting thorough research, and using a professional design that incorporates visuals to enhance communication. Additionally, the document covers the processes of planning, writing, editing, and promoting white papers to ensure they meet their intended goals and effectively engage the target audience.