Embed presentation
Download to read offline

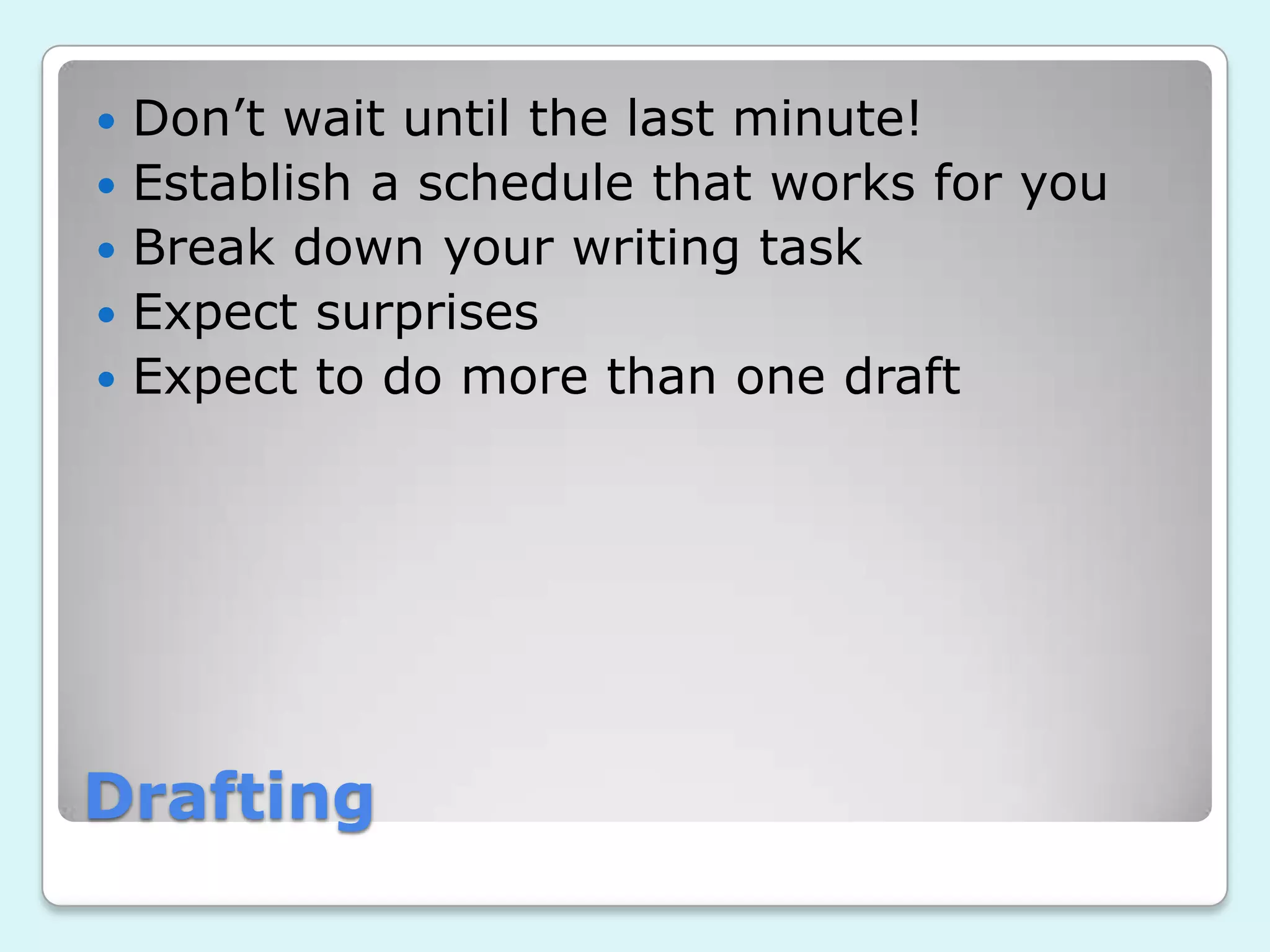








The document discusses the writing process and provides tips for each stage. It recommends starting the drafting process early to avoid procrastination and establishing a schedule. Writers block can be addressed by reframing the task, taking a break, free writing, or researching what others have said on the topic. When writing for others, writers should ensure their points are clear and assess what needs more or less focus. The document also suggests considering the purpose, audience, genre and stance of the writing. Later stages involve getting feedback, revising for clarity and focus, editing sentence-level elements, and proofreading.









