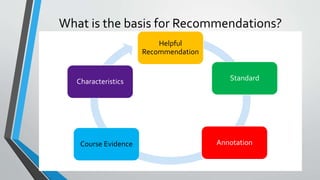
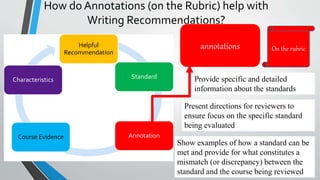
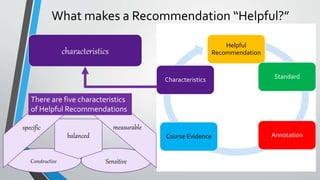
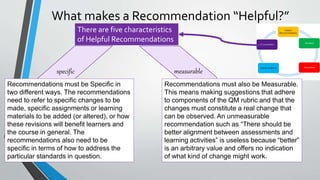
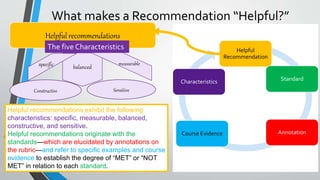
This document discusses how to write helpful recommendations for quality matters reviews. It explains that recommendations should originate from the standards on the rubric and aim to ensure courses continuously improve over time through a collaborative process. Recommendations are most helpful when they are specific, measurable, balanced between constructive criticism and sensitivity, and refer to concrete examples and evidence from the course.